1.研究背景与意义
项目参考AAAI Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence
研究背景与意义
近年来,随着计算机视觉和深度学习的快速发展,图像分割技术在各个领域中得到了广泛应用。图像分割是将图像划分为不同的区域或对象的过程,对于图像理解、目标检测和图像识别等任务具有重要意义。在农业领域中,图像分割技术可以用于农作物的生长监测、病虫害检测和果蔬分级等应用。
香菇是一种重要的食用菌类,其品质的好坏直接影响到市场价值和消费者的满意度。传统的香菇分级方法主要依靠人工进行,存在着效率低、主观性强和易受人为因素影响等问题。因此,开发一种基于计算机视觉和深度学习的香菇分级图像分割系统具有重要的研究意义和实际应用价值。
首先,基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统可以提高分级的准确性和稳定性。传统的图像分割方法往往依赖于手工设计的特征和阈值,容易受到光照、噪声和变形等因素的干扰。而深度学习网络可以自动学习图像的特征表示,具有更强的鲁棒性和泛化能力。通过改进深度学习网络的结构和训练算法,可以提高香菇分级图像分割的准确性和稳定性。
其次,基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统可以提高分级的效率和自动化程度。传统的人工分级方法需要大量的人力和时间成本,且容易受到人为因素的影响。而基于计算机视觉和深度学习的图像分割系统可以实现自动化的分级过程,大大减少了人力和时间成本。通过合理设计算法和优化计算流程,可以提高分级的效率和自动化程度。
最后,基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统可以为农业生产提供科学决策支持。通过对香菇分级图像的分析和处理,可以获取香菇的大小、形状和颜色等信息,为农民提供有针对性的种植和管理建议。同时,分级图像分割系统还可以用于病虫害的检测和预防,提高农作物的产量和质量。
综上所述,基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统具有重要的研究意义和实际应用价值。通过提高分级的准确性和稳定性、提高分级的效率和自动化程度,以及为农业生产提供科学决策支持,该系统可以推动香菇产业的发展,提高农产品的质量和市场竞争力。
2.图片演示



3.视频演示
基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
4.数据集的采集&标注和整理
图片的收集
首先,我们需要收集所需的图片。这可以通过不同的方式来实现,例如使用现有的公开数据集XgDatasets。
eiseg是一个图形化的图像注释工具,支持COCO和YOLO格式。以下是使用eiseg将图片标注为COCO格式的步骤:
(1)下载并安装eiseg。
(2)打开eiseg并选择“Open Dir”来选择你的图片目录。
(3)为你的目标对象设置标签名称。
(4)在图片上绘制矩形框,选择对应的标签。
(5)保存标注信息,这将在图片目录下生成一个与图片同名的JSON文件。
(6)重复此过程,直到所有的图片都标注完毕。
由于YOLO使用的是txt格式的标注,我们需要将VOC格式转换为YOLO格式。可以使用各种转换工具或脚本来实现。
下面是一个简单的方法是使用Python脚本,该脚本读取XML文件,然后将其转换为YOLO所需的txt格式。
import contextlib
import jsonimport cv2
import pandas as pd
from PIL import Image
from collections import defaultdictfrom utils import *# Convert INFOLKS JSON file into YOLO-format labels ----------------------------
def convert_infolks_json(name, files, img_path):# Create folderspath = make_dirs()# Import jsondata = []for file in glob.glob(files):with open(file) as f:jdata = json.load(f)jdata['json_file'] = filedata.append(jdata)# Write images and shapesname = path + os.sep + namefile_id, file_name, wh, cat = [], [], [], []for x in tqdm(data, desc='Files and Shapes'):f = glob.glob(img_path + Path(x['json_file']).stem + '.*')[0]file_name.append(f)wh.append(exif_size(Image.open(f))) # (width, height)cat.extend(a['classTitle'].lower() for a in x['output']['objects']) # categories# filenamewith open(name + '.txt', 'a') as file:file.write('%s\n' % f)# Write *.names filenames = sorted(np.unique(cat))# names.pop(names.index('Missing product')) # removewith open(name + '.names', 'a') as file:[file.write('%s\n' % a) for a in names]# Write labels filefor i, x in enumerate(tqdm(data, desc='Annotations')):label_name = Path(file_name[i]).stem + '.txt'with open(path + '/labels/' + label_name, 'a') as file:for a in x['output']['objects']:# if a['classTitle'] == 'Missing product':# continue # skipcategory_id = names.index(a['classTitle'].lower())# The INFOLKS bounding box format is [x-min, y-min, x-max, y-max]box = np.array(a['points']['exterior'], dtype=np.float32).ravel()box[[0, 2]] /= wh[i][0] # normalize x by widthbox[[1, 3]] /= wh[i][1] # normalize y by heightbox = [box[[0, 2]].mean(), box[[1, 3]].mean(), box[2] - box[0], box[3] - box[1]] # xywhif (box[2] > 0.) and (box[3] > 0.): # if w > 0 and h > 0file.write('%g %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f\n' % (category_id, *box))# Split data into train, test, and validate filessplit_files(name, file_name)write_data_data(name + '.data', nc=len(names))print(f'Done. Output saved to {os.getcwd() + os.sep + path}')# Convert vott JSON file into YOLO-format labels -------------------------------
def convert_vott_json(name, files, img_path):# Create folderspath = make_dirs()name = path + os.sep + name# Import jsondata = []for file in glob.glob(files):with open(file) as f:jdata = json.load(f)jdata['json_file'] = filedata.append(jdata)# Get all categoriesfile_name, wh, cat = [], [], []for i, x in enumerate(tqdm(data, desc='Files and Shapes')):with contextlib.suppress(Exception):cat.extend(a['tags'][0] for a in x['regions']) # categories# Write *.names filenames = sorted(pd.unique(cat))with open(name + '.names', 'a') as file:[file.write('%s\n' % a) for a in names]# Write labels filen1, n2 = 0, 0missing_images = []for i, x in enumerate(tqdm(data, desc='Annotations')):f = glob.glob(img_path + x['asset']['name'] + '.jpg')if len(f):f = f[0]file_name.append(f)wh = exif_size(Image.open(f)) # (width, height)n1 += 1if (len(f) > 0) and (wh[0] > 0) and (wh[1] > 0):n2 += 1# append filename to listwith open(name + '.txt', 'a') as file:file.write('%s\n' % f)# write labelsfilelabel_name = Path(f).stem + '.txt'with open(path + '/labels/' + label_name, 'a') as file:for a in x['regions']:category_id = names.index(a['tags'][0])# The INFOLKS bounding box format is [x-min, y-min, x-max, y-max]box = a['boundingBox']box = np.array([box['left'], box['top'], box['width'], box['height']]).ravel()box[[0, 2]] /= wh[0] # normalize x by widthbox[[1, 3]] /= wh[1] # normalize y by heightbox = [box[0] + box[2] / 2, box[1] + box[3] / 2, box[2], box[3]] # xywhif (box[2] > 0.) and (box[3] > 0.): # if w > 0 and h > 0file.write('%g %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f\n' % (category_id, *box))else:missing_images.append(x['asset']['name'])print('Attempted %g json imports, found %g images, imported %g annotations successfully' % (i, n1, n2))if len(missing_images):print('WARNING, missing images:', missing_images)# Split data into train, test, and validate filessplit_files(name, file_name)print(f'Done. Output saved to {os.getcwd() + os.sep + path}')# Convert ath JSON file into YOLO-format labels --------------------------------
def convert_ath_json(json_dir): # dir contains json annotations and images# Create foldersdir = make_dirs() # output directoryjsons = []for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(json_dir):jsons.extend(os.path.join(dirpath, filename)for filename in [f for f in filenames if f.lower().endswith('.json')])# Import jsonn1, n2, n3 = 0, 0, 0missing_images, file_name = [], []for json_file in sorted(jsons):with open(json_file) as f:data = json.load(f)# # Get classes# try:# classes = list(data['_via_attributes']['region']['class']['options'].values()) # classes# except:# classes = list(data['_via_attributes']['region']['Class']['options'].values()) # classes# # Write *.names file# names = pd.unique(classes) # preserves sort order# with open(dir + 'data.names', 'w') as f:# [f.write('%s\n' % a) for a in names]# Write labels filefor x in tqdm(data['_via_img_metadata'].values(), desc=f'Processing {json_file}'):image_file = str(Path(json_file).parent / x['filename'])f = glob.glob(image_file) # image fileif len(f):f = f[0]file_name.append(f)wh = exif_size(Image.open(f)) # (width, height)n1 += 1 # all imagesif len(f) > 0 and wh[0] > 0 and wh[1] > 0:label_file = dir + 'labels/' + Path(f).stem + '.txt'nlabels = 0try:with open(label_file, 'a') as file: # write labelsfile# try:# category_id = int(a['region_attributes']['class'])# except:# category_id = int(a['region_attributes']['Class'])category_id = 0 # single-classfor a in x['regions']:# bounding box format is [x-min, y-min, x-max, y-max]box = a['shape_attributes']box = np.array([box['x'], box['y'], box['width'], box['height']],dtype=np.float32).ravel()box[[0, 2]] /= wh[0] # normalize x by widthbox[[1, 3]] /= wh[1] # normalize y by heightbox = [box[0] + box[2] / 2, box[1] + box[3] / 2, box[2],box[3]] # xywh (left-top to center x-y)if box[2] > 0. and box[3] > 0.: # if w > 0 and h > 0file.write('%g %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f\n' % (category_id, *box))n3 += 1nlabels += 1if nlabels == 0: # remove non-labelled images from datasetos.system(f'rm {label_file}')# print('no labels for %s' % f)continue # next file# write imageimg_size = 4096 # resize to maximumimg = cv2.imread(f) # BGRassert img is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + fr = img_size / max(img.shape) # size ratioif r < 1: # downsize if necessaryh, w, _ = img.shapeimg = cv2.resize(img, (int(w * r), int(h * r)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)ifile = dir + 'images/' + Path(f).nameif cv2.imwrite(ifile, img): # if success append image to listwith open(dir + 'data.txt', 'a') as file:file.write('%s\n' % ifile)n2 += 1 # correct imagesexcept Exception:os.system(f'rm {label_file}')print(f'problem with {f}')else:missing_images.append(image_file)nm = len(missing_images) # number missingprint('\nFound %g JSONs with %g labels over %g images. Found %g images, labelled %g images successfully' %(len(jsons), n3, n1, n1 - nm, n2))if len(missing_images):print('WARNING, missing images:', missing_images)# Write *.names filenames = ['knife'] # preserves sort orderwith open(dir + 'data.names', 'w') as f:[f.write('%s\n' % a) for a in names]# Split data into train, test, and validate filessplit_rows_simple(dir + 'data.txt')write_data_data(dir + 'data.data', nc=1)print(f'Done. Output saved to {Path(dir).absolute()}')def convert_coco_json(json_dir='../coco/annotations/', use_segments=False, cls91to80=False):save_dir = make_dirs() # output directorycoco80 = coco91_to_coco80_class()# Import jsonfor json_file in sorted(Path(json_dir).resolve().glob('*.json')):fn = Path(save_dir) / 'labels' / json_file.stem.replace('instances_', '') # folder namefn.mkdir()with open(json_file) as f:data = json.load(f)# Create image dictimages = {'%g' % x['id']: x for x in data['images']}# Create image-annotations dictimgToAnns = defaultdict(list)for ann in data['annotations']:imgToAnns[ann['image_id']].append(ann)# Write labels filefor img_id, anns in tqdm(imgToAnns.items(), desc=f'Annotations {json_file}'):img = images['%g' % img_id]h, w, f = img['height'], img['width'], img['file_name']bboxes = []segments = []for ann in anns:if ann['iscrowd']:continue# The COCO box format is [top left x, top left y, width, height]box = np.array(ann['bbox'], dtype=np.float64)box[:2] += box[2:] / 2 # xy top-left corner to centerbox[[0, 2]] /= w # normalize xbox[[1, 3]] /= h # normalize yif box[2] <= 0 or box[3] <= 0: # if w <= 0 and h <= 0continuecls = coco80[ann['category_id'] - 1] if cls91to80 else ann['category_id'] - 1 # classbox = [cls] + box.tolist()if box not in bboxes:bboxes.append(box)# Segmentsif use_segments:if len(ann['segmentation']) > 1:s = merge_multi_segment(ann['segmentation'])s = (np.concatenate(s, axis=0) / np.array([w, h])).reshape(-1).tolist()else:s = [j for i in ann['segmentation'] for j in i] # all segments concatenateds = (np.array(s).reshape(-1, 2) / np.array([w, h])).reshape(-1).tolist()s = [cls] + sif s not in segments:segments.append(s)# Writewith open((fn / f).with_suffix('.txt'), 'a') as file:for i in range(len(bboxes)):line = *(segments[i] if use_segments else bboxes[i]), # cls, box or segmentsfile.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')def min_index(arr1, arr2):"""Find a pair of indexes with the shortest distance. Args:arr1: (N, 2).arr2: (M, 2).Return:a pair of indexes(tuple)."""dis = ((arr1[:, None, :] - arr2[None, :, :]) ** 2).sum(-1)return np.unravel_index(np.argmin(dis, axis=None), dis.shape)def merge_multi_segment(segments):"""Merge multi segments to one list.Find the coordinates with min distance between each segment,then connect these coordinates with one thin line to merge all segments into one.Args:segments(List(List)): original segmentations in coco's json file.like [segmentation1, segmentation2,...], each segmentation is a list of coordinates."""s = []segments = [np.array(i).reshape(-1, 2) for i in segments]idx_list = [[] for _ in range(len(segments))]# record the indexes with min distance between each segmentfor i in range(1, len(segments)):idx1, idx2 = min_index(segments[i - 1], segments[i])idx_list[i - 1].append(idx1)idx_list[i].append(idx2)# use two round to connect all the segmentsfor k in range(2):# forward connectionif k == 0:for i, idx in enumerate(idx_list):# middle segments have two indexes# reverse the index of middle segmentsif len(idx) == 2 and idx[0] > idx[1]:idx = idx[::-1]segments[i] = segments[i][::-1, :]segments[i] = np.roll(segments[i], -idx[0], axis=0)segments[i] = np.concatenate([segments[i], segments[i][:1]])# deal with the first segment and the last oneif i in [0, len(idx_list) - 1]:s.append(segments[i])else:idx = [0, idx[1] - idx[0]]s.append(segments[i][idx[0]:idx[1] + 1])else:for i in range(len(idx_list) - 1, -1, -1):if i not in [0, len(idx_list) - 1]:idx = idx_list[i]nidx = abs(idx[1] - idx[0])s.append(segments[i][nidx:])return sdef delete_dsstore(path='../datasets'):# Delete apple .DS_store filesfrom pathlib import Pathfiles = list(Path(path).rglob('.DS_store'))print(files)for f in files:f.unlink()if __name__ == '__main__':source = 'COCO'if source == 'COCO':convert_coco_json('./annotations', # directory with *.jsonuse_segments=True,cls91to80=True)elif source == 'infolks': # Infolks https://infolks.info/convert_infolks_json(name='out',files='../data/sm4/json/*.json',img_path='../data/sm4/images/')elif source == 'vott': # VoTT https://github.com/microsoft/VoTTconvert_vott_json(name='data',files='../../Downloads/athena_day/20190715/*.json',img_path='../../Downloads/athena_day/20190715/') # images folderelif source == 'ath': # ath formatconvert_ath_json(json_dir='../../Downloads/athena/') # images folder# zip results# os.system('zip -r ../coco.zip ../coco')整理数据文件夹结构
我们需要将数据集整理为以下结构:
-----datasets-----coco128-seg|-----images| |-----train| |-----valid| |-----test||-----labels| |-----train| |-----valid| |-----test|模型训练
Epoch gpu_mem box obj cls labels img_size1/200 20.8G 0.01576 0.01955 0.007536 22 1280: 100%|██████████| 849/849 [14:42<00:00, 1.04s/it]Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100%|██████████| 213/213 [01:14<00:00, 2.87it/s]all 3395 17314 0.994 0.957 0.0957 0.0843Epoch gpu_mem box obj cls labels img_size2/200 20.8G 0.01578 0.01923 0.007006 22 1280: 100%|██████████| 849/849 [14:44<00:00, 1.04s/it]Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100%|██████████| 213/213 [01:12<00:00, 2.95it/s]all 3395 17314 0.996 0.956 0.0957 0.0845Epoch gpu_mem box obj cls labels img_size3/200 20.8G 0.01561 0.0191 0.006895 27 1280: 100%|██████████| 849/849 [10:56<00:00, 1.29it/s]Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100%|███████ | 187/213 [00:52<00:00, 4.04it/s]all 3395 17314 0.996 0.957 0.0957 0.0845
5.核心代码讲解
5.1 export.py
def export_formats():# YOLOv5 export formatsx = [['PyTorch', '-', '.pt', True, True],['TorchScript', 'torchscript', '.torchscript', True, True],['ONNX', 'onnx', '.onnx', True, True],['OpenVINO', 'openvino', '_openvino_model', True, False],['TensorRT', 'engine', '.engine', False, True],['CoreML', 'coreml', '.mlmodel', True, False],['TensorFlow SavedModel', 'saved_model', '_saved_model', True, True],['TensorFlow GraphDef', 'pb', '.pb', True, True],['TensorFlow Lite', 'tflite', '.tflite', True, False],['TensorFlow Edge TPU', 'edgetpu', '_edgetpu.tflite', False, False],['TensorFlow.js', 'tfjs', '_web_model', False, False],['PaddlePaddle', 'paddle', '_paddle_model', True, True],]return pd.DataFrame(x, columns=['Format', 'Argument', 'Suffix', 'CPU', 'GPU'])def try_export(inner_func):# YOLOv5 export decorator, i..e @try_exportinner_args = get_default_args(inner_func)def outer_func(*args, **kwargs):prefix = inner_args['prefix']try:with Profile() as dt:f, model = inner_func(*args, **kwargs)LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} export success ✅ {dt.t:.1f}s, saved as {f} ({file_size(f):.1f} MB)')return f, modelexcept Exception as e:LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} export failure ❌ {dt.t:.1f}s: {e}')return None, Nonereturn outer_func@try_export
def export_torchscript(model, im, file, optimize, prefix=colorstr('TorchScript:')):# YOLOv5 TorchScript model exportLOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with torch {torch.__version__}...')f = file.with_suffix('.torchscript')ts = torch.jit.trace(model, im, strict=False)d = {"shape": im.shape, "stride": int(max(model.stride)), "names": model.names}extra_files = {'config.txt': json.dumps(d)} # torch._C.ExtraFilesMap()if optimize: # https://pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/mobile_interpreter.htmloptimize_for_mobile(ts)._save_for_lite_interpreter(str(f), _extra_files=extra_files)else:ts.save(str(f), _extra_files=extra_files)return f, None@try_export
def export_onnx(model, im, file, opset, dynamic, simplify, prefix=colorstr('ONNX:')):# YOLOv5 ONNX exportcheck_requirements('onnx>=1.12.0')import onnxLOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with onnx {onnx.__version__}...')f = file.with_suffix('.onnx')output_names = ['output0', 'output1'] if isinstance(model, SegmentationModel) else ['output0']if dynamic:dynamic = {'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}} # shape(1,3,640,640)if isinstance(model, SegmentationModel):dynamic['output0'] = {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85)dynamic['output1'] = {0: 'batch', 2: 'mask_height', 3: 'mask_width'} # shape(1,32,160,160)elif isinstance(model, DetectionModel):dynamic['output0'] = {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85)torch.onnx.export(model.cpu() if dynamic else model, # --dynamic only compatible with cpuim.cpu() if dynamic else im,f,verbose=False,opset_version=opset,do_constant_folding=True, # WARNING: DNN inference with torch>=1.12 may require do_constant_folding=Falseinput_names=['images'],output_names=output_names,dynamic_axes=dynamic or None)# Checksmodel_onnx = onnx.load(f) # load onnx modelonnx.checker.check_model(model_onnx) # check onnx model# Metadatad = {'stride': int(max(model.stride)), 'names': model.names}for k, v in d.items():meta = model_onnx.metadata_props.add()meta.key, meta.value = k, str(v)onnx.save(model_onnx, f)# Simplifyif simplify:try:cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()check_requirements(('onnxruntime-gpu' if cuda else 'onnxruntime', 'onnx-simplifier>=0.4.1'))import onnxsimLOGGER.info(f'{prefix} simplifying with onnx-simplifier {onnxsim.__version__}...')model_simp, check = onnxsim.simplify(f, check=True)assert check, 'assert check failed'onnx.save(model_simp, f)except Exception as e:LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} simplifier failure ❌ {e}')return f, None
export.py是一个用于将YOLOv5 PyTorch模型导出为其他格式的程序文件。它支持导出的格式包括PyTorch、TorchScript、ONNX、OpenVINO、TensorRT、CoreML、TensorFlow SavedModel、TensorFlow GraphDef、TensorFlow Lite、TensorFlow Edge TPU、TensorFlow.js和PaddlePaddle。该文件还包含了导出所需的依赖库和使用示例。
在文件中定义了一些辅助函数,如export_formats()用于返回YOLOv5支持的导出格式列表,try_export()用于导出时的异常处理,export_torchscript()用于导出TorchScript模型,export_onnx()用于导出ONNX模型。
整个文件的逻辑是先加载YOLOv5模型,然后根据命令行参数选择要导出的格式,调用相应的导出函数进行导出。导出过程中会进行一些检查和优化操作,最后将导出的模型保存到指定的文件中。
5.2 ui.py
class MushroomDetector:def __init__(self, weights='./best.pt', data=ROOT / 'data/coco128.yaml', device='', half=False, dnn=False):self.weights = weightsself.data = dataself.device = deviceself.half = halfself.dnn = dnnself.model, self.stride, self.names, self.pt = self.load_model()def load_model(self):device = select_device(self.device)model = DetectMultiBackend(self.weights, device=device, dnn=self.dnn, data=self.data, fp16=self.half)stride, names, pt = model.stride, model.names, model.ptreturn model, stride, names, ptdef run(self, img, imgsz=(640, 640), conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, max_det=1000, device='', classes=None,agnostic_nms=False, augment=False, retina_masks=True):imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=self.stride)self.model.warmup(imgsz=(1 if self.pt else 1, 3, *imgsz))cal_detect = []device = select_device(device)names = self.model.module.names if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.model.namesim = letterbox(img, imgsz, self.stride, self.pt)[0]im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]im = np.ascontiguousarray(im)im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)im = im.half() if self.half else im.float()im /= 255if len(im.shape) == 3:im = im[None]pred, proto = self.model(im, augment=augment)[:2]pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det, nm=32)for i, det in enumerate(pred):annotator = Annotator(img, line_width=1, example=str(names))if len(det):det[:, :4] = scale_boxes(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], img.shape).round()masks = process_mask_native(proto[i], det[:, 6:], det[:, :4], img.shape[:2])segments = [scale_segments(img.shape if retina_masks else im.shape[2:], x, img.shape, normalize=True)for x in reversed(masks2segments(masks))]annotator.masks(masks,colors=[colors(x, True) for x in det[:, 5]],im_gpu=torch.as_tensor(img, dtype=torch.float16).to(device).permute(2, 0, 1).flip(0).contiguous() /255 if retina_masks else im[i])for j, (*xyxy, conf, cls) in enumerate(reversed(det[:, :6])):c = int(cls)label = f'xianggu'contours = segments[j]cal_detect.append([label, xyxy, float(conf), contours])return cal_detectdef detect(self, info1):try:image = cv2.imread(info1)results = self.run(self.model, image, self.stride, self.pt)for i in results:box = i[1]contours = []for j in i[3]:contours.append([int(j[0] * image.shape[1]), int(j[1] * image.shape[0])])contours = np.array([contours])area = cv2.contourArea(contours)perimeter = cv2.arcLength(contours, True)circularity = 4 * np.pi * area / (perimeter ** 2) if perimeter > 0 else 0mask = np.zeros(image.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)cv2.drawContours(mask, [contours], -1, 255, -1)color_points = cv2.findNonZero(mask)selected_points = color_points[np.random.choice(color_points.shape[0], 5, replace=False)]colors = np.mean([image[y, x] for x, y in selected_points[:, 0]], axis=0)image = cv2.drawContours(image, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 3)cv2.putText(image, str(i[0]), (int(box[0]), int(box[1]) - 10),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 2)color_str = f"({colors[0]:.1f}, {colors[1]:.1f}, {colors[2]:.1f})"metrics = [("Area", area), ("Perimeter", perimeter),("Circularity", circularity), ("Color", color_str)]area_threshold = 1000if area > area_threshold:mushroom_grade = "Grade: 1"else:mushroom_grade = "Grade: 2"metrics.append((mushroom_grade, ""))for idx, (metric_name, metric_value) in enumerate(metrics):text = f"{metric_name}: {metric_value}"color = (0, 0, 255) if metric_name == "Grade" else (255, 0, 0)cv2.putText(image, text, (int(box[0]), int(box[1]) - 40 - 20 * idx),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, color, 2)try:with open('./message/' + i[0] + '.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:lines = f.readlines()for jjj in lines:print(jjj)except:passcv2.imwrite('./result/' + info1.split('\\')[-1], image)except:cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)while True:_, image = cap.read()if image is None:breakresults = self.run(self.model, image, self.stride, self.pt)for i in results:box = i[1]contours = []for j in i[3]:contours.append([int(j[0] * image.shape[1]), int(j[1] * image.shape[0])])contours = np.array([contours])area = cv2.contourArea(contours)perimeter = cv2.arcLength(contours, True)......
这个程序文件是一个使用PyQt5构建的图形用户界面(UI)程序。它包含了一些导入的模块和函数,以及一些全局变量和常量的定义。
程序的主要功能是使用YOLOv5模型对输入的图像进行目标检测,并在图像上绘制检测结果和相关信息。具体的实现细节如下:
- 导入所需的模块和函数,包括PyQt5、OpenCV、torch等。
- 定义了一些全局变量和常量,包括文件路径、模型参数等。
- 定义了一个
load_model函数,用于加载模型并返回相关参数。 - 定义了一个
run函数,用于运行模型进行目标检测,并返回检测结果。 - 定义了一个
det函数,用于读取输入图像并调用run函数进行目标检测,然后在图像上绘制检测结果和相关信息。 - 最后,程序通过调用
det函数对输入图像进行目标检测,并将结果保存到指定的文件夹中。
总体来说,这个程序文件是一个使用YOLOv5模型进行目标检测的图形用户界面程序,可以对输入的图像进行目标检测并显示检测结果和相关信息。
5.3 val.py
def save_one_txt(predn, save_conf, shape, file):# Save one txt resultgn = torch.tensor(shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwhfor *xyxy, conf, cls in predn.tolist():xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywhline = (cls, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label formatwith open(file, 'a') as f:f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')def save_one_json(predn, jdict, path, class_map):# Save one JSON result {"image_id": 42, "category_id": 18, "bbox": [258.15, 41.29, 348.26, 243.78], "score": 0.236}image_id = int(path.stem) if path.stem.isnumeric() else path.stembox = xyxy2xywh(predn[:, :4]) # xywhbox[:, :2] -= box[:, 2:] / 2 # xy center to top-left cornerfor p, b in zip(predn.tolist(), box.tolist()):jdict.append({'image_id': image_id,'category_id': class_map[int(p[5])],'bbox': [round(x, 3) for x in b],'score': round(p[4], 5)})def process_batch(detections, labels, iouv):"""Return correct prediction matrixArguments:detections (array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, classlabels (array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2Returns:correct (array[N, 10]), for 10 IoU levels"""correct = np.zeros((detections.shape[0], iouv.shape[0])).astype(bool)iou = box_iou(labels[:, 1:], detections[:, :4])correct_class = labels[:, 0:1] == detections[:, 5]for i in range(len(iouv)):x = torch.where((iou >= iouv[i]) & correct_class) # IoU > threshold and classes matchif x[0].shape[0]:matches = torch.cat((torch.stack(x, 1), iou[x[0], x[1]][:, None]), 1).cpu().numpy() # [label, detect, iou]if x[0].shape[0] > 1:matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 1], return_index=True)[1]]# matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 0], return_index=True)[1]]correct[matches[:, 1].astype(int), i] = Truereturn torch.tensor(correct, dtype=torch.bool, device=iouv.device)@smart_inference_mode()
def run(data,weights=None, # model.pt path(s)batch_size=32, # batch sizeimgsz=640, # inference size (pixels)conf_thres=0.001, # confidence thresholdiou_thres=0.6, # NMS IoU thresholdmax_det=300, # maximum detections per imagetask='val', # train, val, test, speed or studydevice='', # cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpuworkers=8, # max dataloader workers (per RANK in DDP mode)single_cls=False, # treat as single-class datasetaugment=False, # augmented inferenceverbose=False, # verbose outputsave_txt=False, # save results to *.txtsave_hybrid=False, # save label+prediction hybrid results to *.txtsave_conf=False, # save confidences in --save-txt labelssave_json=False, # save a COCO-JSON results fileproject=ROOT / 'runs/val', # save to project/namename='exp', # save to project/nameexist_ok=False, # existing project/name ok, do not incrementhalf=True, # use FP16 half-precision inferencednn=False, # use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inferencemodel=None,dataloader=None,save_dir=Path(''),plots=True,callbacks=Callbacks(),compute_loss=None,
):# Initialize/load model and set devicetraining = model is not Noneif training: # called by train.py这是一个用于在检测数据集上验证训练好的YOLOv5检测模型的程序文件。它可以加载训练好的模型并在给定的数据集上进行推理。它还提供了一些参数选项,如权重文件路径、数据集配置文件路径、推理图像大小等。它还支持不同的输出格式,如保存结果为txt文件、json文件等。程序文件还包含了一些辅助函数,用于处理推理结果、计算指标等。
5.4 classify\predict.py
class YOLOv5Classifier:def __init__(self, weights, source, data, imgsz, device, view_img, save_txt, nosave, augment, visualize, update,project, name, exist_ok, half, dnn, vid_stride):self.weights = weightsself.source = sourceself.data = dataself.imgsz = imgszself.device = deviceself.view_img = view_imgself.save_txt = save_txtself.nosave = nosaveself.augment = augmentself.visualize = visualizeself.update = updateself.project = projectself.name = nameself.exist_ok = exist_okself.half = halfself.dnn = dnnself.vid_stride = vid_stridedef run(self):source = str(self.source)save_img = not self.nosave and not source.endswith('.txt') # save inference imagesis_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS + VID_FORMATS)is_url = source.lower().startswith(('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://', 'https://'))webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.streams') or (is_url and not is_file)screenshot = source.lower().startswith('screen')if is_url and is_file:source = check_file(source) # download# Directoriessave_dir = increment_path(Path(self.project) / self.name, exist_ok=self.exist_ok) # increment run(save_dir / 'labels' if self.save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir# Load modeldevice = select_device(self.device)model = DetectMultiBackend(self.weights, device=device, dnn=self.dnn, data=self.data, fp16=self.half)stride, names, pt = model.stride, model.names, model.ptimgsz = check_img_size(self.imgsz, s=stride) # check image size# Dataloaderbs = 1 # batch_sizeif webcam:view_img = check_imshow(warn=True)dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, transforms=classify_transforms(imgsz[0]),vid_stride=self.vid_stride)bs = len(dataset)elif screenshot:dataset = LoadScreenshots(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)else:dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, transforms=classify_transforms(imgsz[0]),vid_stride=self.vid_stride)vid_path, vid_writer = [None] * bs, [None] * bs# Run inferencemodel.warmup(imgsz=(1 if pt else bs, 3, *imgsz)) # warmupseen, windows, dt = 0, [], (Profile(), Profile(), Profile())for path, im, im0s, vid_cap, s in dataset:with dt[0]:im = torch.Tensor(im).to(model.device)im = im.half() if model.fp16 else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32if len(im.shape) == 3:im = im[None] # expand for batch dim# Inferencewith dt[1]:results = model(im)# Post-processwith dt[2]:pred = F.softmax(results, dim=1) # probabilities# Process predictionsfor i, prob in enumerate(pred): # per imageseen += 1if webcam: # batch_size >= 1p, im0, frame = path[i], im0s[i].copy(), dataset.counts += f'{i}: 'else:p, im0, frame = path, im0s.copy(), getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)p = Path(p) # to Pathsave_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # im.jpgtxt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # im.txts += '%gx%g ' % im.shape[2:] # print stringannotator = Annotator(im0, example=str(names), pil=True)# Print resultstop5i = prob.argsort(0, descending=True)[:5].tolist() # top 5 indicess += f"{', '.join(f'{names[j]} {prob[j]:.2f}' for j in top5i)}, "# Write resultstext = '\n'.join(f'{prob[j]:.2f} {names[j]
这个程序文件是一个用于YOLOv5分类推理的脚本。它可以在图像、视频、目录、URL、摄像头等来源上运行YOLOv5分类推理。
该脚本提供了多种用法和格式,可以通过命令行参数进行配置。它使用了YOLOv5模型进行推理,并可以选择不同的模型文件和推理设备。推理结果可以保存为图像文件或文本文件,并可以选择是否显示结果。
该脚本还提供了一些额外的功能,如数据增强、特征可视化和模型更新。
总之,这个程序文件是一个用于YOLOv5分类推理的多功能脚本,可以在不同的数据源上运行,并提供了丰富的配置选项和结果保存功能。
5.6 models\common.py
class Conv(nn.Module):# Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activationdef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):super().__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))def forward_fuse(self, x):return self.act(self.conv(x))
class DWConv(Conv):# Depth-wise convolutiondef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, d=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, dilation, activationsuper().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, g=math.gcd(c1, c2), d=d, act=act)
class DWConvTranspose2d(nn.ConvTranspose2d):# Depth-wise transpose convolutiondef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p1=0, p2=0): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, padding_outsuper().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, p1, p2, groups=math.gcd(c1, c2))
class TransformerLayer(nn.Module):# Transformer layer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 (LayerNorm layers removed for better performance)def __init__(self, c, num_heads):super().__init__()self.q = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)self.k = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)self.v = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)self.ma = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=c, num_heads=num_heads)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)def forward(self, x):x = self.ma(self.q(x), self.k(x), self.v(x))[0] + xx = self.fc2(self.fc1(x)) + xreturn x
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):# Vision Transformer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929def __init__(self, c1, c2, num_heads, num_layers):super().__init__()self.conv = Noneif c1 != c2:self.conv = Conv(c1, c2)self.linear = nn.Linear(c2, c2) # learnable position embeddingself.tr = nn.Sequential(*(TransformerLayer(c2, num_heads) for _ in range(num_layers)))self.c2 = c2def forward(self, x):if self.conv is not None:x = self.conv5.6 models\experimental.py
class Sum(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n, weight=False):super().__init__()self.weight = weightself.iter = range(n - 1)if weight:self.w = nn.Parameter(-torch.arange(1.0, n) / 2, requires_grad=True)def forward(self, x):y = x[0]if self.weight:w = torch.sigmoid(self.w) * 2for i in self.iter:y = y + x[i + 1] * w[i]else:for i in self.iter:y = y + x[i + 1]return yclass MixConv2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(1, 3), s=1, equal_ch=True):super().__init__()n = len(k)if equal_ch:i = torch.linspace(0, n - 1E-6, c2).floor()c_ = [(i == g).sum() for g in range(n)]else:b = [c2] + [0] * na = np.eye(n + 1, n, k=-1)a -= np.roll(a, 1, axis=1)a *= np.array(k) ** 2a[0] = 1c_ = np.linalg.lstsq(a, b, rcond=None)[0].round()self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.Conv2d(c1, int(c_), k, s, k // 2, groups=math.gcd(c1, int(c_)), bias=False) for k, c_ in zip(k, c_)])self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)self.act = nn.SiLU()def forward(self, x):return self.act(self.bn(torch.cat([m(x) for m in self.m], 1)))class Ensemble(nn.ModuleList):def __init__(self):super().__init__()def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):y = [module(x, augment, profile, visualize)[0] for module in self]y = torch.cat(y, 1)return y, Nonedef attempt_load(weights, device=None, inplace=True, fuse=True):from models.yolo import Detect, Modelmodel = Ensemble()for w in weights if isinstance(weights, list) else [weights]:ckpt = torch.load(attempt_download(w), map_location='cpu')ckpt = (ckpt.get('ema') or ckpt['model']).to(device).float()if not hasattr(ckpt, 'stride'):ckpt.stride = torch.tensor([32.])if hasattr(ckpt, 'names') and isinstance(ckpt.names, (list, tuple)):ckpt.names = dict(enumerate(ckpt.names))model.append(ckpt.fuse().eval() if fuse and hasattr(ckpt, 'fuse') else ckpt.eval())for m in model.modules():t = type(m)if t in (nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6, nn.SiLU, Detect, Model):m.inplace = inplaceif t is Detect and not isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list):delattr(m, 'anchor_grid')setattr(m, 'anchor_grid', [torch.zeros(1)] * m.nl)elif t is nn.Upsample and not hasattr(m, 'recompute_scale_factor'):m.recompute_scale_factor = Noneif len(model) == 1:return model[-1]print(f'Ensemble created with {weights}\n')for k in 'names', 'nc', 'yaml':setattr(model, k, getattr(model[0], k))model.stride = model[torch.argmax(torch.tensor([m.stride.max() for m in model])).int()].strideassert all(model[0].nc == m.nc for m in model), f'Models have different class counts: {[m.nc for m in model]}'return model
这个程序文件是YOLOv5的实验模块。它包含了一些实验性的模型和功能。
文件中定义了以下几个类:
-
Sum:实现了多个层的加权求和。可以选择是否应用权重。
-
MixConv2d:实现了混合的深度卷积。可以选择是否在每个组中使用相同数量的通道。
-
Ensemble:模型的集合。可以将多个模型组合在一起。
文件还定义了一个辅助函数attempt_load,用于加载模型权重。可以加载单个模型或多个模型的集合。
这个程序文件是YOLOv5的一部分,用于实现一些实验性的模型和功能。
6.系统整体结构
整体功能和构架概述:
该系统是一个基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统。它包含了多个模块和文件,用于数据处理、模型训练、模型推理和结果可视化等功能。主要的模块包括分类模块和分割模块,分别用于香菇的分类和图像分割任务。
下面是每个文件的功能概述:
| 文件名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| export.py | 导出模型的辅助函数和导出函数 |
| ui.py | 图形用户界面程序,用于运行模型进行目标检测并显示结果 |
| val.py | 在验证集上进行模型评估的辅助函数和评估函数 |
| classify/predict.py | 分类模型的推理函数 |
| classify/train.py | 分类模型的训练函数 |
| classify/val.py | 在验证集上进行分类模型评估的辅助函数和评估函数 |
| models/common.py | 通用的模型定义和函数 |
| models/experimental.py | 实验性的模型定义和函数 |
| models/tf.py | TensorFlow模型定义和函数 |
| models/yolo.py | YOLO模型定义和函数 |
| models/init.py | 模型初始化文件 |
| segment/predict.py | 分割模型的推理函数 |
| segment/train.py | 分割模型的训练函数 |
| segment/val.py | 在验证集上进行分割模型评估的辅助函数和评估函数 |
| utils/activations.py | 激活函数定义和函数 |
| utils/augmentations.py | 数据增强函数 |
| utils/autoanchor.py | 自动锚框计算函数 |
| utils/autobatch.py | 自动批处理函数 |
| utils/callbacks.py | 回调函数定义和函数 |
| utils/dataloaders.py | 数据加载函数 |
| utils/downloads.py | 数据下载函数 |
| utils/general.py | 通用的辅助函数 |
| utils/loss.py | 损失函数定义和函数 |
| utils/metrics.py | 模型评估指标函数 |
| utils/plots.py | 结果可视化函数 |
| utils/torch_utils.py | PyTorch相关的辅助函数 |
| utils/triton.py | Triton Inference Server相关的函数 |
| utils/init.py | 工具函数初始化文件 |
| utils/aws/resume.py | AWS相关的恢复函数 |
| utils/aws/init.py | AWS初始化文件 |
| utils/flask_rest_api/example_request.py | Flask REST API示例请求函数 |
| utils/flask_rest_api/restapi.py | Flask REST API相关的函数 |
| utils/loggers/init.py | 日志记录器初始化文件 |
| utils/loggers/clearml/clearml_utils.py | ClearML日志记录器相关的函数 |
| utils/loggers/clearml/hpo.py | ClearML超参数优化函数 |
| utils/loggers/clearml/init.py | ClearML初始化文件 |
| utils/loggers/comet/comet_utils.py | Comet日志记录器相关的函数 |
| utils/loggers/comet/hpo.py | Comet超参数优化函数 |
| utils/loggers/comet/init.py | Comet初始化文件 |
| utils/loggers/wandb/log_dataset.py | WandB日志记录器相关的函数 |
| utils/loggers/wandb/sweep.py | WandB超参数优化函数 |
| utils/loggers/wandb/wandb_utils.py | WandB工具函数 |
| utils/loggers/wandb/init.py | WandB初始化文件 |
| utils/segment/augmentations.py | 分割模型的数据增强函数 |
| utils/segment/dataloaders.py | 分割模型的数据加载函数 |
| utils/segment/general.py | 分割模型的通用辅助函数 |
| utils/segment/loss.py | 分割模型的损失函数定义和函数 |
| utils/segment/metrics.py | 分割模型的评估指标函数 |
| utils/segment/plots.py | 分割模型的结果可视化函数 |
| utils/segment/init.py | 分割模型初始化文件 |
7.鲜香菇主要形貌特征
本章首先对鲜香菇的分级标准进行分析,选定分级指标,然后对鲜香菇物料参数进行测定和统计分析。在设计鲜香菇分级系统时,物料特性是相关机械结构设计的重要参数,通过对鲜香菇物料特性的了解,有利于分析力学特性和机械损伤特性,减少鲜香菇损伤,使机械装置能更好地满足性能要求。为保证鲜香菇分级的严谨性和准确性,对相关农业标准、行业标准以及企业标准进行对比分析并确定适用于本研究的鲜香菇等级评价指标。试验测定鲜香菇质量、含水率、菇帽直径(大小)、菇柄直径和摩擦特性等物理特性参数,并进行统计分析,为鲜香菇分级系统的主要部件设计提供数据支持。
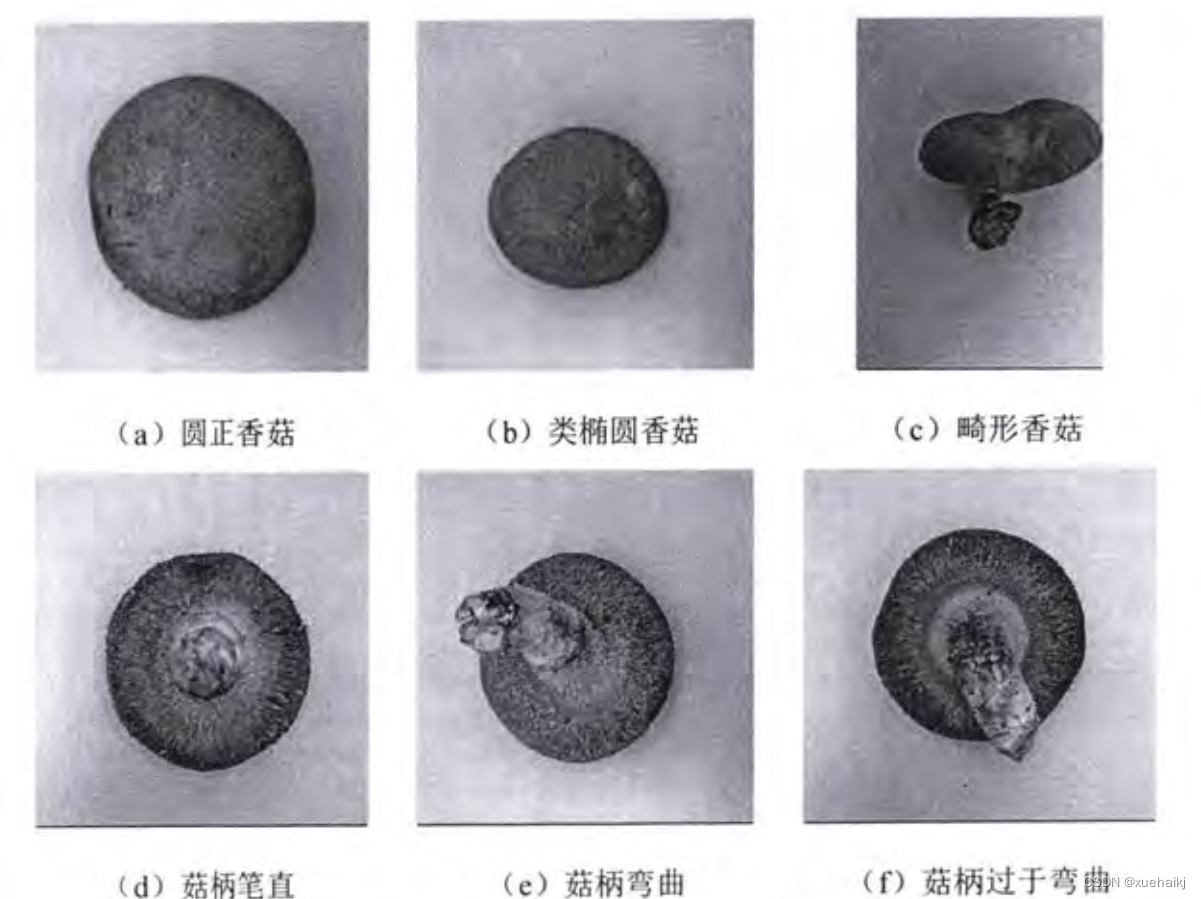
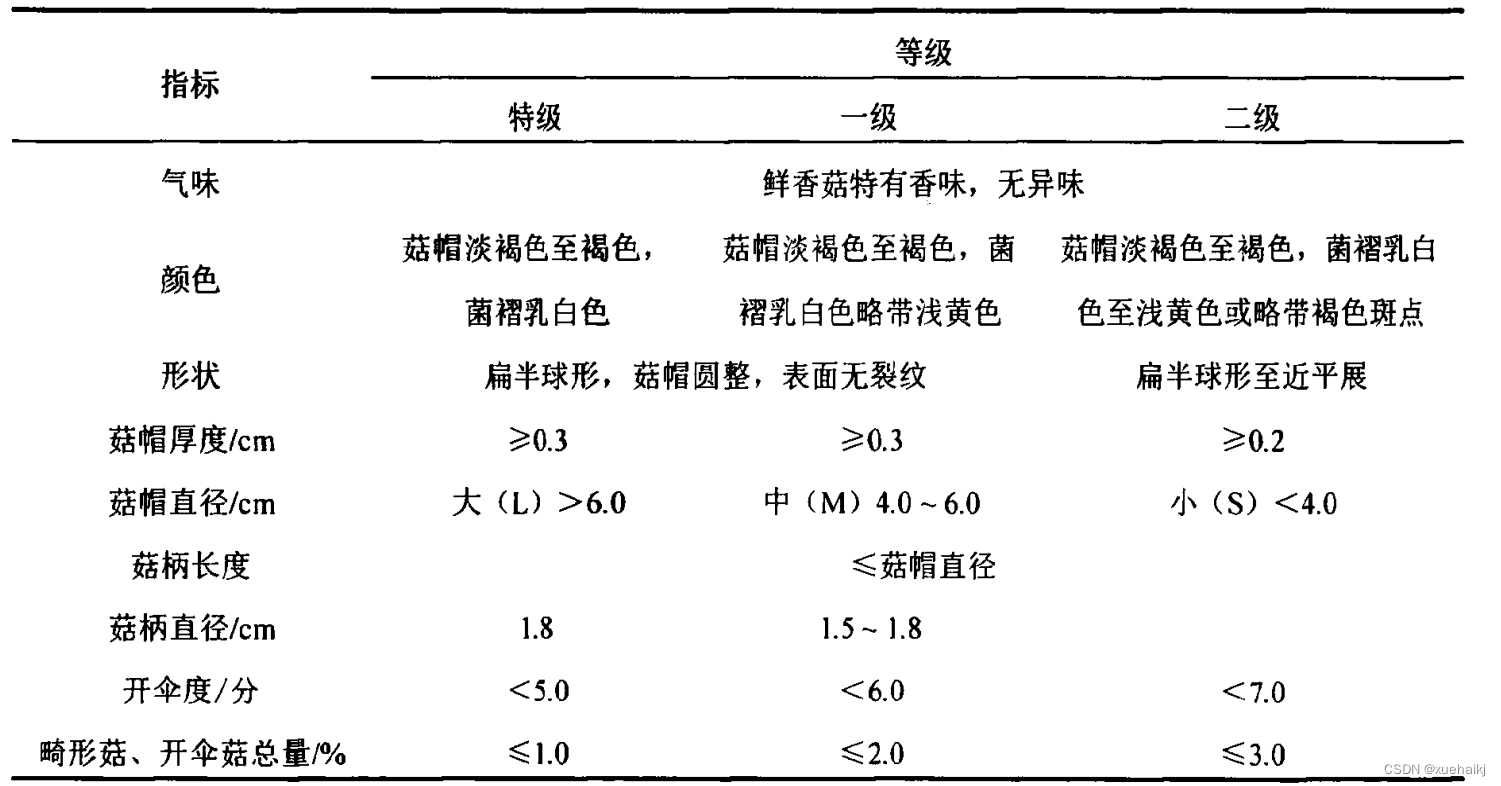
受生长环境影响,出菇时香菇菇帽形状大小不一,有圆正、类椭圆以及畸形等情况,菇柄也有笔直、弯曲以及过于弯曲等情况,如图2-1所示。
(a)圆正香菇
(b)类椭圆香菇
(c)畸形香菇
( d)菇柄笔直
(e)菇柄弯曲
(f)菇柄过于弯曲

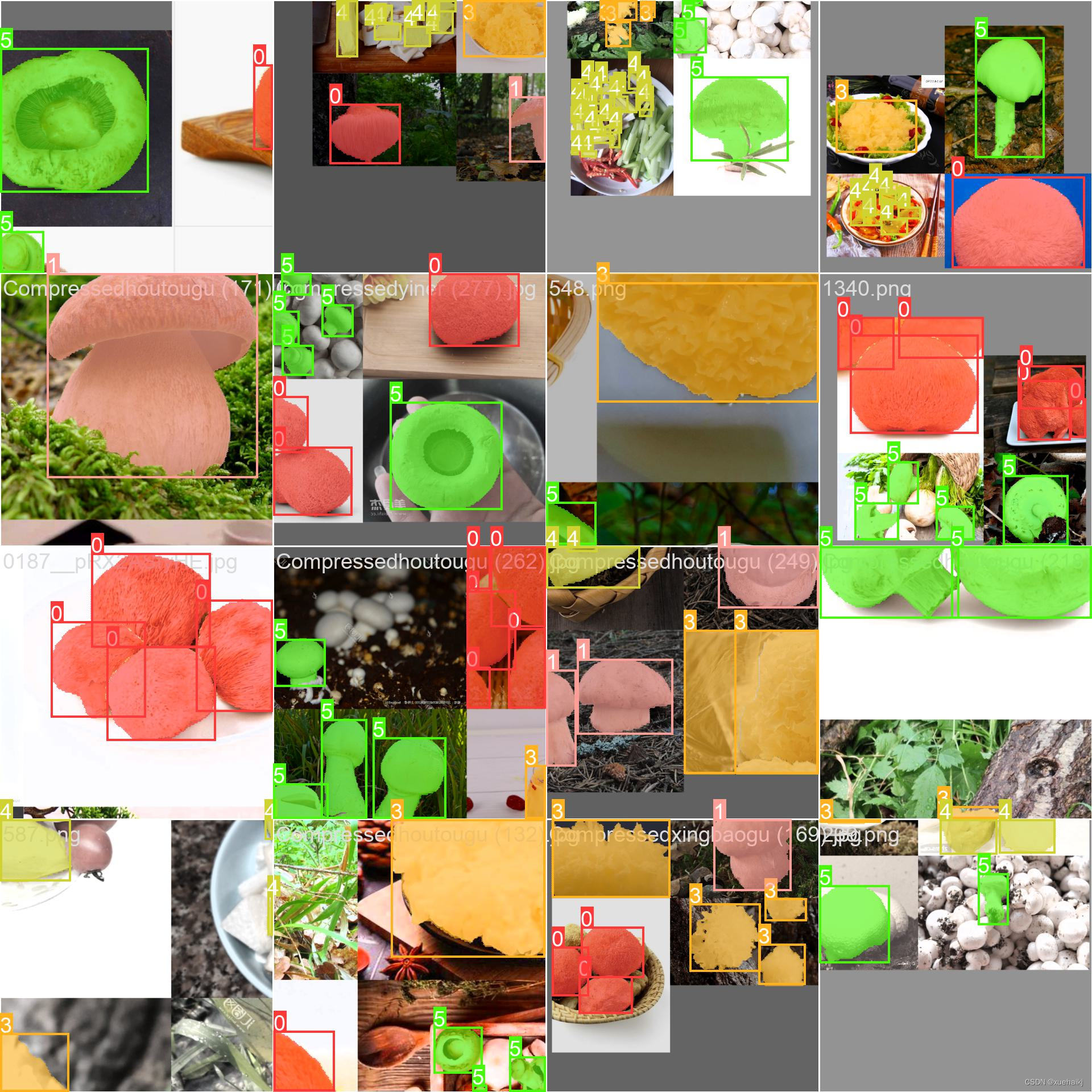
鲜香菇分级标准
不同标准对鲜香菇的评判指标既存在重复交叉也存在差别,对比分析鲜香菇等级规格划分的不同标准,有助于深入了解鲜香菇的分级标准体系。选择NY/T 1061-2006香菇等级规格lS7)、GH/T 1013-2015香菇[58进行对比分析,2种标准的等级指标分别如表所示。
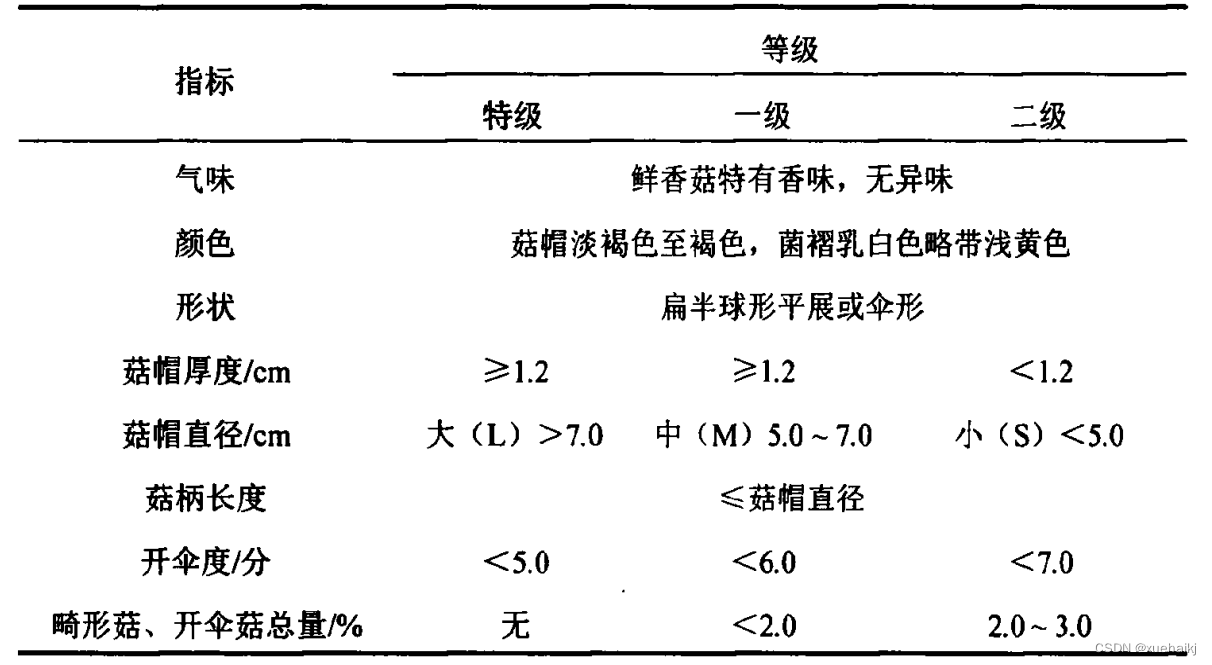
由表可知,鲜香菇在气味、菇柄长度和开伞度3个指标中的要求是相同的,在颜色、形状、菇帽直径(大小)、畸形菇和开伞菇总量5个指标中的要求略有差异,但差异不大,而在菇帽厚度的要求上则差别较大。气味是香菇品质的一个重要特征,但气味的检测需要在密闭环境中进行且需要静置等待鲜香菇气味散发[例;菇帽厚度与菇柄长度从鲜香菇正反面都无法体现,需从侧面才能进行检测。鲜香菇气味、菇帽厚度及菇柄长度的检测会导致检测时间与成本增加,并增大机具结构,而颜色、形状、菇帽直径(大小)和开伞度可以通过正反面得到很好的检测,且鲜香菇是否有畸形能从形状中检测出来。因此,选取颜色、形状、菇帽直径(大小)和开伞度4个指标作为鲜香菇等级评价指标。
8.超参数设置与贝叶斯优化
网络训练前,指定部分训练选项并设置对应超参数,选择带动量的随机梯度下降算法作为模型的优化器,最大训练轮数设置为12,小批量大小为81,总共进行420次迭代训练。学习率调整策略采用分段式常数衰减法,也称步衰减法,即每经过指定的迭代次数,初始学习率将乘以一个衰减系数r(0<n<1)来进行学习率的更新。设置每经过3轮训练学习率乘以衰减系数0.1进行更新,每一轮训练与验证前对数据进行打乱,验证频率为1,使用GPU加速模型的训练与验证过程。
模型的训练过程包括鲜香菇特征提取的前向传播过程,即根据输入图像计算预测输出的过程;参数更新的反向传播过程,即根据实际输出与期望输出的误差,反向传播计算梯度更新各层参数。通过正向传播与反向传播的迭代循环训练,使损失函数值达到最小。
要训练深度神经网络,必须指定网络结构以及训练算法的选项,往往依据经验来选择及调整超参数会很困难并且需要时间。而学习率又是非常重要的需要首先调整的超参数,面对不同数据集、不同优化方式、不同批大小,其最适合的值无法凭借经验确定,学习率设置太大,网络训练振荡甚至无法正常训练,太小则网络训练缓慢,训练时间长久,只用通过不断的试验训练才能找到最适合当前状态的学习率。
自动调参方法可以解决手动调参耗时的问题,自动调参常用算法有网格搜索(Grid Search)、随机搜索(Random Search)和贝叶斯优化(Bayesian Optimization),相比于网格搜索和随机搜索,贝叶斯优化是一种更高效且非常适合对分类模型和回归模型的超参数进行优化的算法6,能够在最少数量的目标函数评估下得到复杂函数最优解。
因此,将利用迁移学习方法快速构建用于鲜香菇等级分类识别的网络模型,同时应用贝叶斯优化算法确定超参数初始学习率、动量和L2正则化系数的最优组合,降低训练难度。
9.训练结果可视化分析
评价指标
Epoch:训练迭代次数。
训练损失:训练过程中的框损失、分割损失、对象损失和类别损失。
训练指标:不同 IoU 阈值下框 (B) 和掩模 (M) 检测的精度、召回率和平均精度 (mAP)。
验证损失:验证过程中的框损失、分割损失、对象损失和类损失。
学习率:网络中不同层或阶段的学习率。
训练结果可视化
为了更好地分析这些数据,我首先将进行数据可视化训练,以显示这些指标随过程的变化。可视化将包括损失函数的变化趋势和性能指标的变化趋势。这将有助于我们理解模型在过程中的表现,以及何时达到了最佳性能。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Setting up the plot configuration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 12))# Subplot for training loss components
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['train/box_loss'], label='Box Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['train/seg_loss'], label='Segmentation Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['train/obj_loss'], label='Object Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['train/cls_loss'], label='Class Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss Components')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()# Subplot for validation loss components
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['val/box_loss'], label='Box Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['val/seg_loss'], label='Segmentation Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['val/obj_loss'], label='Object Loss')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['val/cls_loss'], label='Class Loss')
plt.title('Validation Loss Components')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()# Subplot for metrics for "B" (assuming B stands for a certain category in the data)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/precision(B)'], label='Precision')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/recall(B)'], label='Recall')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/mAP_0.5(B)'], label='mAP@0.5')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/mAP_0.5:0.95(B)'], label='mAP@0.5:0.95')
plt.title('Performance Metrics for Category B')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Metric Value')
plt.legend()# Subplot for metrics for "M" (assuming M stands for another category in the data)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/precision(M)'], label='Precision')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/recall(M)'], label='Recall')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/mAP_0.5(M)'], label='mAP@0.5')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['metrics/mAP_0.5:0.95(M)'], label='mAP@0.5:0.95')
plt.title('Performance Metrics for Category M')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Metric Value')
plt.legend()# Subplot for learning rates
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['x/lr0'], label='LR0')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['x/lr1'], label='LR1')
plt.plot(data['epoch'], data['x/lr2'], label='LR2')
plt.title('Learning Rates')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.legend()plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()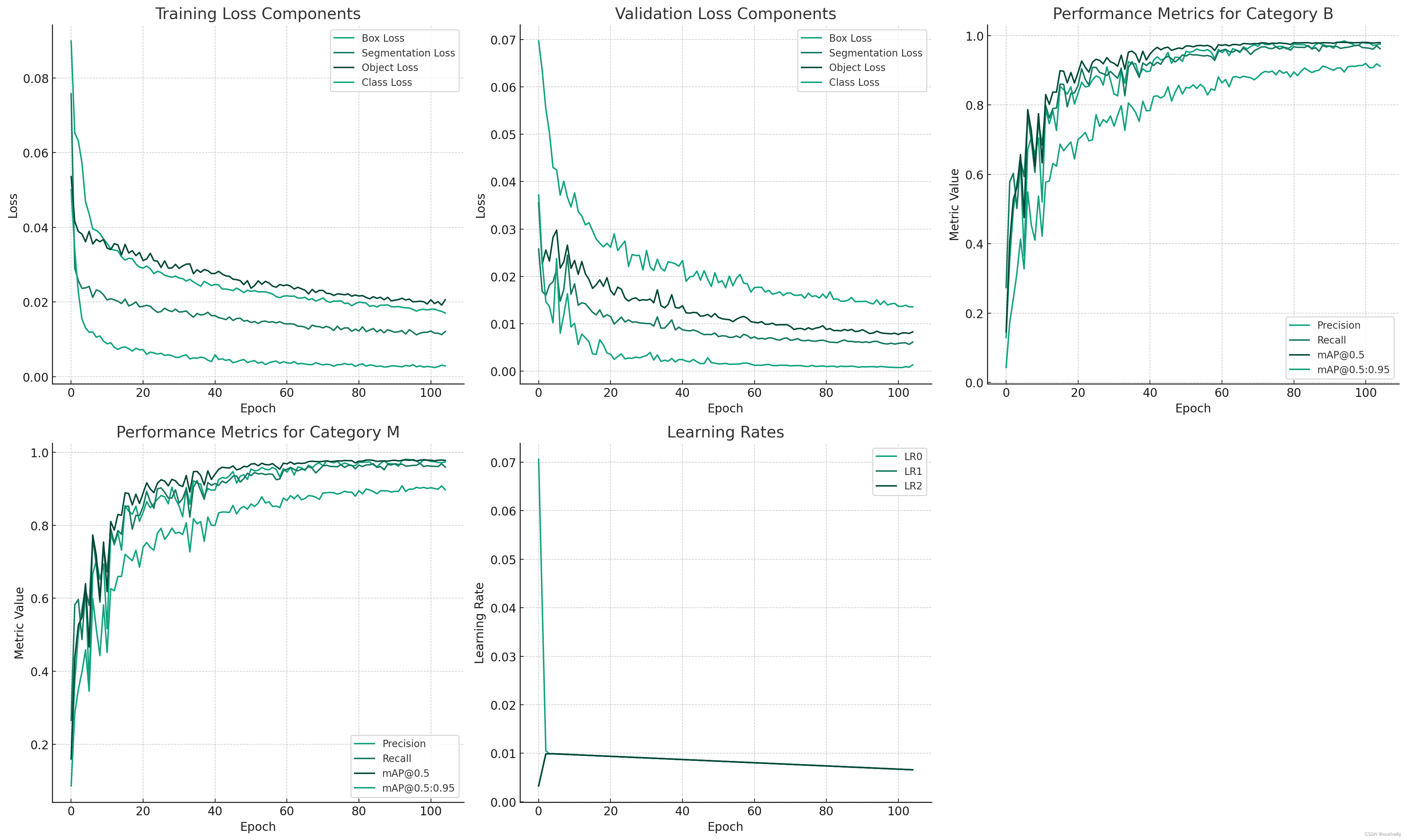
在完成可视化之后,我将根据这些图表进行详细的数据分析,探讨模型性能的关键方面和潜在的改进空间。这将包括对模型收敛性的评估、表面过或欠表面的结构,以及性能指标的详细分析。
训练和验证损失
框损失:表示模型预测蘑菇周围边界框的效果。这种损失的下降趋势表明在图像中定位蘑菇的准确性有所提高。
分割损失:反映模型准确分割蘑菇的能力。这种损失的下降表明分割性能更好。
对象和类损失:指示模型检测蘑菇(对象损失)和对它们进行分类(类损失)的效果。这些损失的减少表明检测和分类能力更好。
准确率和召回率
框 (B):框检测的精度和召回率提供了对模型检测蘑菇的准确性和完整性的见解。更高的精确率意味着更少的误报,而更高的召回率意味着更少的误报。
Mask (M):与框检测类似,但用于分割。这些指标显示了模型对蘑菇进行分割的精确度和完整性。
平均精度 (mAP)
Box (B) 和 Mask (M) mAP:这些指标将精确度和召回率结合到一个测量中。不同 IoU 阈值(0.5 和 0.5:0.95)下的 mAP 值可以深入了解模型在不同严格程度的检测和分割方面的整体性能。
学习率
LR0、LR1 和 LR2:网络不同层或阶段的学习率变化。这些趋势可以表明学习率的调整如何影响模型的学习过程。
主要观察和分析
学习效率:该模型在检测和分割任务方面都显示出稳步改进,如所有类型损失的下降趋势所示。
检测与分割:比较框和掩模的精度和召回率,似乎该模型在一项任务上可能比另一项任务更好。例如,如果掩模的精确度和召回率始终较高,则模型的分割能力更好。
精确率和召回率之间的平衡:平衡精确率和召回率至关重要。过度关注精确度的模型可能会错过真阳性(低召回率),而专注于召回率的模型可能会包含太多假阳性(低精确度)。
mAP 评估:mAP 值,尤其是 mAP_0.5:0.95,对于理解模型的稳健性至关重要。该指标考虑了预测和真实边界框或分割掩模之间不同程度的重叠。
学习率调整的影响:结合损失和准确性指标观察学习率趋势可以揭示学习率策略的有效性。例如,学习率变化后指标的显着改善表明调整成功。
10.系统整合
下图完整源码&数据集&环境部署视频教程&自定义UI界面

参考博客《基于OpenCV和改进深度学习网络的香菇分级图像分割系统》
11.参考文献
[1]杨森,冯全,张建华,等.基于轻量卷积网络的马铃薯外部缺陷无损分级[J].食品科学.2021,(10).DOI:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200412-155 .
[2]周伟亮,王红军,邹湘军.基于机器视觉的荔枝品质快速自动检测[J].中国农机化学报.2020,(1).DOI:10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2020.01.26 .
[3]张瑞青,李张威,郝建军,等.基于迁移学习的卷积神经网络花生荚果等级图像识别[J].农业工程学报.2020,(23).DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.23.020 .
[4]朱云,凌志刚,张雨强.机器视觉技术研究进展及展望[J].图学学报.2020,(6).DOI:10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2020060871 .
[5]王立扬,张瑜,沈群,等.基于改进型LeNet-5的苹果自动分级方法[J].中国农机化学报.2020,(7).DOI:10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2020.07.016 .
[6]薛勇,王立扬,张瑜,等.基于GoogLeNet深度迁移学习的苹果缺陷检测方法[J].农业机械学报.2020,(7).DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.07.004 .
[7]闫彬,杨福增,郭文川.基于机器视觉技术检测裂纹玉米种子[J].农机化研究.2020,(5).DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2020.05.031 .
[8]李颀,胡家坤.基于机器视觉的苹果在线分级[J].食品与机械.2020,(8).DOI:10.13652/ji.ssn.1003-5788.2020.08.022 .
[9]许景辉,邵明烨,王一琛,等.基于迁移学习的卷积神经网络玉米病害图像识别[J].农业机械学报.2020,(2).DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.02.025 .
[10]陈林琳,姜大庆,黄菊,等.基于机器视觉的火龙果自动分级系统设计[J].农机化研究.2020,(5).DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2020.05.022 .




)

覆盖优化 - 附代码)












)