
文章目录
- 比赛链接
- A CodeForces 1481D AB Graph
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- B CodeForces 1481E Sorting Books
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- C CodeForces 1478D Nezzar and Board
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- D CodeForces 1478C Nezzar and Symmetric Array
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- E CodeForces 1478E Nezzar and Binary String
- F CodeForces 1481C Fence Painting
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- G CodeForces 1477E Nezzar and Tournaments
- H CodeForces 1481F AB Tree
- I CodeForces 1478B Nezzar and Lucky Number
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
- J CodeForces 1478F Nezzar and Nice Beatmap
- K CodeForces 1477D Nezzar and Hidden Permutations
- L CodeForces 1481B New Colony
- 题意:
- 题解:
- 代码:
比赛链接
CF699 div2(没有A题),CF698div2(没有A题),CF698div1
A CodeForces 1481D AB Graph
题意:
一张完全图的每一条有向边上写着a或者b,问能否构造一条边数为m的不间断路线使该路线为回文串
题解:
构造题
对于边数为奇数的回文串,随便找两个点都是可以构造出来的(如果两点间的两条边相同,那么肯定是回文串,如果不相同,形如aba也可以构成回文串)
对于边数为偶数的回文串,如果是偶数,那么中间两个肯定是相同的,我们只要找到连着相同的两条边就可以。而这种情况在三元环之间肯定能形成这种情况(因为一共就两种边,所以肯定有相邻的边是一样的),所以当n >= 3时肯定可以构造出来
当n = 2 的情况,m为奇数讨论过(肯定行),m为偶数的话,两点之间的边必须相同才行(也就是双向边必须一样)
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const int M = 5e5 + 10;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
char mp[1005][1005];
int main() {int T; cin >> T;while (T--) {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> mp[i] + 1;if (m & 1) {cout << "YES" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= m+1; i++) cout << i % 2 + 1 << " ";cout << endl;continue;}if (n == 2) {if (mp[1][2] == mp[2][1]) {cout << "YES" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= m+1; i++) cout << i % 2 + 1 << " ";cout << endl;}else cout << "NO" << endl;} else {cout << "YES" << endl;int flag;if (mp[1][2] == mp[2][3]) flag = 1;else if (mp[3][1] == mp[1][2]) flag = 0;else flag = 2;for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) cout << (flag + i + m) % 3 + 1 << " ";cout << endl;}}
}B CodeForces 1481E Sorting Books
题意:
一排书架上有 n 本书排成一排,每本书上有一个颜色ai ,你可以每次将一本书移动到书架的最右端,如果书架上的书,颜色相同的书都排到了一块,我们就认为他是漂亮的,请问将这个书架通过上面的那一种操作排成漂亮的书架,最少需要几次操作?
题解:
代码:
C CodeForces 1478D Nezzar and Board
题意:
n个数组x1 ~ xn,每次可以选择其中两个数x和y,然后将2x-y的值加入到数组中,x和y依旧保留,问通过这系列操作是否能得到数字k
题解:
我们先讲个定理,裴蜀定理:
设a,b是不全为0的整数,则存在整数x,y,使得ax+by = gcd(a,b)
n个整数间的裴蜀定理:
设a1,a2,a3…an为n个整数,d是它们的最大公约数,那么存在整数x1…xn使得x1 * a1+x2 * a2+…xn * an=d
(证明略)
题目给的是2x-y,我们将其拆开x+(x-y),相当于x加上x与y的差值,其实就是本身加上本身与其他数的差值,我们可以处理出所有的差值,但是O(n2)肯定不行(数据范围是1e5),其实不用求出所有差值,因为我们求出a1和a2的差值,a2和a3的差值,也就相当于求出a3和a1的差值(a3-a2+a2-a1=a3-a1),也就是求出a[i]与a[i+1]的差值(O(n),共n-1个
然后我们开始思考裴蜀定理,我们现在有n-1个差值(我们设为a1…an-1),gcd是他们的最大公约数,那么存在整数x1,…xn-1,使得x1 * a1+x2 * a2+…xn-1 * an-1=gcd
我们要求的数是k,我们已经有了每个数a[i],我们需要的是改变值k-a[i],也就是只要n-1个差值能表示出k-a[i]即可,现在n-1个差值可以表达出gcd,那么k-a[i]只要是gcd的倍数就可以被表示,如果不是则不行
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//#define ACM_LOCAL
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int M = 1e6 + 10;
const ll INF = 1e18;
const double eps = 1e-4;
ll d[N];void solve() {int T; cin >> T;while (T--) {ll n, k;cin >> n >> k;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> d[i];ll gcd_ = 0;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) gcd_ = __gcd(d[i]-d[i-1], gcd_);int f = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {if ((k - d[i]) % gcd_ == 0) f = 1;}if (f) cout << "YES" << endl;else cout << "NO" << endl;}
}int main() {solve();return 0;
}D CodeForces 1478C Nezzar and Symmetric Array
题意:
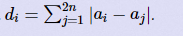
给定一个长度为2n的序列d,问能否通过上述公式得到a序列,输出“YES”/“NO”, a序列中必须成对出现相反数,ai = - aj ,而且不能相同
题解:
这个讲的很详细
这个方法也可以
构造题,题目给了d和a的关系,a数组是成对出现的相反数,且均不相同
我们通过a的性质进行反推,推出数组d 应该有哪些性质
(这里直接将结论,具体推导过程在上面的链接中有写)
d数组满足:
条件一:d是 成对出现
条件二:d都为偶数
条件三:计算过程中的数都是正整数
原始数组a为±2、±7、±9
差值和d为 36 36 46 54 46 54
去重排序除以2(用really数组保存)18 23 27
27/3=9,所以原始数组中最大的数就是9
(23-9)/2=7,所以原始数组中还有一个正数7
(18-9-7)/1=2,所以原始数组中还有一个正数2
所以原始数组为±2、±7、±9,输出YES
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll really[100010]; // Really 记录真正需要处理的数(表格二左边的1/2)
int main()
{int N;cin >> N;while (N--){int n;scanf("%d", &n);bool buxing = 0; //不行的拼音map<ll, int> ma; //用map记录出现了几次(条件一)for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++){ll t;scanf("%lld", &t);if (t % 2) //差值和是否为偶数(条件二)buxing = 1;ma[t]++;}int sum = 1;ll realOriSum = 0; // 已经得出的原来的数,上文样例中便是 9 7 3if (buxing){puts("NO");}else{for (map<ll, int>::iterator it = ma.begin(); it != ma.end(); it++){if (it->second != 2) // 差值和是否都出现了两处(条件一)buxing = 1;really[sum++] = (it->first) / 2;}if (buxing){puts("NO");}else{for (sum--; sum > 0; sum--){ll all = really[sum] - realOriSum; //减去原来的数if (all % sum) //是否可以整除buxing = 1;ll thisReal = all / sum;//除以当前really数组内数的数量realOriSum += thisReal;//对已求出的数组a求和if (thisReal <= 0)//检验计算过程中的数是否都是正整数buxing = 1;}if (buxing){puts("NO");}elseputs("YES");}}}return 0;
}E CodeForces 1478E Nezzar and Binary String
F CodeForces 1481C Fence Painting
题意:
有一个围栏,每一块上都有颜色,用A数组来表示,Bob觉得太单调了,他想涂成B数组的颜色。这时候有m个粉刷匠,每个粉刷匠能且只能粉刷一次围栏,问你通过这m个人的粉刷能否达到Bob的要求。如果可以输出YES,并把每个粉刷匠粉刷的下标输出,否则输出NO。
题解:
因为颜色会覆盖,所以如果让后来的工匠染了某块木板,前面的工匠选择这块木板染色便没有影响,所以我们先把需要进行染色的木板按颜色分类存下来,从后往前扫每位工匠,如果有需要染对应颜色则染,否则选择之后会有人染的木板,或者选择相应颜色的不需要染色的木板染上,颜色不会发生变化
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 100005
using namespace std;
int t,n,m,a[MAXN],b[MAXN],c[MAXN];
queue<int> ve1[MAXN],ve2[MAXN];
int xx,ans[MAXN];
int main()
{scanf("%d",&t);while(t--){scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);//a是原本,b是需求,m是改变 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i){while(!ve1[i].empty())ve1[i].pop();while(!ve2[i].empty())ve2[i].pop();}xx = 0;for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i)scanf("%d",&a[i]);for(int i =1;i <= n;++i){scanf("%d",&b[i]);if(b[i] == a[i])ve1[a[i]].push(i);//已经涂好 elseve2[b[i]].push(i);//需要该颜色 }for(int i = 1;i <= m;++i)scanf("%d",&c[i]);int f = 1;for(int i = m;i >= 1;--i){//xx是可以被涂的地方 if(ve2[c[i]].empty()==0)//即需要该颜色 {int tmp = ve2[c[i]].front();//需要颜色的位置 ans[i] = tmp;xx = tmp;//因为这个地方最后会被改回颜色,所以之前可以涂 ve2[c[i]].pop();}else if(xx)//如果存在可以多涂的地方 {ans[i] = xx;}else if(ve1[c[i]].empty()==0)//涂在该地方没有影响(相当于在本来是1的地方涂1) {ans[i] = ve1[c[i]].front();xx = ans[i];} else{f = 0;break;}}for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i){if(ve2[i].empty()==0)//如果存在地方改变不了颜色 {f = 0;break;}}if(f){printf("YES\n");for(int i = 1;i <= m;++i)printf("%d ",ans[i]);printf("\n");}elseprintf("NO\n");}return 0;
}G CodeForces 1477E Nezzar and Tournaments
H CodeForces 1481F AB Tree
I CodeForces 1478B Nezzar and Lucky Number
题意:
我们定义一个数字x为最喜欢的数(0<x<9),只要是出现了x的数都是幸运树,另外如果一个数可以由多个幸运树相加得到,该数也为幸运数
现给q个数,判断是否为幸运数
题解:
我的思路是:如果x是最喜欢的数,给数w,先查看w的各位是否有x存在,然后将w减去x,得到z,然后再看z的各位是否存在x,然后再减想,依次循环,直到小于x位置或者确定为幸运数为止
我是这样想的,如果w的各位不存在x,那么w可能是由幸运数相加得到,每次减去最小幸运数x
至于证明,我也讲不明白,当时做的时候是举例子推出来的,下面看这个详细证明
详细证明
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+8;
int a[maxn];
int q,d;
bool f(int x)
{if(x<d)return 0;int ans=x;bool flag=0;while(ans){if(ans%10==d){flag=1;break;}ans/=10;}if(flag==1)return 1;if(f(x-d))return 1;return 0;
}
int main()
{int t;cin>>t;while(t--){cin>>q>>d;for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){int x;cin>>x;if(f(x))cout<<"YES"<<endl;else cout<<"NO"<<endl;}}return 0;}
J CodeForces 1478F Nezzar and Nice Beatmap
K CodeForces 1477D Nezzar and Hidden Permutations
L CodeForces 1481B New Colony
题意:
从山顶有石头滚下来,有n个山,山的高度分别是hi
如果hi >= hi+1 ,石头就会滚到下一个山
如果hi < hi+1,石头会停止滚动(停在hi),hi的高度会加一
问第k次滚石会停到什么位置,会不会滚出所有山?
题解:
本题按照题意直接暴力即可
循环k次,记录每次石头滚到的位置,如果石头没有停下来(说明所有的i都满足a[i]>=a[i+1]),说明石头滚出所有山,此时输出-1
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+8;
int a[maxn];
int main()
{int t;cin>>t;while(t--){int n,k;cin>>n>>k;memset(a,0,sizeof(a));for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];int ans=0;while(ans!=k){int i;bool f=0;for(i=1;i<n;i++){if(a[i]>=a[i+1])continue;else {f=1;a[i]++;ans++;break;}}if(f==0){cout<<-1<<endl;break;}if(ans==k){cout<<i<<endl;break;}}}return 0;
}


![[BZOJ 3811]玛里苟斯(线性基)尽量理解的题解](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[BZOJ 3811]玛里苟斯(线性基)尽量理解的题解)
)


)

![P7920-[Kubic]Permutation](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/P7920-[Kubic]Permutation)
)
)



)
)

![AT3877-[ARC089C]GraphXY【构造】](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/AT3877-[ARC089C]GraphXY【构造】)
)
)