大家好,今天要讲的是关于向量相关的API,之前讲的不再进行介绍,想了解的可以看我之前的文章:
C# Solidworks二次开发:向量相关的数学函数API的使用介绍_solidworks二次开发中矩阵变换函数-CSDN博客下面介绍向量其它的相关API:
(1)第一个为Add ,这个API的含义为把一个向量添加到另一个向量中,下面是API的解释:
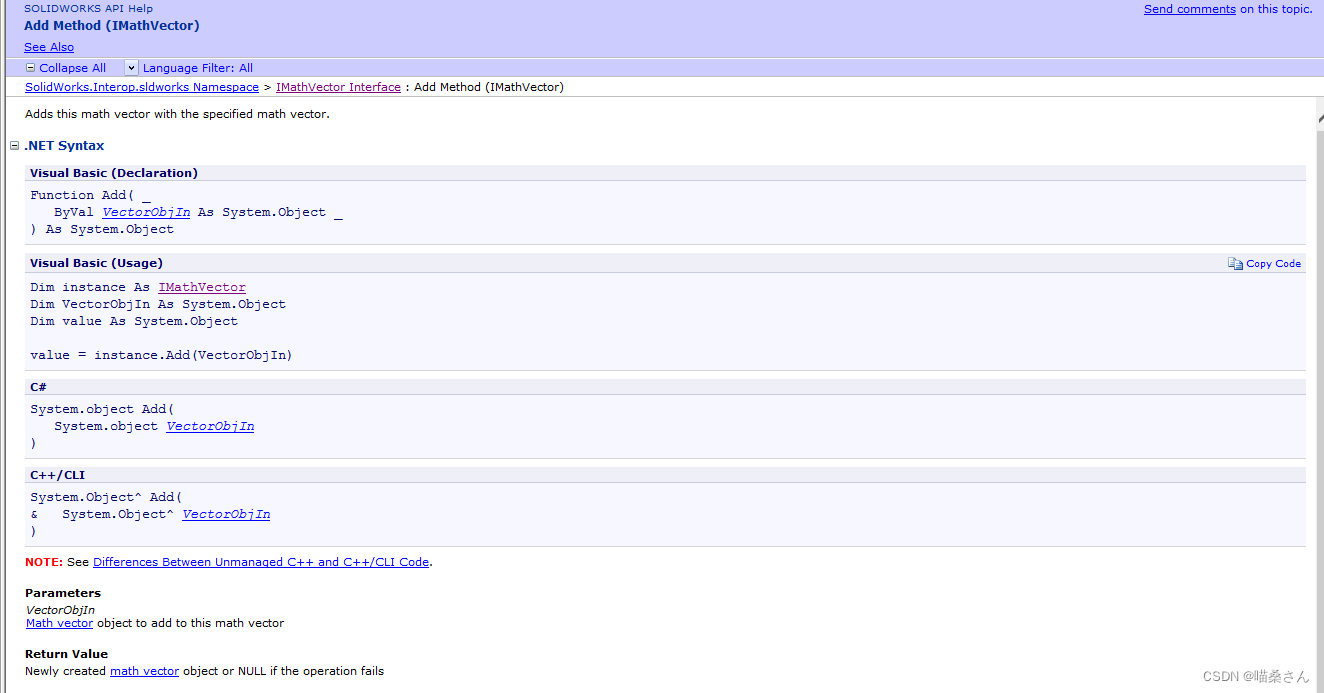
其输入的参数值只有一个,就是Math vector。
其返回值在成功的时候返回的是Math vector,在失败的时候返回的是null。
下面几个API也会涉及vector,这里我运用官方的例子对其进行使用展示:
This example shows how to get the outline of a solid body. This example also creates and inserts a sketch of that outline.
//-----------------------------------------------------
// Preconditions: Open a part document that contains
// at least one solid body.
//
// Postconditions: Processes the body outline curves
// to remove gaps before sketching the outline.
//-----------------------------------------------------
using Microsoft.VisualBasic;
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using SolidWorks.Interop.sldworks;
using SolidWorks.Interop.swconst;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace GetBodyOutline2_CSharp.csproj
{
partial class SolidWorksMacro
{
PartDoc swPart;
ModelDoc2 swModel;
MathVector swMathVector;
MathUtility swMathUtility;
Modeler swModeler;
object dirVar;
object[] bVar;
DispatchWrapper[] arrBodiesIn = new DispatchWrapper[1];
object[] Bodies = new object[1];
object curveOut;
object topol;
object outline;
double[] sEva;
double[] eEva;
double[] sEvaPrev;
double[] eEvaPrev;
double[] sEvaNext;
double[] eEvaNext;
double[] dirArr = new double[3];
double s;
double e;
int nCt;
int i;
int v;
bool isClosed;
bool isPer;
public enum direction
{
X = 1,
Y = 2,
Z = 3,
Xminus = 4,
Yminus = 5,
Zminus = 6
}
public void Main()
{
swPart = (PartDoc)swApp.ActiveDoc;
swModel = (ModelDoc2)swPart;
//Get the bodies in this part
bVar = (object[])swPart.GetBodies2((int)swBodyType_e.swSolidBody, false);
int bdycnt = bVar.GetLength(0);
for (i = 0; i < bdycnt; i++)
{
Bodies[i] = bVar[i];
arrBodiesIn[i] = new DispatchWrapper(Bodies[i]);
}
swModeler = (Modeler)swApp.GetModeler();
swMathUtility = (MathUtility)swApp.GetMathUtility();
//Create the direction vector
dirArr[0] = 0;
dirArr[1] = 0;
dirArr[2] = 0;
direction userDirection = default(direction);
userDirection = direction.Y;
if (userDirection == direction.X)
{
dirArr[0] = 1;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Xminus)
{
dirArr[0] = -1;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Y)
{
dirArr[1] = 1;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Yminus)
{
dirArr[1] = -1;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Z)
{
dirArr[2] = 1;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Zminus)
{
dirArr[2] = -1;
}
dirVar = dirArr;
//Create a MathVector
swMathVector = (MathVector)swMathUtility.CreateVector((dirArr));
//Get the number of curves in the body outline
nCt = swModeler.GetBodyOutline2((arrBodiesIn), swMathVector, 0.00001, true, out curveOut, out topol, out outline);
Object[] crvOut = (Object[])curveOut;
//Open a 3D sketch in the part document
swModel.Insert3DSketch();
//Using the end conditions of the curves, create a 2D sketch of each curve
Curve[] vCurve = null;
int newCt = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= nCt - 1; i++)
{
((Curve)crvOut[i]).GetEndParams(out s, out e, out isClosed, out isPer);
if (((Curve)crvOut[i]).GetLength3(s, e) > 1E-05)
{
Array.Resize(ref vCurve, newCt + 1);
vCurve[newCt] = (Curve)crvOut[i];
newCt = newCt + 1;
}
}
double[] sPoints = null;
double[] ePoints = null;
sPoints = new double[(newCt * 3)];
ePoints = new double[(newCt * 3)];
for (i = 0; i <= newCt - 1; i++)
{
vCurve[i].GetEndParams(out s, out e, out isClosed, out isPer);
sEva = (double[])vCurve[i].Evaluate(s);
eEva = (double[])vCurve[i].Evaluate(e);
if (i > 0)
{
v = i - 1;
}
else
{
v = newCt - 1;
}
vCurve[v].GetEndParams(out s, out e, out isClosed, out isPer);
sEvaPrev = (double[])vCurve[v].Evaluate(s);
eEvaPrev = (double[])vCurve[v].Evaluate(e);
if (i < newCt - 1)
{
v = i + 1;
}
else
{
v = 0;
}
vCurve[v].GetEndParams(out s, out e, out isClosed, out isPer);
sEvaNext = (double[])vCurve[v].Evaluate(s);
eEvaNext = (double[])vCurve[v].Evaluate(e);
sPoints[i * 3] = sEva[0] + 0.5 * (eEvaPrev[0] - sEva[0]);
sPoints[i * 3 + 1] = sEva[1] + 0.5 * (eEvaPrev[1] - sEva[1]);
sPoints[i * 3 + 2] = sEva[2] + 0.5 * (eEvaPrev[2] - sEva[2]);
ePoints[i * 3] = eEva[0] + 0.5 * (sEvaNext[0] - eEva[0]);
ePoints[i * 3 + 1] = eEva[1] + 0.5 * (sEvaNext[1] - eEva[1]);
ePoints[i * 3 + 2] = eEva[2] + 0.5 * (sEvaNext[2] - eEva[2]);
if (userDirection == direction.X | userDirection == direction.Xminus)
{
sPoints[i * 3] = 0;
ePoints[i * 3] = 0;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Y | userDirection == direction.Yminus)
{
sPoints[i * 3 + 1] = 0;
ePoints[i * 3 + 1] = 0;
}
else if (userDirection == direction.Z | userDirection == direction.Zminus)
{
sPoints[i * 3 + 2] = 0;
ePoints[i * 3 + 2] = 0;
}
}
for (i = 0; i <= (newCt * 3) - 1; i += 3)
{
swModel.CreateLine2(sPoints[i], sPoints[i + 1], sPoints[i + 2], ePoints[i], ePoints[i + 1], ePoints[i + 2]);
}
//Insert the sketches
swModel.InsertSketch2(true);
swModel.ClearSelection2(true);
}
public SldWorks swApp;
}
}
(2)第二个为Normalise,这个API的含义获取此数学向量的单位长度向量,下面是API的解释:

其没有输入参数,输出参数为向量。
(3)第三个为Scale,这个API的含义为将这个数学向量的大小,安一个因子缩放,并返回一个新的数学向量,下面是其API的解释:
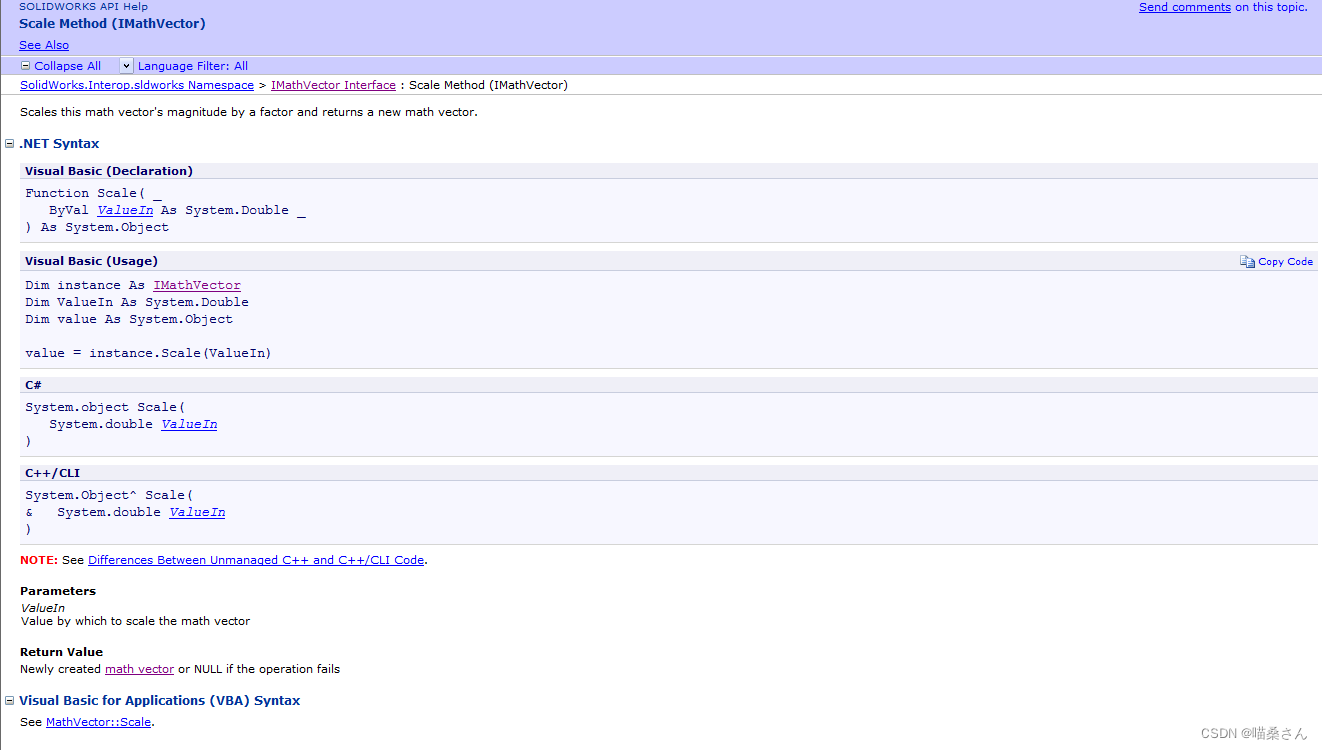
今天这篇文章要介绍的就是这三个API,我们下篇文章再见。
)






—— 绘制图形)


之事件流事件委托其他事件)


】)
)




