【机器学习】梯度、梯度法、python实现神经网络的梯度计算
- 一、python实现求导的代码:
- 二、what is 梯度
- 三、使用梯度法寻找神经网络的最优参数
- 四、神经网络的梯度计算
一、python实现求导的代码:
导数含义也就是:变量x一个微小的变化将导致f(x)的值在多大程度上变化。
def numerical_diff(f, x):h = 1e-4return (f(x+h) - f(x-h)) / (2*h)
偏导数怎么求,对哪个变量求偏导,就把其他变量固定为某个值,然后就像求一元函数导数那样对这个变量求导。
举个例子,对x0^ 2+x1 ^2=y这个二元函数,求x0=3,x1=4时,对x0的偏导数。
代码如下:
def numerical_diff(f, x):h = 1e-4return (f(x+h) - f(x-h)) / (2*h)def func_1(x):return x[0]**2+x[1]**2# 求x0=3,x1=4时,x0的偏导数def func_temp1(x0):return x0**2+4**2if __name__ == '__main__':res = numerical_diff(func_temp1,3.0)print(res)
输出:
6.00000000000378
二、what is 梯度
由全部变量的偏导数汇总而成的向量叫梯度。
求梯度代码如下:
函数 _numerical_gradient_no_batch 的参数f为函数,x为Numpy数组。
grad = np.zeros_like(x)生成一个形状和x相同,所有元素均为0的数组,梯度就存到这里面。
这里面fxh1计算的时候,如果在这(x[0],x[1])这一点对x[0]求编导,变的是x[0],x[1]不变。而且对x[1]求偏导的时候,变的是x[1],x[0]不变。所以,要用tmp_val存变化前的数,并且,在求完偏导后把一切恢复。
下面代码是对x0 ^ 2+x1 ^ 2=y这个二元函数,求点(3,4)处的梯度。
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 为了导入父目录的文件而进行的设定
import numpy as npdef _numerical_gradient_no_batch(f, x):h = 1e-4 # 0.0001grad = np.zeros_like(x)for idx in range(x.size):tmp_val = x[idx]x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + hfxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)x[idx] = tmp_val - hfxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2 * h)x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值return graddef func_1(x):return x[0]**2+x[1]**2if __name__ == '__main__':#求点(3,4)处的梯度res = _numerical_gradient_no_batch(func_1, np.array([3.0, 4.0]))print(res)
结果:
[6. 8.]
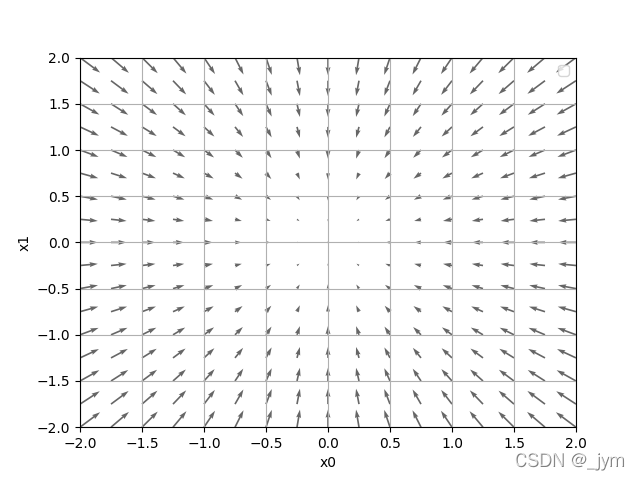
用python画很多点的梯度向量,那么就发现一个很神奇的结果:梯度指向函数最小值,离最小值越远,箭头越大。
严格来讲,梯度指示的方向是各点处函数值减小最多的方向。无法保证梯度所指方向就是函数最小值。
虽然梯度的方向不一定指向最小值,但是沿着它的方向能够最大限度减小函数的值,这就是梯度法。
三、使用梯度法寻找神经网络的最优参数
通过不断地沿着梯度方向前进,逐渐减小函数值的过程就是梯度法。
梯度法的数学表示:

η表示更新量,在神经网络的学习中,称为学习率( learningrate)。学习率决定在一次学习中,应该学习多少,以及在多大程度上更新参数。
这个数学表示是什么意思,其实就是沿着梯度走,如上图,(x0,x1)取(0,2)时,梯度是(0,4)。这里的x0-η乘f在x0处的偏导,表示沿那个梯度方向走的一小步。学习率小的话,每次走的步子会很小,学习率大的话,步子就大。
用python实现梯度法的代码如下:
f是要进行最优化的函数, init_x是初始值, lr是学习率, step_num是梯度法的重复次数。
gradient_descent函数里面调用了numerical_gradient函数,用来求函数的梯度。gradient_descent函数里面会一直循环step_num次梯度法,每一次都用梯度乘以学习率得到新值,并更新。最后如果梯度法进行的顺利,将走到最小值的位置。
def gradient_descent(f, init_x, lr=0.01, step_num=100):x = init_xx_history = []for i in range(step_num):x_history.append( x.copy() )grad = numerical_gradient(f, x)x -= lr * gradreturn x, np.array(x_history)
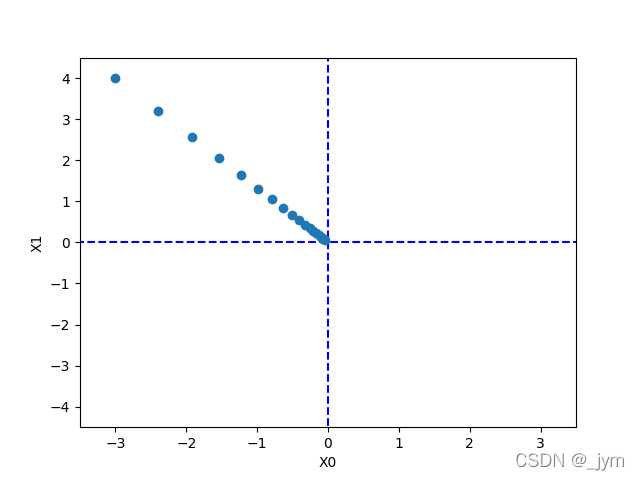
下面这个例子,用了梯度法求f(x0,x1)=x0^ 2+x1 ^2的最小值。最终结果接近(0,0),说明我们的结果基本正确,因为最小值确实是在(0,0)点取到。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
from gradient_2d import numerical_gradientdef gradient_descent(f, init_x, lr=0.01, step_num=100):x = init_xx_history = []for i in range(step_num):x_history.append( x.copy() )grad = numerical_gradient(f, x)x -= lr * gradreturn x, np.array(x_history)def function_2(x):return x[0]**2 + x[1]**2init_x = np.array([-3.0, 4.0]) lr = 0.1
step_num = 20
x, x_history = gradient_descent(function_2, init_x, lr=lr, step_num=step_num)
print(x)plt.plot( [-5, 5], [0,0], '--b')
plt.plot( [0,0], [-5, 5], '--b')
plt.plot(x_history[:,0], x_history[:,1], 'o')plt.xlim(-3.5, 3.5)
plt.ylim(-4.5, 4.5)
plt.xlabel("X0")
plt.ylabel("X1")
plt.show()
输出:
[-0.03458765 0.04611686]
学习率取的过大或者过小都无法得到好结果。
对上面代码进行修改:
学习率过大的话,结果会发散成一个很大的值。
lr = 10
step_num = 100
x, x_history = gradient_descent(function_2, init_x, lr=lr, step_num=step_num)
print(x)
结果:
[-2.58983747e+13 -1.29524862e+12]
学习率过小,基本上没怎么更新就结束了。
lr = 1e-10
step_num = 100
x, x_history = gradient_descent(function_2, init_x, lr=lr, step_num=step_num)
print(x)
结果:
[-2.99999994 3.99999992]
四、神经网络的梯度计算
神经网络的学习中的梯度,指的是损失函数关于权重参数的梯度。
假设,有一个形状为2*3的权重W的神经网络,损失函数是L,下面是该网络权重和梯度的数学表示。

下面是一个例子,首先要实现一个simpleNet类,这个网络的权重矩阵是2*3的。
最后输出的dw如下,这个是梯度。
[[ 0.12894287 0.31807705 -0.44701992][ 0.19341431 0.47711557 -0.67052988]]
比如,如果w11增加h,那么损失函数的值会增加0.47h。从减小损失函数值的观点看,w11应该向负方向更新。
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 为了导入父目录中的文件而进行的设定
import numpy as np
from common.functions import softmax, cross_entropy_error
from common.gradient import numerical_gradientclass simpleNet:def __init__(self):self.W = np.random.randn(2,3)def predict(self, x):return np.dot(x, self.W)def loss(self, x, t):z = self.predict(x)y = softmax(z)loss = cross_entropy_error(y, t)return lossnet = simpleNet()
print(net.W) # 权重参数x = np.array([0.6, 0.9])#输入数据
p = net.predict(x) #由输入经过神经网络得到的输出预测值
print(p)
print(np.argmax(p))#最大值的索引t = np.array([0, 0, 1]) # 正确解标签
print(net.loss(x, t)) #输出损失函数的值def f(W):return net.loss(x, t)
# f = lambda w: net.loss(x, t)dW = numerical_gradient(f, net.W)#求梯度print(dW)
输出:
[[-0.66110535 -2.3121261 0.61870626][-0.43594672 1.66798289 -1.09922476]]
[-0.78901526 0.11390894 -0.61807852]
1
1.366622688011303
[[ 0.12894287 0.31807705 -0.44701992][ 0.19341431 0.47711557 -0.67052988]]



















