文章目录
- 1. 题目
- 2. 解题
- 2.1 超时解
- 2.2 BFS + DFS
1. 题目
「推箱子」是一款风靡全球的益智小游戏,玩家需要将箱子推到仓库中的目标位置。
游戏地图用大小为 n * m 的网格 grid 表示,其中每个元素可以是墙、地板或者是箱子。
现在你将作为玩家参与游戏,按规则将箱子 'B' 移动到目标位置 'T' :
- 玩家用字符
'S'表示,只要他在地板上,就可以在网格中向上、下、左、右四个方向移动。 - 地板用字符
'.'表示,意味着可以自由行走。 - 墙用字符
'#'表示,意味着障碍物,不能通行。 - 箱子仅有一个,用字符
'B'表示。相应地,网格上有一个目标位置'T'。
玩家需要站在箱子旁边,然后沿着箱子的方向进行移动,此时箱子会被移动到相邻的地板单元格。记作一次「推动」。
玩家无法越过箱子。
返回将箱子推到目标位置的最小 推动 次数,如果无法做到,请返回 -1。
示例 1:
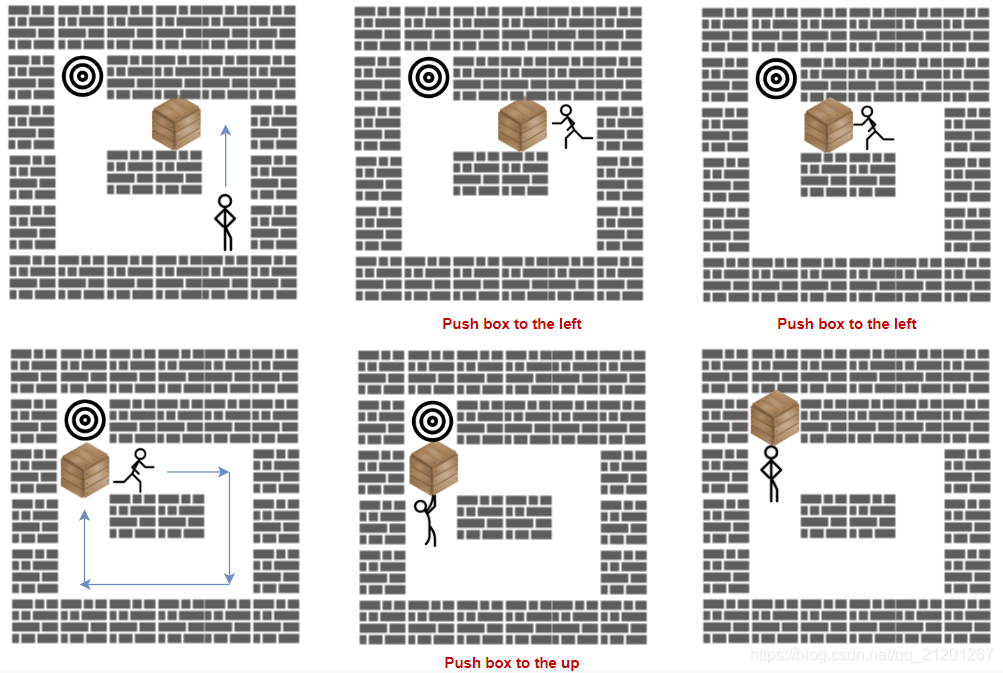
输入:grid = [["#","#","#","#","#","#"],["#","T","#","#","#","#"],["#",".",".","B",".","#"],["#",".","#","#",".","#"],["#",".",".",".","S","#"],["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
输出:3
解释:我们只需要返回推箱子的次数。示例 2:
输入:grid = [["#","#","#","#","#","#"],["#","T","#","#","#","#"],["#",".",".","B",".","#"],["#","#","#","#",".","#"],["#",".",".",".","S","#"],["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
输出:-1示例 3:
输入:grid = [["#","#","#","#","#","#"],["#","T",".",".","#","#"],["#",".","#","B",".","#"],["#",".",".",".",".","#"],["#",".",".",".","S","#"],["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
输出:5
解释:向下、向左、向左、向上再向上。示例 4:
输入:grid = [["#","#","#","#","#","#","#"],["#","S","#",".","B","T","#"],["#","#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
输出:-1提示:
1 <= grid.length <= 20
1 <= grid[i].length <= 20
grid 仅包含字符 '.', '#', 'S' , 'T', 以及 'B'。
grid 中 'S', 'B' 和 'T' 各只能出现一个。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-moves-to-move-a-box-to-their-target-location
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
2. 解题
2.1 超时解
15 / 18 个通过测试用例
- 优先队列里存入 box 和 人的4个坐标位置,以及推的次数,推的次数小的优先
- 队列里存了太多的状态
class node
{
public:int push, bi, bj, pi, pj;node(int n, int a, int b, int c, int d){push = n;bi = a;bj = b;pi = c;pj = d;}
};
struct hashf // 自定义哈希
{unsigned long long operator()(node v) const{return 1ULL*v.push*pow(21,4)+v.bi*pow(21,3)+v.bj*pow(21,2)+v.pi*21+v.pj;}
};
struct eqf // 哈希set 相等判断函数
{bool operator()(node v1, node v2) const//不能写引用,会报错{return v1.push==v2.push && v1.bi==v2.bi && v1.bj==v2.bj&& v1.pi==v2.pi && v1.pj==v2.pj;}
};
struct cmp
{bool operator()(node& a, node& b) const{return a.push > b.push;//推得次数少的优先}
};
class Solution {
public:int minPushBox(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(), k = 21;int targetx, targety, boxi, boxj, peoplei, peoplej, push = 0, size;for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 'S')peoplei = i, peoplej = j;else if(grid[i][j] == 'B')boxi = i, boxj = j;else if(grid[i][j] == 'T')targetx = i, targety = j;}}vector<vector<int>> dir = {{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0}};priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp> q; node state(0, boxi, boxj, peoplei, peoplej);q.push(state);unordered_set<node, hashf, eqf> vis;vis.insert(state);while(!q.empty()){int pj = q.top().pj;int pi = q.top().pi;int bj = q.top().bj;int bi = q.top().bi;push = q.top().push;if(bi==targetx && bj==targety)return push;q.pop();int nextbi, nextbj, nextpi, nextpj;for(int d = 0; d < 4; d++){nextpi = pi+dir[d][0];nextpj = pj+dir[d][1];state.push = push;if(nextpi==bi && nextpj==bj){ // 推动箱子了nextbi = bi+dir[d][0];nextbj = bj+dir[d][1];state.push++;}else{nextbi = bi;nextbj = bj;}state.bi = nextbi;state.bj = nextbj;state.pi = nextpi;state.pj = nextpj;if(nextpi>=0 && nextpi<m && nextpj>=0 && nextpj<n &&nextbi>=0 && nextbi<m && nextbj>=0 && nextbj<n &&grid[nextpi][nextpj] != '#' && grid[nextbi][nextbj] != '#' &&vis.find(state) == vis.end()){vis.insert(state);q.push(state);}}}return -1;}
};
2.2 BFS + DFS
- 队列里面只存能推动箱子的状态
- 中间到达推箱子的过程,不必记录到队列内,采用DFS判断人的位置能否到达推动箱子的位置
- 不采用优先队列也可以
class node
{
public:int push, bi, bj, pi, pj;node(int n, int a, int b, int c, int d){push = n;bi = a;bj = b;pi = c;pj = d;}
};
struct hashf
{unsigned long long operator()(node v) const{return 1ULL*v.bi*pow(21,3)+v.bj*pow(21,2)+v.pi*21+v.pj;}
};
struct eqf
{bool operator()(node v1, node v2) const//不能写引用{return v1.bi==v2.bi && v1.bj==v2.bj&& v1.pi==v2.pi && v1.pj==v2.pj;//2个物品的位置都相等即set中出现过了}
};
struct cmp
{bool operator()(node& a, node& b) const{return a.push > b.push;//推得次数少的优先}
};
class Solution {vector<vector<int>> dir = {{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
public:int minPushBox(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();int targetx, targety, boxi, boxj, peoplei, peoplej, push = 0, size;for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 'S')peoplei = i, peoplej = j;else if(grid[i][j] == 'B')boxi = i, boxj = j;else if(grid[i][j] == 'T')targetx = i, targety = j;}}priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp> q; node state(0, boxi, boxj, peoplei, peoplej);q.push(state);unordered_set<node, hashf, eqf> vis;vis.insert(state);while(!q.empty()){int pj = q.top().pj;int pi = q.top().pi;int bj = q.top().bj;int bi = q.top().bi;push = q.top().push;if(bi==targetx && bj==targety)return push;q.pop();int nextbi, nextbj, nextpi, nextpj, pushPosx, pushPosy;for(int d = 0; d < 4; d++){nextbi = bi+dir[d][0];nextbj = bj+dir[d][1];if(nextbi<0 || nextbi>=m || nextbj<0 || nextbj>=n || grid[nextbi][nextbj] == '#')continue; // 箱子下一个位置不合法nextpi = bi;nextpj = bj;pushPosx = bi-dir[d][0];//人推动箱子前的位置pushPosy = bj-dir[d][1];if(pushPosx<0 || pushPosx>=m || pushPosy<0 || pushPosy>=n || grid[pushPosx][pushPosy] == '#')continue; // 推箱子位置不合法vector<vector<bool>> record(m, vector<bool>(n, false));if(!canReachPushPos(grid,pi,pj,bi,bj,pushPosx,pushPosy,record))continue;//不能从当前位置到达推箱子位置state.push = push+1;state.bi = nextbi;state.bj = nextbj;state.pi = nextpi;state.pj = nextpj;if(vis.find(state) == vis.end()){vis.insert(state);q.push(state);}}}return -1;}bool canReachPushPos(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int x0, int y0, int bi, int bj, int tx, int ty, vector<vector<bool>>& vis){vis[x0][y0] = true;if(x0==tx && y0==ty) return true;int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++){int nx = x0+dir[k][0];int ny = y0+dir[k][1];if(nx>=0 && nx<m && ny>=0 && ny<n && grid[nx][ny] != '#' && !(nx==bi && ny==bj) && !vis[nx][ny]){ // box 也不能穿过if(canReachPushPos(grid,nx, ny,bi,bj,tx,ty, vis))return true;}}return false;}
};
240 ms 20.4 MB C++
我的CSDN博客地址 https://michael.blog.csdn.net/
长按或扫码关注我的公众号(Michael阿明),一起加油、一起学习进步!

)




)


)

![[原创][R语言]股票分析实战[4]:周级别涨幅趋势的相关性](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[原创][R语言]股票分析实战[4]:周级别涨幅趋势的相关性)

)


)


)