第一个最简单的lenet示例请参考这篇文章
一.torch阶段
测试图片:

torch代码:
# coding:utf-8
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torchvision
import os
import struct
import time
import cv2
import numpy as npdef main():print('cuda device count: ', torch.cuda.device_count())os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1"model = torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=True)# net.fc = nn.Linear(512, 2)model = model.to('cuda:0')model.eval()# print(model)st_time = time.time()nums = 10000for i in range(nums):input_ = torch.ones(1, 3, 224, 224).to('cuda:0')out = model(input_)# print('====out.shape:===', out.shape)#(1, 1000)end_time = time.time()print('==avge cost time{}'.format((end_time - st_time)/nums))# input_ = torch.ones(1, 3, 224, 224).to('cuda:0')# save_pth(model, input_)#存储.pth# save_onnx(input_, model)#存储.onnx方便可视化网络# get_wts(model)#提取key value权重def save_pth(model, input_):conv1 = model.conv1(input_)print('===conv1.shape:', conv1.shape)# maxpool_1 = model.maxpool(conv1)# print('===maxpool_1.shape:', maxpool_1.shape)# layer1 = model.layer1(maxpool_1)# print('===layer1.shape:', layer1.shape)# layer2 = model.layer2(layer1)# print('===layer2.shape:', layer2.shape)# layer3 = model.layer3(layer2)# print('===layer3.shape:', layer3.shape)# layer4 = model.layer4(layer3)# print('===layer4.shape:', layer4.shape)# print('resnet50 out:', out.shape)torch.save(model, "resnet50.pth")def get_wts(model):f = open("resnet50.wts", 'w')f.write("{}\n".format(len(model.state_dict().keys())))for k, v in model.state_dict().items():# print('key: ', k)#weight name# print('value: ', v.shape)#weight shapevr = v.reshape(-1).cpu().numpy()f.write("{} {}".format(k, len(vr)))for vv in vr:f.write(" ")f.write(struct.pack(">f", float(vv)).hex())f.write("\n")def save_onnx(input_, model):# torch.onnx.export(model, input_, "./resnet50.onnx", verbose=True)torch.onnx.export(model, # model being runinput_, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)"./resnet50.onnx",opset_version=10,verbose=False, # store the trained parameter weights inside the model filetraining=False,do_constant_folding=True,input_names=['input'],output_names=['output'])def test_real_img():os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1"model = torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=True)# net.fc = nn.Linear(512, 2)model = model.to('cuda:0')model.eval()# print(model)img = cv2.imread('./test2.jpg')print('===img.shape', img.shape)img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224))mean = np.array([0.406, 0.456, 0.485]).astype(np.float32)std = np.array([0.225, 0.224, 0.229]).astype(np.float32)img = (img / 255. - mean) / stdimg = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)print('===img.shape', img.shape)img = np.transpose(img, (0, 3, 1, 2)).astype(np.float32)# img = np.ones((1, 3, 224, 224)).astype(np.float32)nums = 10000img = torch.from_numpy(img)st_time = time.time()for i in range(nums):with torch.no_grad():out = model(img.cuda())end_time = time.time()print('==avge cost time{}'.format((end_time - st_time) / nums))print('====out.shape:===', out.shape) # (1, 1000)with open('./pytorch_result.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:for i in range(1000):file.write(str(out.cpu().numpy()[0][i]) + '\n')torch_value, torch_index = torch.max(out, dim=1)print('====torch_value:===', torch_value)#13.8998print('====torch_index:===', torch_index)#285 Egyptian cattopk = 5topk_index = torch.argsort(out, dim=1, descending=True)[:, :topk]print('===topk_index:', topk_index)out = out.cpu().numpy()index = np.where(out == np.max(out))print('===index:===', index)if __name__ == '__main__':# main()test_real_img()其中:get_wts用于生成16进制权重文件,resnet50.wts,后续tensorrt载入模型权重。
save_onnx用于生成resnet50.onnx文件,可视化网络结构。
结果:
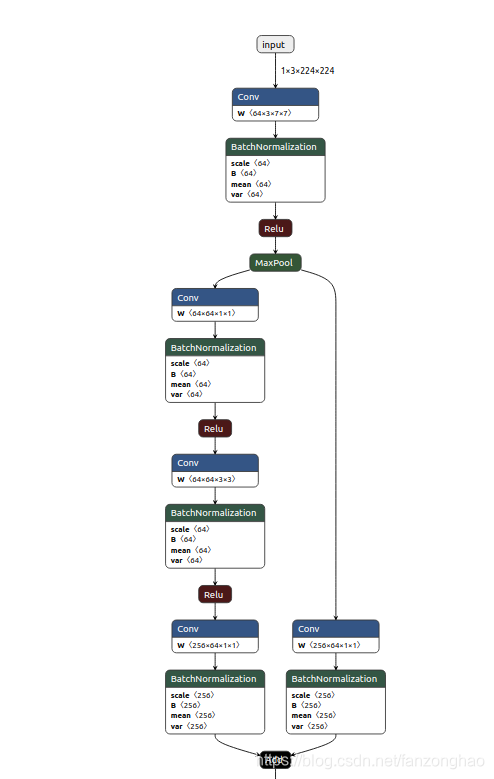

查找imageNet 索引285所对应的标签为:

生成.txt截图如下:

二.tensorrt转换阶段
2.1序列化生成.engine阶段
1.文件代码结构图
其中resnet50.wts是torch阶段生成的,resnet50.engine是本阶段要生成的。
2.代码:
logging.h
/** Copyright (c) 2019, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/#ifndef TENSORRT_LOGGING_H
#define TENSORRT_LOGGING_H#include "NvInferRuntimeCommon.h"
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>using Severity = nvinfer1::ILogger::Severity;class LogStreamConsumerBuffer : public std::stringbuf
{
public:LogStreamConsumerBuffer(std::ostream& stream, const std::string& prefix, bool shouldLog): mOutput(stream), mPrefix(prefix), mShouldLog(shouldLog){}LogStreamConsumerBuffer(LogStreamConsumerBuffer&& other): mOutput(other.mOutput){}~LogStreamConsumerBuffer(){// std::streambuf::pbase() gives a pointer to the beginning of the buffered part of the output sequence// std::streambuf::pptr() gives a pointer to the current position of the output sequence// if the pointer to the beginning is not equal to the pointer to the current position,// call putOutput() to log the output to the streamif (pbase() != pptr()){putOutput();}}// synchronizes the stream buffer and returns 0 on success// synchronizing the stream buffer consists of inserting the buffer contents into the stream,// resetting the buffer and flushing the streamvirtual int sync(){putOutput();return 0;}void putOutput(){if (mShouldLog){// prepend timestampstd::time_t timestamp = std::time(nullptr);tm* tm_local = std::localtime(×tamp);std::cout << "[";std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << 1 + tm_local->tm_mon << "/";std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_mday << "/";std::cout << std::setw(4) << std::setfill('0') << 1900 + tm_local->tm_year << "-";std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_hour << ":";std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_min << ":";std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_sec << "] ";// std::stringbuf::str() gets the string contents of the buffer// insert the buffer contents pre-appended by the appropriate prefix into the streammOutput << mPrefix << str();// set the buffer to emptystr("");// flush the streammOutput.flush();}}void setShouldLog(bool shouldLog){mShouldLog = shouldLog;}private:std::ostream& mOutput;std::string mPrefix;bool mShouldLog;
};//!
//! \class LogStreamConsumerBase
//! \brief Convenience object used to initialize LogStreamConsumerBuffer before std::ostream in LogStreamConsumer
//!
class LogStreamConsumerBase
{
public:LogStreamConsumerBase(std::ostream& stream, const std::string& prefix, bool shouldLog): mBuffer(stream, prefix, shouldLog){}protected:LogStreamConsumerBuffer mBuffer;
};//!
//! \class LogStreamConsumer
//! \brief Convenience object used to facilitate use of C++ stream syntax when logging messages.
//! Order of base classes is LogStreamConsumerBase and then std::ostream.
//! This is because the LogStreamConsumerBase class is used to initialize the LogStreamConsumerBuffer member field
//! in LogStreamConsumer and then the address of the buffer is passed to std::ostream.
//! This is necessary to prevent the address of an uninitialized buffer from being passed to std::ostream.
//! Please do not change the order of the parent classes.
//!
class LogStreamConsumer : protected LogStreamConsumerBase, public std::ostream
{
public://! \brief Creates a LogStreamConsumer which logs messages with level severity.//! Reportable severity determines if the messages are severe enough to be logged.LogStreamConsumer(Severity reportableSeverity, Severity severity): LogStreamConsumerBase(severityOstream(severity), severityPrefix(severity), severity <= reportableSeverity), std::ostream(&mBuffer) // links the stream buffer with the stream, mShouldLog(severity <= reportableSeverity), mSeverity(severity){}LogStreamConsumer(LogStreamConsumer&& other): LogStreamConsumerBase(severityOstream(other.mSeverity), severityPrefix(other.mSeverity), other.mShouldLog), std::ostream(&mBuffer) // links the stream buffer with the stream, mShouldLog(other.mShouldLog), mSeverity(other.mSeverity){}void setReportableSeverity(Severity reportableSeverity){mShouldLog = mSeverity <= reportableSeverity;mBuffer.setShouldLog(mShouldLog);}private:static std::ostream& severityOstream(Severity severity){return severity >= Severity::kINFO ? std::cout : std::cerr;}static std::string severityPrefix(Severity severity){switch (severity){case Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR: return "[F] ";case Severity::kERROR: return "[E] ";case Severity::kWARNING: return "[W] ";case Severity::kINFO: return "[I] ";case Severity::kVERBOSE: return "[V] ";default: assert(0); return "";}}bool mShouldLog;Severity mSeverity;
};//! \class Logger
//!
//! \brief Class which manages logging of TensorRT tools and samples
//!
//! \details This class provides a common interface for TensorRT tools and samples to log information to the console,
//! and supports logging two types of messages:
//!
//! - Debugging messages with an associated severity (info, warning, error, or internal error/fatal)
//! - Test pass/fail messages
//!
//! The advantage of having all samples use this class for logging as opposed to emitting directly to stdout/stderr is
//! that the logic for controlling the verbosity and formatting of sample output is centralized in one location.
//!
//! In the future, this class could be extended to support dumping test results to a file in some standard format
//! (for example, JUnit XML), and providing additional metadata (e.g. timing the duration of a test run).
//!
//! TODO: For backwards compatibility with existing samples, this class inherits directly from the nvinfer1::ILogger
//! interface, which is problematic since there isn't a clean separation between messages coming from the TensorRT
//! library and messages coming from the sample.
//!
//! In the future (once all samples are updated to use Logger::getTRTLogger() to access the ILogger) we can refactor the
//! class to eliminate the inheritance and instead make the nvinfer1::ILogger implementation a member of the Logger
//! object.class Logger : public nvinfer1::ILogger
{
public:Logger(Severity severity = Severity::kWARNING): mReportableSeverity(severity){}//!//! \enum TestResult//! \brief Represents the state of a given test//!enum class TestResult{kRUNNING, //!< The test is runningkPASSED, //!< The test passedkFAILED, //!< The test failedkWAIVED //!< The test was waived};//!//! \brief Forward-compatible method for retrieving the nvinfer::ILogger associated with this Logger//! \return The nvinfer1::ILogger associated with this Logger//!//! TODO Once all samples are updated to use this method to register the logger with TensorRT,//! we can eliminate the inheritance of Logger from ILogger//!nvinfer1::ILogger& getTRTLogger(){return *this;}//!//! \brief Implementation of the nvinfer1::ILogger::log() virtual method//!//! Note samples should not be calling this function directly; it will eventually go away once we eliminate the//! inheritance from nvinfer1::ILogger//!void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) override{LogStreamConsumer(mReportableSeverity, severity) << "[TRT] " << std::string(msg) << std::endl;}//!//! \brief Method for controlling the verbosity of logging output//!//! \param severity The logger will only emit messages that have severity of this level or higher.//!void setReportableSeverity(Severity severity){mReportableSeverity = severity;}//!//! \brief Opaque handle that holds logging information for a particular test//!//! This object is an opaque handle to information used by the Logger to print test results.//! The sample must call Logger::defineTest() in order to obtain a TestAtom that can be used//! with Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().//!class TestAtom{public:TestAtom(TestAtom&&) = default;private:friend class Logger;TestAtom(bool started, const std::string& name, const std::string& cmdline): mStarted(started), mName(name), mCmdline(cmdline){}bool mStarted;std::string mName;std::string mCmdline;};//!//! \brief Define a test for logging//!//! \param[in] name The name of the test. This should be a string starting with//! "TensorRT" and containing dot-separated strings containing//! the characters [A-Za-z0-9_].//! For example, "TensorRT.sample_googlenet"//! \param[in] cmdline The command line used to reproduce the test////! \return a TestAtom that can be used in Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().//!static TestAtom defineTest(const std::string& name, const std::string& cmdline){return TestAtom(false, name, cmdline);}//!//! \brief A convenience overloaded version of defineTest() that accepts an array of command-line arguments//! as input//!//! \param[in] name The name of the test//! \param[in] argc The number of command-line arguments//! \param[in] argv The array of command-line arguments (given as C strings)//!//! \return a TestAtom that can be used in Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().static TestAtom defineTest(const std::string& name, int argc, char const* const* argv){auto cmdline = genCmdlineString(argc, argv);return defineTest(name, cmdline);}//!//! \brief Report that a test has started.//!//! \pre reportTestStart() has not been called yet for the given testAtom//!//! \param[in] testAtom The handle to the test that has started//!static void reportTestStart(TestAtom& testAtom){reportTestResult(testAtom, TestResult::kRUNNING);assert(!testAtom.mStarted);testAtom.mStarted = true;}//!//! \brief Report that a test has ended.//!//! \pre reportTestStart() has been called for the given testAtom//!//! \param[in] testAtom The handle to the test that has ended//! \param[in] result The result of the test. Should be one of TestResult::kPASSED,//! TestResult::kFAILED, TestResult::kWAIVED//!static void reportTestEnd(const TestAtom& testAtom, TestResult result){assert(result != TestResult::kRUNNING);assert(testAtom.mStarted);reportTestResult(testAtom, result);}static int reportPass(const TestAtom& testAtom){reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kPASSED);return EXIT_SUCCESS;}static int reportFail(const TestAtom& testAtom){reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kFAILED);return EXIT_FAILURE;}static int reportWaive(const TestAtom& testAtom){reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kWAIVED);return EXIT_SUCCESS;}static int reportTest(const TestAtom& testAtom, bool pass){return pass ? reportPass(testAtom) : reportFail(testAtom);}Severity getReportableSeverity() const{return mReportableSeverity;}private://!//! \brief returns an appropriate string for prefixing a log message with the given severity//!static const char* severityPrefix(Severity severity){switch (severity){case Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR: return "[F] ";case Severity::kERROR: return "[E] ";case Severity::kWARNING: return "[W] ";case Severity::kINFO: return "[I] ";case Severity::kVERBOSE: return "[V] ";default: assert(0); return "";}}//!//! \brief returns an appropriate string for prefixing a test result message with the given result//!static const char* testResultString(TestResult result){switch (result){case TestResult::kRUNNING: return "RUNNING";case TestResult::kPASSED: return "PASSED";case TestResult::kFAILED: return "FAILED";case TestResult::kWAIVED: return "WAIVED";default: assert(0); return "";}}//!//! \brief returns an appropriate output stream (cout or cerr) to use with the given severity//!static std::ostream& severityOstream(Severity severity){return severity >= Severity::kINFO ? std::cout : std::cerr;}//!//! \brief method that implements logging test results//!static void reportTestResult(const TestAtom& testAtom, TestResult result){severityOstream(Severity::kINFO) << "&&&& " << testResultString(result) << " " << testAtom.mName << " # "<< testAtom.mCmdline << std::endl;}//!//! \brief generate a command line string from the given (argc, argv) values//!static std::string genCmdlineString(int argc, char const* const* argv){std::stringstream ss;for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++){if (i > 0)ss << " ";ss << argv[i];}return ss.str();}Severity mReportableSeverity;
};namespace
{//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kVERBOSE
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_VERBOSE(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_VERBOSE(const Logger& logger)
{return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kVERBOSE);
}//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kINFO
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_INFO(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_INFO(const Logger& logger)
{return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kINFO);
}//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kWARNING
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_WARN(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_WARN(const Logger& logger)
{return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kWARNING);
}//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kERROR
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_ERROR(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_ERROR(const Logger& logger)
{return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kERROR);
}//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kINTERNAL_ERROR
// ("fatal" severity)
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_FATAL(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_FATAL(const Logger& logger)
{return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR);
}} // anonymous namespace#endif // TENSORRT_LOGGING_H
Resnet50Serial.cpp
#include <map>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "logging.h"
#include "cuda_runtime_api.h"
#include <NvInferRuntimeCommon.h>
#include "common.hpp"
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <limits.h>static Logger gLogger;
#define DEVICE 0//gpu id
#define BATCH_SIZE 1
static const int INPUT_H = 224;
static const int INPUT_W = 224;
// static const int BATCH_SIZE=32;
static const int OUTPUT_SIZE=1000;
static const int INFER_NUMS=10000;
const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "image";
const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME1 = "output1";
const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME2 = "output2";using namespace nvinfer1;
using namespace std;#define CHECK(status) \do\{\auto ret = (status);\if (ret != 0)\{\std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << endl;\abort();\}\} while (0)map<string, Weights> loadWeights(const string file)
{cout << "Loading weights: " << file << endl;map<string, Weights> weightMap;// Open weights fileifstream input(file);assert(input.is_open() && "Unable to load weight file.");// Read number of weight blobsint32_t count;input >> count;assert(count > 0 && "Invalid weight map file.");while (count--){Weights wt{DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};uint32_t size;// Read name and type of blobstring name;input >> name >> std::dec >> size;wt.type = DataType::kFLOAT;// Load blobuint32_t* val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size));for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; ++x){input >> std::hex >> val[x];}wt.values = val;wt.count = size;weightMap[name] = wt;}return weightMap;
}//输出每一个维度
void debug_print(ITensor* input_tensor, string head)
{cout<<"==head:"<<head<<":";for(int i = 0; i<input_tensor->getDimensions().nbDims; i++){cout<<input_tensor->getDimensions().d[i]<<" ";}cout<<endl;
}
ICudaEngine* createEngine(const char* weightPath, unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config, DataType dt)
{//开始定义网络 0U无符号整型0INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(0U);ITensor* input = network->addInput(INPUT_BLOB_NAME, dt, Dims3{3, INPUT_H, INPUT_W});assert(input);map<string, Weights> weightMap = loadWeights(weightPath);//载入权重放入weightMapauto id_323 = convBnRelu(network, weightMap, *input, 64, 7, 2, 3,"conv1", "bn1", false);// debug_print(id_323->getOutput(0), "id_323");//debugIPoolingLayer* pool1 = network->addPoolingNd(*id_323->getOutput(0), PoolingType::kMAX, DimsHW{3,3});assert(pool1);pool1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{2, 2});pool1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{1, 1});// debug_print(pool1->getOutput(0), " pool1");//debugauto id_336 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *pool1->getOutput(0), 64, 1, "layer1.0", false);// debug_print(id_336->getOutput(0), "id_336");//debugauto id_346 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_336->getOutput(0), 64, 1, "layer1.1", true);// debug_print(id_346->getOutput(0), "id_346");//debugauto id_356 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_346->getOutput(0), 64, 1, "layer1.2", true);// debug_print(id_356->getOutput(0), "id_356");//debugauto id_368 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_356->getOutput(0), 128, 2, "layer2.0", false);// debug_print(id_368->getOutput(0), "id_368");//debugauto id_378 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_368->getOutput(0), 128, 1, "layer2.1", true);// debug_print(id_378->getOutput(0), "id_378");//debug auto id_388 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_378->getOutput(0), 128, 1, "layer2.2", true);// debug_print(id_388->getOutput(0), "id_388");//debugauto id_398 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_388->getOutput(0), 128, 1, "layer2.3", true);// debug_print(id_398->getOutput(0), "id_398");//debug auto id_410 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_398->getOutput(0), 256, 2, "layer3.0", false);// debug_print(id_410->getOutput(0), "id_410");//debugauto id_420 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_410->getOutput(0), 256, 1, "layer3.1", true);// debug_print(id_420->getOutput(0), "id_420");//debug auto id_430 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_420->getOutput(0), 256, 1, "layer3.2", true);// debug_print(id_430->getOutput(0), "id_430");//debugauto id_440 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_430->getOutput(0), 256, 1, "layer3.3", true);// debug_print(id_440->getOutput(0), "id_440");//debugauto id_450 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_440->getOutput(0), 256, 1, "layer3.4", true);// debug_print(id_450->getOutput(0), "id_450");//debug auto id_460 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_450->getOutput(0), 256, 1, "layer3.5", true);// debug_print(id_460->getOutput(0), "id_460");//debugauto id_472 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_460->getOutput(0), 512, 2, "layer4.0", false);// debug_print(id_472->getOutput(0), "id_472");//debugauto id_482 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_472->getOutput(0), 512, 1, "layer4.1", true);// debug_print(id_482->getOutput(0), "id_482");//debug auto id_492 = bottleneck(network, weightMap, *id_482->getOutput(0), 512, 1, "layer4.2", true);IPoolingLayer* pool2 = network->addPoolingNd(*id_492->getOutput(0), PoolingType::kAVERAGE, DimsHW{7,7});assert(pool2);// debug_print(pool2->getOutput(0), "pool2");//debugIFullyConnectedLayer* fc1 = network->addFullyConnected(*pool2->getOutput(0), 1000, weightMap["fc.weight"], weightMap["fc.bias"]);assert(fc1);// debug_print(fc1->getOutput(0), "fc1");//debugIActivationLayer* fc1_relu = network->addActivation(*fc1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(fc1_relu);// //分类层// ISoftMaxLayer *prob = network->addSoftMax(*fc1->getOutput(0));// assert(prob);fc1->getOutput(0)->setName(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME1);fc1_relu->getOutput(0)->setName(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME2);network->markOutput(*fc1->getOutput(0));network->markOutput(*fc1_relu->getOutput(0));//构造enginebuilder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize);config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1<<20);ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config);//放入engine 所以network可以销毁了network->destroy();// 释放资源for (auto& mem : weightMap){free((void*) (mem.second.values));}return engine;
}
void APIToModel(const char* weightPath, unsigned int maxBatchSize, IHostMemory** modelStream)
{//创建builderIBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger);//网络入口 类似pytorch的modelIBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig();//创建模型 搭建网络层ICudaEngine* engine = createEngine(weightPath, maxBatchSize, builder, config, DataType::kFLOAT);assert(engine!=nullptr);//序列化engine(*modelStream)= engine->serialize();//销毁对象 engine->destroy();config->destroy();builder->destroy();}int main(int args, char **argv)
{ //序列化模型为.engine文件string engine_name = "./resnet50.engine";const char* weightPath = "./resnet50.wts";IHostMemory* modelStream{nullptr};//modelStream是一块内存区域,用来保存序列化文件APIToModel(weightPath, BATCH_SIZE, &modelStream);assert(modelStream!=nullptr);//变换为.engine文件ofstream p(engine_name);if (!p){std::cerr<<"can not open plan file"<<endl;return -1;}p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char *>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size());p.close();//销毁对象modelStream->destroy(); return 0;
}common.hpp
#ifndef COMMON_HPP
#define COMMON_HPP#include <map>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "logging.h"
#include "cuda_runtime_api.h"using namespace nvinfer1;IScaleLayer* addBatchNorm2d(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input,std::string bnname,float eps)
{float* gamma= (float*)weightMap[bnname+".weight"].values;float* beta=(float*)weightMap[bnname+".bias"].values;float* mean=(float*)weightMap[bnname+".running_mean"].values;float* var=(float*)weightMap[bnname+".running_var"].values;int length = weightMap[bnname+".running_var"].count;float* scval = reinterpret_cast<float *>(malloc(sizeof(float)*length));for (int i=0;i<length;i++){ scval[i] = gamma[i]/sqrt(var[i]+eps);}Weights scale{ DataType::kFLOAT, scval, length};//实例化一个weights scale 存放scval指针float* shavl = reinterpret_cast<float *>(malloc(sizeof(float)*length));for (int i=0;i<length;i++){ shavl[i] = beta[i]-mean[i]*gamma[i]/sqrt(var[i]+eps);}Weights shift{ DataType::kFLOAT, shavl, length};//实例化一个weights shift 存放shavl指针float* pval = reinterpret_cast<float *>(malloc(sizeof(float)*length));for (int i=0;i<length;i++){ pval[i] = 1.0;}Weights power{ DataType::kFLOAT, pval, length};//实例化一个weights power 存放pval指针weightMap[bnname+".scale"] = scale;weightMap[bnname+".shift"] = shift;weightMap[bnname+".power"] = power;IScaleLayer* scale_1 = network->addScale(input,ScaleMode::kCHANNEL, shift, scale, power);assert(scale_1);return scale_1;}IActivationLayer* convBnRelu(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input,int outch, int ksize, int s,int p,std::string convname,std::string bnname,bool bias = false)
{Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};//实例化一个空weights emptywts 空指针 长度为0//卷积层IConvolutionLayer* conv1;//先定义指针if (!bias){conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{ksize,ksize}, weightMap[convname+".weight"],emptywts);}else{conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{ksize,ksize}, weightMap[convname+".weight"],weightMap[convname+".bias"]);} //设置步长assert(conv1);conv1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{s, s});conv1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{p, p});IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), bnname, 1e-5);assert(bn1);//激活层IActivationLayer* relu = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu);return relu;
}IActivationLayer* bottleneck(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input, int outch, int stride, std::string lname, bool shortcut_clean)
{Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};//实例化一个空weights emptywts 空指针 长度为0IConvolutionLayer* conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{1,1}, weightMap[lname+".conv1.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv1);IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), lname+".bn1", 1e-5);assert(bn1);IActivationLayer* relu1 = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu1);IConvolutionLayer* conv2 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu1->getOutput(0), outch, DimsHW{3,3}, weightMap[lname+".conv2.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv2);conv2->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});conv2->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{1, 1});IScaleLayer* bn2 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv2->getOutput(0), lname+".bn2", 1e-5);assert(bn2);IActivationLayer* relu2 = network->addActivation(*bn2->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu2);IConvolutionLayer* conv3 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu2->getOutput(0), outch*4, DimsHW{1,1}, weightMap[lname+".conv3.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv3);IScaleLayer* bn3 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv3->getOutput(0), lname+".bn3", 1e-5);assert(bn3);IElementWiseLayer *ew1;if (!shortcut_clean){IConvolutionLayer* conv4 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch*4, DimsHW{1,1}, weightMap[lname+".downsample.0.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv4);conv4->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});IScaleLayer* bn4 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv4->getOutput(0), lname+".downsample.1", 1e-5);assert(bn4);ew1 = network->addElementWise(*bn4->getOutput(0), *bn3->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM);}else{ew1 = network->addElementWise(input, *bn3->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM);}assert(ew1);IActivationLayer* relu3 = network->addActivation(*ew1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu3);return relu3;} ILayer* ResBlock(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input, int inch, int outch, int stride, std::string lname)
{Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};//实例化一个空weights emptywts 空指针 长度为0IConvolutionLayer* conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{1,1}, weightMap[lname+".conv1.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv1);conv1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), lname+".bn1", 1e-5);assert(bn1);IActivationLayer* relu1 = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu1);IConvolutionLayer* conv2 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu1->getOutput(0), outch, DimsHW{3,3}, weightMap[lname+".conv2.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv2);conv2->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});conv2->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{1, 1});IScaleLayer* bn2 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv2->getOutput(0), lname+".bn2", 1e-5);assert(bn2);IActivationLayer* relu2 = network->addActivation(*bn2->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu2);IConvolutionLayer* conv3 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu2->getOutput(0), inch, DimsHW{1,1}, weightMap[lname+".conv3.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv3);conv3->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});IScaleLayer* bn3 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv3->getOutput(0), lname+".bn3", 1e-5);assert(bn3);IElementWiseLayer* ew1 = network->addElementWise(input, *bn3->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM);assert(ew1);IActivationLayer* relu3 = network->addActivation(*ew1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu3);return relu3;
}ILayer* liteResBlock(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input, int outch, int stride, std::string lname)
{Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};//实例化一个空weights emptywts 空指针 长度为0IConvolutionLayer* conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{3,3}, weightMap[lname+".conv1.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv1);conv1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});conv1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{1, 1});IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), lname+".bn1", 1e-5);assert(bn1);IActivationLayer* relu1 = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu1);IConvolutionLayer* conv2 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu1->getOutput(0), outch, DimsHW{3,3}, weightMap[lname+".conv2.weight"], emptywts);assert(conv2);conv2->setStrideNd(DimsHW{stride, stride});conv2->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{1, 1});IScaleLayer* bn2 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv2->getOutput(0), lname+".bn2", 1e-5);assert(bn2);IActivationLayer* relu2 = network->addActivation(*bn2->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu2);IElementWiseLayer* ew1 = network->addElementWise(input, *bn2->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM);assert(ew1);IActivationLayer* relu3 = network->addActivation(*ew1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU);assert(relu3);return relu3;
}
#endifCMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)project(resnet)add_definitions(-std=c++11)option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS)include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include)
# include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different
# cuda
include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include)
link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64)
# tensorrt
include_directories(/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/)
link_directories(/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/)add_executable(Resnet50Serial ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/Resnet50Serial.cpp)target_link_libraries(Resnet50Serial nvinfer)
target_link_libraries(Resnet50Serial cudart)
target_link_libraries(Resnet50Serial ${OpenCV_LIBS})
#add_executable(resnext50 ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/resnext50_32x4d.cpp)
#target_link_libraries(resnext50 nvinfer)
#target_link_libraries(resnext50 cudart)add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
即可生成.engine文件,而如果要量化为fp16,只需要增加:
builder->setHalf2Mode(true);就可以.
下面这句话用来判断是否支持fp16.
bool useFp16 = builder->platformHasFastFp16();2.2反序列化推理阶段
1.文件代码结构图
其中resnet50.engine是上一阶段生成的,logging.h和上一阶段一样。
2.代码:
main.cpp
#include <complex>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "Resnet50Classify.h"
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;bool cmp(int x,int y)
{return x>y;
}template<typename T>
vector<int> sort_indexes(const vector<T> & v, bool reverse=false) {// initialize original index locationsvector<int> idx(v.size());for (int i = 0; i != idx.size(); ++i) idx[i] = i;// sort indexes based on comparing values in vif(reverse){sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(),[& v](int i1, int i2) {return v[i1] > v[i2];});}else{sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(),[& v](int i1, int i2) {return v[i1] < v[i2];});}return idx;
}void get_index_value(int OUTPUT_SIZE, float *prob, vector<float>& res){// res[0] = 1;// res[1] = 0.9898978;float maxp = INT_MIN;int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++){ if(prob[i]>maxp){maxp = prob[i];index = i;}} res[0] = index;res[1] = maxp;
}vector<int> topk_index(int OUTPUT_SIZE, float* prob, vector<float>& ProbIndex){vector<int> sorted_indx;sorted_indx = sort_indexes(ProbIndex, true);return sorted_indx;
} int main(int argc, char** argv){if( argc != 2){cout<<"图片路径没有输入"<<endl;return -1;}ResNet50* model = new ResNet50();//开始推理, 模拟推理10000次,存储推理结果const char* enginePath = "./resnet50.engine";model->InferenceInit(enginePath);//将引擎文件载入显卡,反序列化好环境并启动cuda核const char* imgPath = argv[1];cout<<"=====main cv::CV_VERSION:===="<<CV_VERSION<<endl;auto start = chrono::system_clock::now();//开始时间model->preProcess(imgPath);//图像预处理 for (int i = 0; i < model->INFER_NUMS; i++){ // std::cout<<"data[i]:"<<data[i]<<std::endl;model->doInference(model->data, model->prob1, model->prob2, model->batchSize); //开始推理}auto end = chrono::system_clock::now();//结束时间std::cout << chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl;cout<<"====model->prob1:"<<model->prob1<<endl;//打印地址cout<<"====model->prob2:"<<model->prob2<<endl;//打印地址cout<<"========================================"<<endl; vector<float>res1(2, 0);get_index_value(model->OUTPUT_SIZE, model->prob1, res1);vector<float>res2(2, 0);get_index_value(model->OUTPUT_SIZE, model->prob2, res2);for(int i=0; i<2; i++){cout<<"===res1[i]:==="<<res1[i]<<endl;//打印最大值的索引cout<<"===res2[i]:==="<<res2[i]<<endl;//打印最大值}cout<<"========================================"<<endl;ofstream trt_result("./fc_and_relu.txt");int topk = 100;for (int i = 0; i < topk; i++){ trt_result<<model->prob1[i];trt_result<<",";trt_result<<model->prob2[i]<<endl;cout<<"===model->prob1[i]==="<<model->prob1[i]<<endl;cout<<"===model->prob2[i]==="<<model->prob2[i]<<endl;} trt_result.close();// vector<float> ProbIndex(model->prob1, model->prob1 + model->OUTPUT_SIZE);// vector<int> sorted_indx;// vector<int> res;// sorted_indx = sort_indexes(ProbIndex, true);// vector<float> ProbIndex1(model->prob1, model->prob1 + model->OUTPUT_SIZE);// vector<float> ProbIndex2(model->prob2, model->prob2 + model->OUTPUT_SIZE);// vector<int> sorted_indx1;// vector<int> sorted_indx2;// sorted_indx1 = topk_index(model->OUTPUT_SIZE, model->prob1, ProbIndex1);// sorted_indx2 = topk_index(model->OUTPUT_SIZE, model->prob2, ProbIndex2);// for (int i = 0; i < topk; i++)// { // cout<<"===sorted_indx1[i]==="<<sorted_indx1[i]<<endl;// cout<<"===sorted_indx2[i]==="<<sorted_indx2[i]<<endl;// } delete model;model = nullptr;return 0;
}
Resnet50Classify.h
#ifndef TENSORRT_H
#define TENSORRT_H
#include <map>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "logging.h"
#include "cuda_runtime_api.h"
#include <NvInferRuntimeCommon.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <limits.h>using namespace std;
using namespace nvinfer1;class ResNet50
{public:void InferenceInit(const char* enginePath);void doInference(float* input, float* output1, float* output2, int batchSize);void preProcess(const char* imgPath);ResNet50(){};~ResNet50();public:Logger gLogger;static const int INPUT_H = 224;static const int INPUT_W = 224;static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1000;static const int INFER_NUMS = 10000;const int batchSize = 1;const char* imaPath;const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "image";const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME1 = "output1";const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME2 = "output2";float prob1[OUTPUT_SIZE];float prob2[OUTPUT_SIZE];char *trtModelStream;vector<float> mean_value{ 0.406, 0.456, 0.485 }; // BGRvector<float> std_value{ 0.225, 0.224, 0.229 };float* data = new float[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W];IRuntime* m_runtime;ICudaEngine* m_engine;IExecutionContext* m_context;
};#endifResnet50Classify.cpp
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/types_c.h>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "cuda_runtime_api.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <NvInferRuntimeCommon.h>
#include <c++/5/bits/c++config.h>
#include <cassert>
#include <limits.h>
#include "Resnet50Classify.h"using namespace std;
using namespace nvinfer1;#define CHECK(status) \do\{\auto ret = (status);\if (ret != 0)\{\std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\abort();\}\} while (0)void ResNet50::doInference(float* input, float* output1, float* output2, int batchSize){//输入输出总共有两个,做一下验证assert(m_engine->getNbBindings()==3);//void型指针void* buffers[3];//获取与这个engine相关的输入输出tensor的索引sconst int inputIndex = m_engine->getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME);const int outputIndex1 = m_engine->getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME1);const int outputIndex2 = m_engine->getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME2);//为输入输出tensor开辟显存。CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float)));CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex1], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float)));CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex2], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float)));//创建cuda流,用于管理数据复制,存取,和计算的并发操作cudaStream_t stream;CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream));//从内存到显存,input是读入内存中的数据;buffers[inputIndex]是显存上的存储区域,用于存放输入数据CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize *3* INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream));// //启动cuda核,异步执行推理计算m_context->enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr);//从显存到内存,buffers[outputIndex]是显存中的存储区,存放模型输出;output是内存中的数据CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output1, buffers[outputIndex1], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream));CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output2, buffers[outputIndex2], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream));//如果使用了多个cuda流,需要同步cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);// Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream);CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]));CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex1]));CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex2]));
}void ResNet50::preProcess(const char* imgPath){cv::Mat img = cv::imread(imgPath);cv::Mat src_img;cv::resize(img, src_img, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H));int count = 0;for(int i = 0; i<INPUT_H; i++){uchar* uc_pixel = src_img.data + i * src_img.step;for(int j = 0; j<INPUT_W; j++){//bgr存放data[count] = (uc_pixel[0] / 255. - mean_value[0]) / std_value[0];data[count + src_img.rows * src_img.cols] = (uc_pixel[1] / 255. - mean_value[1]) / std_value[1];data[count + 2 * src_img.rows * src_img.cols] = (uc_pixel[2] / 255. - mean_value[2]) / std_value[2];uc_pixel += 3;count++;}}
}void ResNet50::InferenceInit(const char* enginePath){size_t size;ifstream file(enginePath, std::ios::binary);if(file.good()){//get length of filefile.seekg(0, file.end);size = file.tellg();file.seekg(0, file.beg);//allocate memorytrtModelStream = new char[size];assert(trtModelStream);//read data as blockfile.read(trtModelStream, size);file.close();}//创建运行时环境IRuntime对象IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger);assert(runtime !=nullptr);m_runtime = runtime;//引擎反序列化ICudaEngine* engine = m_runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr);assert(engine !=nullptr);m_engine = engine; //创建上下文环境,主要用与inference函数中启动cuda核IExecutionContext* context = m_engine->createExecutionContext();assert(context !=nullptr); m_context = context;
}
ResNet50::~ResNet50(){if(m_context){m_context->destroy();m_context = nullptr;}if(m_engine){m_engine->destroy();m_engine = nullptr;}if(m_runtime){m_runtime->destroy();m_runtime = nullptr;} if(data){delete[] data;data = nullptr;}if(trtModelStream){delete trtModelStream;trtModelStream = nullptr;}
}CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)project(resnet)add_definitions(-std=c++11)option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS)include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include)
# include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different
# cuda
include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include)
link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64)
# tensorrt
include_directories(/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/)
link_directories(/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/)add_executable(Resnet50Classify ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cpp Resnet50Classify.cpp)
target_link_libraries(Resnet50Classify nvinfer)
target_link_libraries(Resnet50Classify cudart)
target_link_libraries(Resnet50Classify ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)./Resnet50Classify test.jpg
结果:
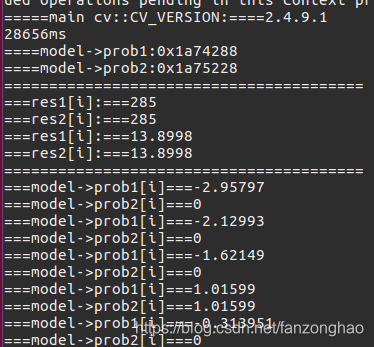
生成的fc_and_relu.txt的结果.
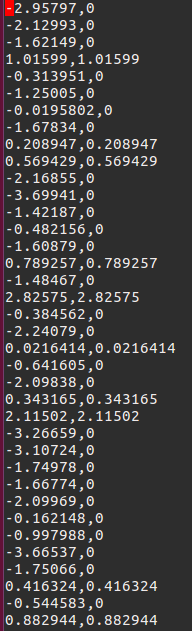
2.3 比较结果
import numpy as nppytorch_res_path = './pytorch_result.txt'
pytorch_res = []
trt_res_path = './fc_and_relu.txt'
trt_res = []
with open(pytorch_res_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:for i, read_info in enumerate(file.readlines()):pytorch_res.append(float(read_info))with open(trt_res_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:for i, read_info in enumerate(file.readlines()):trt_res.append(float(read_info.split(',')[0]))
print('==trt_res:', trt_res)pytorch_res = np.array(pytorch_res)
trt_res = np.array(trt_res)abs_error = np.sum(np.abs((pytorch_res - trt_res)/pytorch_res)) / len(pytorch_res)
print('===abs_error===', abs_error)![]()
可看出和torch的结果误差很小,同时时间由原先的12ms变为28656/10000 = 2.86ms,同时显存占用量减少100M。速度还是得到了4倍左右的提升,同时看出另一个Relu的输出是直接将fc层置为>=0的。




 + python(c++))






| 半导体行业观察)







