作者:李俊才 (jcLee95):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28550263
邮箱 :291148484@163.com
本文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28550263/article/details/134423951
很久前介绍过一个 NodeJS 中的类似工具,叫做 fast-glob,可参见《NodeJS文件系统遍历工具:fast-glob》一文(地址:https://jclee95.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129892856)。这类库对于自己开发底层工具来说是比较常用的。比如在前端中自己去做一些脚手架。本文介绍的 glob库就是 Dart 语言中这样一个类似的工具,在很多常用的命令行工具中,都有它的使用,比如 build_runner 库(一个用于 Dart 代码生成和模块化编译的构建系统),再比如 very_good_cli 等等。当需要自己做类似的 Flutter/Dart 项目的工程化工具时,可以回过头来参考本文中介绍的相关知识。
目 录
1. 概述
glob 库是一个强大的文件系统遍历工具,它提供了一种简洁的方式来描述和匹配文件路径模式。这种模式被称为 glob 模式,它可以包含各种通配符,使得我们可以轻松地匹配多个文件或目录。
glob 库的主要功能是根据给定的 glob 模式来查找和匹配文件系统中的文件和目录。它支持各种通配符,包括 *(匹配任意数量的字符)、?(匹配任意一个字符)、[abc](匹配任意一个列出的字符)等等。此外,它还支持使用 {} 来指定多个模式,以及使用 ** 来匹配任意深度的目录。
在 Dart 和 Flutter 的项目中,glob 库被广泛用于各种工程化工具中,如 build_runner(一个用于 Dart 代码生成和模块化编译的构建系统)和一些cli 工具中。当我们需要开发自己的工程化工具时,glob 库将是一个非常有用的工具。
2. glob 库入门
2.1 安装 glob 库
和安装其它的 Dart/Flutter 模块一样。首先,你需要在项目的 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加 glob 库的依赖。在 dependencies 部分添加以下代码:
dependencies:glob: ^2.1.2
然后,运行 flutter或dart pub get 命令来下载和安装 glob 库:
dart pub get
这样,glob 库就被成功安装到你的项目中了。
或者直接使用 pub add 命令安装当前发布的最新版本:
flutter pub add glob
着将自动添加依赖到 pubspec.yaml 文件中并隐式运行 pub get命令。
2.2 初体验:使用 glob 库进行文件匹配
使用 glob 库进行文件匹配也非常简单。首先,你需要导入 glob 库:
import 'package:glob/glob.dart';
然后,你可以创建一个 Glob 对象,并使用 matches 方法来检查一个路径是否匹配给定的 glob 模式:
var glob = Glob('**.dart');
if (glob.matches('lib/main.dart')) {print('The path matches the glob pattern');
} else {print('The path does not match the glob pattern');
}
3. glob 模式的基本语法
3.1 glob 模式中的 通配符
在 glob 模式中,* 字符匹配除 / 之外的零个或多个任何字符。这意味着它可以用来匹配给定目录中匹配模式的所有文件,而不会匹配子目录中的文件。例如,lib/*.dart 将匹配 lib/glob.dart,但不匹配 lib/src/utils.dart。
** 是类似 *,但也匹配 /。它对于匹配文件或递归列出目录很有用。例如,lib/**.dart 将匹配 lib/glob.dart 和 lib/src/utils.dart。
? 字符匹配除 / 之外的单个字符。与 * 不同,它不会匹配多于或少于一个字符。例如,test?.dart 将匹配 test1.dart,但不匹配 test10.dart 或 test.dart。
3.2 glob 模式中的 字符集
[...] 构造匹配几个字符中的一个。它可以包含单个字符,如 [abc],在这种情况下,它将匹配任何这些字符;它可以包含范围,如 [a-zA-Z],在这种情况下,它将匹配任何落在范围内的字符;或者它可以包含两者的混合。它只会匹配一个字符。例如,test[a-zA-Z_].dart 将匹配 testx.dart、testA.dart 和 test_.dart,但不匹配 test-.dart。
如果它以 ^ 或 ! 开头,构造将匹配所有未提到的字符。例如,test[^a-z].dart 将匹配 test1.dart,但不匹配 testa.dart。
3.3 glob 模式中的 选择器
{...,...} 构造匹配几个选项中的一个,每个选项都是一个 glob。例如,lib/{*.dart,src/*} 匹配 lib/glob.dart 和 lib/src/data.txt。它可以包含大于一个的任何数量的选项,甚至可以包含嵌套的选项。
3.4 glob 模式中的 目录匹配
所有 globs 使用 POSIX 路径语法,包括使用 / 作为目录分隔符,无论它们在哪个平台上。这对于 Windows 根目录也是如此;例如,匹配 C 驱动器中所有文件的 glob 将是 C:/*。
默认情况下,glob 在 Posix 系统和浏览器上是 区分大小写的,在 Windows 上不区分大小写。
4. 使用 glob 库进行文件系统遍历
4.1 如何使用 glob 库查找文件
使用 glob 库查找文件,你可以使用 Glob.list() 或 Glob.listSync() 方法列出所有匹配 glob 的文件:
import 'package:glob/glob.dart';
import 'package:glob/list_local_fs.dart';final dartFile = Glob("**.dart");// 列出当前目录中的所有 Dart 文件。
void main(List<String> arguments) {for (var entity in dartFile.listSync()) {print(entity.path);}
}
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个 glob 模式 **.dart,它会匹配所有的 Dart 文件。然后,我们使用 listSync() 方法列出所有匹配这个模式的文件。
下面是一个新建的项目,运行 glob_demo.dart:
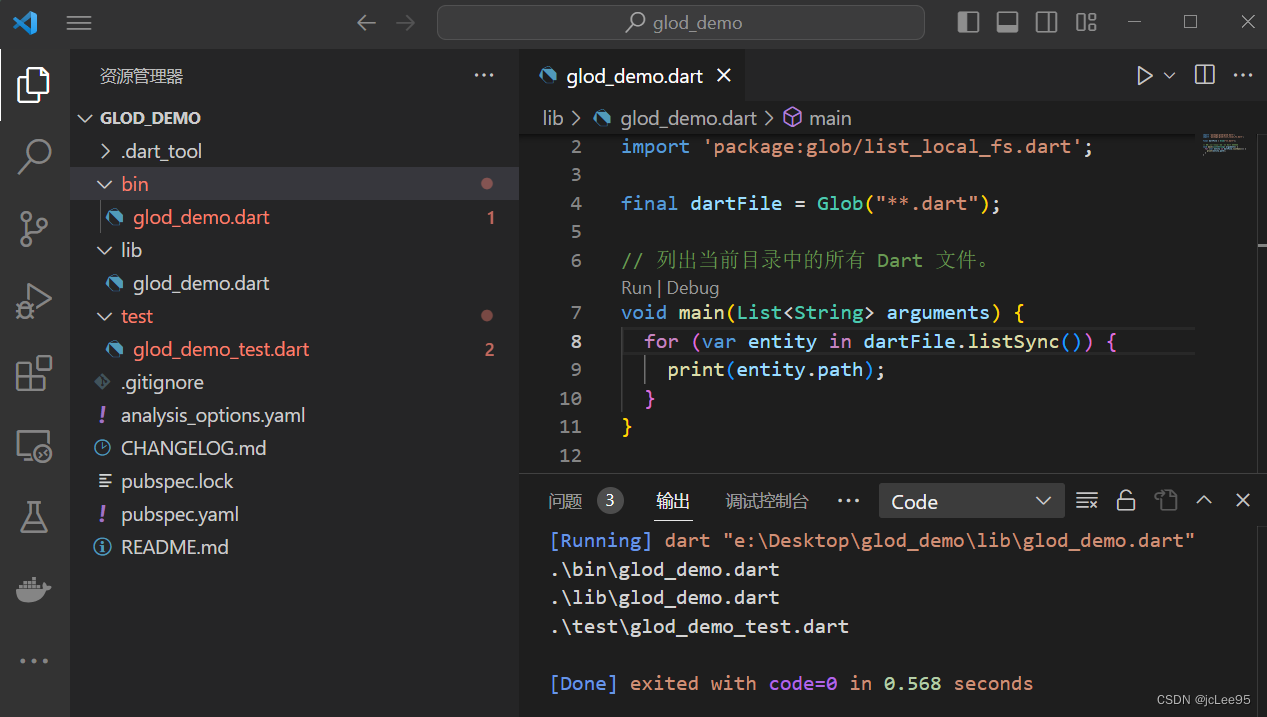
从图中可以看到,其输出结果为:
.\bin\glod_demo.dart
.\lib\glod_demo.dart
.\test\glod_demo_test.dart
4.2 如何使用 glob 库查找目录
使用 glob 库查找目录,你可以创建一个 glob 模式来匹配目录,然后使用 Glob.list() 或 Glob.listSync() 方法列出所有匹配 glob 的目录:
import 'package:glob/glob.dart';
import 'package:glob/list_local_fs.dart';final directory = Glob("**/");// 列出当前目录中的所有子目录。
void main(List<String> arguments) {for (var entity in directory.listSync()) {print(entity.path);}
}
还是那个demo项目,其运行结果如图:
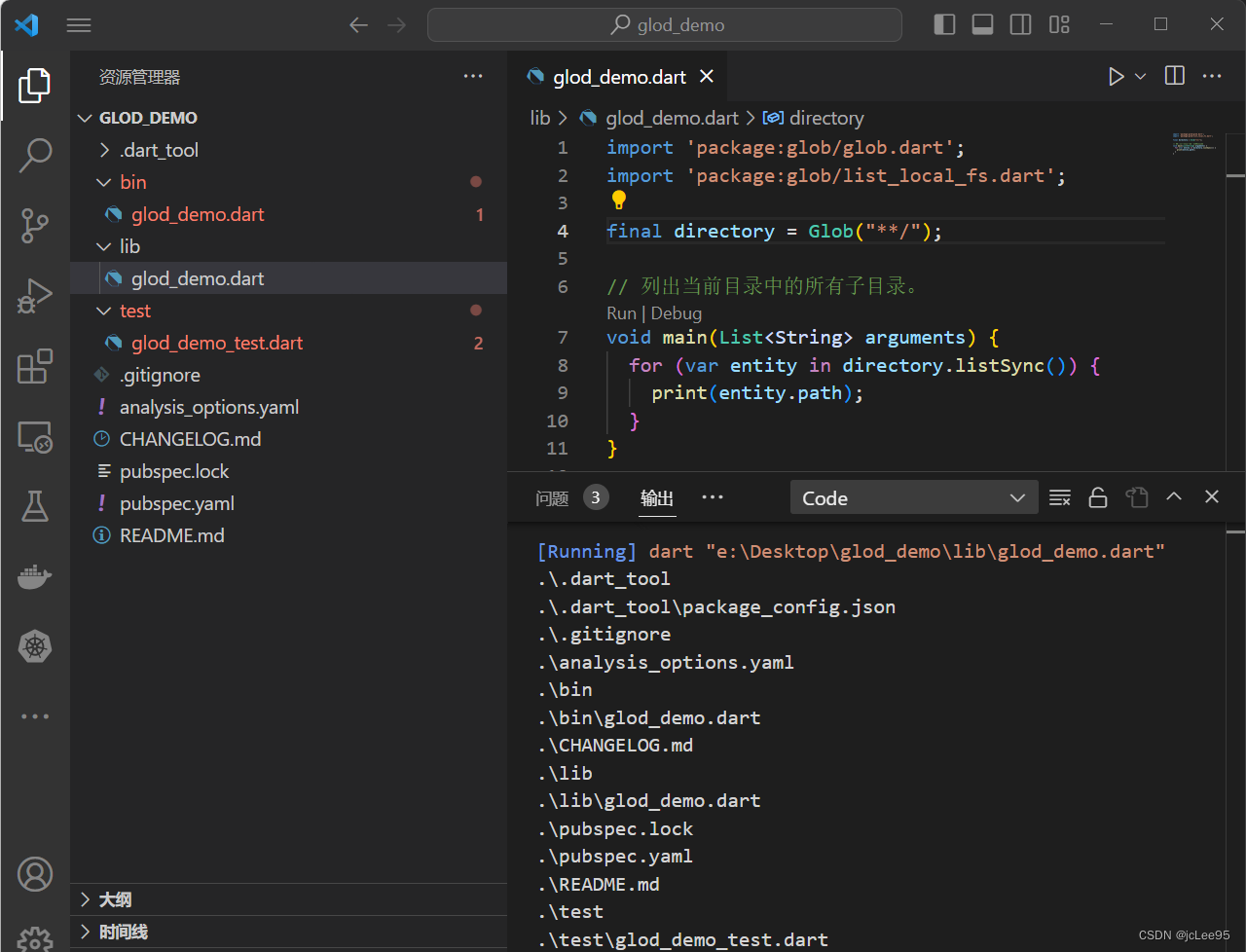
可以看到输出为:
.\.dart_tool
.\.dart_tool\package_config.json
.\.gitignore
.\analysis_options.yaml
.\bin
.\bin\glod_demo.dart
.\CHANGELOG.md
.\lib
.\lib\glod_demo.dart
.\pubspec.lock
.\pubspec.yaml
.\README.md
.\test
.\test\glod_demo_test.dart
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个 glob 模式 **/,它会匹配所有的子目录。然后,我们使用 listSync() 方法列出所有匹配这个模式的目录。
4.3 关于在 glob 库中 是否递归的说明
在 glob 库中,递归查找是通过 glob 模式中的 ** 来控制的。** 表示匹配任意深度的目录,因此,如果你在 glob 模式中使用了 **,那么 glob 库将会递归地查找所有子目录。
例如,以下代码将递归列出当前目录及其所有子目录中的所有 Dart 文件:
import 'package:glob/glob.dart';
import 'package:glob/list_local_fs.dart';final dartFile = Glob("**.dart");// 递归列出当前目录中的所有 Dart 文件。
void main(List<String> arguments) {for (var entity in dartFile.listSync()) {print(entity.path);}
}在这个例子中,**.dart 会递归匹配当前目录及其所有子目录中的所有 Dart 文件。
如果你只想在当前目录(不包括子目录)中查找文件,你应该使用单个星号 *。例如,以下代码将只列出当前目录中的所有 Dart 文件,不会查找子目录:
import 'package:glob/glob.dart';
import 'package:glob/list_local_fs.dart';final dartFile = Glob("*.dart");// 列出当前目录中的所有 Dart 文件。
void main(List<String> arguments) {for (var entity in dartFile.listSync()) {print(entity.path);}
}在这个例子中,*.dart 只会匹配当前目录中的 Dart 文件,不会匹配子目录中的文件。
5. list 和 listSync函数说明
这两个方法都是 Glob 类的扩展方法,定义在 package:glob/list_local_fs.dart 中。它们都用于列出匹配 glob 模式的文件系统实体(文件、目录等)。
/// Platform specific extensions for where `dart:io` exists, which use the
/// local file system.
extension ListLocalFileSystem on Glob {/// Convenience method for [Glob.listFileSystem] which uses the local file/// system.Stream<FileSystemEntity> list({String? root, bool followLinks = true}) =>listFileSystem(const LocalFileSystem(),root: root, followLinks: followLinks);/// Convenience method for [Glob.listFileSystemSync] which uses the local/// file system.List<FileSystemEntity> listSync({String? root, bool followLinks = true}) =>listFileSystemSync(const LocalFileSystem(),root: root, followLinks: followLinks);
}
使用时,需要做以下导入:
import 'package:glob/list_local_fs.dart';
5.1 list 方法
list 方法是一个异步方法,返回一个 Stream。这个 Stream 包含所有匹配 *glob 模式的文件系统实体。由于它是异步的,所以它不会阻塞主线程。
list 方法接受两个可选参数:root 和 followLinks。
root参数用于指定搜索的根目录,如果不指定,则默认为当前目录;followLinks参数决定是否跟随符号链接,如果设置为true,则会跟随符号链接,否则不会。
list 方法内部调用了 listFileSystem 方法,并传入了一个 LocalFileSystem 实例,这表示它在本地文件系统上进行操作。
5.1 listSync 方法
listSync 方法是一个同步方法,返回一个 List,包含所有匹配 glob 模式的文件系统实体。由于它是同步的,所以它会立即返回所有匹配的文件系统实体。
listSync 方法也接受 root 和 followLinks 两个可选参数,含义与 list 方法中的相同。
listSync 方法内部调用了 listFileSystemSync 方法,并传入了一个 LocalFileSystem 实例,这表示它在本地文件系统上进行操作。
F. 附录
F.1 Glob 类
/// 用于引用 globs 的正则表达式。
final _quoteRegExp = RegExp(r'[*{[?\\}\],\-()]');/// 用于匹配和列出文件和目录的 glob。
///
/// glob 作为路径匹配整个字符串。虽然 glob 模式使用 POSIX 语法,但它可以匹配 POSIX、Windows 或 URL 路径。它期望路径使用的格式基于 [Glob.new] 的 `context` 参数;默认为当前系统的语法。
///
/// 在与 glob 匹配之前,路径会被规范化,所以例如 glob `foo/bar` 匹配路径 `foo/./bar`。相对 glob 可以匹配绝对路径,反之亦然;globs 和路径都被解释为相对于 `context.current`,默认为当前工作目录。
///
/// 当用作 [Pattern] 时,glob 将根据整个字符串是否匹配 glob 返回一个或零个匹配。这些匹配目前没有捕获组,尽管这可能在未来会改变。
class Glob implements Pattern {/// 用于创建此 glob 的模式。final String pattern;/// 根据此 glob 解释路径的上下文。final p.Context context;/// 如果为 true,如果路径匹配 glob 本身或递归地包含在匹配的目录中,则路径匹配。final bool recursive;/// glob 是否区分大小写匹配路径。bool get caseSensitive => _ast.caseSensitive;/// glob 的解析 AST。final AstNode _ast;/// 用于实现 [list] 和 [listSync] 的底层对象。////// 这不应在 [_listTreeForFileSystem] 之外直接读取。ListTree? _listTree;/// 跟踪之前使用的文件系统。如果这改变了,那么/// [_listTree] 必须被废弃。////// 这在 [_listTreeForFileSystem] 中处理。FileSystem? _previousFileSystem;/// [context] 的当前目录是否是绝对的。bool get _contextIsAbsolute =>_contextIsAbsoluteCache ??= context.isAbsolute(context.current);bool? _contextIsAbsoluteCache;/// [pattern] 是否可以匹配绝对路径。bool get _patternCanMatchAbsolute =>_patternCanMatchAbsoluteCache ??= _ast.canMatchAbsolute;bool? _patternCanMatchAbsoluteCache;/// [pattern] 是否可以匹配相对路径。bool get _patternCanMatchRelative =>_patternCanMatchRelativeCache ??= _ast.canMatchRelative;bool? _patternCanMatchRelativeCache;/// 返回 [contents],其中包含在 globs 中有意义的字符,这些字符被反斜杠转义。static String quote(String contents) =>contents.replaceAllMapped(_quoteRegExp, (match) => '\\${match[0]}');/// 使用 [pattern] 创建一个新的 glob。////// 根据 [context] 解释与 glob 匹配的路径。默认为系统上下文。////// 如果 [recursive] 为 true,此 glob 不仅匹配和列出它明确匹配的文件和目录,而且还匹配那些下面的任何内容。////// 如果 [caseSensitive] 为 true,此 glob 只匹配和列出那些大小写与 glob 中的字符匹配的文件。否则,它无论大小写都匹配。当 [context] 为 Windows 时,默认为 `false`,否则为 `true`。factory Glob(String pattern,{p.Context? context, bool recursive = false, bool? caseSensitive}) {context ??= p.context;caseSensitive ??= context.style == p.Style.windows ? false : true;if (recursive) pattern += '{,/**}';var parser = Parser(pattern, context, caseSensitive: caseSensitive);return Glob._(pattern, context, parser.parse(), recursive);}Glob._(this.pattern, this.context, this._ast, this.recursive);/// 列出在提供的 [fileSystem] 中与 glob 匹配的 [root] 下的所有 [FileSystemEntity]。////// 这与 [Directory.list] 工作方式类似,但它只列出可能包含匹配 glob 的实体的目录。它不保证返回实体的顺序,尽管它确保只返回给定路径的一个实体。////// [root] 默认为当前工作目录。////// [followLinks] 与 [Directory.list] 的工作方式相同。Stream<FileSystemEntity> listFileSystem(FileSystem fileSystem,{String? root, bool followLinks = true}) {if (context.style != p.style) {throw StateError("Can't list glob \"$this\"; it matches "'${context.style} paths, but this platform uses ${p.style} paths.');}return _listTreeForFileSystem(fileSystem).list(root: root, followLinks: followLinks);}/// 在提供的 [fileSystem] 中,同步列出在 [root] 下的所有与 glob 匹配的 [FileSystemEntity]。////// 这与 [Directory.listSync] 的工作方式类似,但它只列出可能包含匹配 glob 的实体的目录。它不保证返回实体的顺序,尽管它确保只返回给定路径的一个实体。////// [root] 默认为当前工作目录。////// [followLinks] 与 [Directory.list] 的工作方式相同。List<FileSystemEntity> listFileSystemSync(FileSystem fileSystem,{String? root, bool followLinks = true}) {if (context.style != p.style) {throw StateError("Can't list glob \"$this\"; it matches "'${context.style} paths, but this platform uses ${p.style} paths.');}return _listTreeForFileSystem(fileSystem).listSync(root: root, followLinks: followLinks);}/// 返回此 glob 是否匹配 [path]。bool matches(String path) => matchAsPrefix(path) != null;Match? matchAsPrefix(String path, [int start = 0]) {// Globs 就像锚定的 RegExps,只匹配整个路径,所以如果匹配从第一个字符之后的任何地方开始,它就不能成功。if (start != 0) return null;if (_patternCanMatchAbsolute &&(_contextIsAbsolute || context.isAbsolute(path))) {var absolutePath = context.normalize(context.absolute(path));if (_ast.matches(toPosixPath(context, absolutePath))) {return GlobMatch(path, this);}}if (_patternCanMatchRelative) {var relativePath = context.relative(path);if (_ast.matches(toPosixPath(context, relativePath))) {return GlobMatch(path, this);}}return null;}Iterable<Match> allMatches(String path, [int start = 0]) {var match = matchAsPrefix(path, start);return match == null ? [] : [match];}String toString() => pattern;/// 处理获取可能缓存的 [ListTree] 为 [fileSystem]。ListTree _listTreeForFileSystem(FileSystem fileSystem) {// 不要为内存文件系统使用缓存的树,以避免内存泄漏。if (fileSystem is MemoryFileSystem) return ListTree(_ast, fileSystem);// 如果文件系统不同,丢弃我们缓存的 `_listTree`。if (fileSystem != _previousFileSystem) {_listTree = null;_previousFileSystem = fileSystem;}return _listTree ??= ListTree(_ast, fileSystem);}
}
)

)









)
,检查crl(证书吊销列表))





