单链表经典算法专题
一、 单链表相关经典算法OJ题1:移除链表元素

解法一:在原链表中删除Node.next=next的节点
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements( ListNode* head, int val) {ListNode* pcur = head;ListNode* pre = head;while (pcur){while (pcur->val != val ){pre = pcur;pcur = pcur->next;if (pcur == NULL){return head;}}if (head->val == val){head = head->next;pcur = head;pre = head;}else if (pcur->val == val){pcur = pcur->next;pre->next = pcur;}}return head;
}注意:当头节点的val==val时,要改变头节点的位置
解法二:创建新的指向头尾的链表
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ListNode * newHead=NULL;ListNode * newTail=NULL;ListNode* pcur=head;while(pcur){if(pcur->val!=val){if(newHead==NULL){newHead=pcur;//注意这里不能写headnewTail=pcur;}else {newTail->next=pcur;newTail=newTail->next;}}pcur=pcur->next;}if(newTail){newTail->next=NULL;}return newHead;}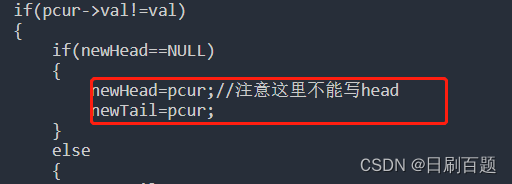 注意:这里如果写head的话,当一个节点是要删除的节点,头节点还是那个删除的节点。
注意:这里如果写head的话,当一个节点是要删除的节点,头节点还是那个删除的节点。
二、单链表相关经典算法OJ题2:反转链表

解法一:创建新链表,对新链表进行头插
typedef struct ListNode SLNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){SLNode* newHead = NULL;SLNode* newTail = NULL;SLNode* pcur = head;SLNode* last = head;while (head!=NULL){if (newHead == NULL){newHead = newTail = head;head = head->next;}else{last = head;head = head->next;pcur = last;pcur->next = newHead;newHead = pcur;}}if (newTail!=NULL){newTail->next = NULL;}return newHead;}解法二:定义三个变量,n1,n2,n3(n1,n2用来反转指向,n3在前面遍历)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList( ListNode* head) {if(head==NULL){return NULL;}ListNode * n1=NULL;ListNode * n2=head;ListNode * n3=head->next;while(n2){n2->next=n1;n1=n2;n2=n3;if(n3){n3=n3->next;}}return n1;
}三、 单链表相关经典算法OJ题3:合并两个有序链表

解法一:在原链表基础上进行修改,会使用到指定位置之前插入数
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if (list1 == NULL){return list2;}if (list2 == NULL){return list1;}ListNode* pcur1 = list1;ListNode* pre =list1;ListNode* pcur2 = list2;ListNode* pcur3 = list2->next;while (pcur1 && pcur2){while (pcur1->val < pcur2->val){pre = pcur1;pcur1 = pcur1->next;if (pcur1 == NULL){pre->next = pcur2;return list1;}}if (list1->val > pcur2->val){pcur2->next = list1;list1 = pcur2;pre = list1;pcur2 = pcur3;if (pcur3 != NULL){pcur3 = pcur3->next;}}//在pur1实现头插else{pre->next = pcur2;pcur2->next = pcur1;pcur2 = pcur3;if (pcur3 != NULL){pcur3 = pcur3->next;}}}return list1;
}输出结果:
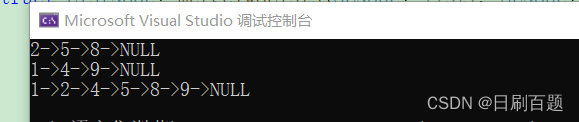
解法二:创建一个新的空链表,遍历俩个链表,进行新链表的尾插
(使用单链表)无头单向不循环链表
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if (list1 == NULL){return list2;}if (list2 == NULL){return list1;}ListNode* newhead=NULL;ListNode* newtail=NULL;ListNode* pcur1=list1;ListNode* pcur2=list2;while(pcur1&&pcur2){if(pcur1->val<pcur2->val){if(newhead==NULL)//插入新链表{newhead=newtail=pcur1;}else{newtail->next=pcur1;newtail=newtail->next;}pcur1=pcur1->next;}else{if(newhead==NULL)//插入新链表{newhead=newtail=pcur2;}else{newtail->next=pcur2;newtail=newtail->next;}pcur2=pcur2->next;}}if(pcur1==NULL){newtail->next=pcur2;}if(pcur2==NULL){newtail->next=pcur1;}return newhead;
}优化解法二(使用带头单向不循环链表)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if (list1 == NULL){return list2;}if (list2 == NULL){return list1;}ListNode* newhead,*newtail;newhead= newtail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* pcur1=list1;ListNode* pcur2=list2;while(pcur1&&pcur2){if(pcur1->val<pcur2->val){//直接插入新链表newtail->next=pcur1;newtail=newtail->next;pcur1=pcur1->next;}else{newtail->next=pcur2;newtail=newtail->next;pcur2=pcur2->next;}}if(pcur1==NULL){newtail->next=pcur2;}if(pcur2==NULL){newtail->next=pcur1;}ListNode * rethead=newhead->next;free(newhead);newhead=NULL;return rethead;;
}注:相比较与不带头链表,带头链表省略了反复判断头节点是否为空,直接插入头的后面,所带的头不带任何数据,所以返回的时候,返回头的next.
四、单链表相关经典算法OJ题4:链表的中间结点

解法一:使用快慢指针
//快慢指针
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){if(head==NULL){return NULL;}ListNode * slow,*fast;slow=head;fast=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;}return slow;}注:这种快慢指针可以运用到寻找单链表的倒数第几个节点,比如说,找倒数第3个节点,只需要让慢指针与快指针相差3个节点,当快指针走到NULL,此时慢指针为倒数第3个节点。
还有一点值得注意的是 while(fast&&fast->next)该位置判断不能颠倒,因为可能fast为空,此时先判断fast->next会报错。
五、 循环链表经典应⽤-环形链表的约瑟夫问题
著名的Josephus问题
据说著名犹太 历史学家 Josephus有过以下的故事:在罗⻢⼈占领乔塔帕特后,39 个犹太⼈与
Josephus及他的朋友躲到⼀个洞中,39个犹太⼈决定宁愿死也不要被⼈抓到,于是决定了⼀个⾃杀 ⽅式,41个⼈排成⼀个圆圈,由第1个⼈开始报数,每报数到第3⼈该⼈就必须⾃杀,然后再由下⼀ 个重新报数,直到所有⼈都⾃杀⾝亡为⽌。 然⽽Josephus 和他的朋友并不想遵从,Josephus要他的朋友先假装遵从,他将朋友与⾃⼰安排在第16个与第31个位置,于是逃过了这场死亡游戏。

解法一:创建一个单向循环链表,遇到计数等于m的节点删除,剩下最后一个节点的val值即为所求编号
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
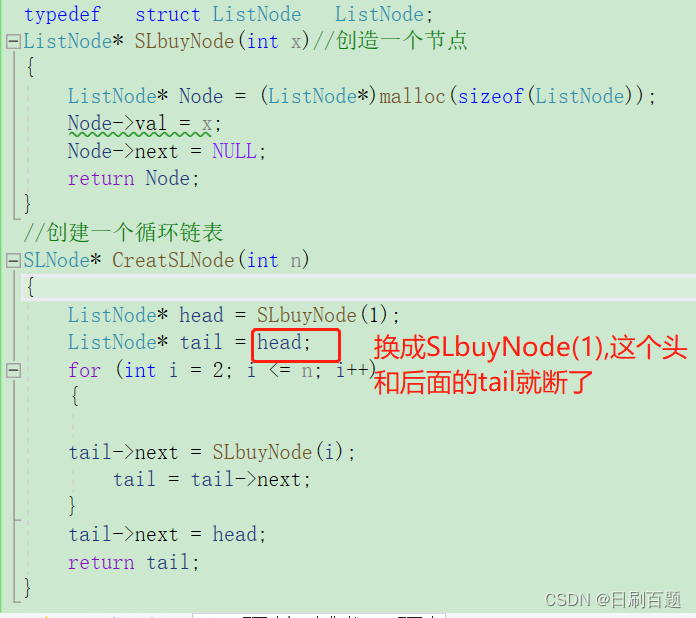
ListNode * SLbuyNode(int x)//创造一个节点
{ListNode * Node=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));Node->val=x;Node->next= NULL;return Node;
}
//创建一个循环链表
ListNode *CreatSLNode(int n)
{ListNode * head=SLbuyNode(1);ListNode * tail=head;for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){tail->next=SLbuyNode(i);tail=tail->next;}tail->next=head;return tail;
}int ysf(int n, int m ) {ListNode* prev=CreatSLNode(n);ListNode* pcur=prev->next;int count=1;while(pcur->next!=pcur){if(count==m)//报到m的节点删除{prev->next=pcur->next;free(pcur);pcur=prev->next;count=1;}else //没报m继续往前走{prev=pcur;pcur=pcur->next;count++;}}return pcur->val;
}
注意:红框若改成SLbuyNode(1),表示tail又重新开辟一块空间,和head不是同一片空间,所以连不起来。
六、 单链表相关经典算法OJ题5:分割链表
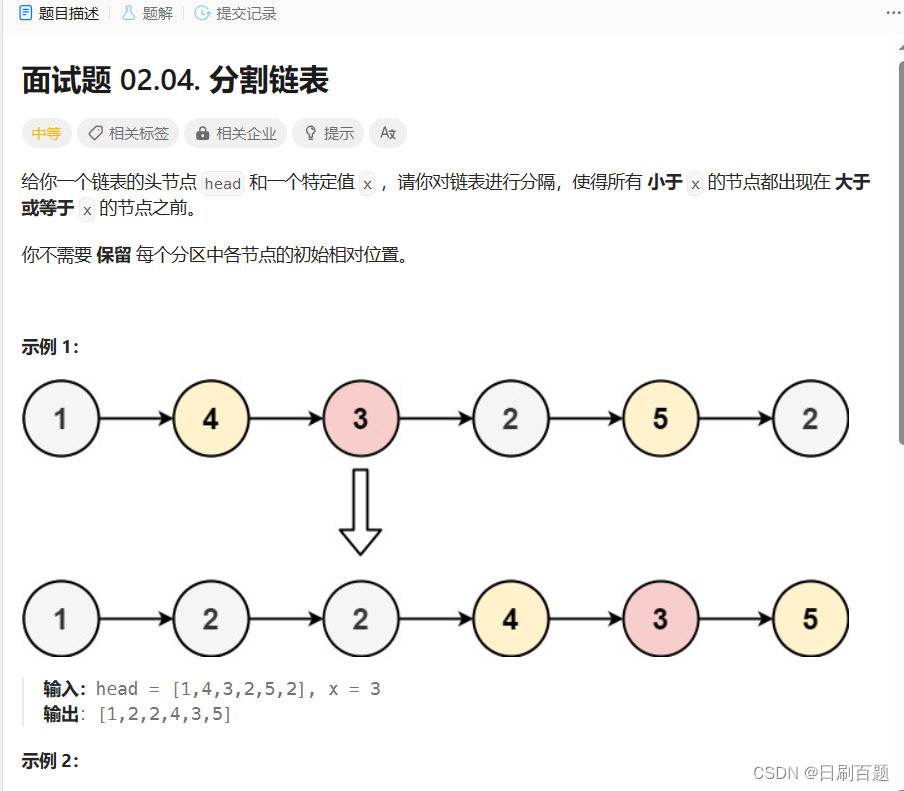
解法一:创建俩个带头单向不循环链表,将大于等于x和小于x的节点,分别放入俩个空链表,然后小链表和大链表头尾相接
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){if(head==NULL){return NULL;}ListNode * maxhead,*maxtail;ListNode * minhead,*mintail;maxhead= maxtail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));minhead=mintail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode *pcur=head;while(pcur){if(pcur->val<x){mintail->next=pcur;mintail=mintail->next;pcur=pcur->next;}else{maxtail->next=pcur;maxtail=maxtail->next;pcur=pcur->next;}}if(maxtail->next!=NULL){maxtail->next=NULL;}mintail->next=maxhead->next;ListNode*ret= minhead->next;free(maxhead);maxhead=NULL;free(minhead);minhead=NULL;return ret;
}

PC端自动化测试-C#微信接收消息并自动回复)
直升机技术)

)














