
前面留的一个问题,后文更跟新回答
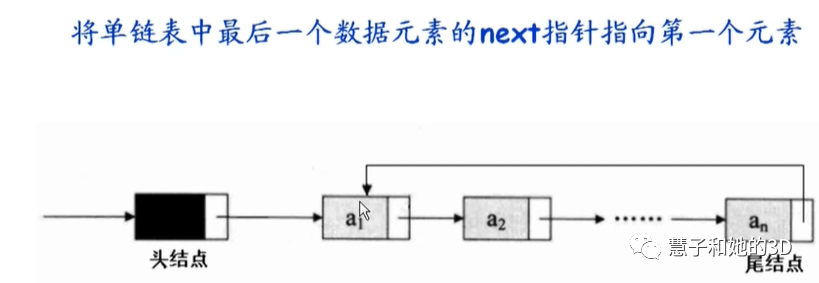
单链表可以表示任意的线性关系,有些线性关系是循环的,既没有队尾元素。
将单链表中的终端结点指针端由空指针改为指向头结点,这时的单链表形成国恒一个环,改为循环链表。
插入与删除与单链表的原理甚至一模一样,工程CircleListPro,将单链表改成循环链表。
CircleList.h文件
ifndef _CIRCLELIST_H_#define _CIRCLELIST_H_typedef void CircleList;typedef struct _tag_CircleListNode CircleListNote;struct _tag_CircleListNode{ CircleListNode* next; }CircleList* CircleList_Creat(int capacity);void CircleList_Destory(CircleList* list);void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list);int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list);int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node,int pos);CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list,int pos);CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list,int pos);#endifCiecleList.c
#include #include #include "CircleList.h"#define AVAILABLE -1//空闲位置的宏//静态链表结构体定义typedef struct _tag_CircleList{ CircleListNode header;//链表头 int length;}TCircleList; CircleList* CircleList_Create()//o(1){ TCircleList* ret = (TCircleList*)malloc(sizeof(TCircleList)); if(ret != NULL)//指针不为0时可以继续赋值操作 { ret->length = 0; ret->header.next = NULL; } return ret;}void CircleList_Destory(CircleList* list){ free(list);}void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list) //o(1){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 if(sList != NULL)//链表不为空是合法的,可以继续清空操作 { sList->length = 0; sList->header.next = NULL;//第一个元素下标没有了 }}int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list)//o(1){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 int ret = -1;//定义一个返回值 if(sList !=NULL)//链表不为空是合法的,可以继续清空操作 { ret = sList->length; } return ret;}// 插入时,如果表头是空的指向NULL,元素是空的,进行单链表元素插入时,现将插入元素// 尾结点与NULL相连,再把插入元素数据与前结点相连,再把该节点next与自己相连,去除原来NULL,构成循环链表int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node,int pos)//o(n)n是插入元素的位置·{ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 int ret =(sList !=NULL)&& (pos >=0) && (node != NULL);//单链表方法完成判断 int i=0; if(ret)//在数组中找空闲位置index { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; for(i = 0;(inext != NULL); i++) { current = current->next; } node->next = current->next; current->next = node; if(sList->length == 0)// 插入的元素是第一个,length的值为0 { node->next = node;// 新元素node的next指针指向自己 } sList->length++ ;}return ret;}CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list,int pos)// o(n){TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值int i = 0;if((sList != NULL) &&(0 <= pos)//链表不为空是合法的,长度正常,与单链表不同的是不需要pos { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; for(i=0;i { current = current->next;//第一个元素所在下标 } ret = current->next; }return ret;}//获取第pos个元素,将第pos个元素从链表里删除//特殊的删除第一个元素,除了将表头next移到第二个元素之外,还要将最后一个next移到第二个nextCircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list,int pos)//o(n){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 int i = 0; if( (sList !=NULL) && (0 <= pos) )//链表不为空是合法的,长度正常 { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; CircleListNode* first = sList->header.next;// 标记第一个元素 CircleListNode* last = (CircleListNode*)CircleList_Get(sList,sList->length - 1); // 由get函数得到最后一个元素 for(i=0;i { current = current->next;//第一个元素所在下标 } ret = current->next; current->next = ret->next; sList->length--; if(first == ret)// 判断删除元素是否是原来表头,first指针与原来ret指针是否是同一个 { sList->header.next = ret->next;// 将表头指向ret last->next = ret->next;// 指针移动到原来的第二个元素 } if(sList->length == 0)// 如果链表空了则前面操作没有意义 { sList->header.next = NULL;// 复原 } } return ret;}main.c
#include #include #include "CircleList.h"//自己创建的文件,而不是系统文件用双引号struct Value{ CircleListNode header;// 定义域 int v;// 真正保存数据的域}int main(int argc,char *argv[]){ int i = 0; CircleList* list = CircleList_Create(); struct Value v1; struct Value v2; struct Value v3; struct Value v4; struct Value v5; struct Value v6; struct Value v7; struct Value v8; v1.v = 1 ; v2.v = 2 ; v3.v = 3 ; v4.v = 4 ; v5.v = 5 ; v6.v = 6 ; v7.v = 7 ; v8.v = 8 ; // 尾插法,插入到最后一个元素后面 CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V1, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V2, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V3, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V4, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V5,5); CircleList_Delete(list,0); // 证明是循环链表,删除第一个元素,循环两遍 for(i=0;i 2*CircleList_Length( { struct Value* pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Get(list,i) printf("%d\n",pv->v); } printf("\n"); while( CircleList_Length(list) > 0)// 循环链表还有元素从头开始删 { struct Value* pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Delete(list,0); printf("%d\n",pv->v); } CircleList_Destory(list); return 0;}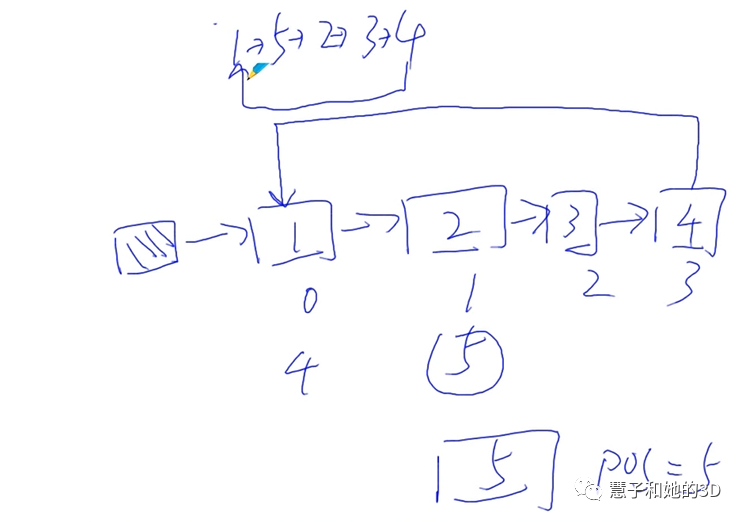
为了体现循环链表的威力,引入游标:在循环链表中定义一个“当前”指针,这个指针通常称为游标,可以通过这个游标来遍历链表中所有元素。

加了游标新操作CircleList.h文件
#ifndef _CIRCLELIST_H_#define _CIRCLELIST_H_typedef void CircleList;typedef struct _tag_CircleListNode CircleListNote;struct _tag_CircleListNode{ CircleListNode* next; }CircleList* CircleList_Creat(int capacity);void CircleList_Destory(CircleList* list);void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list);int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list);int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node,int pos);CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list,int pos);CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list,int pos);// 加入游标新操作// 获取当前游标指向的数据元素,可以删除链表里某个数据元素,不需要先得到所要删除的数据下标CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node);// 将游标重置指向链表中的第一个元素CircleListNode* CircleList_Resert(CircleList* list);// 将游标移动到链表的下一个数据元素CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list);// 直接删除链表中某个数据元素CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list);#endif#include #include #include "CircleList.h"#define AVAILABLE -1//空闲位置的宏//静态链表结构体定义typedef struct _tag_CircleList{ CircleListNode header;//链表头 CircleListNode* sLidrer;// 定义游标 int length;}TCircleList; CircleList* CircleList_Create()//o(1){ TCircleList* ret = (TCircleList*)malloc(sizeof(TCircleList)); if(ret != NULL)//指针不为0时可以继续赋值操作 { ret->length = 0; ret->header.next = NULL; ret->slider = NULL;// 在循环链表创建的时候,没有元素,游标定义为空 } return ret;}void CircleList_Destory(CircleList* list){ free(list);}void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list) //o(1){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 if(sList != NULL)//链表不为空是合法的,可以继续清空操作 { sList->length = 0; sList->header.next = NULL;//第一个元素下标没有了 sList->slider = NULL;// 循环链表重置为复原状态。游标也重置为空 }}int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list)//o(1){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 int ret = -1;//定义一个返回值 if(sList !=NULL)//链表不为空是合法的,可以继续清空操作 { ret = sList->length; } return ret;}// 插入时,如果表头是空的指向NULL,元素是空的,进行单链表元素插入时,现将插入元素// 尾结点与NULL相连,再把插入元素数据与前结点相连,再把该节点next与自己相连,去除原来NULL,构成循环链表int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node,int pos)//o(n)n是插入元素的位置·{ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 int ret =(sList !=NULL)&& (pos >=0) && (node != NULL);//单链表方法完成判断 int i=0; if(ret)//在数组中找空闲位置index { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; for(i = 0;(inext != NULL); i++) { current = current->next; } node->next = current->next; current->next = node; if(sList->length == 0)// 插入的元素是第一个,length的值为0 { slider->slider = node;// 游标指向插入的第一个结点 node->next = node;// 游标默认初始位置为0,新元素node的next指针指向自己 } sList->length++ ;}return ret;}CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list,int pos)// o(n){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 int i = 0; if((sList != NULL) &&(0 <= pos)//链表不为空是合法的,长度正常,与单链表不同的是不需要pos { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; for(i=0;i { current = current->next;//第一个元素所在下标 } ret = current->next; } return ret;}//获取第pos个元素,将第pos个元素从链表里删除//特殊的删除第一个元素,除了将表头next移到第二个元素之外,还要将最后一个next移到第二个nextCircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list,int pos)//o(n){ TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 int i = 0; if( (sList !=NULL) && (0 <= pos) )//链表不为空是合法的,长度正常 { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList; CircleListNode* first = sList->header.next;// 标记第一个元素 CircleListNode* last = (CircleListNode*)CircleList_Get(sList,sList->length - 1); // 由get函数得到最后一个元素 for(i=0;i { current = current->next;//第一个元素所在下标 } ret = current->next; current->next = ret->next; sList->length--; if(first == ret)// 判断删除元素是否是原来表头,first指针与原来ret指针是否是同一个 { sList->header.next = ret->next;// 将表头指向ret last->next = ret->next;// 指针移动到原来的第二个元素 } if(slider->slider == ret)// SLIDER指向的元素和要删除的元素指针一致 { sList->slider = ret->next ;// slider指向ret的下一个元素 } if(sList->length == 0)// 如果链表空了则前面操作没有意义 { sList->header.next = NULL;// 复原 sList->slider = NULL;// 删除的元素刚好为链表最后一个元素,游标复原为空 } } return ret;}// 获取当前游标指向的数据元素,删除对应的CircleListNode* node这个元素o(n0CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list,CircleListNode* node){// 该做的检测正常做 TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 int i = 0; if (sList != NULL) { CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;// 做移动,查找node在循环链表的逻辑位置 for(i=0;ilength;i++) { if(current->next == node) { ret =current->next; break; } current = current->next; } if(ret != NULL )// 找不到,非法元素 { circleList_Delete(sList,i);// i就是所找到的删除位置,调用delete删除即可 } } return ret;}CircleListNode* CircleList_Resert(CircleList* list)// o(1)将游标重置指向链表中的第一个元素{// 该做的检测正常做 TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 if(sList != NULL ) { slist->slider = sList->header.next;// slider重置到第一个元素 ret = sList->slider ;// 返回判断重置是否成功 } return ret;}CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list)// o(1)将游标移动指向到链表中的下一个数据元素{// 该做的检测正常做 TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 if(sList != NULL ) { ret = sList->slider ; } return ret; }CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list)// o(1)直接删除链表中的某个数据元素 {// 该做的检测正常做 TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;//用到了数据封装,所以强制类型转换 CircleListNode* ret = NULL;//定义一个返回值 // 当前游标指向下一个元素 if((sList != NULL ) && (sList->slider != NULL )) { ret = sList->slider ;// 在移动之前把当前值保存作为返回值返回 sList->slider = ret->next;// 真正移动 } return ret;}循环链表的应用:约瑟夫问题
n个人围成一个圆圈,首先从第一个人从1开始报数,报到第m个人,令其出列;然后再从下一个人继续报数,报到第m个人,再另其出列……如此下去,求其出列顺序。
main.c
#include #include #include "CircleList.h"//自己创建的文件,而不是系统文件用双引号struct Value{ CircleListNode header;// 定义域 int v;// 真正保存数据的域}int main(int argc,char *argv[]){ int i = 0; CircleList* list = CircleList_Create(); struct Value v1; struct Value v2; struct Value v3; struct Value v4; struct Value v5; struct Value v6; struct Value v7; struct Value v8; v1.v = 1 ; v2.v = 2 ; v3.v = 3 ; v4.v = 4 ; v5.v = 5 ; v6.v = 6 ; v7.v = 7 ; v8.v = 8 ; // 尾插法,插入到最后一个元素后面 CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V1, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V2, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V3, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V4, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V5,5); CircleList_Delete(list,0); // 证明是循环链表,删除第一个元素,循环两遍 for(i=0;i 2*CircleList_Length( { struct Value* pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Get(list,i) printf("%d\n",pv->v); } printf("\n"); while( CircleList_Length(list) > 0)// 循环链表还有元素从头开始删 { struct Value* pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Delete(list,0); printf("%d\n",pv->v); } printf("\n"); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V1, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V2, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V3, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V4, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V5, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V6, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V7, CircleList_Length(list)); CircleList_Insert(list,( CircleListNode*)&V8, CircleList_Length(list)); for(i=0;i < CircleList_Length(list);i++)// 查看八个人是否在循环链表中 { struct Value* pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Next(list) // 先将当前的返回再移动 printf("%d\n",pv->v); } printf("\n"); CircleList_Resert(list); // 重置游标 // 解决约瑟夫问题 while( CircleList_Length(list) > 0)// 当链表中没有元素的时候停止出列 { struct Value* pv = NULL; for(i = 1;i < 3;i++) { CircleList_Next (list);// 这里的移动用游标来移动,所以很高效 } pv = (struct Value*) CircleList_Current(list); printf("%d\n",pv->v); CircleList_DeleteNode(list,(CircleListNode*) pv ); } CircleList_Destory(list); return 0;}小结;
循环链表只是在单链表的基础上做了一个加强
循环链表完全可以代替单链表
循环链表的Next和Current操作可以高效的遍历链表中的每个元素
)





)




![oracle函数 INSTR(C1,C2[,I[,J]])](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/oracle函数 INSTR(C1,C2[,I[,J]]))





聚合函数)

