Rinne Loves Data Structure
思路
我们插入的位置大概分了四种:
第一种
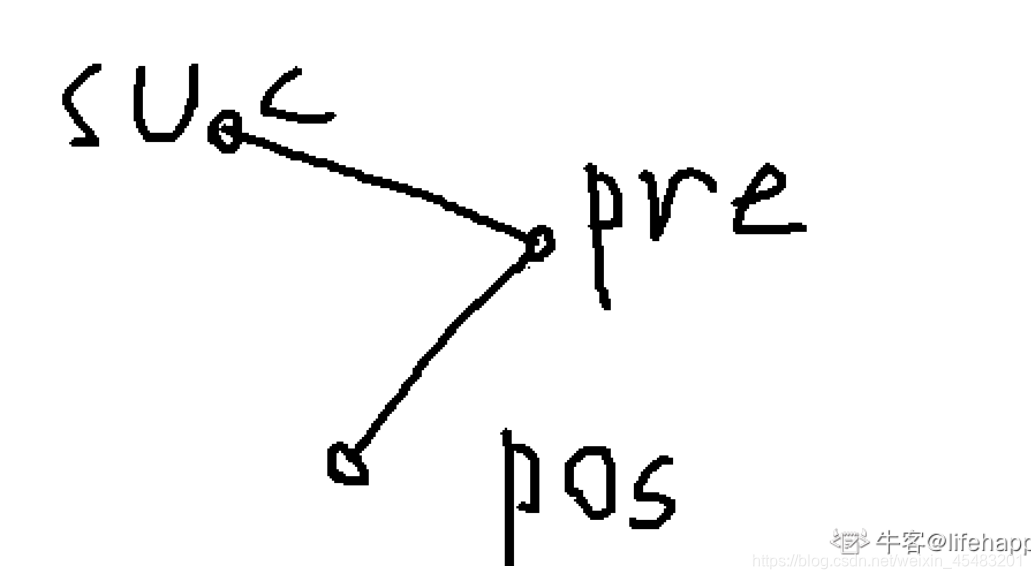
显然我们找到比当前插入的值的pre,也就是比当前节点大的最小值。
第二种
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aXr0RbM2-1595317787701)(https://uploadfiles.nowcoder.com/images/20200721/581797790_1595316800472_B79CB8409ED7617CFC7ED831FAF6AB9A "图片标题")]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2020072115513051.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NTQ4MzIwMQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
我们只要找到当前节点的suc,也就是比当前节点小的,最大值。
第三种
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-eJnwc7J0-1595317787703)(https://uploadfiles.nowcoder.com/images/20200721/581797790_1595316952732_D4737C305FB69C02F55624A5629111A0 "图片标题")]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200721155145746.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NTQ4MzIwMQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
我们只要找到当前节点的suc,也就是比当前节点小的,最大值。
第四种
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Nu8gc7js-1595317787706)(https://uploadfiles.nowcoder.com/images/20200721/581797790_1595317025533_BF2DA4AE269DFE1ECEFCAA2A465F37AC "图片标题")]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200721155157580.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NTQ4MzIwMQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
显然我们找到比当前插入的值的pre,也就是比当前节点大的最小值。
综上,一,三我们可以直接去dep[now]=max(dep[pre],dep[suc])+1dep[now] = max(dep[pre], dep[suc]) + 1dep[now]=max(dep[pre],dep[suc])+1
第二种是没有preprepre的,我们也可以直接特判,得到它的sucsucsuc,更新dep[now]=dep[suc]+1dep[now] = dep[suc] + 1dep[now]=dep[suc]+1
第四种是没有sucsucsuc的,我们可以直接特判,然后得到它的preprepre,所以dep[now]=dep[pre]+1dep[now] = dep[pre] + 1dep[now]=dep[pre]+1
插入第一个元素的时候我们既没有前驱,也没有后驱,需要单独考虑。
代码
/*Author : lifehappy
*/
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define endl '\n'using namespace std;typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;const double pi = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;inline ll read() {ll f = 1, x = 0;char c = getchar();while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return f * x;
}void print(ll x) {if(x < 10) {putchar(x + 48);return ;}print(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + 48);
}const int N = 3e5 + 10;int dep[N], n;set<int> st;int main() {// freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);// ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);int n = read();ll ans = 0;while(n--) {int x = read();if(st.size() == 0) {puts("0");st.insert(x);continue;}// auto p = lower_bound(st.begin(), st.end(), x);//用这个给tle了,不懂原理。auto p = st.lower_bound(x);if(p == st.begin()) {dep[x] = dep[*p] + 1;ans += dep[x];}else if(p == st.end()) {p--;dep[x] = dep[*p] + 1;ans += dep[x];}else {dep[x] = dep[*p] + 1;p--;dep[x] = max(dep[x], dep[*p] + 1);ans += dep[x];}st.insert(x);printf("%lld\n", ans);}return 0;
}






![基于@media (prefers-color-scheme: [dark|light])的暗黑与亮色主题切换](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/基于@media (prefers-color-scheme: [dark|light])的暗黑与亮色主题切换)




 D. You Are Given a Tree 根号分治 + dp)
)






 D. Not Adding 数学gcd)