支持向量机SVM算法原理及应用(R)
只要接触到数据挖掘/机器学习,相比都会听过“支持向量机”的大名。在机器学习领域,支持向量机SVM(Support Vector Machine)是一个有监督的学习模型,通常用来进行模式识别、分类、以及回归分析。SVM涉及的知识面非常广,目标函数、优化过程、并行方法、算法收敛性、样本复杂度等。学习SVM可以看《统计学习方法》、Andrew Ng支持向量机等,这里推荐一个博客,讲的非常详细,我就不搬过来了,大家可以直接去看那篇博客,最好能静下心来直接拿起笔跟着博主推理一边,这样更能加深印象。
http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7624837
学习完原理,接下来就该应用了,应用后更能加深对SVM的理解。
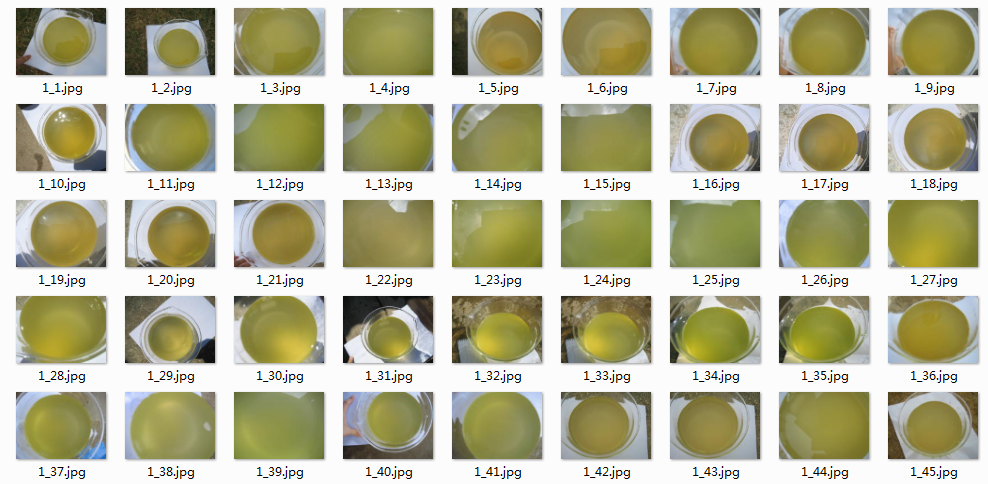
从事渔业生产有经验的从业者可通过观察水色变化调控水质,以维持养殖水体生态系统中浮游植物、微生物类、浮游动物等合理的动态平衡。由于这些多是通过经验和肉眼观察进行判断,存在主观性引起的观察性偏倚,使观察结果的可比性、可重复性降低,不易推广应用。当前,数字图像处理技术为计算机监控技术在水产养殖业的应用提供更大的空间。在水质在线监测方面,数字图像处理技术是基于计算机视觉,以专家经验为基础,对池塘水色进行优劣分级,达到对池塘水色的准确快速判别。
水色分类
| 水色 | 浅绿色(清水或浊水) | 灰蓝色 | 黄褐色 | 茶褐色 (姜黄、茶褐、红褐、褐中带绿等) | 绿色(黄绿、油绿、蓝绿、墨绿、绿中带褐等) |
| 水质类别 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
标准条件下拍摄的水样图像
每个水质图片命名规则为“类别-编号.jpg”,如“1_1.jpg”说明当前图片属于第1类的样本。
接下来进行特征提取
采用颜色矩来提取水样图像的特征
水色图像特征与相应的水色类别的部分数据
| 水质类别 | 序号 | R通道一阶矩 | G通道一阶矩 | B通道一阶矩 | R通道二阶矩 | G通道二阶矩 | B通道二阶矩 | R通道三阶矩 | G通道三阶矩 | B通道三阶矩 |
| 1 | 1 | 0.582823 | 0.543774 | 0.252829 | 0.014192 | 0.016144 | 0.041075 | -0.01264 | -0.01609 | -0.04154 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.495169 | 0.539358 | 0.416124 | 0.011314 | 0.009811 | 0.014751 | 0.015367 | 0.01601 | 0.019748 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.510911 | 0.489695 | 0.186255 | 0.012417 | 0.010816 | 0.011644 | -0.00747 | -0.00768 | -0.00509 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.420351 | 0.436173 | 0.167221 | 0.01122 | 0.007195 | 0.010565 | -0.00628 | 0.003173 | -0.00729 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.211567 | 0.335537 | 0.111969 | 0.012056 | 0.013296 | 0.00838 | 0.007305 | 0.007503 | 0.00365 |
| 1 | 2 | 0.563773 | 0.534851 | 0.271672 | 0.009723 | 0.007856 | 0.011873 | -0.00513 | 0.003032 | -0.00547 |
| 2 | 2 | 0.465186 | 0.508643 | 0.361016 | 0.013753 | 0.012709 | 0.019557 | 0.022785 | 0.022329 | 0.031616 |
| 3 | 2 | 0.533052 | 0.506734 | 0.185972 | 0.011104 | 0.007902 | 0.01265 | 0.004797 | -0.0029 | 0.004214 |
| 4 | 2 | 0.398801 | 0.42556 | 0.191341 | 0.014424 | 0.010462 | 0.01547 | 0.009207 | 0.006471 | 0.006764 |
| 5 | 2 | 0.298194 | 0.427725 | 0.097936 | 0.014778 | 0.012456 | 0.008322 | 0.00851 | 0.006117 | 0.00347 |
| 1 | 3 | 0.630328 | 0.594269 | 0.298577 | 0.007731 | 0.005877 | 0.010148 | 0.003447 | -0.00345 | -0.00653 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.491916 | 0.546367 | 0.425871 | 0.010344 | 0.008293 | 0.01226 | 0.009285 | 0.009663 | 0.011549 |
| 3 | 3 | 0.559437 | 0.522702 | 0.194201 | 0.012478 | 0.007927 | 0.012183 | 0.004477 | -0.00341 | -0.00529 |
| 4 | 3 | 0.402068 | 0.431443 | 0.177364 | 0.010554 | 0.007287 | 0.010748 | 0.006261 | -0.00341 | 0.006419 |
| 5 | 3 | 0.408963 | 0.486953 | 0.178113 | 0.012662 | 0.009752 | 0.014497 | -0.00672 | 0.002168 | 0.009992 |
| 1 | 4 | 0.638606 | 0.61926 | 0.319711 | 0.008125 | 0.006045 | 0.009746 | -0.00487 | 0.003083 | -0.0045 |
SVM预测模型输入变量
| 序号 | 变量名称 | 变量描述 | 取值范围 |
| 1 | R通道一阶矩 | 水样图像在R颜色通道的一阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 2 | G通道一阶矩 | 水样图像在G颜色通道的一阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 3 | B通道一阶矩 | 水样图像在B颜色通道的一阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 4 | R通道二阶矩 | 水样图像在R颜色通道的二阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 5 | G通道二阶矩 | 水样图像在G颜色通道的二阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 6 | B通道二阶矩 | 水样图像在B颜色通道的二阶矩 | 0~1 |
| 7 | R通道三阶矩 | 水样图像在R颜色通道的三阶矩 | -1~1 |
| 8 | G通道三阶矩 | 水样图像在G颜色通道的三阶矩 | -1~1 |
| 9 | B通道三阶矩 | 水样图像在B颜色通道的三阶矩 | -1~1 |
| 10 | 水质类别 | 不同类别能表征水中浮游植物的种类和多少 | 1,2,3,4,5 |
建模之前,我来介绍下R语言的SVM用法。使用SVM需安装e1071包
第一种简单方式建模:
svm(formula, data= NULL, subset, na.action = na.omit , scale= TRUE)
data:模型中包含的有变量的一组可选格式数据。
参数na.action用于指定当样本数据中存在无效的空数据时系统应该进行的处理。默认值na.omit表明程序会忽略那些数据缺失的样本。另外一个可选的赋值是na.fail,它指示系统在遇到空数据时给出一条错误信息。
参数scale为一个逻辑向量,指定特征数据是否需要标准化(默认标准化为均值0,方差1)。索引向量subset用于指定那些将被来训练模型的采样数据。
第二种根据所给的数据建模:
svm(x, y = NULL, scale = TRUE, type = NULL, kernel = "radial",degree = 3, gamma = if (is.vector(x)) 1 else 1 / ncol(x),coef0 = 0, cost = 1, nu = 0.5, subset, na.action = na.omit)参数type用于指定建立模型的类别。支持向量机模型通常可以用作分类模型、回归模型或者异常检测模型。根据用途的差异,在svm()函数中的type可取的值有C-classification、nu-classification、one-classification、eps-regression和nu-regression这五种类型中。其中,前三种是针对于字符型结果变量的分类方式,其中第三种方式是逻辑判别,即判别结果输出所需判别的样本是否属于该类别;而后两种则是针对数值型结果变量的分类方式。
此外,kernel是指在模型建立过程中使用的核函数。针对线性不可分的问题,为了提高模型预测精度,通常会使用核函数对原始特征进行变换,提高原始特征维度,解决支持向量机模型线性不可分问题。svm()函数中的kernel参数有四个可选核函数,分别为线性核函数、多项式核函数、高斯核函数及神经网络核函数。其中,高斯核函数与多项式核函数被认为是性能最好、也最常用的核函数。
核函数有两种主要类型:局部性核函数和全局性核函数,高斯核函数是一个典型的局部性核函数,而多项式核函数则是一个典型的全局性核函数。局部性核函数仅仅在测试点附近小领域内对数据点有影响,其学习能力强、泛化性能较弱;而全局性核函数则相对来说泛化性能较强、学习能力较弱。
对于选定的核函数,degree参数是指核函数多项式内积函数中的参数,其默认值为3。gamma参数给出了核函数中除线性内积函数以外的所有函数的参数,默认值为l。coef0参数是指核函数中多项式内积函数与sigmoid内积函数中的参数,默认值为0。
另外,参数cost就是软间隔模型中的离群点权重。最后,参数nu是用于nu-regression、nu-classification和one-classification类型中的参数。
一个经验性的结论是,在利用svm()函数建立支持向量机模型时,使用标准化后的数据建立的模型效果更好。
- colnames(Data)<-c("class","id","R1","G1","B1","R2","G2","B2","R3","G3","B3")
- head(Data)
- ## class id R1 G1 B1 R2 G2
- ## 1 1 1 0.5828229 0.5437737 0.2528287 0.014192030 0.016143875
- ## 2 1 10 0.6416595 0.5706572 0.2137280 0.015438840 0.011177918
- ## 3 1 11 0.6036844 0.5767189 0.2822538 0.008658572 0.007074807
- ## 4 1 12 0.5897057 0.5937430 0.2522425 0.007908293 0.005940868
- ## 5 1 13 0.5910962 0.5920930 0.2535949 0.007448469 0.006494667
- ## 6 1 14 0.5886801 0.5696339 0.3189053 0.007527690 0.005046087
- ## B2 R3 G3 B3
- ## 1 0.041075252 -0.012643137 -0.016090364 -0.041536239
- ## 2 0.013707795 0.009727136 -0.003723814 -0.003779448
- ## 3 0.012203640 -0.004694985 -0.002570890 -0.009450531
- ## 4 0.010568364 0.003303400 -0.003416659 -0.005273416
- ## 5 0.012151602 0.000496116 -0.002235644 -0.005095575
- ## 6 0.008386259 -0.003529253 0.001746734 -0.005790924
-
- set.seed(1234)
-
- ind <- sample(2, nrow(Data), replace=TRUE, prob=c(0.8, 0.2))
- traindata <-Data[ind==1,]
- testdata <- Data[ind==2,]
-
- traindata<-transform(traindata,class=as.factor(class))
- testdata<-transform(testdata,class=as.factor(class))
-
- library(e1071)
-
- svm.model<-svm(class~., traindata[,-2])
- summary(svm.model)
- ##
- ## Call:
- ## svm(formula = class ~ ., data = traindata[, -2])
- ##
- ##
- ## Parameters:
- ## SVM-Type: C-classification
- ## SVM-Kernel: radial
- ## cost: 1
- ## gamma: 0.1111111
- ##
- ## Number of Support Vectors: 119
- ##
- ## ( 31 26 41 16 5 )
- ##
- ##
- ## Number of Classes: 5
- ##
- ## Levels:
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
#通过summary函数可以得到关于模型的相关信息。其中,SVM-Type项目说明本模型的类别为C分类器模型;SVM-Kernel项目说明本模型所使用的核函数为高斯内积函数且核函数中参数gamma的取值为0.11;cost项目说明本模型确定的约束违反成本为l。而且我们还可以看到,模型找到了119个支持向量:第一类包含有31个支持向量,第二类包含有26个支持向量,第三类包含41个支持向量,第四类包含有16个支持向量,第三类包含5个支持向量。最后一行说明模型中的三个类别分别为1、2、3、4、5.
- #建立混淆矩阵
- #训练集
- confusion.train.svm=table(traindata$class,predict(svm.model,traindata,type="class"))
- accuracy.train.svm=sum(diag(confusion.train.svm))/sum(confusion.train.svm)
- confusion.train.svm
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 41 0 2 0 0
- ## 2 0 37 0 0 0
- ## 3 1 0 61 0 0
- ## 4 0 0 2 15 0
- ## 5 1 0 0 0 4
accuracy.train.svm## [1] 0.9634146- #测试集
- confusion.test.svm=table(testdata$class,predict(svm.model,testdata,type="class"))
- accuracy.test.svm=sum(diag(confusion.test.svm))/sum(confusion.test.svm)
- confusion.test.svm
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 8 0 0 0 0
- ## 2 0 7 0 0 0
- ## 3 0 0 16 0 0
- ## 4 0 1 2 4 0
- ## 5 0 0 0 0 1
accuracy.test.svm## [1] 0.9230769- #随机森林
- library(randomForest)
## randomForest 4.6-12## Type rfNews() to see new features/changes/bug fixes.- randomForest.model<-randomForest(class~., traindata[,-2])
- summary(randomForest.model)
- ## Length Class Mode
- ## call 3 -none- call
- ## type 1 -none- character
- ## predicted 164 factor numeric
- ## err.rate 3000 -none- numeric
- ## confusion 30 -none- numeric
- ## votes 820 matrix numeric
- ## oob.times 164 -none- numeric
- ## classes 5 -none- character
- ## importance 9 -none- numeric
- ## importanceSD 0 -none- NULL
- ## localImportance 0 -none- NULL
- ## proximity 0 -none- NULL
- ## ntree 1 -none- numeric
- ## mtry 1 -none- numeric
- ## forest 14 -none- list
- ## y 164 factor numeric
- ## test 0 -none- NULL
- ## inbag 0 -none- NULL
- ## terms 3 terms call
randomForest.model- #训练集
- confusion.train.randomForest=table(traindata$class,predict(randomForest.model,traindata,type="class"))
- accuracy.train.randomForest=sum(diag(confusion.train.randomForest))/sum(confusion.train.randomForest)
- confusion.train.randomForest
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 43 0 0 0 0
- ## 2 0 37 0 0 0
- ## 3 0 0 62 0 0
- ## 4 0 0 0 17 0
- ## 5 0 0 0 0 5
accuracy.train.randomForest## [1] 1- #测试集
- confusion.test.randomForest=table(testdata$class,predict(randomForest.model,testdata,type="class"))
- accuracy.test.randomForest=sum(diag(confusion.test.randomForest))/sum(confusion.test.randomForest)
- confusion.test.randomForest
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 7 0 1 0 0
- ## 2 0 7 0 0 0
- ## 3 1 0 15 0 0
- ## 4 0 0 2 5 0
- ## 5 0 0 0 0 1
accuracy.test.randomForest## [1] 0.8974359
- #神经网络
- library(nnet)
- nnet.model<-nnet(class~., traindata[,-2],size=30,decay=.001)
- ## # weights: 455
- ## initial value 318.920319
- ## iter 10 value 176.714302
- ## iter 20 value 57.798855
- ## iter 30 value 42.657486
- ## iter 40 value 27.296733
- ## iter 50 value 20.803959
- ## iter 60 value 18.519644
- ## iter 70 value 16.706718
- ## iter 80 value 15.700517
- ## iter 90 value 15.200025
- ## iter 100 value 14.797823
- ## final value 14.797823
- ## stopped after 100 iterations
summary(nnet.model)- ## a 9-30-5 network with 455 weights
- ## options were - softmax modelling decay=0.001
- ## b->h1 i1->h1 i2->h1 i3->h1 i4->h1 i5->h1 i6->h1 i7->h1 i8->h1 i9->h1
- ## -2.75 -1.05 -1.31 -0.04 0.00 0.00 -0.03 0.06 0.00 0.11
- ## b->h2 i1->h2 i2->h2 i3->h2 i4->h2 i5->h2 i6->h2 i7->h2 i8->h2 i9->h2
- ## 1.55 -2.29 -0.37 -0.76 1.02 1.46 1.91 -1.90 -2.21 -2.26
- ## b->h3 i1->h3 i2->h3 i3->h3 i4->h3 i5->h3 i6->h3 i7->h3 i8->h3 i9->h3
- ## 3.06 2.93 2.01 -17.11 1.57 0.56 0.62 -0.89 0.67 3.71
- ## b->h4 i1->h4 i2->h4 i3->h4 i4->h4 i5->h4 i6->h4 i7->h4 i8->h4 i9->h4
- ## 13.76 -20.60 -2.70 -13.91 0.05 0.26 1.69 -0.41 -0.87 -1.86
- ## b->h5 i1->h5 i2->h5 i3->h5 i4->h5 i5->h5 i6->h5 i7->h5 i8->h5 i9->h5
- ## 8.63 -7.74 -8.29 -0.52 -5.14 -4.83 -5.11 6.94 2.07 0.17
- ## b->h6 i1->h6 i2->h6 i3->h6 i4->h6 i5->h6 i6->h6 i7->h6 i8->h6 i9->h6
- ## 2.16 -7.64 0.96 4.96 1.28 2.07 2.49 -2.65 -1.87 -3.63
- ## b->h7 i1->h7 i2->h7 i3->h7 i4->h7 i5->h7 i6->h7 i7->h7 i8->h7 i9->h7
- ## 7.74 -7.29 -6.89 -4.14 -1.00 -0.61 0.63 1.61 -1.54 -5.57
- ## b->h8 i1->h8 i2->h8 i3->h8 i4->h8 i5->h8 i6->h8 i7->h8 i8->h8 i9->h8
- ## -6.20 6.18 5.23 -0.35 4.25 3.92 4.70 -5.18 -2.24 -3.47
- ## b->h9 i1->h9 i2->h9 i3->h9 i4->h9 i5->h9 i6->h9 i7->h9 i8->h9 i9->h9
- ## 7.43 -6.77 -11.18 7.93 -5.95 -5.05 -4.73 7.39 1.18 -4.61
- ## b->h10 i1->h10 i2->h10 i3->h10 i4->h10 i5->h10 i6->h10 i7->h10 i8->h10
- ## 2.12 0.33 0.54 -0.99 0.11 0.04 0.11 -0.03 -0.09
- ## i9->h10
- ## 0.06
- ## b->h11 i1->h11 i2->h11 i3->h11 i4->h11 i5->h11 i6->h11 i7->h11 i8->h11
- ## -2.55 0.01 -0.82 -0.21 -0.22 -0.18 -0.32 0.06 0.12
- ## i9->h11
- ## 0.54
- ## b->h12 i1->h12 i2->h12 i3->h12 i4->h12 i5->h12 i6->h12 i7->h12 i8->h12
- ## -18.76 15.10 9.42 20.70 1.89 0.88 2.24 1.13 3.40
- ## i9->h12
- ## -11.18
- ## b->h13 i1->h13 i2->h13 i3->h13 i4->h13 i5->h13 i6->h13 i7->h13 i8->h13
- ## 2.17 -11.66 0.77 13.47 -2.00 -0.48 -1.18 -0.16 -0.14
- ## i9->h13
- ## -0.44
- ## b->h14 i1->h14 i2->h14 i3->h14 i4->h14 i5->h14 i6->h14 i7->h14 i8->h14
- ## 4.90 -14.11 4.32 -7.64 1.13 1.22 1.62 -2.77 -0.60
- ## i9->h14
- ## 1.82
- ## b->h15 i1->h15 i2->h15 i3->h15 i4->h15 i5->h15 i6->h15 i7->h15 i8->h15
- ## -2.00 -0.21 -1.04 -0.65 -0.22 -0.17 -0.26 0.19 0.06
- ## i9->h15
- ## 0.34
- ## b->h16 i1->h16 i2->h16 i3->h16 i4->h16 i5->h16 i6->h16 i7->h16 i8->h16
- ## 0.55 -0.72 1.13 1.70 0.21 0.33 0.16 -0.40 -0.18
- ## i9->h16
- ## 0.23
- ## b->h17 i1->h17 i2->h17 i3->h17 i4->h17 i5->h17 i6->h17 i7->h17 i8->h17
- ## 1.95 -1.02 0.93 -0.71 0.08 0.13 0.02 -0.18 -0.07
- ## i9->h17
- ## -0.02
- ## b->h18 i1->h18 i2->h18 i3->h18 i4->h18 i5->h18 i6->h18 i7->h18 i8->h18
- ## -1.94 0.39 -0.65 -0.33 -0.43 -0.58 -0.58 0.56 0.36
- ## i9->h18
- ## 0.89
- ## b->h19 i1->h19 i2->h19 i3->h19 i4->h19 i5->h19 i6->h19 i7->h19 i8->h19
- ## -2.89 -0.62 -1.17 -0.62 -0.03 -0.05 -0.15 0.05 0.05
- ## i9->h19
- ## 0.25
- ## b->h20 i1->h20 i2->h20 i3->h20 i4->h20 i5->h20 i6->h20 i7->h20 i8->h20
- ## 2.69 0.93 1.39 0.74 0.30 0.32 0.45 -0.33 -0.34
- ## i9->h20
- ## -0.31
- ## b->h21 i1->h21 i2->h21 i3->h21 i4->h21 i5->h21 i6->h21 i7->h21 i8->h21
- ## -2.97 -0.45 -1.26 0.46 -0.13 -0.19 -0.35 0.24 0.15
- ## i9->h21
- ## 0.53
- ## b->h22 i1->h22 i2->h22 i3->h22 i4->h22 i5->h22 i6->h22 i7->h22 i8->h22
- ## -2.02 -0.48 -1.09 -0.70 -0.07 -0.14 -0.26 0.21 0.04
- ## i9->h22
- ## 0.34
- ## b->h23 i1->h23 i2->h23 i3->h23 i4->h23 i5->h23 i6->h23 i7->h23 i8->h23
- ## 11.00 -9.85 -5.03 -7.26 -5.00 -5.03 -6.66 6.29 3.49
- ## i9->h23
- ## 9.93
- ## b->h24 i1->h24 i2->h24 i3->h24 i4->h24 i5->h24 i6->h24 i7->h24 i8->h24
- ## 0.09 0.10 1.19 0.87 0.15 0.18 0.02 -0.27 -0.03
- ## i9->h24
- ## 0.35
- ## b->h25 i1->h25 i2->h25 i3->h25 i4->h25 i5->h25 i6->h25 i7->h25 i8->h25
- ## -1.65 4.19 -0.24 -1.84 -1.58 -2.09 -3.09 2.29 2.50
- ## i9->h25
- ## 6.02
- ## b->h26 i1->h26 i2->h26 i3->h26 i4->h26 i5->h26 i6->h26 i7->h26 i8->h26
- ## 1.60 2.12 0.63 -9.24 3.25 3.09 3.24 -3.76 -2.22
- ## i9->h26
- ## -0.40
- ## b->h27 i1->h27 i2->h27 i3->h27 i4->h27 i5->h27 i6->h27 i7->h27 i8->h27
- ## -1.77 1.13 -1.39 -1.13 -0.43 -0.47 -0.68 0.41 0.18
- ## i9->h27
- ## 1.08
- ## b->h28 i1->h28 i2->h28 i3->h28 i4->h28 i5->h28 i6->h28 i7->h28 i8->h28
- ## -0.24 4.65 0.83 -9.53 2.28 2.06 2.00 -2.98 -2.04
- ## i9->h28
- ## 1.40
- ## b->h29 i1->h29 i2->h29 i3->h29 i4->h29 i5->h29 i6->h29 i7->h29 i8->h29
- ## -2.92 -0.57 -1.21 0.07 -0.18 -0.08 -0.14 0.13 0.06
- ## i9->h29
- ## 0.25
- ## b->h30 i1->h30 i2->h30 i3->h30 i4->h30 i5->h30 i6->h30 i7->h30 i8->h30
- ## -2.17 2.89 2.08 -0.17 -0.80 -1.19 -2.03 1.25 2.02
- ## i9->h30
- ## 5.09
- ## b->o1 h1->o1 h2->o1 h3->o1 h4->o1 h5->o1 h6->o1 h7->o1 h8->o1
- ## -1.61 -0.73 -1.36 11.20 -5.48 -8.67 -3.12 -5.21 5.32
- ## h9->o1 h10->o1 h11->o1 h12->o1 h13->o1 h14->o1 h15->o1 h16->o1 h17->o1
- ## -12.47 -0.23 -0.50 15.65 -11.70 -3.57 -1.02 -1.60 -0.80
- ## h18->o1 h19->o1 h20->o1 h21->o1 h22->o1 h23->o1 h24->o1 h25->o1 h26->o1
- ## 0.30 -0.47 1.03 -2.01 -0.76 -4.20 -0.88 3.70 3.09
- ## h27->o1 h28->o1 h29->o1 h30->o1
- ## -0.48 3.23 -0.84 2.52
- ## b->o2 h1->o2 h2->o2 h3->o2 h4->o2 h5->o2 h6->o2 h7->o2 h8->o2
- ## 4.22 -0.06 -2.83 -10.27 -4.22 5.12 1.71 -2.68 -4.57
- ## h9->o2 h10->o2 h11->o2 h12->o2 h13->o2 h14->o2 h15->o2 h16->o2 h17->o2
- ## 8.36 -1.34 -0.73 5.57 13.82 -2.43 -0.22 1.78 0.33
- ## h18->o2 h19->o2 h20->o2 h21->o2 h22->o2 h23->o2 h24->o2 h25->o2 h26->o2
- ## -0.10 -0.19 -0.19 0.28 -0.18 6.00 1.17 1.99 -10.20
- ## h27->o2 h28->o2 h29->o2 h30->o2
- ## -0.72 -9.77 -0.24 0.65
- ## b->o3 h1->o3 h2->o3 h3->o3 h4->o3 h5->o3 h6->o3 h7->o3 h8->o3
- ## -1.54 4.15 -0.36 5.06 -15.39 -0.59 -4.92 -3.20 0.79
- ## h9->o3 h10->o3 h11->o3 h12->o3 h13->o3 h14->o3 h15->o3 h16->o3 h17->o3
- ## -6.78 2.10 2.95 -16.51 -4.10 -4.52 2.53 0.26 0.79
- ## h18->o3 h19->o3 h20->o3 h21->o3 h22->o3 h23->o3 h24->o3 h25->o3 h26->o3
- ## 1.46 3.31 -1.69 5.18 2.72 7.33 1.37 3.03 5.39
- ## h27->o3 h28->o3 h29->o3 h30->o3
- ## 1.82 8.05 5.08 3.49
- ## b->o4 h1->o4 h2->o4 h3->o4 h4->o4 h5->o4 h6->o4 h7->o4 h8->o4
- ## -0.22 0.95 -0.08 -2.06 5.33 11.89 -2.25 8.77 -5.54
- ## h9->o4 h10->o4 h11->o4 h12->o4 h13->o4 h14->o4 h15->o4 h16->o4 h17->o4
- ## 13.74 -2.61 0.54 -9.44 -4.01 -4.70 1.03 -2.56 -1.48
- ## h18->o4 h19->o4 h20->o4 h21->o4 h22->o4 h23->o4 h24->o4 h25->o4 h26->o4
- ## 0.51 0.74 -2.16 1.63 1.09 5.32 -2.31 -0.28 -0.19
- ## h27->o4 h28->o4 h29->o4 h30->o4
- ## 1.54 -0.34 1.04 -2.99
- ## b->o5 h1->o5 h2->o5 h3->o5 h4->o5 h5->o5 h6->o5 h7->o5 h8->o5
- ## -0.96 -4.20 4.76 -4.01 19.82 -7.68 8.59 2.49 3.97
- ## h9->o5 h10->o5 h11->o5 h12->o5 h13->o5 h14->o5 h15->o5 h16->o5 h17->o5
- ## -2.97 2.07 -2.33 4.71 6.04 15.20 -2.48 2.17 1.26
- ## h18->o5 h19->o5 h20->o5 h21->o5 h22->o5 h23->o5 h24->o5 h25->o5 h26->o5
- ## -1.96 -3.36 2.99 -5.00 -2.73 -14.51 0.60 -8.41 1.90
- ## h27->o5 h28->o5 h29->o5 h30->o5
- ## -2.11 -1.15 -5.09 -3.74
nnet.model- ## a 9-30-5 network with 455 weights
- ## inputs: R1 G1 B1 R2 G2 B2 R3 G3 B3
- ## output(s): class
- ## options were - softmax modelling decay=0.001
- #训练集
- confusion.train.nnet=table(traindata$class,predict(nnet.model,traindata,type="class"))
- accuracy.train.nnet=sum(diag(confusion.train.nnet))/sum(confusion.train.nnet)
- confusion.train.nnet
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 43 0 0 0 0
- ## 2 0 37 0 0 0
- ## 3 0 0 62 0 0
- ## 4 0 0 0 17 0
- ## 5 0 0 0 0 5
accuracy.train.nnet## [1] 1- #测试集
- confusion.test.nnet=table(testdata$class,predict(nnet.model,testdata,type="class"))
- accuracy.test.nnet=sum(diag(confusion.test.nnet))/sum(confusion.test.nnet)
- confusion.test.nnet
- ##
- ## 1 2 3 4 5
- ## 1 8 0 0 0 0
- ## 2 0 7 0 0 0
- ## 3 0 0 16 0 0
- ## 4 0 0 1 6 0
- ## 5 0 0 0 0 1
accuracy.test.nnet## [1] 0.974359- #对比支持向量机、随机森林、人工神经网络算法的准确率
- accuracy.svm <-c(accuracy.train.svm,accuracy.test.svm)
- accuracy.randomForest<-c(accuracy.train.randomForest,accuracy.test.randomForest)
- accuracy.nnet <-c(accuracy.train.nnet,accuracy.test.nnet)
- accuracy.data <-data.frame(accuracy.svm,accuracy.randomForest,accuracy.nnet)
- accuracy.data
- ## accuracy.svm accuracy.randomForest accuracy.nnet
- ## 1 0.9634146 1.0000000 1.000000
- ## 2 0.9230769 0.8974359 0.974359
第一行是训练集准确率,第二行是测试集准确率。
1.支持向量机虽然在训练集拟合度不如随机森林和神经网络,但是测试集准确率较高;
2.随机森林明显过拟合;
3.对比发现神经网络不管训练集还是测试集效果都最好。
该对比只是简单的对比,不能直接说明哪种算法最好。
原因:
1.数据样本过少;
2.实际使用算法中还要考虑到算法运行的时间,当面对海量数据时,准确复杂的算法往往运行过慢。
3.算法得出的模型“好坏”,不仅仅只看准确率,还要看其他指标比如:recall、percision、F1-score等。比如地震预测更看重recall指标
4.实际中还是要结合具体情况,选择合适的算法。
以后有时间再将各种算法进行复杂的对比。






![bzoj1222: [HNOI2001]产品加工](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/bzoj1222: [HNOI2001]产品加工)












