在salesforce的classic中,我们使用{!expresion}在前台页面展示信息,在lightning中,上一篇我们也提及了,如果展示attribute的值,可以使用{!v.expresion}展示信息。
lightning在component中解析动态值的时候,会将{!} 这个里面的变量进行动态的解析以及展示。当然这个变量可以是基础类型,自定义类型,数组集合等等,当然如果表达式为空字符串或者是空格则不会解析。偶尔特殊的要求为需要输出‘{!}’这个字符串,官方文档说可以使用<aura:text/>进行展示,因为这个标签不会将‘{!’作为头进行解析。当然,不要被这句话所欺骗,正常的理解应该为当value的值非tag或者attribute值的情况下,才会被解析成平滑的字符串。这里做个demo看一下渲染效果:
1 <aura:component> 2 <aura:attribute name="test" type="String" default="testValue"/> 3 {!v.test} 4 <br/> 5 <aura:text value="{!v.test}"/> 6 <br/> 7 {!} 8 <br/> 9 <aura:text value="{!}"/> 10 <br/> 11 <aura:text value="{!v.test2}"/> 12 <br/> 13 <aura:text value="{!test2}"/> 14 </aura:component>
demo中分了几种情况:输出正常的attribute值、通过aura:text输出attribute值、输出{!}值、输出一个不存在的属性的值、输出一个不存在的变量的值。结果展示如下图所示。
通过结果我们可以看出来,aura:text并不是不解析{!开头的内容,而是如果{!}不包含任何表达式情况下,会默认作为文本进行输出,其实不是用aura:text 直接输出{!}也可以作为文本进行输出。如果解析的内容不存在情况下,则默认返回null。

使用{!}方式标签仅能用于在.cmp 以及.app文件中,即只能用在lightning component以及lightning application中。
表达式除了简单的通过{!v.attribute} 展示attribute的内容或者{!123}等展示字面内容的内容外,还可以使用条件表达式这种方式展示内容,通常有两种常用的方式:三目运算和使用<aura:if>。
三目运算:下面的代码为当attribute xxx的值为xxx的情况下,这个classs设置为'xxx',否则,class为空。
<a class="{!v.xxx == 'xxx' ? 'xxx' : ''}" >test </a>
<aura:if>:此标签通常和aura:set一起用。当aura:if判断部分为true,显示aura:if为true的逻辑,否则使用aura:set设置attribute为else,走false的逻辑。下面的例子为如果有edit权限则展示Edit的Button,否则展示'You can't edit this'的文字。
1 <aura:attribute name="edit" type="Boolean" default="true"/> 2 <aura:if isTrue="{!v.edit}"> 3 <ui:button label="Edit"/> 4 <aura:set attribute="else"> 5 You can’t edit this. 6 </aura:set> 7 </aura:if>
我们在项目中会经常用到lightning component中嵌套其他的子的lightning component情况,比如列表中包含<aura:iterator> 标签嵌套item的lightning component从而实现一个自定义列表展示。
嵌套lightning component就会涉及到attribute 赋值的部分,针对attribute赋值,可以赋值一个写死的值,比如赋值‘123’等。lightning也提供了两种动态方式赋值:{!attributeValue}以及{#attributeValue}。两者赋值区别还是很大的,具体如下:
一. !方式:此种方式又可以理解为绑定的表达式,即对attribute的赋值非一次性的,改变会贯穿着始终。子项如果修改了这个attribute的赋值,也会影响到父中此attribute的值;同样的,如果父中对此attribute有更改,也会作用到子component中的引用上。
这里做一个例子:
1.boundSonComponent.cmp:声明一个attribute名称为sonAttribute,使用一个aura:text展示这个值,点击按钮后更新这个sonAttribute的value。
<aura:component><aura:attribute type="String" name="sonAttribute"/>son attribute : <aura:text value="{!v.sonAttribute}"/><br/><lightning:button onclick="{!c.handleSonClick}" label="son button"/> </aura:component>
2.boundSonComponentController.js : 更新sonAttribute的value。
({handleSonClick : function(component, event, helper) {var sonAttributeValue = 'Updated Son Attribute';component.set('v.sonAttribute', sonAttributeValue);} })
3.boundParentComponent.cmp :声明一个attribute名称为parentAttribute,展示此attribute的值并且提供按钮可以修改值,在这个基础上引入了一个boundSonComponent,并且将parentAttribute的值传给了sonAttribute。注意,这里通过‘!’方式进行传递值。
<aura:component><aura:attribute name="parentAttribute" type="String" default="parentAttributeValue"/>parentAttribute : <aura:text value="{!v.parentAttribute}"/><br/><lightning:button label="parent button" onclick="{!c.handleParentClick}" /><br/><c:boundSonComponent sonAttribute = '{!v.parentAttribute}'/> </aura:component>
4.boundParentComponentController.js :更新parentAttribute的value。
({handleParentClick : function(component, event, helper) {component.set('v.parentAttribute', 'updated parent attribute');} })
因为lightning无法直接运行lightning:component,所以需要将lightning:component放在 lightning app builder视图中或者放在Lightning application中,lightning app builder 可以重新定义 page layout,分为App Page, Home Page 和Record Page。这个和page layout 很像,需要注意的一点为显示在不同类型的页面需要实现不同的接口,具体可以查看上一篇内容,感兴趣的可以自己玩一玩。

demo以创建Lightning application为主。
5.创建boundApplication.app 用来包含boundParentComponent从而展示。
<aura:application><c:boundParentComponent/> </aura:application>
运行lightning application可以通过developer console -> File -> Opening Lighting Resource 找到此bundle,然后Open Selected,打开后点击Preview便可以看到显示方式。

结果展示:
1.默认进来情况:因为parentAttribute的值作为了sonAttribute的值,所以二者显示相同的值。
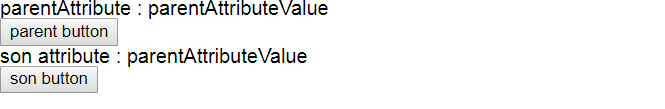
2.点击 parent button:点击parent button后,后台会更新parentAttribute的value。由于sonAttribute传递的值通过parentAttribute值传递,并且是通过!(bound)方式,所以当更改了parentAttribute后,sonAttribute也同样的改变成了parentAttribute的值。

3. 点击son button:点击son button后,后台会更新sonAttribute的值。由于sonAttribute是通过parentAttribute值传递,并且是通过!(bound)方式,所以当更改了sonAttribute后,parentAttribute也同样的受到了改变。

这种操作结果可能让人感到意外,因为我们有的时候只是想将attribute的值作为一个一次性初始化的值传递给子的component 的attribute,针对父或者针对子的改动并不希望后期在影响当前component外的其他的父或者子的component attribute。接下来的方式即可以做到非绑定表达式,即使用 # 方式进行值的传递。
二. # 方式:可以理解成非绑定的表达式,即有嵌套的lightning component,父对子传值仅初始化有效,后期父对这个attribute value的变化不会影响到子,同样子对这个attribute value的变化同样不会影响到父。
在这里重用boundSonComponent,新建unboundParentComponent,使用#方式传递值。
1.unboundParentComponent:和boundParentComponent唯一的区别为在对boundSonComponent传值的时候,将! 修改成了 # .
<aura:component><aura:attribute name="parentAttribute" type="String" default="parentAttributeValue"/>parentAttribute : <aura:text value="{!v.parentAttribute}"/><br/><lightning:button label="parent button" onclick="{!c.handleParentClick}" /><br/><c:boundSonComponent sonAttribute = '{#v.parentAttribute}'/> </aura:component>
结果展示:
1.当点击parent button时,仅更改了parentAttribute的值,sonAttribute值不会受到影响。

2.当点击son button时,金更改了sonAttribute的值,parentAttribute的值同样不会受到影响。

上一篇我们有简单的提到过lightning 提供了一些标准的事件,比如init,change。这里我们对change事件进行一个思考。如果aura:handler针对sonAttribute绑定了一个change事件,使用! 和使用# 是否会有上述的影响。
我们在boundSonComponent以及boundParentComponent添加一下change handler内容。监听一下使用!情况下属性值改变造成的change的影响。
1.boundSonComponent.cmp
<aura:component><aura:attribute type="String" name="sonAttribute"/><aura:handler name="change" value="{!v.sonAttribute}" action="{!c.onSonAttributeChange}"/>son attribute : <aura:text value="{!v.sonAttribute}"/><br/><lightning:button onclick="{!c.handleSonClick}" label="son button"/> </aura:component>
2.boundSonComponentController.js
({handleSonClick : function(component, event, helper) {var sonAttributeValue = 'Updated Son Attribute';component.set('v.sonAttribute', sonAttributeValue);},onSonAttributeChange : function(component,event,helper) {console.log("son attribute has changed");console.log("old value: " + event.getParam("oldValue"));console.log("current value: " + event.getParam("value"));} })
boundParentComponent改动和上述内容相似,都是在component中添加了aura:handler声明,后台添加了函数输出内容。
结果展示:
1.先点击son Button,通过输出结果可以看到,先执行了son Attribute的更新,因为采用的是!(绑定表达式方式),所以更新了parentAttribute的更新事件,当更新了parentAttribute后,又重新执行了一下子的component中的事件更新。
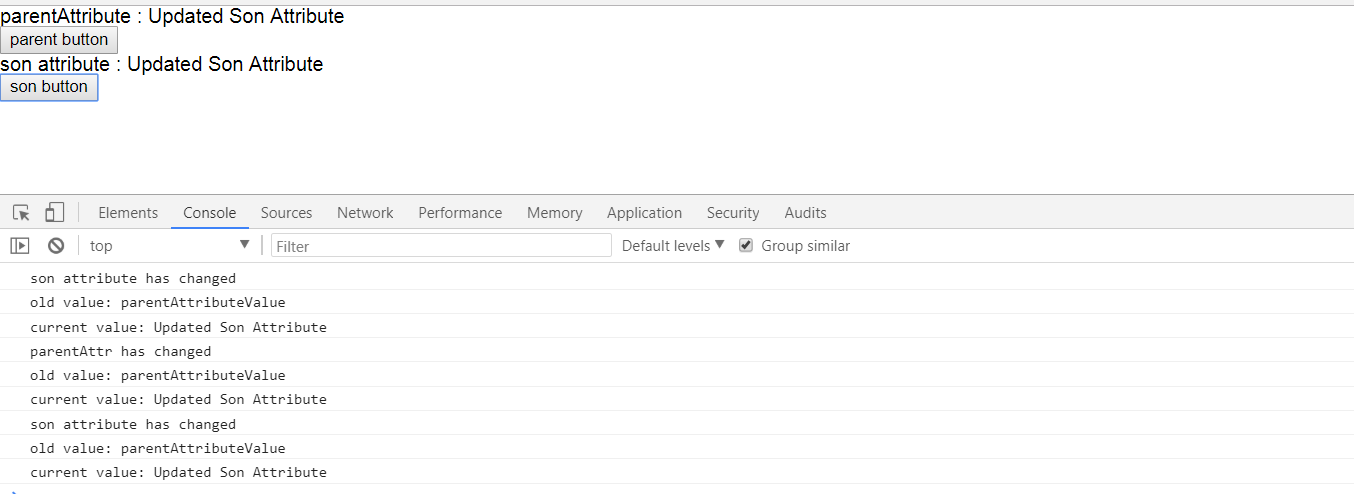
2.点击parent button,更新了属性值以后先执行了parentAttribute change的事件,然后又执行了他的子component的事件。
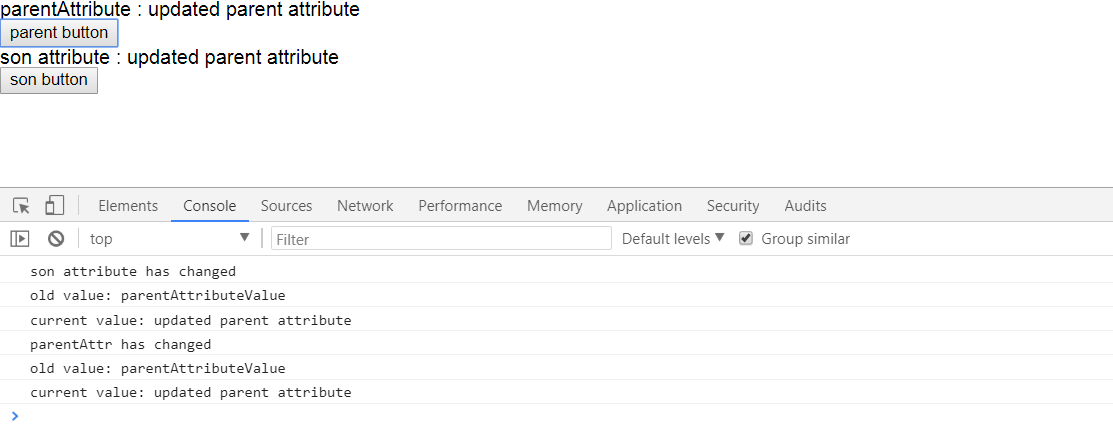
使用#方式就不会级联的对事件进行调用,只会调用到自己的那层change事件。这里就不做实验。
总结: 通过上述的两个例子的展示结果可以看出来:对子component的attribute进行动态赋值时, !(绑定表达式) 与 #(非绑定表达式)差距还是很大的。使用!方式关系贯穿始终,无论父还是子对attribute改动都会对其关联的受到影响,而且使用change handler也会有绑定关系,贯穿始终。使用#方式仅在初始化时有效,后期针对引用的attribute的值进行任何修改,都不会同步修改引用的地方。具体使用哪种方式看项目中用到的场景,同步操作则使用!方式传值;仅需要其传值作为初始化,后期改动无关则选择#方式传值。篇中有错误地方欢迎指出,有问题欢迎留言。


![JavaScript --- [学习笔记] 原型模式](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/JavaScript --- [学习笔记] 原型模式)

问题解决方法)

——解码(2):封装和界面设计)


)





方法)

![node --- [express项目] 开发环境下使用morgan控制台输出访问信息](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/node --- [express项目] 开发环境下使用morgan控制台输出访问信息)


![node --- [express] cookie/session 机制与 中间件的使用(路由守卫)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/node --- [express] cookie/session 机制与 中间件的使用(路由守卫))