目录
一、升序
二、降序
(1)类实现接口
(2)匿名内部类
三、自定义排序规则
四、集合中的sort排序
(1)升序
(2)降序
(3)自定义排序
一、升序
升序排序就是按照从小到大排序。(注意,想进行排序的话,基本数据类型要换成包装类,就像int型要写成Integer)
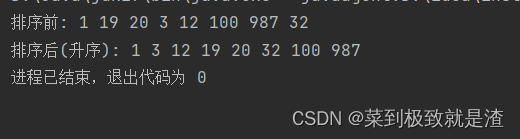
public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32};System.out.print("排序前: ");for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}System.out.println();System.out.print("排序后(升序): ");//开始使用sort进行升序排序Arrays.sort(a);for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}}
二、降序
想要使用sort进行降序排序,我们需要使用Comparator接口,这里有两种方式可以实现,一种是类实现接口,一种是匿名内部类,我们都讲一下。
(1)类实现接口
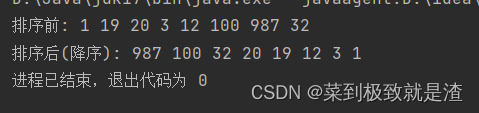
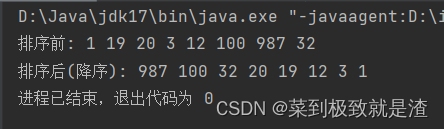
//程序入口 public class main1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32};System.out.print("排序前: ");for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}System.out.println();System.out.print("排序后(降序): ");Arrays.sort(a,new myCom());for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}} }//排序类 class myCom implements Comparator<Integer>{@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2-o1;} }
(2)匿名内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32};System.out.print("排序前: ");for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}System.out.println();System.out.print("排序后(降序): ");Arrays.sort(a, new Comparator<Integer>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2-o1;}});for(int i:a){System.out.print(i+" ");}}
三、自定义排序规则
这里我们自定义一个学生类,有name属性和age属性,我们按照年龄从大到小排序,如果年龄相等,就按照名字降序。
public static void main(String[] args) {student[] students=new student[5];//这里创建对象数组的时候,还要new一下,别忘了!这个很容易忽略,当然,你也可以声明数组的时候就初始化数据students[0]=new student();students[0].setAge(10);students[0].setName("bac");students[1]=new student();students[1].setAge(10);students[1].setName("cac");students[2]=new student();students[2].setAge(10);students[2].setName("aac");students[3]=new student();students[3].setAge(18);students[3].setName("op");students[4]=new student();students[4].setAge(8);students[4].setName("lisi");System.out.println(students[0]);System.out.print("排序之前");for(int i=0;i<students.length;i++){System.out.println(students[i].getName()+" "+students[i].getAge());}Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(student o1, student o2) {if(o1.getAge()==o2.getAge()){return o2.getName().compareTo(o1.getName());}return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();}});System.out.println();for(int i=0;i<students.length;i++){System.out.println(students[i].getName()+" "+students[i].getAge());}}
四、集合中的sort排序
前面介绍的sort是数组的排序,集合中其实也一样,只不过Arrays.sort换成了Collections.sort
(1)升序
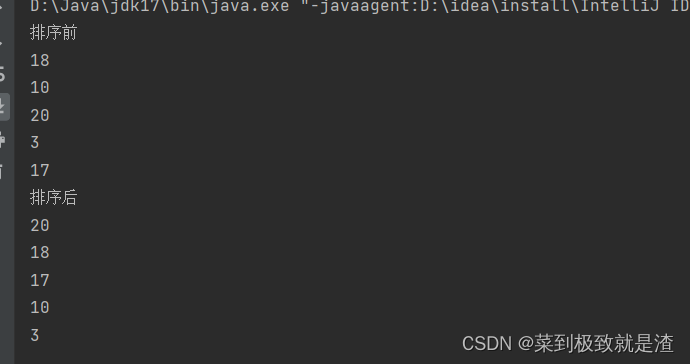
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> integerList=new ArrayList<>();integerList.add(18);integerList.add(10);integerList.add(20);integerList.add(3);integerList.add(17);System.out.println("排序前");for(Integer i:integerList){System.out.println(i);}System.out.println("排序后");//进行升序排序Collections.sort(integerList);for(Integer i:integerList){System.out.println(i);}}
(2)降序
与上面一样有两种方式实现,匿名内部类和类的实现接口,这里我就只写了匿名内部类的方法,另外一种可以看上面的数组排序。
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> integerList=new ArrayList<>();integerList.add(18);integerList.add(10);integerList.add(20);integerList.add(3);integerList.add(17);System.out.println("排序前");for(Integer i:integerList){System.out.println(i);}System.out.println("排序后");Collections.sort(integerList, new Comparator<Integer>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2-o1;}});for(Integer i:integerList){System.out.println(i);}}
(3)自定义排序
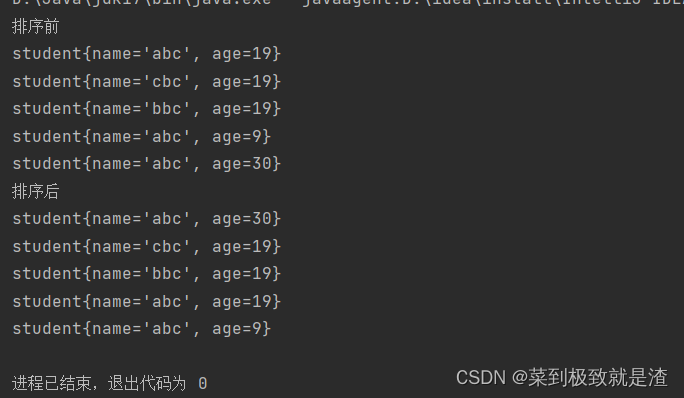
还是和上面的需求一样,年龄从小到大排序,年龄一样按照名字大的在前面
public static void main(String[] args) {List<student> students=new ArrayList<>();students.add(new student("abc",19));students.add(new student("cbc",19));students.add(new student("bbc",19));students.add(new student("abc",9));students.add(new student("abc",30));System.out.println("排序前");for(student i:students){System.out.println(i);}System.out.println("排序后");//进行自定义排序Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(student o1, student o2) {if(o1.getAge()==o2.getAge()){return o2.getName().compareTo(o1.getName());}return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();}});for(student i:students){System.out.println(i);}}




)
”)




)


)




:接口详解)

