目录
CAS概念
乐观锁与悲观锁
ABA问题
Unsafe类
编辑
原子类
基本类型原子类
原子引用类
原子数组
原子更新器类
原子累加器
CAS概念
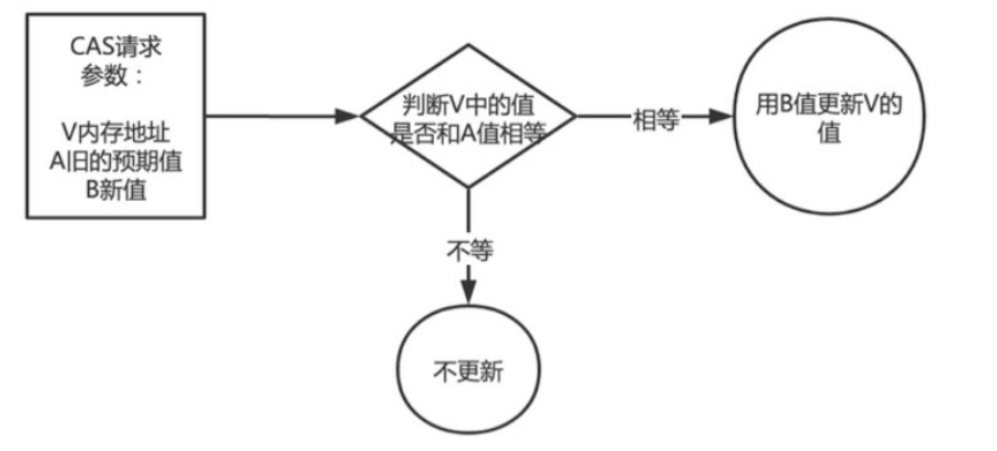
CAS是Compare And Swap的缩写,中文翻译成:比较并交换,实现无锁并发时常用到的一种技术。它一般包含三个操作数——内存位置(V)、预期原值(A)及更新值(B)。某线程执行CAS操作的时候,将内存位置的值与预期原值比较:
- 如果相匹配,那么处理器会自动将该位置值更新为新值
- 如果不匹配,那么重新获取该内存位置的值,然后线程进行自旋,到下次循环才有机会执行。
底层原理:CAS 是CPU并发原语,底层是 lock cmpxchg 指令(X86 架构),在单核和多核 CPU 下都能够保证比较交换的原子性。
-
程序是在单核处理器上运行,会省略 lock 前缀,单处理器自身会维护处理器内的顺序一致性,不需要 lock 前缀的内存屏障效果
-
程序是在多核处理器上运行,会为 cmpxchg 指令加上 lock 前缀。当某个核执行到带 lock 的指令时,CPU 会执行总线锁定或缓存锁定,将修改的变量写入到主存,这个过程不会被线程的调度机制所打断,保证了多个线程对内存操作的原子性
CAS 特点:
-
CAS 体现的是无锁并发、无阻塞并发,线程不会陷入阻塞,线程不需要频繁切换状态(上下文切换,系统调用,用户态转换为内核态)
-
CAS 是基于乐观锁的思想
CAS 缺点:
-
执行的是循环操作,如果比较不成功一直在循环,最差的情况某个线程一直取到的值和预期值都不一样,就会无限循环导致饥饿,使用 CAS 线程数不要超过 CPU 的核心数,采用分段 CAS 和自动迁移机制
-
只能保证一个共享变量的原子操作
-
对于一个共享变量执行操作时,可以通过循环 CAS 的方式来保证原子操作
-
对于多个共享变量操作时,循环 CAS 就无法保证操作的原子性,这个时候只能用锁来保证原子性
-
-
引出来 ABA 问题
乐观锁与悲观锁
悲观锁:
悲观锁就是我们常说的Synchronized 锁。对于悲观锁来说,它总是认为每次访问共享资源时会发生竞争,所以必须对每次对共享资源的操作加上锁,以保证临界区的程序同一时间只能有一个线程在执行。
乐观锁:
乐观锁又称为“无锁”,顾名思义,它是乐观派。乐观锁总是假设对共享资源的访问没有竞争的,线程可以不停地执行,无需加锁也无需等待。 乐观锁的一种实现方式 CAS 实现的 。
ABA问题
当一个主线程获取主内存值时,该内存值在写入主内存时已经被修改了 N 次,但是最终又改成原来的值,比如其他线程先把 A 改成 B 又改回 A,主线程使用CAS操作仅能判断出共享变量的值与最初值 A 是否相同,不能感知到这种从 A 改为 B 又 改回 A 的情况,这时 CAS 虽然成功,但是过程存在问题。
解决方法:使用AtomicStampedReference(加版本号解决ABA问题)
-
构造方法:
-
public AtomicStampedReference(V initialRef, int initialStamp) -
initialRef:初始值 -
initialStamp:初始版本号
-
-
常用API:
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference, int expectedStamp, int newStamp):expectedReference:预期值、newReference:修改值expectedStamp:期望版本号、expectedReference:操作成功之后的版本号。-
public void set(V newReference, int newStamp):设置值和版本号 -
public V getReference():返回引用的值 -
public int getStamp():返回当前版本号
public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(100,1);int startStamp = atomicReference.getStamp();new Thread(() ->{int stamp = atomicReference.getStamp();atomicReference.compareAndSet(100, 101, stamp, stamp + 1);stamp = atomicReference.getStamp();atomicReference.compareAndSet(101, 100, stamp, stamp + 1);},"t1").start();
new Thread(() ->{try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(100, 200, startStamp, startStamp + 1)) {System.out.println(atomicReference.getReference());//100System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程修改失败");}},"t2").start();
}
执行结果:
100
t2线程修改失败Unsafe类
Unsafe 是 CAS 的核心类,由于 Java 无法直接访问底层系统,需要通过本地(Native)方法来访问
Unsafe 类存在 sun.misc 包,其中所有方法都是 native 修饰的,都是直接调用操作系统底层资源执行相应的任务,基于该类可以直接操作特定的内存数据,其内部方法操作类似 C 的指针
可以看到AtomicInteger底层调用的就是Unsafe类中的compareAndSwapInt()方法
原子类
基本类型原子类
常用API
常见原子类:AtomicInteger、AtomicBoolean、AtomicLong
以AtomicInteger为例进行介绍
构造方法:
-
public AtomicInteger():初始化一个默认值为 0 的原子型 Integer -
public AtomicInteger(int initialValue):初始化一个指定值的原子型 Integer
常用API:
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public final int get() | 获取 AtomicInteger 的值 |
| public final int getAndIncrement() | 以原子方式将当前值加 1,返回的是自增前的值 |
| public final int incrementAndGet() | 以原子方式将当前值加 1,返回的是自增后的值 |
| public final int getAndSet(int value) | 以原子方式设置为 newValue 的值,返回旧值 |
| public final int addAndGet(int data) | 以原子方式将输入的数值与实例中的值相加并返回 实例:AtomicInteger 里的 value |
原子引用类
原子引用:对 Object 进行原子操作,提供一种读和写都是原子性的对象引用变量
原子引用类:AtomicReference、AtomicStampedReference、AtomicMarkableReference
AtomicReference 类:
-
构造方法:
AtomicReference<T> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<T>() -
常用 API:
-
public final boolean compareAndSet(V expectedValue, V newValue):CAS 操作 -
public final void set(V newValue):将值设置为 newValue -
public final V get():返回当前值
-
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1 = new Student(33, "z3");// 创建原子引用包装类AtomicReference<Student> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();// 设置主内存共享变量为s1atomicReference.set(s1);
// 比较并交换,如果现在主物理内存的值为 z3,那么交换成 l4while (true) {Student s2 = new Student(44, "l4");if (atomicReference.compareAndSet(s1, s2)) {break;}}System.out.println(atomicReference.get());}
}
class Student {private int id;private String name;//。。。。
}原子数组
原子数组类:AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray、AtomicReferenceArray
常用API:(以AtomicIntegerArray)
- addAndGet(int i, int delta):以原子更新的方式将数组中索引为i的元素与输入值相加;
- getAndIncrement(int i):以原子更新的方式将数组中索引为i的元素自增加1;
- compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update):将数组中索引为i的位置的元素进行更新
public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[5]);int t = 0;t = atomicIntegerArray.getAndSet(0,1);System.out.println(t+"\t"+atomicIntegerArray.get(0)); //0 1atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);t = atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);System.out.println(t+"\t"+atomicIntegerArray.get(1));//2 3}原子更新器类
原子更新器类:AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater、AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater、AtomicLongFieldUpdater
利用字段更新器,可以针对对象的某个域(Field)进行原子操作,只能配合 volatile 修饰的字段使用,否则会出现异常 IllegalArgumentException: Must be volatile type
常用 API:
-
static <U> AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<U> newUpdater(Class<U> c, String fieldName):构造方法 -
abstract boolean compareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update):CAS
public class UpdateDemo {private volatile int field;public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater fieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(UpdateDemo.class, "field");UpdateDemo updateDemo = new UpdateDemo();fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(updateDemo, 0, 10);System.out.println(updateDemo.field);//10}
}原子累加器
原子累加器类:LongAdder、DoubleAdder、LongAccumulator、DoubleAccumulator
LongAdder 和 LongAccumulator 区别:
相同点:
-
LongAddr 与 LongAccumulator 类都是使用非阻塞算法 CAS 实现的
-
LongAddr 类是 LongAccumulator 类的一个特例,只是 LongAccumulator 提供了更强大的功能,可以自定义累加规则,当accumulatorFunction 为 null 时就等价于 LongAddr
不同点:
-
调用 casBase 时,LongAccumulator 使用 function.applyAsLong(b = base, x) 来计算,LongAddr 使用 casBase(b = base, b + x)
-
LongAccumulator 类功能更加强大,构造方法参数中
-
accumulatorFunction 是一个双目运算器接口,可以指定累加规则,比如累加或者相乘,其根据输入的两个参数返回一个计算值,LongAdder 内置累加规则
-
identity 则是 LongAccumulator 累加器的初始值,LongAccumulator 可以为累加器提供非0的初始值,而 LongAdder 只能提供默认的 0
-
常用API:
- add():将当前value加x
- increment():将当前的value加1
- decrement():将当前的value减1
- sum():放回当前值。注意:在没有并发更新value的情况下,sum会返回一个精确值,在存在并发的情况下,sum不保证返回精确值。
- reset():将value重置为0,可用来代替重新new一个LongAdder,单词方法只可以在没有并发更新的情况下使用。
public static void main(String[] args) {LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();//0longAdder.increment();longAdder.increment();longAdder.increment();System.out.println(longAdder.longValue());// 3//初始化的时候传入自定义函数操作LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x * y,2);// 2longAccumulator.accumulate(1);//2longAccumulator.accumulate(2);//4longAccumulator.accumulate(3);//12System.out.println(longAccumulator.longValue());// 12}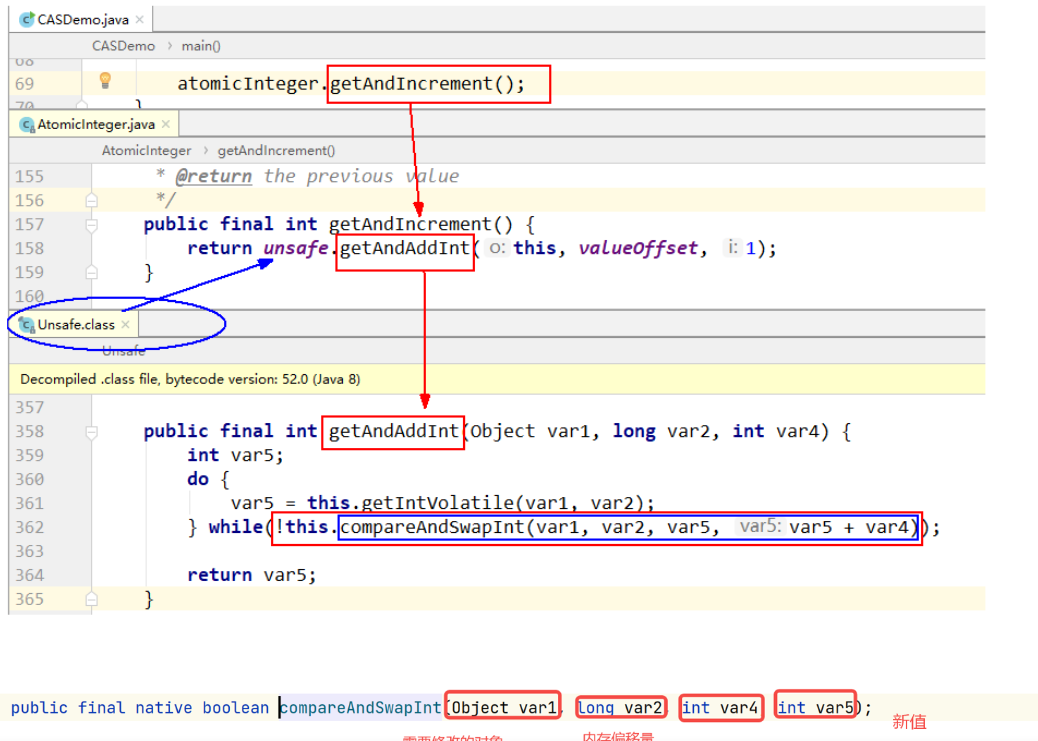
 — 字符串及路径的用法汇总)
:PyQt5实现打开深度摄像头功能)

)





-聊天室的编写 -01)

)






)
