主要常见下面几个知识点:

1-1.请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
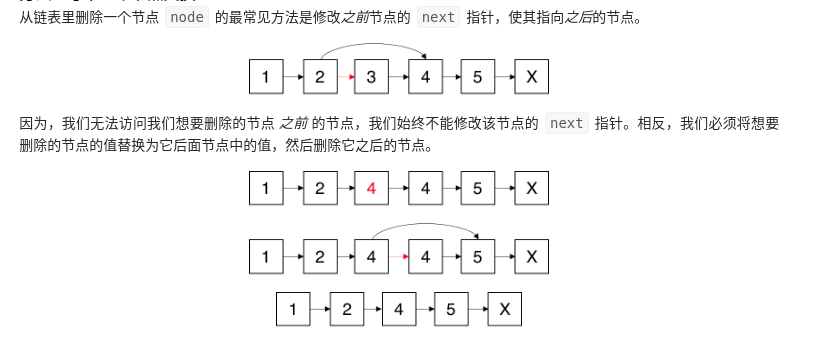
python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def deleteNode(self, node):""":type node: ListNode:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead."""node.val = node.next.valnode.next = node.next.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {node->val = node->next->val;node->next = node->next->next;}
};1-2.删除排序链表中的重复元素

通过将结点的值与它之后的结点进行比较来确定它是否为重复结点。如果它是重复的,我们更改当前结点的 next 指针,以便它跳过下一个结点并直接指向下一个结点之后的结点。如果不是重复的,则节点进行下移。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:node = headwhile node and node.next:if node.val == node.next.val:node.next = node.next.nextelse:node = node.nextreturn head
c++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* new_node;Solution(){};Solution(const Solution& sol){this->new_node = new ListNode(0, NULL);this->new_node = sol.new_node;}//深拷贝 堆区开辟空间重新赋值 解决释放内存的问题ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {this->new_node = head;while(this->new_node && this->new_node->next){if(this->new_node->val == this->new_node->next->val){this->new_node->next = this->new_node->next->next;}else{this->new_node = this->new_node->next;}}return head;}virtual ~Solution(){if(this->new_node !=NULL){this->new_node = NULL;}}
};1-3.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II

思路:通过while循环一直去掉重复的元素
python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:dummy_head = ListNode(0, head)cur = dummy_headwhile cur.next and cur.next.next:if cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val:x = cur.next.valwhile cur.next and cur.next.val == x:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn dummy_head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* dummy_head;ListNode* cur_node;Solution(){};Solution(const Solution& sol){dummy_head = sol.dummy_head;cur_node = sol.cur_node;}ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {dummy_head = new ListNode(0, head);cur_node = dummy_head;while(cur_node->next && cur_node->next->next){if(cur_node->next->val == cur_node->next->next->val){int x = cur_node->next->val;while(cur_node->next && cur_node->next->val == x){cur_node->next = cur_node->next->next;}}else{cur_node = cur_node->next;}}return dummy_head->next;}virtual ~Solution(){if(dummy_head != NULL){delete dummy_head;dummy_head = NULL;}if(cur_node != NULL){cur_node = NULL;}}
};1-4.删除链表的倒数第N个节点

思路:找到链表长度,通过在头结点补充一个节点找到要删除的节点的上一个节点,然后在进行删除
方法1:循环
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:length = 0 node = head#获取链表长度while node:length+=1node= node.next# print(length)curr_length = 0new_head = ListNode(0)new_head.next = headnode2=new_headstop_length = length - n#循环走到要删除节点的前一个节点while stop_length:stop_length-=1node2 = node2.next#跳过要删除的节点即可node2.next = node2.next.nextreturn new_head.next
方法2:递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def __init__(self):self.count = 0def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:if not head: return head head.next = self.removeNthFromEnd(head.next, n) # 递归调用self.count += 1 # 回溯时进行节点计数return head.next if self.count == n else head
方法3:双指针
fist 指针与second指针相隔n,这样first跑到尾部,second的下一个节点就是倒数第n个

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:# def __init__(self):# self.count = 0def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:new_head = ListNode(0)new_head.next = headfirst = headsecond = new_headfor i in range(n):first = first.nextwhile first:first = first.nextsecond = second.nextsecond.next = second.next.nextreturn new_head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* new_head = new ListNode(0);new_head ->next = head;ListNode* first = head;ListNode* second = new_head;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){first = first->next;}while(first){first = first->next;second = second->next;}second->next = second->next->next;return new_head->next;}
};1-5. 删除链表的节点

思路:双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:def deleteNode(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:if head is None:return headnew_head = ListNode(0)new_head.next = headpre = new_headcur = headwhile cur.val != val:pre = curcur = cur.nextpre.next = cur.nextreturn new_head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {if(head == NULL){return NULL;}ListNode* new_head = new ListNode(0);new_head->next = head;ListNode* pre = new_head;ListNode* cur = head;while(cur->val != val){pre = cur;cur = cur->next;}pre->next = cur->next;return new_head->next;}
};1-6.两两交换链表中的节点

思路:迭代法

python代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:new_head = ListNode(0)new_head.next = headtemp = new_headwhile temp.next and temp.next.next:node1 = temp.nextnode2 = temp.next.nexttemp.next = node2node1.next = node2.nextnode2.next = node1temp = node1return new_head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {ListNode* new_head = new ListNode(0);new_head->next = head;ListNode* temp = new_head;while(temp->next && temp->next->next){ListNode* head1 = temp->next;ListNode* head2 = temp->next->next;temp->next = head2;head1->next = head2->next;head2->next = head1;temp = head1;}return new_head->next;}
};思路:递归法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:if head is None or head.next is None:return headnew_head = head.nexthead.next = self.swapPairs(new_head.next)new_head.next = headreturn new_headc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr){return head;}ListNode* new_head;new_head = head->next;head->next = swapPairs(new_head->next);new_head->next = head;return new_head;}
};2-1.反转链表

思路1:双指针
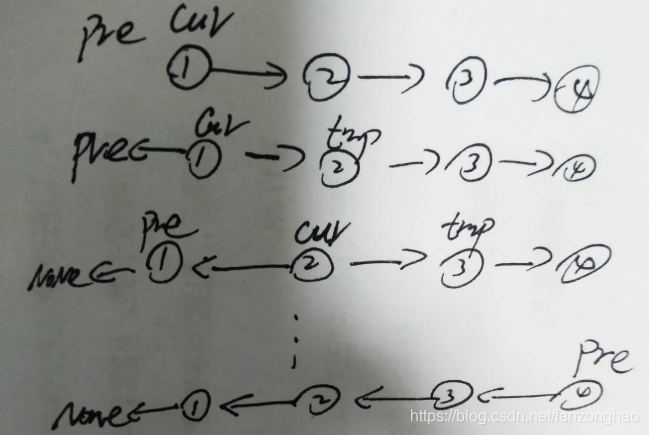
class Solution(object):def reverseList(self, head):""":type head: ListNode:rtype: ListNode"""# 申请两个节点,pre和 cur,pre指向Nonepre = Nonecur = head# 遍历链表,while循环里面的内容其实可以写成一行while cur:# 记录当前节点的下一个节点tmp = cur.next# 然后将当前节点指向precur.next = pre# pre和cur节点都前进一位pre = curcur = tmpreturn pre c++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* pre = nullptr;ListNode* temp = head;while(head){temp = head->next;head->next = pre;pre = head;head = temp;}return pre;}
};思路2.递归法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:# pre = None# cur = head# while cur:# node = cur.next# cur.next = pre# pre = cur# cur = node# return preif head is None or head.next is None:return headnew_node = self.reverseList(head.next)print('head.val',head.val)head.next.next = headhead.next = Nonereturn new_node
2-2:旋转链表

思路:
构成循环列表以后 找到移动的节点 在拆分

python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def rotateRight(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:if k == 0 or head is None or head.next is None:return head#计算链表长度cur = head n = 1while cur.next:cur = cur.nextn += 1# print('==n:', n) add = n - k % nif add == n:#k是n的整数倍直接返回原节点return headcur.next = head #构成环while add:cur = cur.nextadd -= 1new_head = cur.next#找到移动后的开始节点cur.next = None#拆开return new_headc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {if(k == 0 || head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr){return head;}int n = 1;//得到环长度ListNode* cur = head;while(cur->next){cur = cur->next;n++;}//找到移动的add长度int add = n - k % n;if(add == n){return head;}cur->next = head;//构成环while(add){cur = cur->next;add--;}ListNode* new_node = cur->next;cur->next = nullptr;//拆环return new_node;}
};3-1.合并两个排序的链表
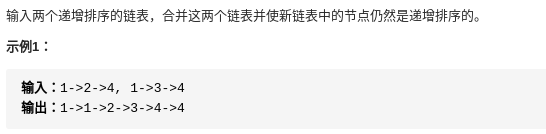
思路:引入一个指针头 python实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:head = ListNode(0)node = headwhile l1 and l2:if l1.val < l2.val:node.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:node.next = l2l2 = l2.nextnode = node.nextif l1 is not None:node.next= l1if l2 is not None:node.next= l2return head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode* new_head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* node = new_head;while(l1!=NULL && l2 !=NULL){if(l1->val<l2->val){node->next = l1;l1 = l1->next;}else{node->next = l2;l2 = l2->next; }node = node->next;}if (l1!=NULL){node->next = l1;}if(l2!=NULL){node->next = l2;}return new_head->next;}
};思路:递归
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {if(l1 == nullptr){return l2;}if(l2 == nullptr){return l1;}if(l1->val < l2->val){l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);return l1;}else{l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);return l2;}}
};3-2.合并K个升序链表

思路1:上一题合并两个变成for循环顺序合并
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def mergeTwo(self, l1, l2):if l1 is None:return l2if l2 is None:return l1head = ListNode(0)node = headwhile l1 and l2:if l1.val <l2.val:node.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:node.next = l2l2 = l2.nextnode = node.nextif l1:node.next = l1if l2:node.next = l2return head.nextdef mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:ans = Nonefor i in range(len(lists)):ans = self.mergeTwo(ans,lists[i])return ansc++:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergtwo(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){if(l1==nullptr){return l2;}if(l2==nullptr){return l1;}ListNode* new_head= new ListNode(0);ListNode* node = new_head;while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val<l2->val){node->next = l1;l1= l1->next;}else{node->next = l2;l2= l2->next;}node = node->next;}if(l1){node->next = l1;}if(l2){node->next = l2;}return new_head->next;}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {ListNode* res = nullptr;for (int i=0;i<lists.size();i++){res = mergtwo(res,lists[i]);}return res;}
};思路2:分治归并1
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def mergeTwo(self, l1, l2):if l1 is None:return l2if l2 is None:return l1head = ListNode(0)node = headwhile l1 and l2:if l1.val <l2.val:node.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:node.next = l2l2 = l2.nextnode = node.nextif l1:node.next = l1if l2:node.next = l2return head.nextdef mergeSort(self, lists, left, right):if left==right:return lists[left]middle = left + (right-left)//2# print('== middle:', middle)l1 = self.mergeSort(lists,left,middle)# print('== l1:', l1)l2 = self.mergeSort(lists,middle+1,right)return self.mergeTwo(l1, l2)def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:# print('==hahah')if len(lists)==0:return Nonereturn self.mergeSort(lists,0,len(lists) - 1)c++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergetwo(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){if(l1==nullptr){return l2;}if(l2==nullptr){return l1;}ListNode* new_head= new ListNode(0);ListNode* node = new_head;while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val<l2->val){node->next = l1;l1= l1->next;}else{node->next = l2;l2= l2->next;}node = node->next;}if(l1){node->next = l1;}if(l2){node->next = l2;}return new_head->next;}ListNode* mergesort(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int left, int right){if(left==right){return lists[left];}int middle = left+(right -left)/2;ListNode* l1 = mergesort(lists,left,middle);ListNode* l2 = mergesort(lists,middle+1,right);return mergetwo(l1,l2);}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {// ListNode* res = nullptr;// for (int i=0;i<lists.size();i++){// res = mergtwo(res,lists[i]);// }// return res;if (lists.size()==0){return nullptr;}return mergesort(lists,0,lists.size()-1);}
};思路3:分支归并2 参考排序算法的归并排序 排序算法--(冒泡排序,插入排序,选择排序,归并排序,快速排序,桶排序,计数排序,基数排序)_智障变智能-CSDN博客
class Solution:def mergeTwo(self, l1, l2):if l1 is None:return l2if l2 is None:return l1head = ListNode(0)node = headwhile l1 and l2:if l1.val < l2.val:node.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:node.next = l2l2 = l2.nextnode = node.nextif l1:node.next = l1if l2:node.next = l2return head.nextdef mergeSort(self, L):if len(L) <= 1:return L[0]mid = len(L) // 2 l1 = self.mergeSort(L[:mid])l2 = self.mergeSort(L[mid:])return self.mergeTwo(l1, l2)def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:if len(lists)==0:return Nonereturn self.mergeSort(lists)3-3.合并两个有序链表

思路:递归 终止条件就是节点为None.
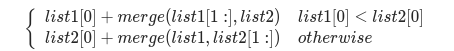
1.递归法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:#递归的终止条件if l1 is None:return l2elif l2 is None:return l1 elif l1.val < l2.val:l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2)return l1else:l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next)return l22.迭代法:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:fake_head_node = ListNode(0)cur = fake_head_nodewhile l1 and l2:if l1.val<l2.val:cur.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:cur.next = l2l2 = l2.next cur = cur.nextif l1:cur.next = l1else:cur.next = l2return fake_head_node.next3-4.排序链表

思路1:归并排序 先通过快慢指针找到中心点 进行截断以后一直递归拆开 在进行合并即可
python代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def merge(self, left, right):res = ListNode(0)temp = reswhile left and right:if left.val < right.val:temp.next, left = left, left.nextelse:temp.next, right = right, right.nexttemp = temp.nexttemp.next = left if left else rightreturn res.nextdef sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:if head is None or head.next is None:return head #快慢指针找到链表中心点slow, fast = head, head.nextwhile fast and fast.next:fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.nextmid, slow.next = slow.next, None#将找到的中心点进行截断故 slow.next = Noneleft, right = self.sortList(head), self.sortList(mid)#递归一直进行拆分return self.merge(left, right)#合并操作c++代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergetwo(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2){ListNode* new_head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* node = new_head;while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val<l2->val){node->next = l1;l1 = l1->next;}else{node->next = l2;l2 = l2->next;}node = node->next;}if(l1){node->next = l1;}if(l2){node->next = l2;}return new_head->next;}ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr){return head;}ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head->next;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}ListNode* middle = slow->next;slow->next = nullptr;ListNode* l1 = sortList(head);ListNode* l2 = sortList(middle);return mergetwo(l1,l2);}
};思路2:合并也是递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:# def merge(self, left, right):# res = ListNode(0)# temp = res# while left and right:# if left.val < right.val:# temp.next, left = left, left.next# else:# temp.next, right = right, right.next# temp = temp.next# temp.next = left if left else right# return res.nextdef merge(self,left,right):if left is None:return rightif right is None:return leftif left.val < right.val:left.next = self.merge(left.next, right)return leftelse:right.next = self.merge(left, right.next)return rightdef sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:if head is None or head.next is None:return head #快慢指针找到链表中心点slow, fast = head, head.nextwhile fast and fast.next:fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.nextmid, slow.next = slow.next, None#将找到的中心点进行截断故 slow.next = Noneleft, right = self.sortList(head), self.sortList(mid)#递归一直进行拆分return self.merge(left, right)#合并操作3-5.两数相加

思路:开出一个head头,利用一个指针进行遍历,需要注意的是进位
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:head = ListNode(0)new_node = headcarry = 0while l1 and l2:new_node.next =ListNode(l1.val+l2.val+carry)carry = new_node.next.val//10 new_node.next.val = new_node.next.val%10l1 = l1.nextl2= l2.nextnew_node = new_node.next# print(carry)while l1:new_node.next = ListNode(l1.val+carry)carry = new_node.next.val//10new_node.next.val = new_node.next.val%10l1 = l1.nextnew_node = new_node.nextwhile l2:new_node.next = ListNode(l2.val+carry)carry = new_node.next.val//10new_node.next.val = new_node.next.val%10l2 = l2.nextnew_node = new_node.nextif carry:new_node.next = ListNode(carry)return head.nextc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode* head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* new_head = head;int carry = 0;while(l1 && l2){new_head->next = new ListNode(l1->val + l2->val + carry);carry = new_head->next->val/10;new_head->next->val = new_head->next->val%10; new_head = new_head->next;l1 = l1->next;l2 = l2->next;}while(l1){new_head->next = new ListNode(l1->val + carry);carry = new_head->next->val/10;new_head->next->val = new_head->next->val%10; new_head = new_head->next;l1 = l1->next;}while(l2){new_head->next = new ListNode(l2->val + carry);carry = new_head->next->val/10;new_head->next->val = new_head->next->val%10; new_head = new_head->next;l2 = l2->next;}if(carry){new_head->next = new ListNode(carry);}return head->next;}
};3-5.2 两数相加 II

思路:在上一题基础上加一个栈
python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:value1,value2 = [], []while l1:value1.append(l1.val)l1 = l1.nextwhile l2:value2.append(l2.val)l2 = l2.nextcarry = 0res = Nonewhile len(value1) > 0 or len(value2) > 0 or carry != 0:if len(value1):temp_1 = value1.pop()else:temp_1 = 0if len(value2):temp_2 = value2.pop()else:temp_2 = 0cur = temp_1 + temp_2 + carrycarry = cur // 10cur %= 10node = ListNode(cur)node.next = resres = nodereturn resc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {stack<int> value1, value2;while(l1){value1.push(l1->val);l1 = l1->next;}while(l2){value2.push(l2->val);l2 = l2->next;}int carry = 0;ListNode* res = nullptr;while(!value1.empty() || !value2.empty() || carry != 0){int temp_1 = 0, temp_2 = 0;if(!value1.empty()){temp_1 = value1.top();value1.pop();}if(!value2.empty()){temp_2 = value2.top();value2.pop();}int cur = temp_1 + temp_2 + carry;carry = cur / 10;cur %= 10;ListNode* node = new ListNode(cur);node->next = res;res = node;}return res;}
};3-6.合并两个链表

思路:找出被截断的两个链表点,开始节点指向要加入的链表,加入的链表在指向结束节点就行。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def mergeInBetween(self, list1: ListNode, a: int, b: int, list2: ListNode) -> ListNode:node = list1length = 0while list1:if length == a - 1:start = list1if length == b + 1:end = list1length += 1 list1 = list1.nextstart.next = list2while list2.next:list2 = list2.nextlist2.next = endreturn nodec++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {ListNode* node = list1;ListNode* start; ListNode* end;int length = 0;while(list1){if(length == a-1){start = list1;}if(length == b+1){end = list1;}length++;list1 = list1->next;}start->next = list2;while(list2->next){list2 = list2->next;}list2->next = end;return node;}
};3-7. 重排链表

思路:利用线性表存储该链表节点,然后利用线性表可以下标访问的特点,直接按顺序访问指定元素,重建该链表即可。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:"""Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead."""nodes_list = []node = headwhile node:nodes_list.append(node)node = node.nextstart, end = 0, len(nodes_list) - 1while start < end:nodes_list[start].next = nodes_list[end]start += 1if start == end:breaknodes_list[end].next = nodes_list[start]end -= 1nodes_list[start].next = Nonec++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void reorderList(ListNode* head) {vector<ListNode*> nodes_list;ListNode* node = head;while(node){nodes_list.push_back(node);node = node->next;}int start = 0, end = nodes_list.size() - 1;while(start < end){nodes_list[start]->next = nodes_list[end];start++;if(start == end){break;}nodes_list[end]->next = nodes_list[start];end--;}nodes_list[start]->next = nullptr;}
};4-1.环形链表

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:#快慢指针 人追人slow,fast = head,headwhile fast and fast.next:fast = fast.next.nextslow = slow.nextif slow==fast:return True return Falsec++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){return true;}}return false;}
};4-2.给定一个有环链表,实现一个算法返回环路的开头节点。

假设有两个指针,分别为快慢指针fast和slow, 快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次前进一步,如果有环则两个指针必定相遇;
反证法:假设快指针真的 越过 了慢指针,且快指针处于位置 i+1,而慢指针处于位置 i,那么在前一步,快指针处于位置 i-1,慢指针也处于位置 i-1,它们相遇了。
A:链表起点
B:环起点
C:相遇点
X:环起点到相遇点距离
Y:链表起点到环起点距离
R:环的长度
S:第一次相遇时走过的路程
1.慢指针slow第一次相遇走过的路程 S1 = Y + X;(11)
快指针fast第一次相遇走过的路程 S2=2S1 = Y + X + NR;(2)
说明:快指针的速度是慢指针的两倍,相同时间内路程应该是慢指针的两倍,Y + X + NR是因为快指针可能经过N圈后两者才相遇;
把(1)式代入(2)式得:Y = NR -X;
2..在将慢指针回到A点,满指针和快指针同时走,在B点相遇,此处就是环节点.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:slow = headfast = head;while fast:if fast and fast.next:slow = slow.nextfast = fast.next.nextelse:return Noneif slow==fast:breakif fast ==None or fast.next==None:return Noneslow= headwhile slow!=fast:slow = slow.nextfast = fast.nextreturn slowc++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while(fast){if(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}else{return NULL;}if(slow==fast){break;}}if(!fast || !fast->next){return NULL;}slow = head;while(slow!=fast){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return slow;}
};4-3.链表相交

如这题应该是比较明显的双指针题,要是能实现一种算法让两个指针分别从A和B点往C点走,两个指针分别走到C后,又各自从另外一个指针的起点,也就是A指针第二次走从B点开始走,B指针同理,这样,A指针走的路径长度 AO + OC + BO 必定等于B指针走的路径长度 BO + OC + AO,这也就意味着这两个指针第二轮走必定会在O点相遇,相遇后也即到达了退出循环的条件,代码如下:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:index_a = headAindex_b = headBwhile index_a !=index_b:if index_a !=None:index_a = index_a.nextelse:index_a = headBif index_b != None:index_b = index_b.nextelse:index_b = headAreturn index_ac++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {ListNode* node_A = headA;ListNode* node_B = headB;while(node_A!=node_B){if(node_A!=NULL){node_A=node_A->next;}else{node_A = headB;}if(node_B!=NULL){node_B=node_B->next;}else{node_B = headA;}}return node_A;}
};4-4.两个链表的第一个公共节点

思路:双指针 两个指针轮流走一遍各自的路程,这样相遇就是公共节点,对于没有公共节点的情况,所以需要判断自身节点不是none,而不是.next是none,在去交换指针,否则会陷入无穷循环,而此时输出就是none。
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:first_head = headAsecond_head = headBwhile first_head !=second_head:if first_head is not None:first_head = first_head.next else:first_head = headBif second_head is not None:second_head = second_head.nextelse:second_head = headA# print(first_head)return first_headc++:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {ListNode *first_node;first_node = headA;ListNode *second_node;second_node= headB;while(first_node != second_node){if(first_node !=NULL){first_node = first_node->next;}else{first_node = headB;}if(second_node !=NULL){second_node = second_node->next;}else{second_node = headA;}}return first_node;}
};5-1.输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
1.借用栈
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:stack = []while head:stack.append(head.val)head = head.nextreturn stack[::-1]c++:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {vector<int> res;while(head){res.push_back(head->val);head = head->next;}reverse(res.begin(),res.end());return res;}
};2.递归回溯
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:if head:return self.reversePrint(head.next)+[head.val]else:return []5-2.请判断一个链表是否为回文链表
利用列表将列表值进行拷贝,在判断是否是回文字符串
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:stack= []while head:stack.append(head.val)head = head.nextreturn stack==stack[::-1]c++实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {vector<int> res;while(head){res.push_back(head->val);head = head->next;}int left=0;int right=res.size()-1;while(left<right){if(res[left]==res[right]){left+=1;right-=1;}else{return false;}}return true;}
};5-3.分隔链表

思路:开出两个大小节点,用于指向大于x和小于x的,遍历结束以后在合并即可
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = Noneclass Solution:def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:small_head = ListNode(0)large_head = ListNode(0)small_node = small_headlarge_node = large_headwhile head:if head.val < x:small_node.next = headsmall_node = small_node.nextelse:large_node.next = headlarge_node = large_node.nexthead= head.nextlarge_node.next = Nonesmall_node.next = large_head.nextreturn small_head.nextc++写法:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {ListNode* small_head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* big_head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* small_node =small_head;ListNode* big_node = big_head;while(head){if (head->val<x){small_node->next = head; small_node = small_node->next;}else{big_node->next = head;big_node = big_node->next;}head = head->next;}big_node->next = nullptr;small_node->next = big_head->next;return small_head->next;}
};6-1.二叉树展开为链表

思路:可看出是根据前序遍历的节点统统放在右子树上
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def help(self, node):if node is not None:self.res.append(node)self.help(node.left)self.help(node.right)def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:"""Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead."""self.res = []self.help(root)# print(self.res)length = len(self.res)for i in range(1,length):pre,cur = self.res[i-1],self.res[i]pre.left = Nonepre.right = curreturn rootc++实现:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<TreeNode* >res;void help(TreeNode* node){if(node){res.push_back(node);help(node->left);help(node->right);}}void flatten(TreeNode* root) {help(root);for(int i=1;i<res.size();i++){TreeNode* pre = res[i-1];TreeNode* cur = res[i];pre->left = nullptr;pre->right = cur;}// return root;}
};双向链表例题:
7-1:LRU 缓存机制

思路:双向链表,这样优先将get的移到头部

class Node:def __init__(self, key=0, value=0):self.key = keyself.value = valueself.prev = Noneself.next = Noneclass LRUCache:def __init__(self, capacity: int):self.cache = {}self.head = Node()self.tail = Node()self.head.next = self.tailself.tail.prev = self.headself.capacity = capacityself.size = 0def get(self, key: int) -> int:if key not in self.cache:return -1# 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部node = self.cache[key]self.moveToHead(node)return node.valuedef put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:if key not in self.cache:# 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点node = Node(key, value)# 添加进哈希表self.cache[key] = node# 添加至双向链表的头部self.addToHead(node)self.size += 1if self.size > self.capacity:# 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点removed = self.removeTail()# 删除哈希表中对应的项self.cache.pop(removed.key)self.size -= 1else:# 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部node = self.cache[key]node.value = valueself.moveToHead(node)def addToHead(self, node):node.prev = self.headnode.next = self.head.nextself.head.next.prev = nodeself.head.next = nodedef removeNode(self, node):node.prev.next = node.nextnode.next.prev = node.prevdef moveToHead(self, node):self.removeNode(node)self.addToHead(node)def removeTail(self):node = self.tail.prevself.removeNode(node)return node


)






 + python(c++))








转c++ tensorrt)
