目录
- 原理
- 函数
- 类+模板函数
- 使用switch...case...
- 不使用switch...case...
- 知识点
- decltype
- std::remove_reference
原理

函数
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <map>void fun1(int a, int b)
{std::cout << "fun1 : a ="<<a<<" b ="<<b;
}void fun2(int a, int b)
{std::cout << "fun2 : a =" << a << " b =" << b;
}int main()
{// 可以改变这个值来调用不同的函数int id = 1;#if 0switch (id){case 1:fun1(0, 0);break;case 2:fun1(0, 0);break;}
#endifstd::map<int, std::function<void(int,int)>> functionMap;functionMap[1] = [](int a, int b) { fun1(a,b); };functionMap[2] = [](int a, int b) { fun2(a, b); };if (functionMap.find(id) != functionMap.end()) {// 调用对应的函数并传递参数functionMap[id](0,0);}else {std::cout << "Invalid id" << std::endl;}return 0;
}类+模板函数
因为工作职位低,无权对父类进行修改;
业务上又大量使用switch…case…操作模板函数;搞得代码量暴涨!
使用switch…case…
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
#include <type_traits>// 因为没有Equip的修改权限
struct Equip {std::string code; //装备
};struct FATable:public Equip {int idFA; //方案IDstd::string nameId; //名称IDstd::string equipId; //装备IDint equipNum; //装备数量
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "FATable = " << info;};
};struct NTable {std::string name; //装备名称std::string nameId; //装备IDint classify; //分类ID
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "NTable = " << info;};
};struct CTable {int classify; //分类IDstd::string className; //分类名称
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "CTable = "<< info;};
};template<typename T>
inline void writeIn(int info) {T().write(info);
};int main()
{// 可以改变这个值来调用不同的函数const int id = 1;#if 1switch (id){case 0:writeIn<FATable>(0);break;case 1:writeIn<NTable>(0);break;case 2:writeIn<CTable>(0);break;}
#endifreturn 0;
}不使用switch…case…
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
#include <type_traits>// 因为没有Equip的修改权限
struct Equip {std::string code; //装备
};struct FATable:public Equip {int idFA; //方案IDstd::string nameId; //名称IDstd::string equipId; //装备IDint equipNum; //装备数量
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "FATable = " << info;};
};struct NTable {std::string name; //装备名称std::string nameId; //装备IDint classify; //分类ID
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "NTable = " << info;};
};struct CTable {int classify; //分类IDstd::string className; //分类名称
public:void write(int info) {std::cout << "CTable = "<< info;};
};template<typename T>
inline void writeIn(int info) {T().write(info);
};int main()
{// 可以改变这个值来调用不同的函数const int id = 1;std::tuple<FATable, NTable, CTable> g_type = { FATable(), NTable(), CTable()};// 使用 decltype 来获取 g_type 中的元素类型,并将其命名为 _mT。using _mT = decltype(std::get<id>(g_type));// 使用 std::remove_reference 来移除 _mT 类型的引用修饰符,将结果命名为 CleanType。using CleanType = typename std::remove_reference<_mT>::type;// 将 CleanType 作为模板参数传递writeIn<CleanType>(0);return 0;
}知识点
decltype
decltype是 C++11 引入的一个关键字,用于获取表达式的类型。它可以用于编译时推导表达式的类型,而不需要显式地指定类型。
- 以下是 decltype 的一些重要知识点:
decltype 的语法:decltype(expression)
-
expression是一个表达式,可以是变量、函数调用、成员访问等。 -
decltype的返回类型:
如果
expression是一个标识符或类成员访问表达式,decltype返回该标识符或成员的类型。
如果
expression是一个函数调用表达式,decltype返回函数的返回类型。
如果
expression是一个右值表达式,decltype返回右值的类型。
如果
expression是一个左值表达式,decltype返回左值的引用类型。
decltype的应用场景:
在模板编程中,可以使用
decltype推导模板参数的类型,以便在编译时确定类型。
可以使用
decltype推导lambda表达式的返回类型。
可以使用
decltype推导复杂表达式的类型,避免手动指定类型。
-以下是一些使用 decltype 的示例:
int x = 42;decltype(x) y; // y 的类型为 intstd::vector<int> vec = { 1, 2, 3 };decltype(vec.size()) size; // size 的类型为 std::vector<int>::size_typeauto lambda = [](int a, int b) -> int { std::cout << "a + b = " << a + b;return a + b; };decltype(lambda) func = lambda; // func 的类型为 lambda 表达式的类型func(1,1);template <typename T, typename U>auto add(T t, U u) -> decltype(t + u) {return t + u;}auto result = add(3, 4.5); // result 的类型为 double#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
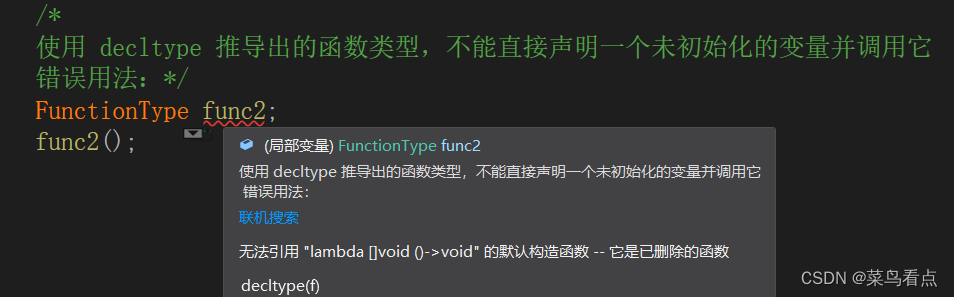
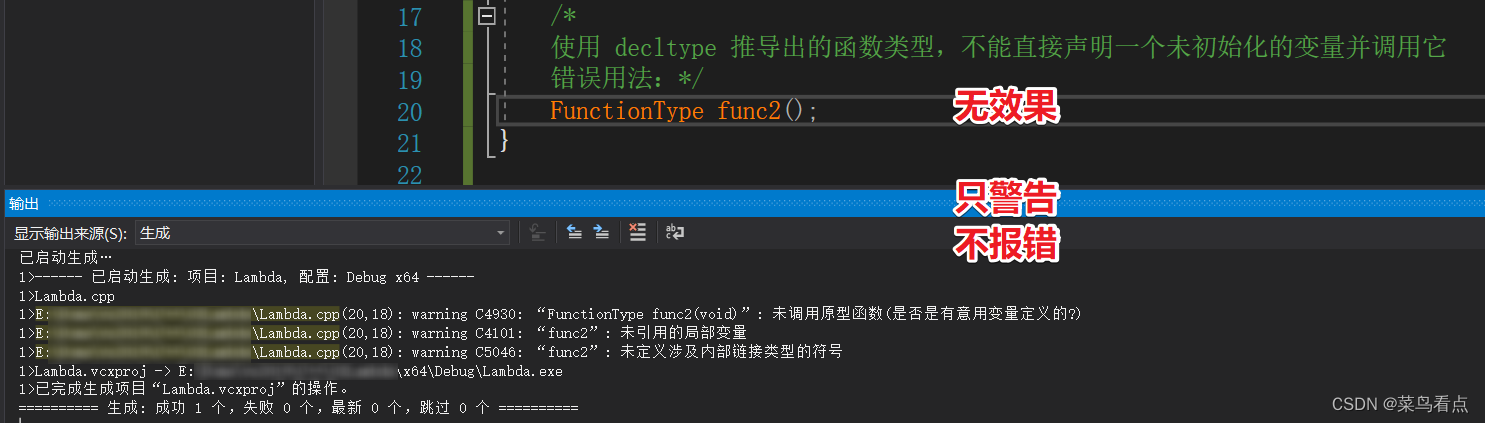
int main() {auto f = []()->void {std::cout << "hello---19" << std::endl;};using FunctionType = decltype(f); // 使用 decltype(f) 定义类型别名 FunctionTypestd::cout << typeid(f).name() << std::endl; // 输出类型名称std::cout << typeid(FunctionType).name() << std::endl; // 输出类型别名的名称FunctionType func = f; // 使用类型别名创建变量,并将 f 赋值给它func(); // 调用函数对象/*使用 decltype 推导出的函数类型,不能直接声明一个未初始化的变量并调用它错误用法:FunctionType func;func();*/return 0;
}
std::remove_reference
std::remove_reference是 C++ 标准库中的一个模板元函数,用于移除类型的引用修饰符。
当您使用std::remove_reference时,它将返回一个新类型,该类型是从给定类型中移除了引用修饰符的版本。
- 以下是
std::remove_reference的示例用法:
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>int main() {// 定义一个带有引用修饰符的类型using TypeWithReference = int&;// 使用 std::remove_reference 移除引用修饰符using TypeWithoutReference = std::remove_reference<TypeWithReference>::type;// 输出移除引用修饰符后的类型名称std::cout << "Type without reference: " << typeid(TypeWithoutReference).name() << std::endl;return 0;
}
在这个示例中,TypeWithReference 是一个带有引用修饰符的类型,然后我们使用 std::remove_reference 来移除引用修饰符,得到了 TypeWithoutReference。最后,我们输出了移除引用修饰符后的类型名称。
请注意,在 C ++14及更高版本中,你可以使用简化形式
std :: remove _ reference _ t代替
typename std :: remove _ reference < T >:: type以缩短代码:
using CleanType = std::remove_reference_t<TypeWithReference>;
这提供了相同的结果,即从类型中去除引用




 - 重复打印)





数据接收)





:索引篇)


的RDS MySQL性能对比)