算法组合 优化算法
In the last post, we saw how actual algorithms are developed and tested. In this post, we will figure out the level of exposure so that can always protect our investments from significant downturns. And find the best performing portfolio given several assets.
在上一篇文章中,我们看到了如何开发和测试实际算法。 在这篇文章中,我们将弄清风险敞口水平,从而始终可以保护我们的投资免受重大衰退的影响。 并根据几种资产找到表现最佳的投资组合。
Why quantify the risk?
为什么要量化风险?
To invest or trade with confidence. Knowing Value at Risk (VaR) helps us to gauge the potential loss of equity, both in scale and frequency. Not managing this volatility can lead to significant (and avoidable) losses.
有信心地进行投资或交易。 了解风险价值(VaR)帮助我们从规模和频率上衡量潜在的股权损失。 不控制这种波动会导致重大(和可避免)的损失。
Why Optimize Portfolio?
为什么要优化投资组合?
We are all risk-averse and we want to maximize our profits. Diversification can potentially achieve both of these goals. We can select assets with the best returns that are less correlated with each other. Portfolio return and risk however depend upon final mix or weight allocation to each asset. Not getting allocation right will lead to lower returns/higher risks. We will use mean-variance optimization to find desired weights to construct the best performing portfolio(modern portfolio theory by Markowitz).
我们都规避风险,我们希望最大限度地提高利润。 多样化可以潜在地实现这两个目标。 我们可以选择相互之间关联度较低的最佳收益资产。 但是,投资组合的回报和风险取决于最终组合或对每种资产的权重分配。 分配不正确将导致较低的回报/较高的风险。 我们将使用均值方差优化来找到所需的权重,以构建表现最佳的投资组合(Markowitz的现代投资组合理论)。
Short explanation/definition of key terms
简要解释/定义关键术语
Value at Risk (VaR): Maximum dollar amount (or percentage) expected to be lost over a given time horizon, at a pre-defined confidence/probability level.
风险价值(VaR) :在给定的时间范围内,在预定义的置信度/概率水平下,预期损失的最大金额(或百分比)。
Portfolio optimization and efficient frontier: Finding best weights for selected assets such that the expected return is highest for a given risk or vice versa. An efficient frontier is simply a collection of all such dominant/optimized portfolios for all possible risk level.
投资组合优化和有效边界 :找到选定资产的最佳权重,以使给定风险的预期收益最高,反之亦然。 有效边界只是针对所有可能的风险水平的所有此类主导/优化投资组合的集合。
Sharpe ratio: Sharpe ratio is the measure of risk-adjusted return of a portfolio. Degree of excess return beyond risk-free asset for taking extra risk.
夏普比率 :夏普比率是对投资组合进行风险调整后的收益的度量。 超出无风险资产的超额收益程度,以承担额外风险。
Capital Market Line (CML): Theoretical concept that gives optimal combinations of a risk-free asset and the market portfolio (portfolio of risky assets).
资本市场线(CML) :提供无风险资产和市场投资组合(风险资产组合)的最佳组合的理论概念。
Convex optimization: Solving a mean-variance problem as convex functions, here with the help of Solvers.
凸优化 :在此处借助求解器,将均方差问题解决为凸函数。
Part 1: Value at Risk (VaR)
第1部分:风险价值(VaR)
VaR represents portfolio variance at one extreme (of the distribution). Portfolio risk is calculated as portfolio variance (equivalently standard deviation). Portfolio variance plays a major role in determining the risk characteristic of asset as a whole. Portfolio variance depends upon variance of each asset within the portfolio as well their covariance. Thus when assets are uncorrelated (do not tend to move together) portfolio risks are lower compared to portfolio of assets are highly positively correlated.
VaR代表(分布中)一种极端的投资组合方差。 投资组合风险计算为投资组合方差(等同于标准差)。 投资组合方差在确定整个资产的风险特征中起着重要作用。 投资组合方差取决于投资组合中每个资产的方差及其协方差。 因此,与不高度相关的资产组合相比,当资产不相关(不倾向于一起移动)时,资产组合的风险较低。
For a 2 asset portfolio, portfolio variance is given by following equation where w1, w2 are weights, sigma1, sigma2 are standard deviation of each asset and Cov12 denotes covariance between them.
对于2个资产投资组合,投资组合方差由以下等式给出,其中w1,w2是权重,sigma1,sigma2是每种资产的标准差,Cov12表示它们之间的协方差。
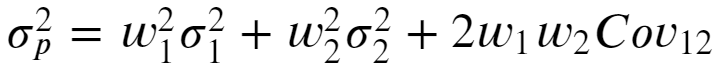
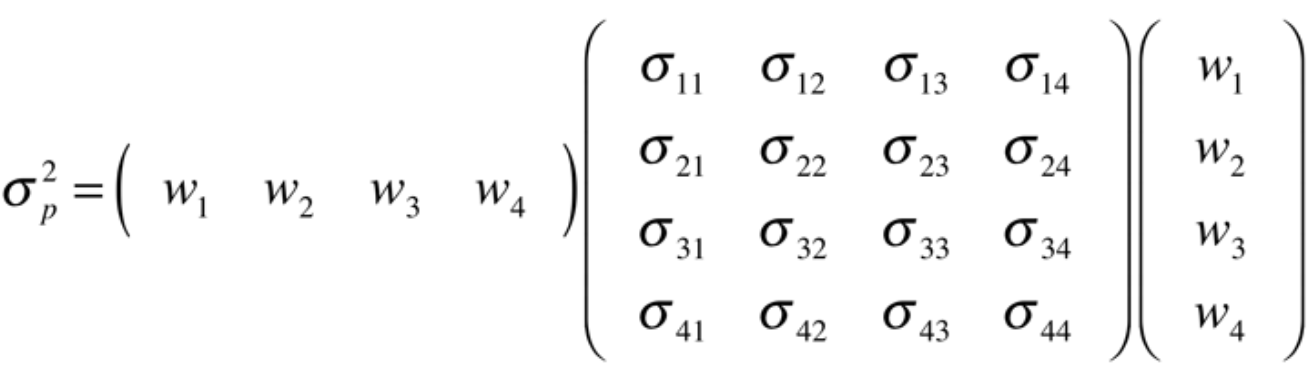
For multiple asset portfolio, position vector and covariance matrix make it much easier to express portfolio variance rather than writing a long summation.
对于多资产投资组合,位置矢量和协方差矩阵使表达投资组合方差比编写长总和变得容易得多。
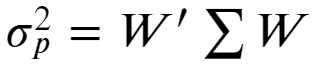
Following is an expanded view of the matrix operation.
以下是矩阵运算的扩展视图。
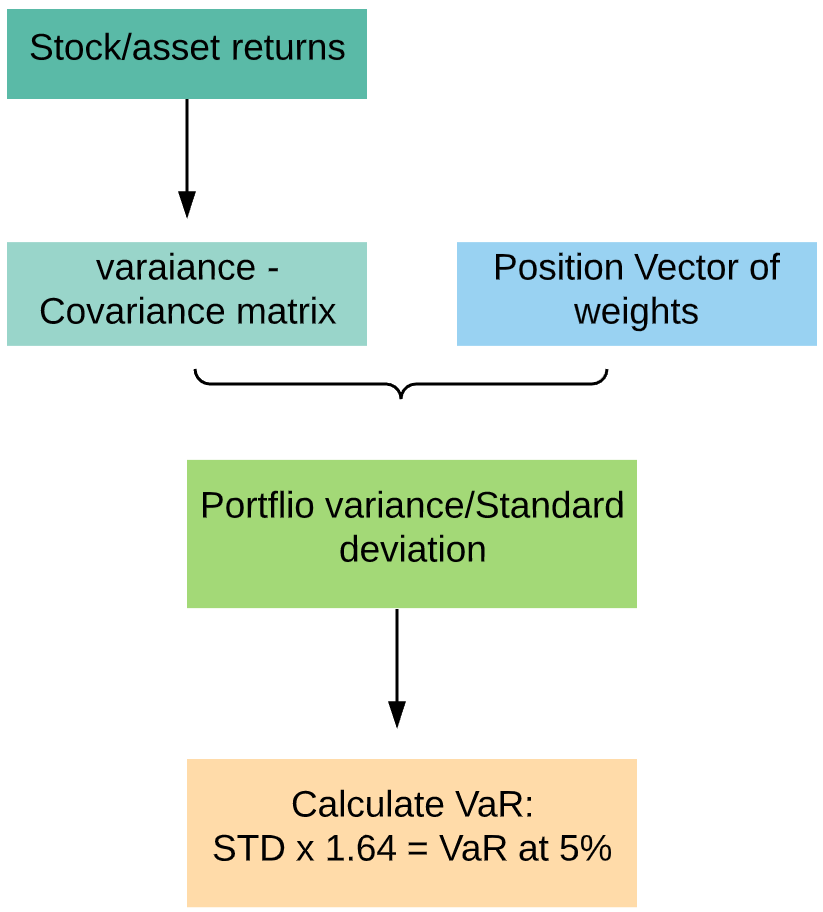
With python (Pandas/Numpy or other tools) it is straight forward to calculate the covariance matrix for the whole asset given the series of returns. Matrix multiplication is then used to get portfolio variance.For illustration, I have taken stocks from the Nepal Stock Exchange (NEPSE). 4 highly traded stocks from different sectors were selected. The process involves loading data, calculating return for each stock, computing covariance, and finally calculating portfolio variance as given below.
使用python(Pandas / Numpy或其他工具),可以很容易地在给定一系列收益的情况下为整个资产计算协方差矩阵。 然后使用矩阵乘法获得投资组合方差。为说明起见,我从尼泊尔证券交易所(NEPSE)提取了股票。 选择了4个来自不同行业的高交易量股票。 该过程包括加载数据,计算每只股票的回报,计算协方差,最后计算投资组合方差,如下所示。
While standard deviation tells how much asset can fluctuate every day on average, VaR represents how much asset can fall a single day during a highly volatile period. VaR is expressed as a potential loss of asset (e.g. 4% of the total asset) with a certain probability (e.g. 2% chance or 98% confidence) within a certain time frame (e.g. daily/weekly). Being aware of VaR allows us to keep the right-sized asset or the right mix of assets such that we can avoid unexpected and huge losses.The image below shows that return could be as worse as or worse than -1.64 standard deviation 1 out of 20 trading days (5% probability).
标准差表示平均每天有多少资产波动,而VaR表示在高度波动的时期中一天会有多少资产下跌。 VaR表示为在特定时间范围(例如每天/每周)内具有一定概率(例如2%机会或98%的置信度)的潜在资产损失(例如总资产的4%)。 意识到VaR可以使我们保留适当大小的资产或正确的资产组合,从而避免出现意外的巨大损失。下图显示,收益可能比-1.64标准差1差或更差。 20个交易日(5%的概率)。
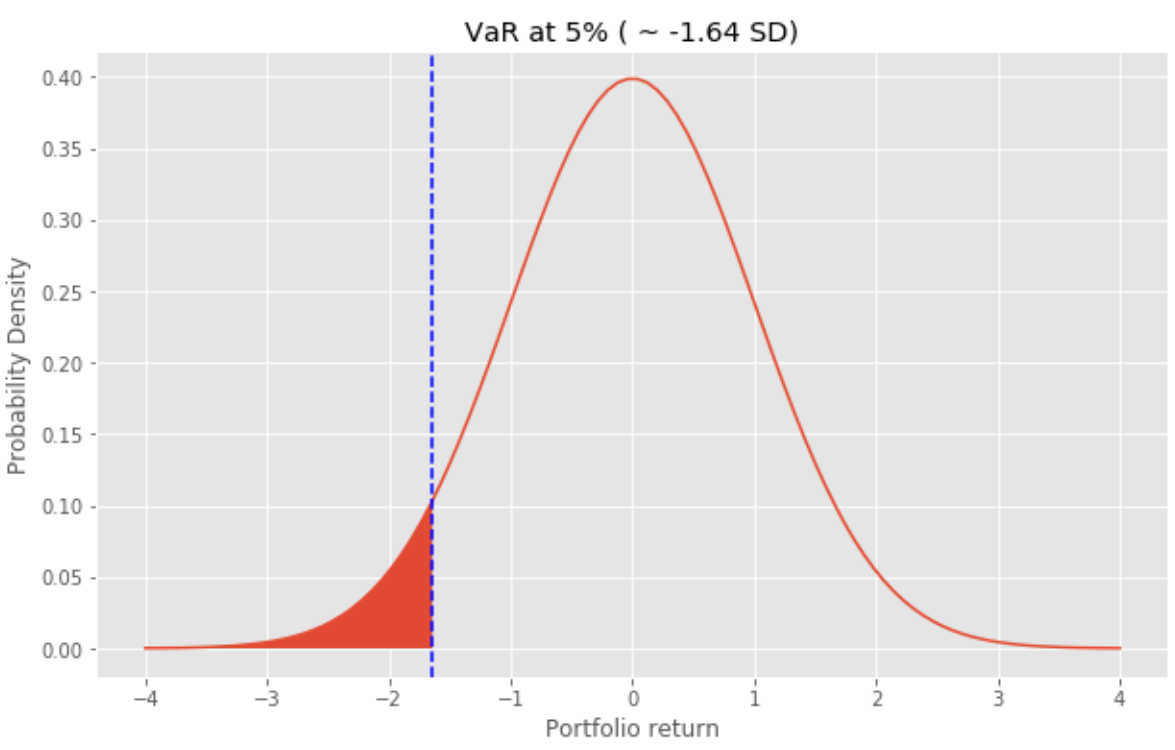
It is obvious that we would want a portfolio and with minimum VaR as possible for any given return. Next, we will find such a portfolio with an optimal combination of weights that has a minimum variance for a specific return. Alternatively, portfolio optimization will help us to maximize our return for any selected risk level.
显然,我们希望有一个投资组合,并且对于任何给定的回报,都需要尽可能降低VaR。 接下来,我们将找到这样的投资组合,其权重的最佳组合对于特定收益具有最小的方差。 另外,投资组合优化将帮助我们针对任何选定的风险水平最大化收益。
Example: For some random positions(weights) in 4 stocks [0.08, 0.2, 0.58, 0.14] calculated portfolio variance is 0.005, and standard deviation is 0.022 or 2.2% daily std. Assuming a normal distribution of returns, the worst 5% outcomes lie -1.64 SD away from the center. That is returns can be worse than -0.0367 or -3.67% (-1.645*0.022) in 1/20 trading days (5% chance). If we have $100000 invested, our Var at 5% probability is $3670. In other words, we tend to lose $3670 (or more) once in every 20 trading days.
例如:对于4只股票中的一些随机头寸(权重)[0.08,0.2,0.58,0.14],计算出的投资组合方差为0.005,标准差为每日std的0.022或2.2%。 假设收益呈正态分布,则最差的5%收益位于远离中心的-1.64 SD。 也就是说,在1/20个交易日内(低于5%的机会)回报可能低于-0.0367或-3.67%(-1.645 * 0.022)。 如果我们投资了100000美元,则我们以5%概率出现的Var为3670美元。 换句话说,我们倾向于每20个交易日损失3670美元(或更多)。
Part 2. Portfolio Optimization
第2部分。投资组合优化
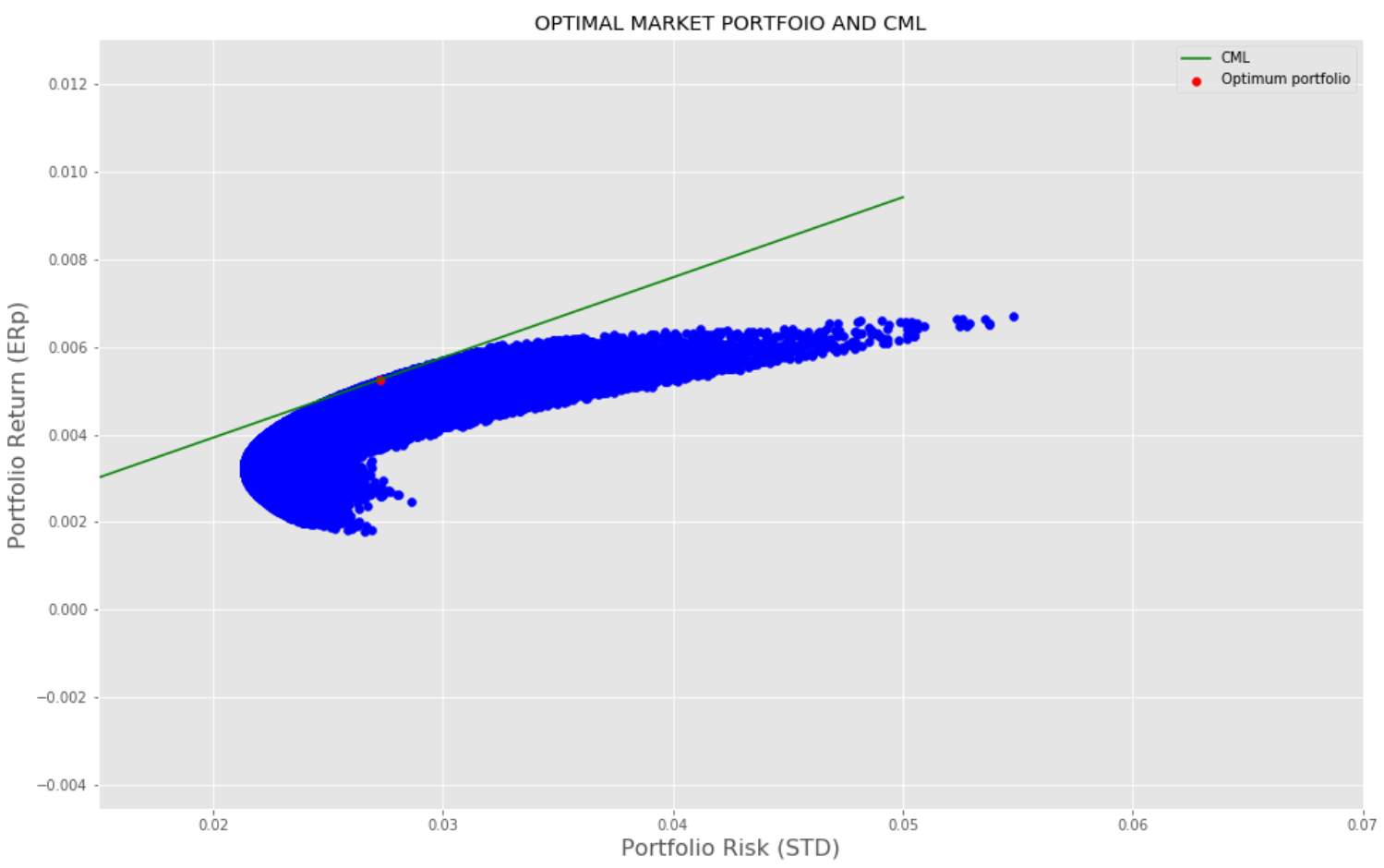
We will gradually discover the portfolio we want in few steps. We shall start with completely random allocation (i.e. use random weights). Some of these random weight portfolios have better risk-return trade-off, hence are dominant portfolios. Those lying most upper/outer in the risk-return plot make the efficient frontier. Next, we shall find the Market portfolio by comparing the Sharpe ratio for each random portfolio. Needless to say, the Market portfolio lies on the efficient frontier and has the highest/maximum Sharpe ratio. The line tangent to this point and passing through risk-free asset is the Capital Market Line. The slope and intercept to this line are Sharpe ratio and risk-free rate respectively. Ideally, all investors select their portfolio somewhere on this line depending upon their risk/return preferences.
我们将通过几个步骤逐步发现我们想要的产品组合。 我们将从完全随机的分配开始(即使用随机权重)。 这些随机权重投资组合中的一些具有更好的风险-收益权衡 ,因此是占主导地位的投资组合 。 那些在风险收益图上位于最上/最外的人成为有效的前沿 。 接下来,我们将通过比较每个随机投资组合的夏普比率来找到市场投资组合。 不用说,市场组合位于有效的边界上,并且具有最高/最大的夏普比率。 与此切线相交并穿过无风险资产的线是资本市场线 。 这条线的斜率和截距分别是夏普比率和无风险利率。 理想情况下,所有投资者都根据风险/回报偏好选择投资组合。
A. Random allocation of weights: We will visualize the effect of random allocation weights. 1000s of portfolios are taken with random weights, respective mean and variance are calculated (and scattered for visualization). Some combination weight has better risk-return characteristics and therefore are dominating/desirable portfolios.
A.权重的随机分配:我们将可视化随机分配权重的效果。 以随机权重获取1000个投资组合,计算各自的均值和方差(并分散显示)。 一些组合权重具有更好的风险收益特性,因此是主导/理想的投资组合。
Portfolio return:
投资组合收益:
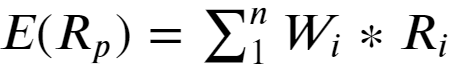
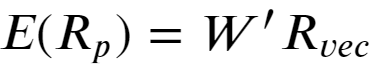
Portfolio risk:
投资组合风险:

B. Market portfolio: Among all possible combinations of dominating portfolios in the efficient frontier, one which gives the highest return for taking additional risk beyond a risk-free rate is designated as a Market portfolio. we can calculate the Sharpe ratio for all portfolios given a risk-free rate and the winning portfolio with the highest Sharpe ratio is the Market Portfolio. All the rational investors gravitate towards to this best performing portfolio.This model of combining risk-free assets with the Market portfolio is known as the Capital asset pricing model (CAPM). All portfolios in CML is optimally compensated for risk above the risk-free rate. Mathematically CAPM is expressed as:
B.市场投资组合:在有效边界中所有主导投资组合的可能组合中,将承担无风险利率以外的附加风险获得最高回报的投资组合指定为市场投资组合。 在无风险利率的情况下,我们可以计算所有投资组合的夏普比率,而夏普比率最高的获胜投资组合是市场投资组合。 所有理性投资者都倾向于使用这种表现最佳的投资组合。这种将无风险资产与市场投资组合在一起的模型被称为资本资产定价模型(CAPM)。 CML中的所有投资组合都能获得高于无风险利率的最佳风险补偿。 在数学上,CAPM表示为:
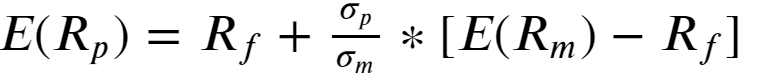
Rearranging, we have Sharpe ratio for combined portfolio :
重新排列后,我们得到了组合资产组合的夏普比率:

Using Rm and Sigma_m calculated from stock return and covariance Sharpe ratio for each random portfolio is calculated, one with the highest Sharpe ratio is the market/optimal portfolio.C. Capital Market Line (CML): Capital Market line represents all combinations of the risk-free asset and the optimal market portfolio. It’s easy to see that the slope of this line is the Sharpe ratio itself and the intercept is a risk-free rate. Given this information, CML can be readily drawn as seen below.
使用从股票收益率和协方差计算得出的Rm和Sigma_m,计算每个随机投资组合的Sharpe比率,夏普比率最高的是市场/最优投资组合。 资本市场线(CML):资本市场线代表无风险资产和最佳市场投资组合的所有组合。 不难看出,这条线的斜率就是夏普比率本身,截距是无风险比率。 有了这些信息,就可以很容易地绘制CML,如下所示。
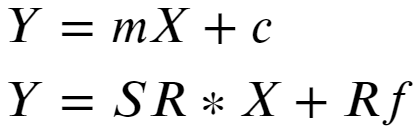
Code for constructing random portfolios, finding a market portfolio, and drawing CML line.
用于构建随机投资组合,查找市场投资组合和绘制CML线的代码。
Part 3. Solvers
第3部分。求解器
Random initialization of weights can work for a portfolio with few assets but when assets grow large, the cost of computing and time it takes can be forbidding. However, solving for the best portfolio is an optimization problem with constraints. We can use Solvers from python either for getting single best return (or risk) or get the entire efficient frontier. These are solved as convex problems and the global optimum is always reached.
权重的随机初始化可以用于资产很少的投资组合,但是当资产变大时,计算成本和花费的时间可能会被禁止。 但是,求解最佳投资组合是具有约束的优化问题。 我们可以使用python的Solvers来获得单个最佳回报(或风险)或获取整个有效边界。 这些问题解决为凸问题,并且始终可以达到全局最优。
The optimization objective is expressed as:
优化目标表示为:

Here weights are represented by x and we are solving for optimal x. Objectives and constraints are written in matrix form. As a rule objective function is stated as a minimization problem. All the inequalities are similarly stated as lesser than some value.
这里的权重用x表示,我们正在求解最优x。 目标和约束以矩阵形式编写。 通常将目标函数表示为最小化问题。 类似地,所有不平等程度均小于某个值。
Inputs for Solvers:
解算器的输入:
The algorithm solves for ‘x’ with the help of inputs
该算法借助输入来求解“ x”
P or quadratic part (here it’s sigma or variance-covariance matrix, cov)
P或二次部分(此处为sigma或方差-协方差矩阵,cov)
q or linear part of the objective function (here represented by a vector of returns r or ER_stocks, above)
q或目标函数的线性部分(此处由上面的收益r或ER_stocks的向量表示)
G and h make the lower bound for weights i.e 0. We can input G as an identity matrix of size n x n (n: number of weights/stocks). Stated as matmul(G, x) < h, hence h is a vector of 0s of size n. while weights are non-negative, while solving they are stated as: -weights < 0.
G和h为权重的下限,即0。我们可以输入G作为大小为nxn的单位矩阵(n:权重/库存数)。 表示为matmul(G,x)<h,因此h是大小为n的0s的向量。 权重为非负数,而求解时权重表示为:-weights <0。
A and b make the equality part of the constraint. For our purpose the sum of all weights must equal 1. Hence A is a vector of 1s of size n. matmul(A, r_transpose) = 1, or b is simply 1.
A和b使相等性成为约束的一部分。 为了我们的目的,所有权重的总和必须等于1。因此,A是大小为n的1s的向量。 matmul(A,r_transpose)= 1或b就是1。
We can get the frontier and plot along with random portfolios:
我们可以得到边界和情节以及随机投资组合:

Code to solve using Solvers.
使用求解器求解的代码。
Limitations and Conclusion
局限性和结论
The biggest limitations of this model are the assumption of a normal distribution of returns and the validity of covariance. Actual returns are rarely normal and in fact, highly negative and positive returns are much more common giving rise to so-called fat-tailed distribution. As such the model underestimates the risks. Portfolio variance/risk is very sensitive to variance and covariance pairs i.e. the covariance matrix. Covariance rarely remains the same for a long time, hence finding a robust/valid covariance matrix is challenging.
该模型的最大局限性是假设收益呈正态分布且协方差有效。 实际收益很少是正常的,实际上,高度负收益和正收益更为普遍,从而导致所谓的肥尾分布。 因此,该模型低估了风险。 投资组合方差/风险对方差和协方差对(即协方差矩阵)非常敏感。 协方差很少会长时间保持相同,因此要找到鲁棒/有效的协方差矩阵具有挑战性。
Despite some limitations, risk modeling with VaR is a very helpful and probably most used indicator. Portfolio optimization leads to the most efficient use of our resources and any allocation decisions should be based upon these considerations. Solvers can be used to quickly find the efficient frontier or market portfolio has given return series for each stock.
尽管有一些限制,但使用VaR进行风险建模是一个非常有用且可能是最常用的指标。 投资组合优化可最有效地利用我们的资源,任何分配决策均应基于这些考虑。 解算器可用于快速找到有效的前沿或市场投资组合,从而为每只股票提供收益系列。
翻译自: https://medium.com/@mnshonco/algorithmic-trading-simplified-value-at-risk-and-portfolio-optimization-ce8f0977d09
算法组合 优化算法
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.mzph.cn/news/389332.shtml
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系多彩编程网进行投诉反馈email:809451989@qq.com,一经查实,立即删除!


















