以下内容源于朱有鹏嵌入式课程的学习,如有侵权请告知删除。
一、前言
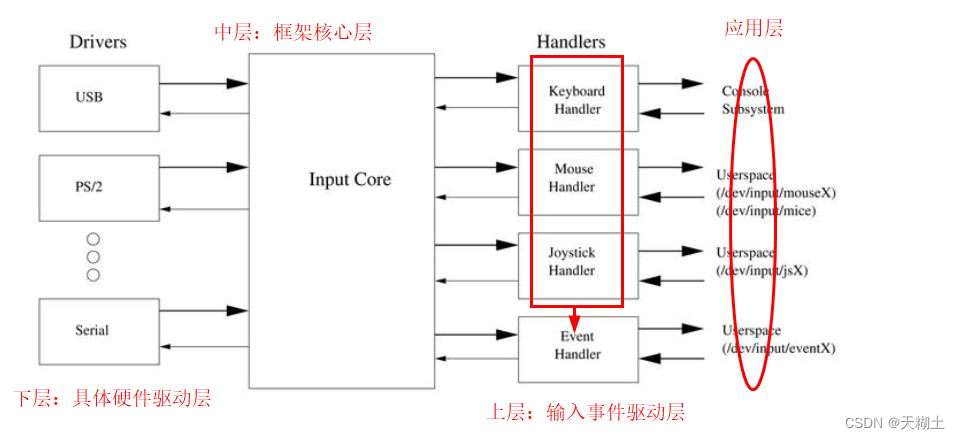
由input子系统简介可知,input子系统分为三层:
1、上层输入事件驱动层
涉及的文件有x210_kernel\drivers\input\evdev.c、mousedev.c 和 joydev.c文件,分别对应上层的各个不同的handler的源代码。但如图所示,一般集中采用 event handlers的方式,但这种方式不是排他性的,可以同时存在。该层负责将 struct input_event 呈送给应用层。
2、中层框架核心层
涉及的文件有x210_kernel\drivers\input\input.c文件。
3、下层具体硬件驱动层
涉及的文件包括x210_kernel\drivers\input目录中的各个文件夹,比如joystick文件、mouse文件夹、keyboard文件夹、touchscreen文件夹等。
下面将对框架核心层进行分析。
二、 框架核心层分析
这里分析的内核版本为2.6.35.7。框架核心层涉及的文件是x210_kernel\drivers\input\input.c。
1、相关的数据结构
(1)struct input_dev结构体
/*** struct input_dev - represents an input device* @name: name of the device* @phys: physical path to the device in the system hierarchy* @uniq: unique identification code for the device (if device has it)* @id: id of the device (struct input_id)* @evbit: bitmap of types of events supported by the device (EV_KEY,* EV_REL, etc.)* @keybit: bitmap of keys/buttons this device has* @relbit: bitmap of relative axes for the device* @absbit: bitmap of absolute axes for the device* @mscbit: bitmap of miscellaneous events supported by the device* @ledbit: bitmap of leds present on the device* @sndbit: bitmap of sound effects supported by the device* @ffbit: bitmap of force feedback effects supported by the device* @swbit: bitmap of switches present on the device* @keycodemax: size of keycode table* @keycodesize: size of elements in keycode table* @keycode: map of scancodes to keycodes for this device* @setkeycode: optional method to alter current keymap, used to implement* sparse keymaps. If not supplied default mechanism will be used.* The method is being called while holding event_lock and thus must* not sleep* @getkeycode: optional method to retrieve current keymap. If not supplied* default mechanism will be used. The method is being called while* holding event_lock and thus must not sleep* @ff: force feedback structure associated with the device if device* supports force feedback effects* @repeat_key: stores key code of the last key pressed; used to implement* software autorepeat* @timer: timer for software autorepeat* @sync: set to 1 when there were no new events since last EV_SYNC* @abs: current values for reports from absolute axes* @rep: current values for autorepeat parameters (delay, rate)* @key: reflects current state of device's keys/buttons* @led: reflects current state of device's LEDs* @snd: reflects current state of sound effects* @sw: reflects current state of device's switches* @absmax: maximum values for events coming from absolute axes* @absmin: minimum values for events coming from absolute axes* @absfuzz: describes noisiness for axes* @absflat: size of the center flat position (used by joydev)* @absres: resolution used for events coming form absolute axes* @open: this method is called when the very first user calls* input_open_device(). The driver must prepare the device* to start generating events (start polling thread,* request an IRQ, submit URB, etc.)* @close: this method is called when the very last user calls* input_close_device().* @flush: purges the device. Most commonly used to get rid of force* feedback effects loaded into the device when disconnecting* from it* @event: event handler for events sent _to_ the device, like EV_LED* or EV_SND. The device is expected to carry out the requested* action (turn on a LED, play sound, etc.) The call is protected* by @event_lock and must not sleep* @grab: input handle that currently has the device grabbed (via* EVIOCGRAB ioctl). When a handle grabs a device it becomes sole* recipient for all input events coming from the device* @event_lock: this spinlock is is taken when input core receives* and processes a new event for the device (in input_event()).* Code that accesses and/or modifies parameters of a device* (such as keymap or absmin, absmax, absfuzz, etc.) after device* has been registered with input core must take this lock.* @mutex: serializes calls to open(), close() and flush() methods* @users: stores number of users (input handlers) that opened this* device. It is used by input_open_device() and input_close_device()* to make sure that dev->open() is only called when the first* user opens device and dev->close() is called when the very* last user closes the device* @going_away: marks devices that are in a middle of unregistering and* causes input_open_device*() fail with -ENODEV.* @dev: driver model's view of this device* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the device. When* accessing the list dev->mutex must be held* @node: used to place the device onto input_dev_list*/ struct input_dev {const char *name;const char *phys;const char *uniq;struct input_id id;unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)];unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];unsigned int keycodemax;unsigned int keycodesize;void *keycode;int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int scancode, unsigned int keycode);int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int scancode, unsigned int *keycode);struct ff_device *ff;unsigned int repeat_key;struct timer_list timer;int sync;int abs[ABS_CNT];int rep[REP_MAX + 1];unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];int absmax[ABS_CNT];int absmin[ABS_CNT];int absfuzz[ABS_CNT];int absflat[ABS_CNT];int absres[ABS_CNT];int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, \unsigned int code, int value);struct input_handle *grab;spinlock_t event_lock;struct mutex mutex;unsigned int users;bool going_away;struct device dev;struct list_head h_list;struct list_head node; };(2)struct input_handler结构体
/*** struct input_handler - implements one of interfaces for input devices* @private: driver-specific data* @event: event handler. This method is being called by input core with* interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock spinlock held and so* it may not sleep* @filter: similar to @event; separates normal event handlers from* "filters".* @match: called after comparing device's id with handler's id_table* to perform fine-grained matching between device and handler* @connect: called when attaching a handler to an input device* @disconnect: disconnects a handler from input device* @start: starts handler for given handle. This function is called by* input core right after connect() method and also when a process* that "grabbed" a device releases it* @fops: file operations this driver implements* @minor: beginning of range of 32 minors for devices this driver* can provide* @name: name of the handler, to be shown in /proc/bus/input/handlers* @id_table: pointer to a table of input_device_ids this driver can* handle* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the handler* @node: for placing the driver onto input_handler_list** Input handlers attach to input devices and create input handles. There* are likely several handlers attached to any given input device at the* same time. All of them will get their copy of input event generated by* the device.** The very same structure is used to implement input filters. Input core* allows filters to run first and will not pass event to regular handlers* if any of the filters indicate that the event should be filtered (by* returning %true from their filter() method).** Note that input core serializes calls to connect() and disconnect()* methods.*/ struct input_handler {void *private;void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);const struct file_operations *fops;int minor;const char *name;const struct input_device_id *id_table;struct list_head h_list;struct list_head node; };(3)struct input_handle结构体
/*** struct input_handler - implements one of interfaces for input devices* @private: driver-specific data* @event: event handler. This method is being called by input core with* interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock spinlock held and so* it may not sleep* @filter: similar to @event; separates normal event handlers from* "filters".* @match: called after comparing device's id with handler's id_table* to perform fine-grained matching between device and handler* @connect: called when attaching a handler to an input device* @disconnect: disconnects a handler from input device* @start: starts handler for given handle. This function is called by* input core right after connect() method and also when a process* that "grabbed" a device releases it* @fops: file operations this driver implements* @minor: beginning of range of 32 minors for devices this driver* can provide* @name: name of the handler, to be shown in /proc/bus/input/handlers* @id_table: pointer to a table of input_device_ids this driver can* handle* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the handler* @node: for placing the driver onto input_handler_list** Input handlers attach to input devices and create input handles. There* are likely several handlers attached to any given input device at the* same time. All of them will get their copy of input event generated by* the device.** The very same structure is used to implement input filters. Input core* allows filters to run first and will not pass event to regular handlers* if any of the filters indicate that the event should be filtered (by* returning %true from their filter() method).** Note that input core serializes calls to connect() and disconnect()* methods.*/ struct input_handler {void *private;void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);const struct file_operations *fops;int minor;const char *name;const struct input_device_id *id_table;struct list_head h_list;struct list_head node; };(4)struct input_device_id结构体
struct input_device_id {kernel_ulong_t flags;//此flag 表示我们的这个 input_device_id 是用来匹配下面的4个情况的哪一项//flag == 1表示匹配总线 2表示匹配供应商 4表示匹配产品 8表示匹配版本__u16 bustype;__u16 vendor;__u16 product;__u16 version;kernel_ulong_t evbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_EV_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t keybit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_KEY_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t relbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_REL_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t absbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_ABS_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t mscbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MSC_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t ledbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_LED_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t sndbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_SND_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t ffbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_FF_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t swbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_SW_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];kernel_ulong_t driver_info; };
2、框架核心层模块注册函数input_init()
在Linux中实现为一个模块的方法,所以可以进行动态的加载和卸载。这样做的原由是,如果有些系统不需要任何的输入类设备,这样就可以将input输入子系统这个模块去掉(上层也是实现为模块),使得内核尽量变得更小。
static int __init input_init(void) {int err;input_init_abs_bypass();err = class_register(&input_class);// 创建设备类/sys/class/inputif (err) {printk(KERN_ERR "input: unable to register input_dev class\n");return err;}err = input_proc_init();//proc文件系统相关的初始化if (err)goto fail1;//注册字符设备驱动,主设备号13//input_fops中只实现了open函数,所以其原理和misc其实是一样的err = register_chrdev(INPUT_MAJOR, "input", &input_fops);if (err) {printk(KERN_ERR "input: unable to register char major %d", INPUT_MAJOR);goto fail2;}return 0;fail2: input_proc_exit();fail1: class_unregister(&input_class);return err; }(1)input_proc_init函数
启动系统后,在/proc/bus/input/目录下有两个文件devices和handlers,它们就是在此函数中创建的。我们cat devices 和 cat handlers时对应的操作方法(show)就被封装在input_devices_fileops和input_handlers_fileops结构体中。
static int __init input_proc_init(void) {struct proc_dir_entry *entry;/* 在/proc/bus/目录下创建input目录 */proc_bus_input_dir = proc_mkdir("bus/input", NULL); if (!proc_bus_input_dir)return -ENOMEM;/* 在/proc/bus/input/目录下创建devices文件 */entry = proc_create("devices", 0, proc_bus_input_dir, &input_devices_fileops);if (!entry)goto fail1;/* 在/proc/bus/input/目录下创建handlers文件 */entry = proc_create("handlers", 0, proc_bus_input_dir, &input_handlers_fileops);if (!entry)goto fail2;return 0;fail2: remove_proc_entry("devices", proc_bus_input_dir); fail1: remove_proc_entry("bus/input", NULL);return -ENOMEM; }(2)input_fops变量
static const struct file_operations input_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = input_open_file, };由此可知,input_fops中只实现了open函数,其指向input_open_file函数,内容如下:
static int input_open_file(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {struct input_handler *handler; // 定义一个input_handler指针//定义两个file_operations指针const struct file_operations *old_fops, *new_fops = NULL; int err;err = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);if (err)return err;/* No load-on-demand here? */// 通过次设备号在 input_table 数组中找到对应的 handlerhandler = input_table[iminor(inode) >> 5]; if (handler)// 将handler 中的fops 指针赋值给 new_fopsnew_fops = fops_get(handler->fops); mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);/** That's _really_ odd. Usually NULL ->open means "nothing special",* not "no device". Oh, well...*/if (!new_fops || !new_fops->open) {fops_put(new_fops);err = -ENODEV;goto out;}old_fops = file->f_op; //将 file->fops 先保存到 old_fops 中,以便出错时能够恢复file->f_op = new_fops; //用new_fops 替换 file 中 fopserr = new_fops->open(inode, file); // 执行 file->open 函数if (err) {fops_put(file->f_op);file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops);}fops_put(old_fops); out:return err; }
3、框架核心层开放给具体硬件驱动层的接口函数
驱动框架核心层开放给具体硬件驱动层的接口函数主要有3个:
input_allocate_device(),用于分配一块input_dev结构体类型大小的内存。input_set_capability(),用于设置输入设备可以上报哪些输入事件。
input_register_device,用于向input核心层注册设备。
(1)input_allocate_device函数
struct input_dev *input_allocate_device(void) {struct input_dev *dev; // 定义一个 input_dev 指针dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct input_dev), GFP_KERNEL); // 申请分配内存if (dev) {dev->dev.type = &input_dev_type; // 确定input设备的 设备类型 input_dev_typedev->dev.class = &input_class; // 确定input设备所属的设备类 classdevice_initialize(&dev->dev); // input设备的初始化mutex_init(&dev->mutex); // 互斥锁初始化spin_lock_init(&dev->event_lock); // 自旋锁初始化INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->h_list); // input_dev -> h_list 链表初始化INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->node); // input_dev -> node 链表初始化__module_get(THIS_MODULE);}return dev; }(2)input_set_capability函数
函数内容
/*** input_set_capability - mark device as capable of a certain event* @dev: device that is capable of emitting or accepting event* @type: type of the event (EV_KEY, EV_REL, etc...)* @code: event code** In addition to setting up corresponding bit in appropriate capability* bitmap the function also adjusts dev->evbit.*/void input_set_capability(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code) {switch (type) {case EV_KEY:__set_bit(code, dev->keybit);break;case EV_REL:__set_bit(code, dev->relbit);break;case EV_ABS:__set_bit(code, dev->absbit);break;case EV_MSC:__set_bit(code, dev->mscbit);break;case EV_SW:__set_bit(code, dev->swbit);break;case EV_LED:__set_bit(code, dev->ledbit);break;case EV_SND:__set_bit(code, dev->sndbit);break;case EV_FF:__set_bit(code, dev->ffbit);break;case EV_PWR:/* do nothing */break;default:printk(KERN_ERR"input_set_capability: unknown type %u (code %u)\n",type, code);dump_stack();return;}__set_bit(type, dev->evbit); }参数说明
参数dev表示设备的input_dev结构体变量
参数type表示设备可以上报的事件类型
参数code表示上报这类事件中的那个事件。注意事项
1)input_set_capability函数一次只能设置一个具体事件,如果设备可以上报多个事件,则需要重复调用这个函数来进行设置,例如:
input_set_capability(dev, EV_KEY, KEY_Q); input_set_capability(dev, EV_KEY, KEY_W); input_set_capability(dev, EV_KEY, KEY_E);2)具体有哪些输入事件,在drivers\input\input.h 这个文件中有定义。比如
/** Event types*/#define EV_SYN 0x00 //同步 #define EV_KEY 0x01 //按键 #define EV_REL 0x02 //相对运动 #define EV_ABS 0x03 //绝对运动 #define EV_MSC 0x04 //其他杂类 #define EV_SW 0x05 //转换 #define EV_LED 0x11 //设备上的LED #define EV_SND 0x12 //声音效果 #define EV_REP 0x14 #define EV_FF 0x15 #define EV_PWR 0x16 #define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17 #define EV_MAX 0x1f #define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1)(3)input_register_device函数
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev) // 注册input输入设备 {static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT(0);struct input_handler *handler; // 定义一个 input_handler 结构体指针const char *path;int error;/* Every input device generates EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events. */__set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit); // 每一个input输入设备都会发生这个事件/* KEY_RESERVED is not supposed to be transmitted to userspace. */__clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit); // 清除KEY_RESERVED 事件对应的bit位,也就是不传输这种类型的事件/* Make sure that bitmasks not mentioned in dev->evbit are clean. */input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev); // 确保input_dev中的用来记录事件的变量中没有提到的位掩码是干净的。/** If delay and period are pre-set by the driver, then autorepeating* is handled by the driver itself and we don't do it in input.c.*/init_timer(&dev->timer);if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]) {dev->timer.data = (long) dev;dev->timer.function = input_repeat_key;dev->rep[REP_DELAY] = 250;dev->rep[REP_PERIOD] = 33;}if (!dev->getkeycode)dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode;if (!dev->setkeycode)dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode;dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "input%ld", // 设置input设备对象的名字 input+数字(unsigned long) atomic_inc_return(&input_no) - 1);error = device_add(&dev->dev); // 添加设备 例如: /sys/devices/virtual/input/input0if (error)return error;path = kobject_get_path(&dev->dev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL); // 获取input设备对象所在的路径 /sys/devices/virtual/input/input_xxxprintk(KERN_INFO "input: %s as %s\n",dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device", path ? path : "N/A");kfree(path);error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);if (error) {device_del(&dev->dev);return error;}list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list); // 链表挂接: 将 input_dev->node 作为节点挂接到 input_dev_list 链表上list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node) // 遍历input_handler_list 链表上的所有handlerinput_attach_handler(dev, handler); // 将handler与input设备进行匹配input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); // 更新proc 文件系统mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);return 0; }(4)input_attach_handler函数
input_attach_handler函数就是input_register_device函数中用来对下层的设备驱动和上层的handler进行匹配的一个函数,匹配成功之后就会调用上层handler中的connect函数来进行连接绑定。
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler) {const struct input_device_id *id; // 定义一个input_device_id 的指针int error;id = input_match_device(handler, dev); // 通过这个函数进行handler与input设备的匹配工作if (!id)return -ENODEV;error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); // 匹配成功则调用 handler 中的 connect 函数进行连接if (error && error != -ENODEV)printk(KERN_ERR"input: failed to attach handler %s to device %s, ""error: %d\n",handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);return error; }static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(struct input_handler *handler,struct input_dev *dev) {const struct input_device_id *id; // 定义一个 input_device_id 指针int i;for (id = handler->id_table; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) { // 依次遍历handler->id_table 所指向的input_device_id 数组中的各个元素// 依次进行下面的匹配过程if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS) // 匹配总线if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype)continue;if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR) // 匹配供应商if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor)continue;if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT) // 匹配产品if (id->product != dev->id.product)continue;if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION) // 匹配版本if (id->version != dev->id.version)continue;// 下面的这些是匹配我们上传的事件是否属实MATCH_BIT(evbit, EV_MAX);MATCH_BIT(keybit, KEY_MAX);MATCH_BIT(relbit, REL_MAX);MATCH_BIT(absbit, ABS_MAX);MATCH_BIT(mscbit, MSC_MAX);MATCH_BIT(ledbit, LED_MAX);MATCH_BIT(sndbit, SND_MAX);MATCH_BIT(ffbit, FF_MAX);MATCH_BIT(swbit, SW_MAX);if (!handler->match || handler->match(handler, dev))return id; // 如果数组中的某个匹配成功了就返回他的地址}return NULL; }input_attach_handler函数做的事情有两件:调用input_match_device函数进行设备与handler的匹配;匹配成功调用handler的连接函数进行连接。
4、框架核心层开放给事件驱动层的接口函数
框架核心层向输入事件驱动层提供的接口主要有两个:
input_register_handler(),用于事件驱动层向核心层注册handler;
input_register_handle(),用于事件驱动层向核心层注册handle。
(1)input_register_handler函数
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler) // 向核心层注册handler {struct input_dev *dev; // 定义一个input_dev 指针int retval;retval = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);if (retval)return retval;INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list); // 初始化 handler->h_list 链表if (handler->fops != NULL) { // 如果 handler -> fops 存在if (input_table[handler->minor >> 5]) { // 如果input_table 数组中没有该handler 的位置了 则返回retval = -EBUSY;goto out;}input_table[handler->minor >> 5] = handler; // 将 handler 指针存放在input_table 数组中去}list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); // 将 handler 通过 handler -> node 节点 挂接到 input_handler_list 链表上list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node) // 遍历 input_dev_list 链表下挂接的所有的 input_dev 设备input_attach_handler(dev, handler); // 然后进行匹配input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); // 更新proc 文件系统out:mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);return retval; }通过分析了上面的input_register_device和这里的input_register_handler函数可以知道:注册设备的时候,不一定是先注册了handler才能够注册设备。当注册设备时,会先将
设备挂接到设备管理链表(input_dev_list)上,然后再去遍历input_handler_list链表匹配hander。同样对于handler注册的时候,也会先将handler挂接到handler管理链表
(input_handler_list)上,然后再去遍历input_dev_list链表匹配设备。所以从这里可以看出来,这种机制好像之前说过的platform总线下设备和驱动的匹配过程。
而且一个input_dev可以与多个handler匹配成功,从而可以在sysfs中创建多个设备文件,也可以在/dev/目录下创建多个设备节点,并且他们的次设备号是不一样的,这个很好理解。
所以就是导致一个设备对应多个次设备号,那这样有没有错呢?当然是没有错的。例如在我们的Ubuntu中,/dev/input/event3 和
/dev/input/mouse1 都是对应鼠标这个设备。
(2)input_register_handle函数
这个函数的作用就是注册一个handle,也就是实现上图中的将各个handle连接起来构成一个环形的结构,再调用这个函数之前已经将handle中的dev和handler已经是填充好了的,
具体的这个函数代码就不去分析了。
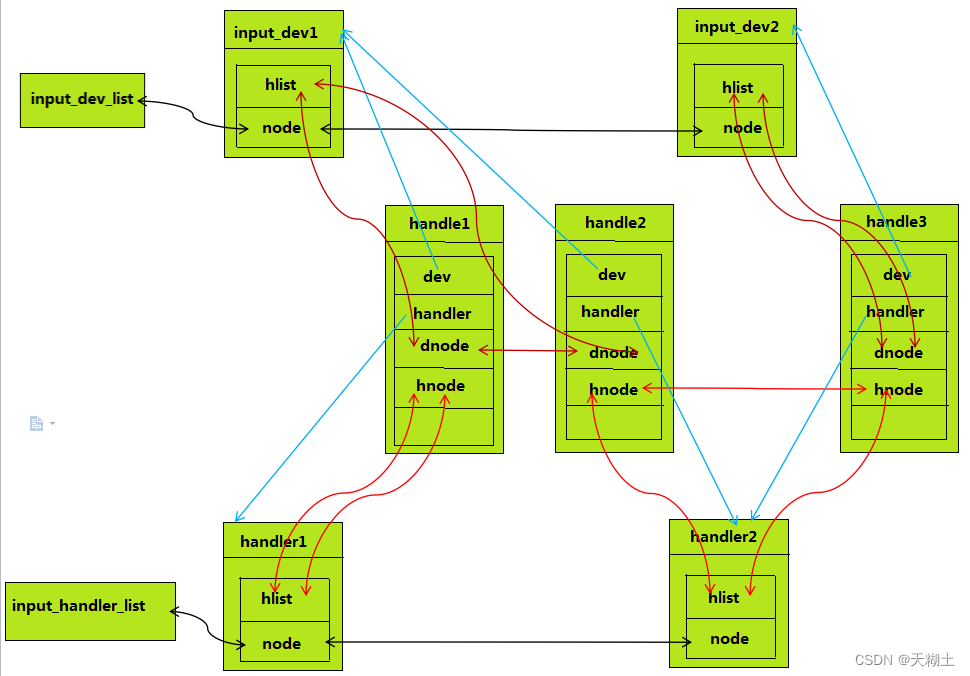
其实handler、input_dev、handle3这之间的关系,在之前就已经接触过了,讲Linux设备驱动模型底层架构的时候遇到过,下面用一副关系图来描述他们之间的一个关系:
从本质上讲,input_dev与handler是多对多的关系,从上图可以看出来,一个input_dev可以对应多个handler,一个handler也可以对应多个input_dev。因为在匹配的时候,
一个input_dev会与所有的handler都进行匹配的,并不是匹配成功一次就退出。
从图中可以看出来,一个handle就是用来记录系统中一对匹配成功的handler和device,我们可以从这个handle出发得到handler的信息,还可以得到device的信息。所以正因为有这样的
功能,所以可以由handler经过handle最终获取到device的信息,同理也可以从device从发经过handle最终获取到handler的信息。这种运用方法将会在后面的分析中看到。
5、总结
框架核心层提供的服务包括以下内容:
(1)创建设备类、注册字符设备
(2)向设备驱动层提供注册接口
(3)提供上层handler和下层device之间的匹配函数
(4)向上层提供注册handler的接口






)


)








)
