文章目录
- Format介绍
- Format方法
- - format(格式化)
- - parseObject(解析)
- 格式化分类
- 日期时间格式化
- 1. DateFormat
- 常用方法
- getInstance
- getDateInstance
- getTimeInstance
- getDateTimeInstance
- 方法入参
- style
- Locale
- 2. SimpleDateFormat
- 常用模式元素
- 使用方法
- 格式化
- 解析
- 3. ClassicFormat
- 数字格式化
- 1. NumberFormat
- 常用方法
- getInstance
- getNumberInstance
- getIntegerInstance
- getPercentInstance
- getCurrencyInstance
- 方法示例
- 2. DecimalFormat
- 手动设置模式
- 使用模式符号串
- 使用方法
- 格式化
- 解析
- 3. ChoiceFormat
- 常用方法
- nextDouble(double d)
- nextDouble(double d, boolean positive)
- previousDouble(double d)
- ChoiceFormat(double[] limits, String[] formats)
- ChoiceFormat(String newPattern)
- 占位符
- 字符串格式化
- 1. MessageFormat
- 模式元素
- 格式化类型
- 格式化样式
- 使用示例
- 2. String.format
- format参数
- 模块
- 标识
- 转换符
Format介绍
java.text.Format是Java格式化的抽象基类。主要用于将对象格式化为指定模式的字符串,或者将指定模式的字符串解析为对象。
Format方法
- format(格式化)
格式化:对象格式化为字符串。
-
public final String format (Object obj)
public final String format (Object obj) {return format(obj, new StringBuffer(), new FieldPosition(0)).toString(); }一般使用此方法来将对象格式化为字符串,该方法为不可变方法,方法内部调用抽象方法的具体子类实现。
-
public abstract StringBuffer format(Object obj, StringBuffer toAppendTo, FieldPosition pos)
抽象方法,子类必须实现该方法,定义子类自己具体的对象格式化为字符串的逻辑。
- parseObject(解析)
解析:字符串解析为对象。
-
public Object parseObject(String source) throws ParseException
public Object parseObject(String source) throws ParseException {ParsePosition pos = new ParsePosition(0);Object result = parseObject(source, pos);if (pos.index == 0) {throw new ParseException("Format.parseObject(String) failed",pos.errorIndex);}return result; }一般使用此方法来将字符串解析为对象,该方法为不可变方法,方法内部调用抽象方法的具体子类实现。
-
public abstract Object parseObject (String source, ParsePosition pos)
抽象方法,子类必须实现该方法,定义子类自己具体的字符串解析为对象的逻辑。
格式化分类
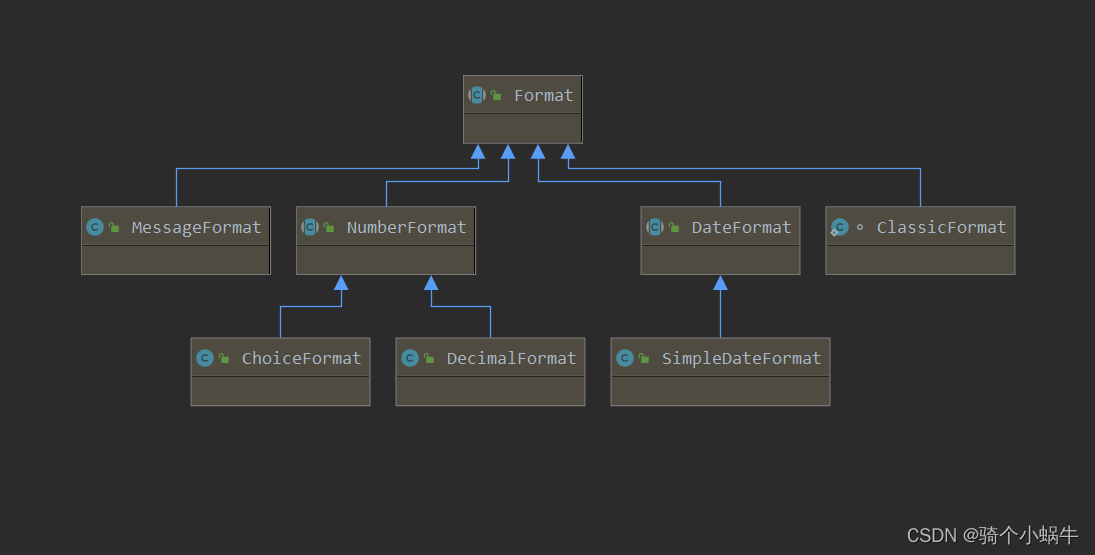
| 格式化分类 | 格式化类 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 日期时间格式化 | DateFormat | 格式化日期时间的抽象类 |
| SimpleDateFormat | DateFormat的实现类,用于格式化和解析日期时间,非线程安全 | |
| ClassicFormat | DateTimeFormatter的内部类,提供日期时间的格式化和解析 | |
| 数字格式化 | NumberFormat | 格式化数字的抽象类 |
| DecimalFormat | NumberFormat的实现类,提供数字格式化和解析 | |
| ChoiceFormat | NumberFormat的实现类,可以根据特定的值范围来选择相应的格式 | |
| 字符串格式化 | MessageFormat | 用于字符串格式化的类。它可以将带有占位符的模板字符串和对应的参数值进行格式化 |
| String | String类的format方法用于字符串的格式化 |
日期时间格式化
1. DateFormat
日期格式化抽象类,根据当前语言环境格式化日期和时间。
因为DateFormat是一个抽象类,所以不能直接new创建实例对象。但DateFormat提供了一些静态方法便于我们构建DateFormat子类的实例。
常用方法
getInstance
获取格式化的日期时间
- getInstance():输出样式:22-8-30 下午4:14
getDateInstance
获取格式化的日期
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getDateInstance() | 输出样式:2022-8-30 |
| getDateInstance(int style) | 指定样式 |
| getDateInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) | 指定样式和语言环境 |
getTimeInstance
获取格式化的时间
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getTimeInstance() | 输出样式:16:14:32 |
| getTimeInstance(int style) | 指定样式 |
| getTimeInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) | 指定样式和语言环境 |
getDateTimeInstance
获取格式化的日期时间
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getDateTimeInstance() | 输出样式:2022-8-30 16:14:32 |
| getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle) | 指定样式 |
| getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle, Locale aLocale) | 指定样式和语言环境 |
方法入参
style
设置输出样式。
DateFormat提供了多种输出样式:
/*** 完整样式*/public static final int FULL = 0;/*** 长样式*/public static final int LONG = 1;/*** 中等样式*/public static final int MEDIUM = 2;/*** 短样式*/public static final int SHORT = 3;/*** 默认样式:中等样式*/public static final int DEFAULT = MEDIUM;
| 样式 | 输出格式(日期Date) | 输出格式(时间Time) |
|---|---|---|
| SHORT | 22-8-30 | 下午4:03 |
| MEDIUM DEFAULT | 2022-8-30 | 16:03:06 |
| LONG | 2022年8月30日 | 下午04时03分06秒 |
| FULL | 2022年8月30日 星期二 | 下午04时03分06秒 CST |
Locale
设置语言环境。
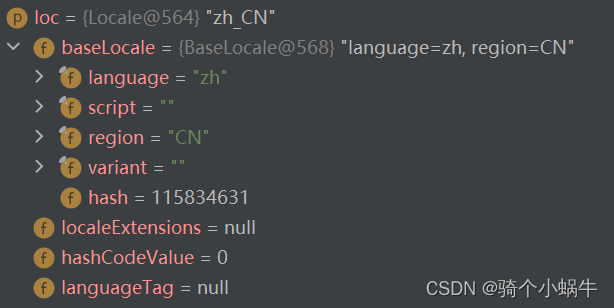
- language:语言(zh:中文)
- region:地区(CN:China)
2. SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat是DateFormat的一个具体实现类,是非线程安全的。
因为DateFormat直接支持的样式比较少,经常满足不了实际需求,于是SimpleDateFormat就来了,SimpleDateFormat提供了丰富的样式且可自定义样式。
在使用SimpleDateFormat的时候,需要通过字母来描述时间元素,并组装成想要的日期和时间模式。
常用模式元素
常用的日期时间元素和字母的对应表如下:
| 字母 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| G | 年代标志符(公元、公元前) | AD、BC |
| y | 年 | 2015 |
| Y | 周年 | 2016 |
| M | 年中的月份 | 12 |
| w | 年中的周数 | 50 |
| W | 月份中的周数 | 02 |
| D | 年中的天数 | 344 |
| d | 月份中的天数 | 10 |
| F | 月份中的星期 | 02 |
| E | 周中的天数(星期几) | Thu |
| u | 周中的天数(第几天,星期一=1,星期日=7) | 1 |
| a | AM/PM标记 | AM、PM、上午、下午 |
| H | 一天中的小时数(0~23) | 21 |
| k | 一天中的小时数(1~24) | 21 |
| K | AM/PM中的小时数(0~11) | 09 |
| h | AM/PM中的小时数(1~12) | 09 |
| m | 小时中的分钟数 | 31 |
| s | 分钟中的秒数 | 08 |
| S | 毫秒数 | 716 |
| z | 时区 | CST |
| Z | 时区(RFC 822标准时区) | +0800 |
| X | 时区(ISO 8601标准时区) | +08 |
y与Y的区别:
- YY是周年
- yy是日历年,推荐使用y
举例:今天是2019年12月30日,日历年是 2019,但周年是 2020,因为本周是 2020 年的第 1 周。所以yy是19,而YY是20。
使用方法
格式化
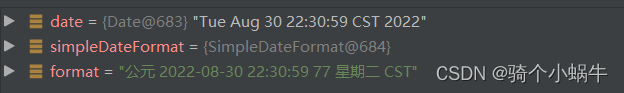
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {Date date = new Date();SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("G yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss S E z");String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
}
debug:
解析
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {String str = "公元 2022-08-30 22:10:03 530 星期二 CST";SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("G yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss S E z");Date date1 = (Date) simpleDateFormat.parseObject(str);
}
debug:

3. ClassicFormat
暂不分析。
数字格式化
1. NumberFormat
数字格式化抽象类,根据当前语言环境格式化数字。
NumberFormat是一个抽象类,不能直接new创建实例对象。NumberFormat提供了一些静态方法便于我们构建NumberFormat子类的实例。
常用方法
getInstance
获取格式化的常规数值
- getInstance()
- getInstance(Locale inLocale)
getNumberInstance
获取格式化的常规数值
- getNumberInstance()
- getNumberInstance(Locale inLocale)
getIntegerInstance
获取格式化的整型数值
- getIntegerInstance()
- getIntegerInstance(Locale inLocale)
getPercentInstance
获取格式化的百分比数值
- getPercentInstance()
- getPercentInstance(Locale inLocale)
getCurrencyInstance
获取格式化的指定语言环境的货币数值
- getCurrencyInstance()
- getCurrencyInstance(Locale inLocale)
方法示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {NumberFormat instance = NumberFormat.getInstance();String format = instance.format(2.3);System.out.println("getInstance=====================" + format);NumberFormat integerInstance = NumberFormat.getIntegerInstance();String format1 = integerInstance.format(2.3);System.out.println("getIntegerInstance==============" + format1);NumberFormat percentInstance = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();String format2 = percentInstance.format(2.3);System.out.println("getPercentInstance==============" + format2);NumberFormat currencyInstance = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();String format3 = currencyInstance.format(2.3);System.out.println("getCurrencyInstance=============" + format3);NumberFormat currencyInstance1 = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.US);String format4 = currencyInstance1.format(2.3);System.out.println("getCurrencyInstance(Locale.US)==" + format4);
}
控制台日志:
getInstance=====================2.3
getIntegerInstance==============2
getPercentInstance==============230%
getCurrencyInstance=============¥2.30
getCurrencyInstance(Locale.US)==$2.30
2. DecimalFormat
DecimalFormat是NumberFormat的一个具体子类,用于格式化十进制数字。
DecimalFormat能够分析和格式化任意语言环境中的数字:
- 包括对西方语言、阿拉伯语和印度语数字的支持。
- 支持整数 (123)、定点数 (123.4)、科学记数法表示的数 (1.23E4)、百分数 (12%) 和金额 ($123)等。
- 所有的内容都可以本地化(本地化:使用本地的语言环境)。
需要注意的是:DecimalFormat是非线程安全的。
DecimalFormat支持手动配置模式和使用模式符号。
手动设置模式
- setMaximumFractionDigits(int newValue):设置小数部分中允许的最大数字位数
- setMinimumFractionDigits(int newValue):设置小数部分中允许的最小数字位数,如果原数小数位数不够的话,会补零。
- setGroupingSize(int i):设置分组中一组的位数(整数部分,默认3个数字为一组)。
- setGroupingUsed(boolean value):设置是否使用分组,true表示使用,false表示取消分组
- setMaximumIntegerDigits(int newValue):设置整数部分允许的最大数字位数
- setMinimumIntegerDigits(int newValue):设置整数部分允许的最小数字位数
使用模式符号串
| 符号 | 位置 | 是否本地化 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 数字 | 是 | 阿拉伯数字,位数不足时补0 |
| # | 数字 | 是 | 阿拉伯数字,位数不足时不管 |
| . | 数字 | 是 | 小数分隔符或货币小数分隔符 |
| - | 数字 | 是 | 减号 |
| , | 数字 | 是 | 分组分隔符 |
| E | 数字 | 是 | 分隔科学计数法中的尾数和指数 |
| ; | 子模式边界 | 是 | 分隔正数和负数子模式 分号前是正常模式,分号后是负数输入的的输出前缀 - 如果输入为正数,输出:正常模式的结果 - 如果输入为正数,输出:负数的前缀+正常模式的结果的绝对值 |
| % | 前缀或后缀 | 是 | 乘以100并显示为百分数 |
| \u2030 | 前缀或后缀 | 是 | 乘以1000并显示为千分数 |
| ¤(\u00A4) | 前缀或后缀 | 否 | 货币记号,由货币符号替换。 如果同时出现两个该符号,则用国际货币符号替换。 如果出现在某个模式中,则使用货币小数分隔符,而不使用小数分隔符。 |
| ' | 前缀或后缀 | 否 | 用于在前缀或后缀中为特殊字符加引号,使特殊符号变为普通字符(如要创建单引号本身,请连续使用两个单引号)。 例如:"'#'#" 将123格式化为 "#123" |
使用方法
格式化
① 手动配置模式
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {DecimalFormat decimalFormat = new DecimalFormat();decimalFormat.setGroupingUsed(true);// 使用分组decimalFormat.setGroupingSize(4);// 分组中一组的位数decimalFormat.setMinimumIntegerDigits(2);// 整数部分最小位数decimalFormat.setMaximumIntegerDigits(8);// 整数部分最大位数decimalFormat.setMinimumFractionDigits(2);// 小数部分最小位数decimalFormat.setMaximumFractionDigits(4);// 小数部分最大位数System.out.println(decimalFormat.format(1.11));// 01.11System.out.println(decimalFormat.format(11111.222));// 1,1111.222System.out.println(decimalFormat.format(11111111111.222222222222));// 1111,1111.2222}
② 使用模式符号串
public static void main(String[] args){double pi = 3.1415926;// 取整数部分,整数部分不足2位补0System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("00").format(pi));// 03// 取整数部分和10位小数,整数部分不足2位补0,小数部分不足10位补0System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("00.0000000000").format(pi));// 03.1415926000// 取整数部分,整数部分不足2位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("##").format(pi));// 3// ###和上面的##没区别System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("###").format(pi));// 3// 取整数部分和10位小数,整数部分不足2位不管,小数部分不足10位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("##.##########").format(pi));// 3.1415926// 若输入为非负数,按;前面的正常模式输出// 若输入为负数,按;后面的(负数输入的输出前缀+正常模式输出的绝对值)输出System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##;前缀").format(3.1415926));// 3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##;前缀").format(-3.1415926));// 前缀3.14// 百分比方式计数(百分号在末位),取整数部分和2位小数,小数部分不足2位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##%").format(pi));// 314.16%// 百分比方式计数(百分号在首位),取整数部分和2位小数,小数部分不足2位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("%#.##").format(pi));// %314.16// 千分比方式计数(千分号在末位),取整数部分和2位小数,小数部分不足2位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##\u2030").format(pi));// 3141.59‰// 千分比方式计数(千分号在首位),取整数部分和2位小数,小数部分不足2位不管System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("\u2030#.##").format(pi));// ‰3141.59//显示为科学计数法,并取五位小数System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.#####E0").format(pi));// 3.14159E0//显示为两位整数的科学计数法,并取四位小数System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("00.####E0").format(pi));// 31.4159E-1//取整数部分,每三位以逗号进行分隔。System.out.println(new DecimalFormat(",###").format(pi));// 3// 添加货币符号在首位,如果同时出现两个该符号,则用国际货币符号System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("¤#.##").format(pi));// ¥3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("\u00A4#.##").format(pi));// ¥3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("¤¤#.##").format(pi));// CNY3.14// 添加货币符号在末位,如果同时出现两个该符号,则用国际货币符号System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##¤").format(pi));// 3.14¥System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##\u00A4").format(pi));// 3.14¥System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##¤¤").format(pi));// 3.14CNY// 将特殊字符变为普通字符System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("''#.##").format(pi));// '3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##''").format(pi));// 3.14'System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("'#'#.##").format(pi));// #3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##'#'").format(pi));// 3.14#//将格式嵌入文本System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("圆周率π:#.##").format(pi));// 圆周率π:3.14}
解析
解析也可以手动配置模式或者使用模式符号串,这里只以使用模式符号串方式举例。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("圆周率π:#.##").parseObject("圆周率π:3.14"));// 3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##;前缀").parseObject("前缀3.14"));// -3.14System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("00.####E0").parseObject("31.4159E-1"));// 3.14159}
3. ChoiceFormat
ChoiceFormat将格式化运用到某个范围的数。
ChoiceFormat与其他Format类的不同之处在于,它使用构造函数放入方式(而不是使用getInstance样式工厂方法)创建ChoiceFormat对象。
注意:limits数组需要升序排列(否则结果会出错)
常用方法
nextDouble(double d)
查找大于d的最小double值,一般用在limits数组中,从而使limits数组形成一个右开区间数组
例如:limits = {0,1,ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(1)}
nextDouble(double d, boolean positive)
- positive=true,表示查找大于d的最小double值,一般用在limits数组中,从而使limits数组形成一个右开区间数组
- positive=false,表示查找小于d的最大double值,一般用在limits数组中,从而使limits数组形成一个左开区间数组
previousDouble(double d)
查找小于d的最大double值,一般用在limits数组中,从而使limits数组形成一个左开区间数组
public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(1));// 1.0000000000000002System.out.println(ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(1,true));// 1.0000000000000002System.out.println(ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(1,false));// 0.9999999999999999System.out.println(ChoiceFormat.previousDouble(1));// 0.9999999999999999
}
上面三个方法的使用场景:
如果有个这样的需求:
- 当number < 1时,取值0
- 当1 <= number <= 2时,取值1
- 当2 < number <= 3时,取值2
- 当number > 3时,取值3
代码实现:
double[] limits = {0, 1, 2, 3};String[] formats = {"0","1","2","3"};ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats);
如果这样的写法,显然不能满足:
- number = 2时,取值1
- number = 3时,取值2
我们可以这么写
public static void main(String[] args) {double[] limits = {0, 1, ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(2), ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(3)};String[] formats = {"0","1","2","3"};ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats);System.out.println(format.format(0));System.out.println(format.format(1));System.out.println(format.format(2));System.out.println(format.format(3));System.out.println(format.format(4));
}
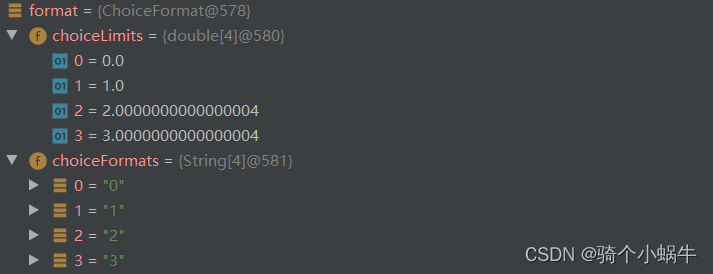
能完全满足上面的需求(number = 2时,取值1;number = 3时,取值2)。
ChoiceFormat(double[] limits, String[] formats)
构造函数中接收一个formats数组和一个limits数组,这两个数组必须具有相同数量的元素。
- 第一个数组是原始双精度数组,表示每个间隔的最小值(起始值)。
- 第二个数组是一个字符串数组,代表与每个间隔关联的名称。
limits数组实际上是个区间,可开可闭,并且必须按升序排列,如果不按升序排列,格式化结果将会不正确,还可以使用\u221E(表示无穷大)。
匹配规则:limits[i] <= number <limits[i+1]
number表示使用format方法传入的值,i表示limit数组中的索引。当且仅当上述公式成立时,number匹配i,如果不能匹配,则会根据number是太小还是太大,匹配limits数组的第一个索引或最后一个索引,然后使用匹配的limits数组中的索引,去formats数组中寻找相同索引的值。
public static void main(String[] args) {double[] limits = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};String[] formats = { "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日" };ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats);System.out.println(format.format(-1));// 星期一System.out.println(format.format(0));// 星期一System.out.println(format.format(1));// 星期二System.out.println(format.format(2.5));// 星期三System.out.println(format.format(6.6));// 星期日System.out.println(format.format(7));// 星期日System.out.println(format.format(8));// 星期日
}
| namber取值范围 | 匹配formats索引位置 | 匹配值 |
|---|---|---|
| number < 0 | 匹配formats[0] | 星期一 |
| 0 <= number < 1 | 匹配formats[0] | 星期一 |
| 1 <= number < 2 | 匹配formats[1] | 星期二 |
| 2 <= number < 3 | 匹配formats[2] | 星期三 |
| 3 <= number < 4 | 匹配formats[3] | 星期四 |
| 4 <= number < 5 | 匹配formats[4] | 星期五 |
| 5 <= number < 6 | 匹配formats[5] | 星期六 |
| numbe >= 6 | 匹配formats[6] | 星期日 |
ChoiceFormat(String newPattern)
ChoiceFormat类的构造方法也允许我们传入一个模式字符串,format方法会根据这个模式字符串执行格式化操作。
模式元素的格式:doubleNum [占位符] formatStr
占位符
| 占位符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| # | 等于 |
| < | 大于 |
| \u2264(<=) | 大于等于 |
注意:比较运算符和平时实现相反的,因为该地方类似于变量在比较运算符的右边(平时是在左边)
模式字符串中的每个模式元素之间使用 | 分割,| 前后可以添加空格以美化代码。
其实在ChoiceFormat(String newPattern)构造方法的内部,模式字符串还是被转换为limits和formats两个数组。
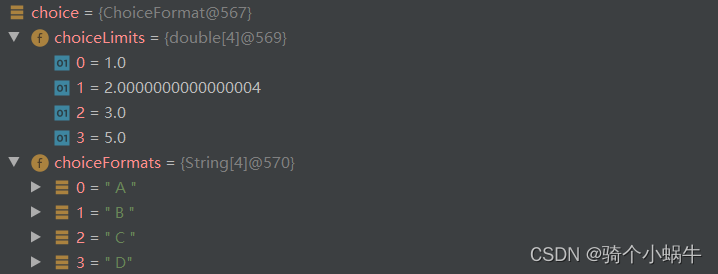
public static void main(String[] args) {ChoiceFormat choice=new ChoiceFormat("1 # A | 2 < B | 3 \u2264 C | 5 # D");System.out.println(choice.format(0));System.out.println(choice.format(1));System.out.println(choice.format(2));System.out.println(choice.format(3));System.out.println(choice.format(4));System.out.println(choice.format(5));System.out.println(choice.format(6));
}
字符串格式化
1. MessageFormat
MessageFormat提供与语言环境无关的生成连接消息的方式。
通常用MessageFormat的静态方法format,该方法接收一个字符串的模式和一组对象(对象数组),按照模式形式将格式化的对象插入到模式中,然后返回字符串结果。
static String format(String pattern, Object … arguments)
- pattern:字符串模式
- arguments:对象数组
模式元素
模式元素格式:ArgumentIndex[,FormatType[,FormatStyle]]
- ArgumentIndex:入参索引位置(从0开始)
- FormatType:格式化类型
- FormatStyle:格式化样式
格式化类型
- date:调用DateFormat进行格式化
- time:调用DateFormat进行格式化
- number:调用NumberFormat进行格式化
- choice:调用ChoiceFormat进行格式化
格式化样式
- short
- medium
- long
- full
- integer
- currency
- percent
- SubformatPattern(子模式)
使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {Date date = new Date();System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0},{1},{2}", date, date, 1.11));System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0,date},{1,time},{2,number}", date, date, 1.11));System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0,date,MEDIUM},{1,time,MEDIUM},{2,number,integer},{3,number,#.#}", date, date, 1.11, 2.22));
}输出:
22-9-5 下午10:47,22-9-5 下午10:47,1.11
2022-9-5,22:47:39,1.11
2022-9-5,22:47:39,1,2.2
2. String.format
String有两个格式化方法
- format(String format, Object… args)
- format(Locale l, String format, Object… args)
format参数
format参数格式:%[index$][flags][width][.precision]conversion
模块
| 模块 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| index$ | 否 | 参数在参数列表中的位置,十进制整数。 第一个参数由 "1$" 引用,第二个参数由 "2$"引用 |
| flags | 否 | 标识,用来控制输出格式 |
| width | 否 | 输出的最小长度,正整数 |
| .precision | 否 | 精度,限定输出字符数 |
| conversion | 是 | 转换符,指定如何格式化参数 |
标识
| 标识 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| - | 在最小宽度内左对齐,不可与0标识一起使用 |
| 0 | 若内容长度不足最小宽度,则在左边用0来填充 |
| # | 对8进制和16进制,8进制前添加一个0,16进制前添加0x |
| + | 结果总包含一个+或-号 |
| 空格 | 正数前加空格,负数前加-号 |
| , | 只用与十进制,每3位数字间用,分隔 |
| ( | 若结果为负数,则用括号括住,且不显示符号 |
转换符
| s | 字符串类型 |
| c | 字符类型 |
| b | 布尔类型,只要实参为非false的布尔类型,均格式化为字符串true,否则为字符串false |
| d | 整数类型(十进制) |
| x | 整数类型(八进制) |
| o | 整数类型(十六进制) |
| f | 浮点数型(十进制)。显示9位有效数字,且会进行四舍五入。如99.99 |
| a | 浮点数型(十六进制) |
| g | 浮点数型(比%f,%a长度短些,显示6位有效数字,且会进行四舍五入) |
| e | 指数类型。如9.38e+5 |
| h | 散列码 |
| % | 百分比 |
| tx | 日期与时间类型(x代表不同的日期与时间转换符) |
| n | 换行符 |
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(String.format("%2$06.2f======%1$d", 2, 11.1111));// 011.11======2
}
)


















![[格式化字符串漏洞+堆溢出] Suctf2019_sudrv](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[格式化字符串漏洞+堆溢出] Suctf2019_sudrv)