文章目录
- 1. 题目
- 2. 解题
- 2.1 递归
- 2.2 BFS
1. 题目
设计一个算法,可以将 N 叉树编码为二叉树,并能将该二叉树解码为原 N 叉树。
一个 N 叉树是指每个节点都有不超过 N 个孩子节点的有根树。
类似地,一个二叉树是指每个节点都有不超过 2 个孩子节点的有根树。
你的编码 / 解码的算法的实现没有限制,你只需要保证一个 N 叉树可以编码为二叉树且该二叉树可以解码回原始 N 叉树即可。
例如,你可以将下面的 3-叉 树以该种方式编码:

注意,上面的方法仅仅是一个例子,可能可行也可能不可行。
你没有必要遵循这种形式转化,你可以自己创造和实现不同的方法。
注意:
N 的范围在 [1, 1000]
不要使用类成员 / 全局变量 / 静态变量来存储状态。
你的编码和解码算法应是无状态的。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/encode-n-ary-tree-to-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
2. 解题
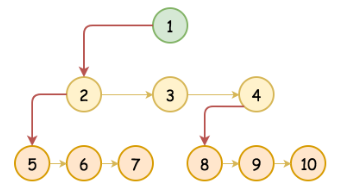
- 参考官方思路,第一个子节点2接到父节点1的
left,其余的兄弟节点 3,4 都接在其左边兄弟节点的right
2.1 递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:int val;vector<Node*> children;Node() {}Node(int _val) {val = _val;}Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}
};
*//*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/class Codec {
public:// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.TreeNode* encode(Node* root) {if(!root) return NULL;TreeNode* newroot = new TreeNode(root->val);TreeNode* cur = NULL;if(!root->children.empty()){newroot->left = encode(root->children[0]);cur = newroot->left;}for(int i = 1; i < root->children.size(); ++i){cur->right = encode(root->children[i]);cur = cur->right;}return newroot;}// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.Node* decode(TreeNode* root) {if(!root) return NULL;Node *newroot = new Node(root->val);TreeNode *cur = NULL;if(root->left){newroot->children.push_back(decode(root->left));cur = root->left;}while(cur && cur->right){newroot->children.push_back(decode(cur->right));cur = cur->right;}return newroot;}
};
108 ms 179.4 MB
2.2 BFS
class Codec {
public:// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.TreeNode* encode(Node* root) {if(!root) return NULL;TreeNode* newroot = new TreeNode(root->val), *newTreeNode = NULL;TreeNode* cur = NULL;queue<pair<Node*, TreeNode*>> q;q.push({root,newroot});while(!q.empty()){int size = q.size();while(size--){root = q.front().first;newTreeNode = q.front().second;q.pop();if(!root->children.empty()){newTreeNode->left = new TreeNode(root->children[0]->val);cur = newTreeNode->left;q.push({root->children[0], cur});}for(int i = 1; i < root->children.size(); ++i){cur->right = new TreeNode(root->children[i]->val);;cur = cur->right;q.push({root->children[i], cur});}}}return newroot;}// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.Node* decode(TreeNode* root) {if(!root) return NULL;Node *newroot = new Node(root->val), *newNode = NULL;Node *cur = NULL;queue<pair<TreeNode*, Node*>> q;q.push({root,newroot});while(!q.empty()){int size = q.size();while(size--){root = q.front().first;cur = q.front().second;q.pop();if(root->left){newNode = new Node(root->left->val);cur->children.push_back(newNode);q.push({root->left, newNode});root = root->left;while(root->right){newNode = new Node(root->right->val);cur->children.push_back(newNode);q.push({root->right, newNode});root = root->right;}}}}return newroot;}
};
80 ms 173.6 MB
我的CSDN博客地址 https://michael.blog.csdn.net/
长按或扫码关注我的公众号(Michael阿明),一起加油、一起学习进步!



)


 - 文件系统)
*)


)
)

)


)


)