文章目录
- 队列和栈的区别
- 一.用队列模拟实现栈
- 1.1入栈
- 1.2出栈
- 1.3返回栈顶元素
- 1.4判断栈是否为空
- 二.用栈模拟实现队列
- 2.1 入队
- 2.2出队
- 2.3peek
- 2.4判断队列是否为空
- 三.完整代码
- 3.1 队列模拟实现栈
- 3.2栈模拟实现队列
队列和栈的区别
栈和队列都是常用的数据结构,它们的主要区别在于数据的插入和删除顺序。
栈 (Stack) 是一种后进先出 (Last-In-First-Out, LIFO) 的数据结构,只允许在一端进行插入和删除操作,这一端称为栈顶。新元素插入后成为新的栈顶,而删除时也只能删除栈顶元素。
队列 (Queue) 是一种先进先出 (First-In-First-Out, FIFO) 的数据结构,允许在两端进行插入和删除操作,插入在队尾,删除在队头。新元素插入时成为新的队尾,而删除时也只能删除队头元素。
一.用队列模拟实现栈
1.void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
2.int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
3.int top() 返回栈顶元素。
4.boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
如上便是需要用队列来实现栈的四个基本操作。
我们试想,实现这些栈的操作,一个队列可以完成吗?
显然不可以,我们使用两个队列来实现栈的模拟

大体流程
1.入栈时:
如果两个都为空,那么想
1.1入栈
当我们要放入18 25 35 48 这一串数字入栈时,先放入18 25 35(放入时选择的队列是不为空的队列),模拟入队以及入栈时的状况,如下图
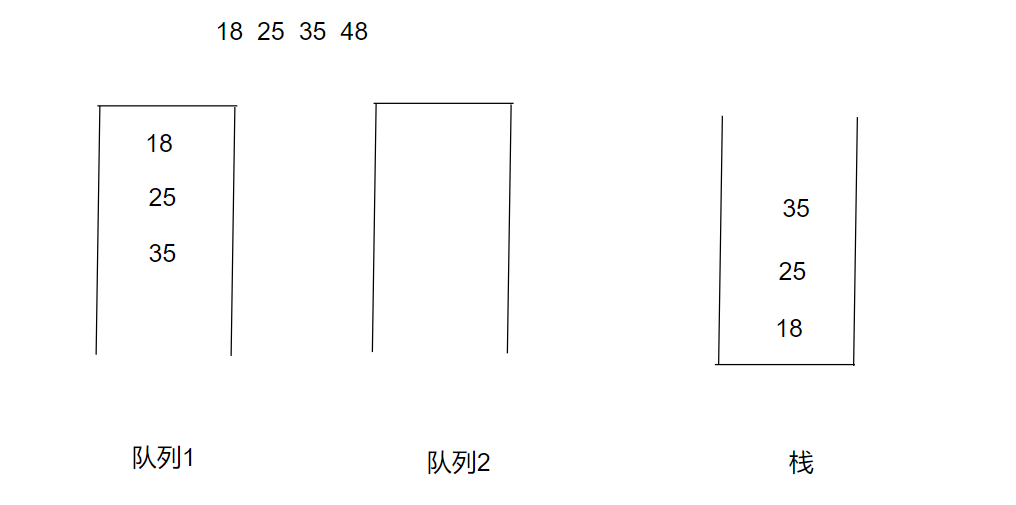
public void push(int x) {if(empty()){queue1.offer(x);return;}if(!queue1.isEmpty()){queue1.offer(x);}else {queue2.offer(x);}}
1.2出栈
此时如果我们要将35出栈时,又该如何操作呢?此时我们就需要用到第二个队列,将队列一的前size-1个元素(也就是18 25)从队列一中出队,放入队列二中。此时队列一中的元素为35,队列二的元素为18 25 如下图。
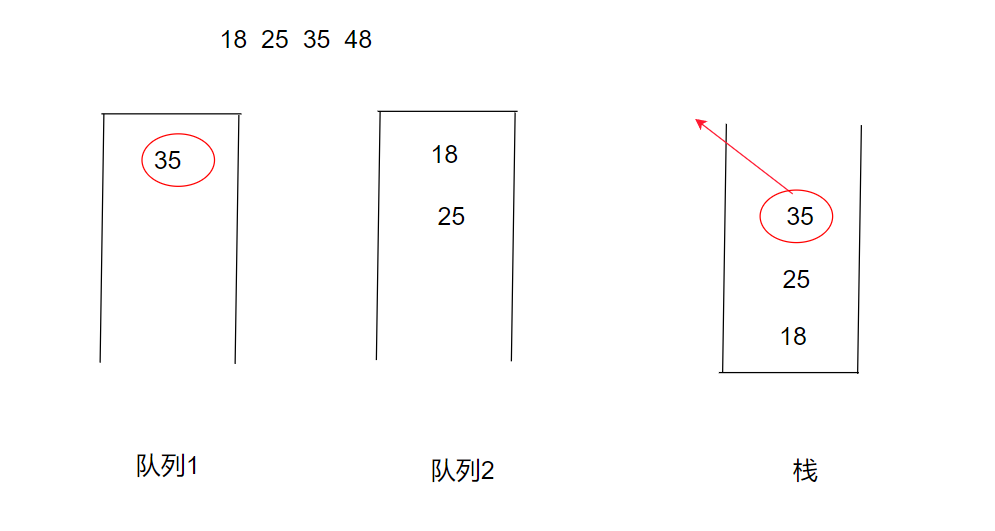
当初栈完成时,我们此时要将48入栈时,又该放入哪个栈中呢?我们考虑栈的特点(先入后出),我们将再入栈的元素放到不为空的队列中。
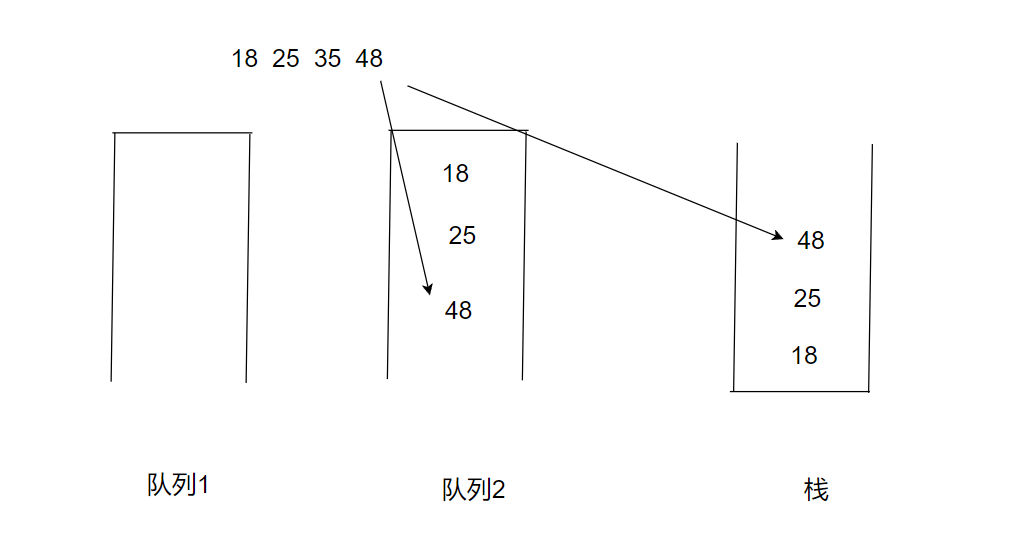
public int pop() {if(empty()){return -1;}if(!queue1.isEmpty()){int size = queue1.size();for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {queue2.offer(queue1.poll());}return queue1.poll();}else {int size = queue2.size();for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {queue1.offer(queue2.poll());}return queue2.poll();}}1.3返回栈顶元素
在实现pop的基础上,我们将声明一个变量temp来储存每次要移除的元素。
public int top() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (!queue1.isEmpty()){int temp = -1;int size = queue1.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {temp = queue1.poll();queue2.offer(temp);}return temp;}else {int size = queue2.size();int temp = -1;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {temp = queue2.poll();queue1.offer(temp);}return temp;}}
1.4判断栈是否为空
当队列一和队列二都为空时,此时栈就为空。
public boolean empty() {return queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty();}
二.用栈模拟实现队列
我们也是用两个栈来模拟实现队列
2.1 入队
我们将所有入队的元素都放入栈一中,如下图

public void push(int x) {stack1.push(x);}
2.2出队
要出栈时,如果栈二不为空,就出栈二中的元素,如果栈二为空,将栈一中的所有元素一次性的全部push到栈二中,此时就将入栈的元素全部倒转过来了,(例如入栈时在栈中的入栈顺序依次排序为18 25 35,栈二中此时的元素入栈顺序是35 25 18,出栈时就先出18,就完成了转换)如下图
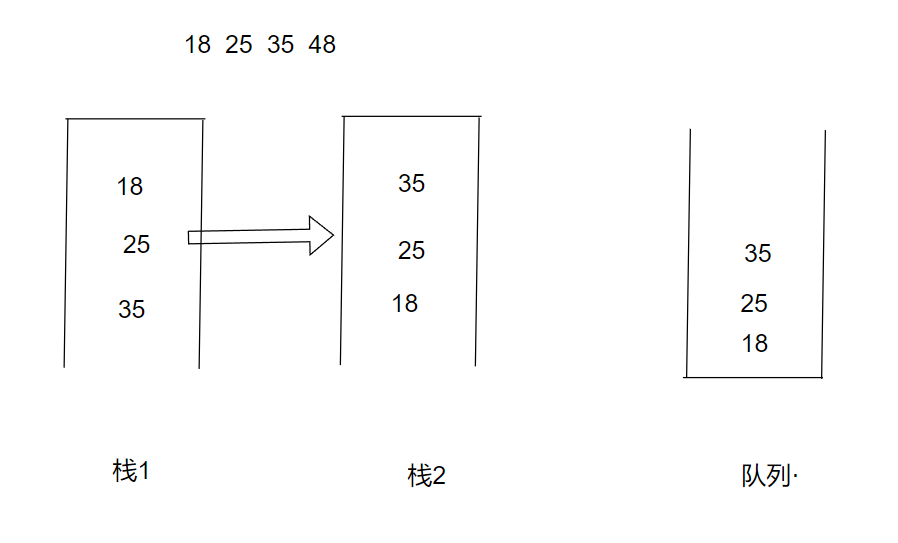
public int pop() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (stack2.isEmpty()){while (!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.pop();}
2.3peek
peek只是将出队时的pop换成peek,就可以完成要求。
public int peek() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (stack2.isEmpty()){while (!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.peek();}
2.4判断队列是否为空
如果栈一和栈二都为空时,那么队列就为空。
public boolean empty() {return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();}
三.完整代码
3.1 队列模拟实现栈
class MyStack {Queue<Integer> queue1 ;Queue<Integer> queue2 ;public MyStack() {queue1 = new LinkedList<>();queue2 = new LinkedList<>();}public void push(int x) {if(empty()){queue1.offer(x);return;}if(!queue1.isEmpty()){queue1.offer(x);}else {queue2.offer(x);}}public int pop() {if(empty()){return -1;}if(!queue1.isEmpty()){int size = queue1.size();for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {queue2.offer(queue1.poll());}return queue1.poll();}else {int size = queue2.size();for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {queue1.offer(queue2.poll());}return queue2.poll();}}public int top() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (!queue1.isEmpty()){int temp = -1;int size = queue1.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {temp = queue1.poll();queue2.offer(temp);}return temp;}else {int size = queue2.size();int temp = -1;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {temp = queue2.poll();queue1.offer(temp);}return temp;}}public boolean empty() {return queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty();}
}
3.2栈模拟实现队列
class MyQueue {public Stack<Integer> stack1 ;public Stack<Integer> stack2;public MyQueue() {stack1 = new Stack<>();stack2 = new Stack<>();}public void push(int x) {stack1.push(x);}public int pop() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (stack2.isEmpty()){while (!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.pop();}public int peek() {if(empty()){return -1;}if (stack2.isEmpty()){while (!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.peek();}public boolean empty() {return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();}
}




笔记】操作系统概论)

)


 概述)









