C语言的结构体你真的了解吗? 一起来看一下吧!!!
1.结构体是啥?
结构体是多种数据类型的组合体
2.格式(一般放在主函数前,也就是int main()前面 )
关键字 结构体名字 {成员列表}
sturct 结构体名字 {成员列表}
//例如
struct date{
int year;
int month; // 类型名 + 成员名
int day;
}; // !!!不要忘记这里的‘;’3.简单结构体展示
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct date{int year;int month;int day;
};
int main(){struct date today; //定义结构体变量today.year = 2024; // 输入结构体成员的值(!!!法一)today.month = 1;today.day = 10;printf("today is %d.%02d.%02d",today.year,today.month,today.day);// %02d 是将不足两位的补零return 0;
}运行结果:
today is 2024.01.10
声明两个日期(声明变量):
法一:(注意today,tomoorrow;位置)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct date{int year;int month;int day;
}today,tomoorrow; //在在在在在在在这声明了两个日期,后面可以直接用了
int main(){today.year = 2024; // 输入结构体成员的值today.month = 1;today.day = 10;struct date tomorrow = {.year = 2024,.month = 1,.day = 11 };printf("today is %d.%02d.%02d\n",today.year,today.month,today.day);printf("tomorrow is %d.%02d.%02d",tomorrow.year,tomorrow.month,tomorrow.day);// %02d 是将不足两位的补零return 0;
}法二:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct date{int year;int month;int day;
};
int main(){struct date today,tomoorrow; //在在在在在在在这声明了两个日期today.year = 2024; // 法法法111输入结构体成员的值today.month = 1;today.day = 10;struct date tomorrow = {.year = 2024,.month = 1,.day = 11 };//法法法222输入输入结构体成员的值printf("today is %d.%02d.%02d\n",today.year,today.month,today.day);printf("tomorrow is %d.%02d.%02d",tomorrow.year,tomorrow.month,tomorrow.day);// %02d 是将不足两位的补零return 0;
}运行结果:
today is 2024.01.10
tomorrow is 2024.01.11先不要着急,为什么看不懂,前两个代码的运行和结果让你先看看结构体,看看就行,有个了解
4.上题目:实践起来
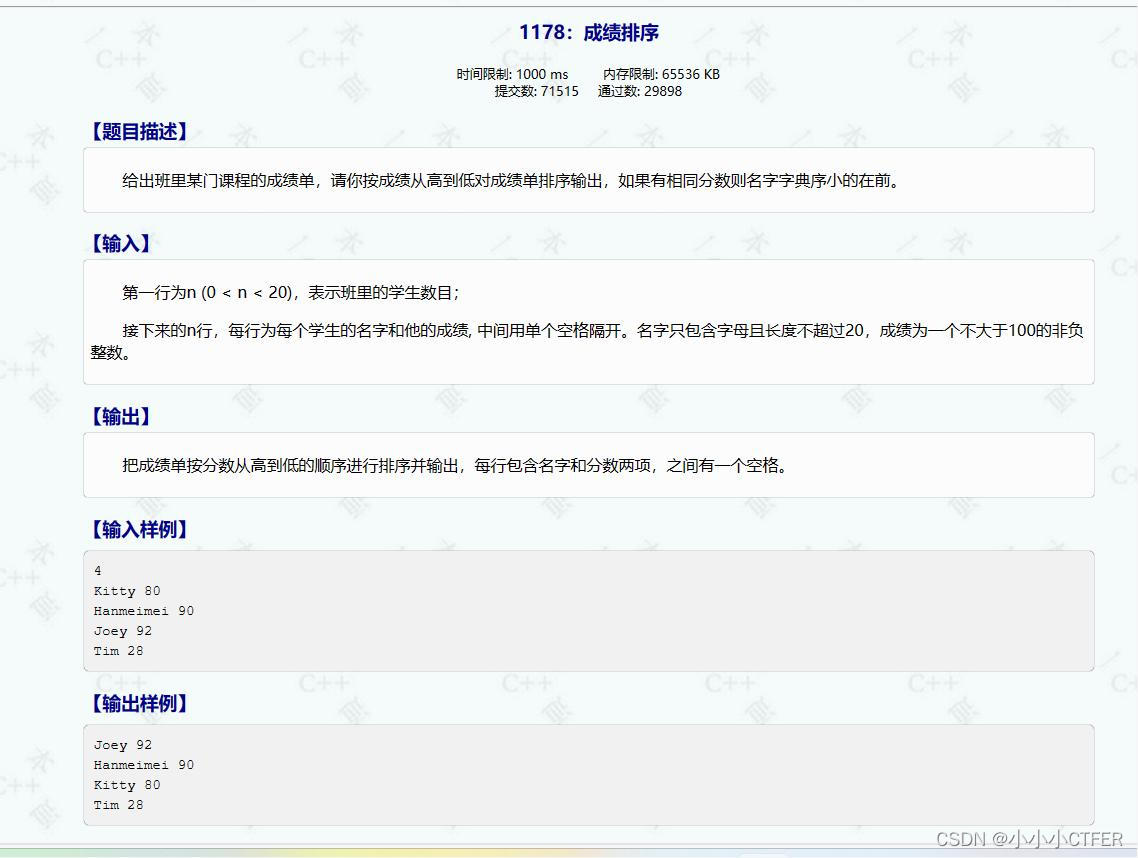
5.代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct student {string name; int g;
}a[25]; //定义结构体
bool cmp(student x,student y){if (x.g == y.g) return x.name < y.name; //如果结构体中x的成绩与y的成绩一样,就比较名字的首字母字典排序 else return x.g>y.g;} // 找出结构体中成绩高的
int main()
{int n;cin >> n;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i].name>>a[i].g; //输入结构体成员的值 }sort(a,a+n,cmp); //sort排序 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {cout<<a[i].name<<" "<<a[i].g<<endl; //输出结构体 }return 0;
}6.主要知识点:
(1)怎样写结构体的cmp函数;
bool cmp(student x,student y){ //类型很重要,这里用结构体的类型if (x.g == y.g) return x.name < y.name; //如果结构体中x的成绩与y的成绩一样,就比较名字的首字母字典排序 else return x.g>y.g;} // 找出结构体中成绩高的 (2)cmp的字典排序:
因为return x.g>y.g返回的是倒序,这个字母大小是按ascll码排序的 所以要用
return x.name < y.name //因为name是字符,不用考虑其他的东西(3)输入结构体成员:(输出同理)
int n;cin >> n;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i].name>>a[i].g; //输入结构体成员的值 }7.来再刷一道题,巩固巩固刚刚学到的知识
题目:
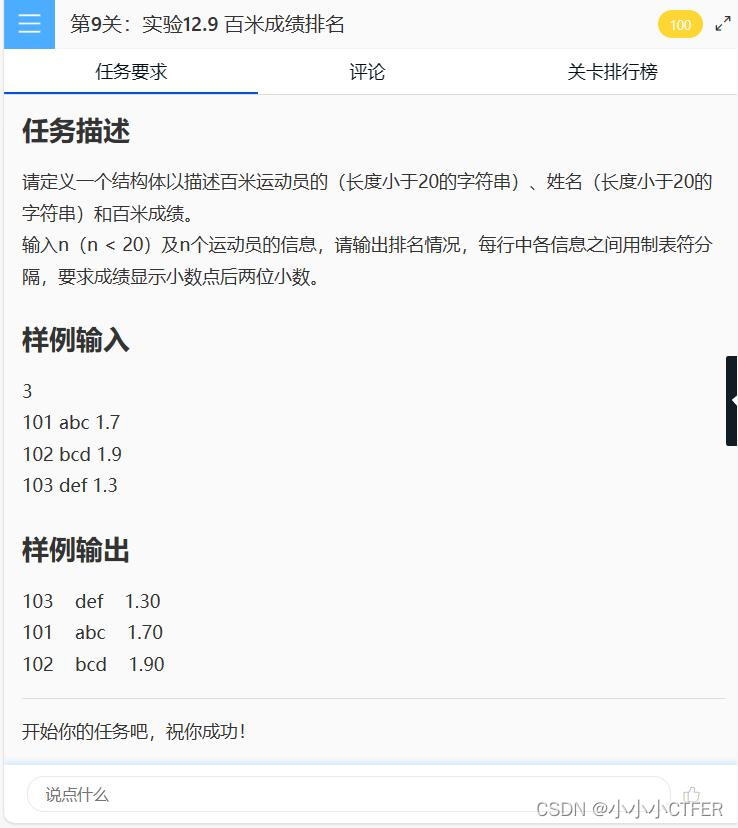
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu{string x;string y;double z;}a[25];bool cmp(stu a,stu b)
{return a.z<b.z;
}
int main()
{int n;cin>>n;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y>>a[i].z;}sort(a,a+n,cmp);for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<a[i].x<<"\t"<<a[i].y<<"\t"<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<a[i].z<<endl;return 0;
}100.补充:使用typedef 简化结构体
每次定义时都要输入struct 结构体名字 xxx;我们想办法让他简单一点,就使用typedef函数,因为时间原因,作为码农的你去收集资料弄懂吧!!!


![[足式机器人]Part3 机构运动学与动力学分析与建模 Ch00-2(1) 质量刚体的在坐标系下运动](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[足式机器人]Part3 机构运动学与动力学分析与建模 Ch00-2(1) 质量刚体的在坐标系下运动)

![[Linux]网卡配置修改](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Linux]网卡配置修改)














