🐶博主主页:@ᰔᩚ. 一怀明月ꦿ
❤️🔥专栏系列:线性代数,C初学者入门训练,题解C,C的使用文章,「初学」C++
🔥座右铭:“不要等到什么都没有了,才下定决心去做”
🚀🚀🚀大家觉不错的话,就恳求大家点点关注,点点小爱心,指点指点🚀🚀🚀
目录
冒泡排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
稳定性
算法分析
选择排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
稳定性
算法分析
直接插入排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
稳定性
算法分析
希尔排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
稳定性
算法分析
希尔排序的特性总结
堆排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
算法分析
快速排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
算法分析
hoare 版
挖坑版
前后指针版
拓展延伸
快速排序的非递归
算法:
快速排序的优化
1.三数取中
算法:
2.三路划分
算法:
归并排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
算法分析
拓展延伸
归并非递归
基数排序
概念
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
算法分析
排序算法对比
排序10000个,统计所需要的时间
结果
冒泡排序
概念
它重复地访问排序的数列,依次比较两个相邻的数,如果顺序(从小到大)错误就把它们交换过来,访问数列是重复地进行,直到没有相邻数需要交换,就可以认为该数列已经排序完成。这个算法的名字由来是因为越小的数会经由交换慢慢“浮”到数列的顶端(升序或降序排列),就如同汽水中的气泡最终会上浮到顶端一样,故名“冒泡排序”。
时间复杂度
O(N^2)
空间复杂度
O(1)
稳定性
稳定
算法分析
void BubbleSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){for(int j=0;j<n-1-i;j++){if(a[j]>a[j+1])Swap(&a[j], &a[j+1]);//交换函数}} }
选择排序
概念
选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观排序算法。它的工作原理是:第一次从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,存放在序列的起始位置,然后再从剩余的未排序元素中寻找到最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序的序列的末尾。以此类推,直到全部待排序的数据元素的个数为零。时间复杂度
O(N^2)空间复杂度
O(1)稳定性
不稳定算法分析
算法分析 void SelectSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){if(a[i]>a[j])Swap(&a[i], &a[j]);}} }
直接插入排序
概念
插入排序,一般也被称为直接插入排序。对于少量元素的排序,它是一个有效的算法 。插入排序是一种最简单的排序方法,它的基本思想是将一个记录插入到已经排好序的有序表中,从而一个新的、记录数增1的有序表。在其实现过程使用双层循环,外层循环对除了第一个元素之外的所有元素,内层循环对当前元素前面有序表进行待插入位置查找,并进行移动。
时间复杂度
O(N^2)
空间复杂度
O(1)
稳定性
稳定
算法分析
void InsertSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)//i<n-1,为了temp=a[i+1]越界{int end=i;int temp=a[i+1];while(end>=0){if(a[end]>temp){a[end+1]=a[end];end--;}else//如果a[end]<temp说明0-i区间已经是有序的,不需在比较了,这样既提高了效率也防止了越界break;}a[end+1]=temp;//这一步千万别忘记了} }
希尔排序
概念
希尔排序(Shell's Sort)是插入的一种又称“缩小增量排序”(Diminishing Increment Sort),是直接插入排序算法的一种更高效的改进版本。希尔排序是非稳定排序算法。该方法因 D.L.Shell 于 1959 年提出而得名。希尔排序是把记录按下标的一定增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序;随着增量逐渐减少,每组包含的关键词越来越多,当增量减至 1 时,整个文件恰被分成一组,算法便终止。时间复杂度
O(N*logN)空间复杂度
O(1)稳定性
不稳定算法分析
void ShellSort(int* a,int n) {int gap=n;//增量,初始值为 nwhile(gap>1){gap=gap/3+1;//这里不固定,也可以是gap/3,gap/2+1,gap/2...,但是gap/3+1 更优for(int i=0;i<n-gap;i++)//i<n-gap是防止end+gap 越界{int end=i;int temp=a[i+gap];while(end>=0){if(a[end]>temp){a[end+gap]=a[end];end-=gap;}elsebreak;}a[end+gap]=temp;}} }希尔排序的特性总结
1. 希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化。
2. 当gap > 1时都是预排序,目的是让数组更接近于有序。当gap == 1时,数组已经接近有序的了,这样就会很快。这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果。我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比。
3. 希尔排序的时间复杂度不好计算,因为gap的取值方法很多,导致很难去计算,因此在好些树中给出的希尔排序的时间复杂度都不固定,因为我们的gap是按照Knuth提出的方式取值的,而且Knuth进行了大量的试验统计,我们暂时就按照:O(N^1.25)到O(1.6*N^1.25)来算。
堆排序
概念
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆积树(堆)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,它是选择排序的一种。它是
通过堆来进行选择数据。需要注意的是排升序要建大堆,排降序建小堆。
时间复杂度
O(N*logN)
空间复杂度
O(1)
算法分析
//向下建堆_大堆 //一次建堆 void AdjustDown(int* a,int n,int parent) {int child=parent*2+1;while(child<n){if(child+1<n&&a[child]<a[child+1])child++;if(a[child]>a[parent]){Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent=child;child=parent*2+1;}elsebreak;} } //堆排序 void HeapSort(int* a,int n) {//这里建堆,其实这里也可以是// for(int i=1;i<n;i++)// {// AdjustDown(a, n,i);// }//这种是从第二层到第 n-1 层的建堆,效率不高//下面这种是从第n-1层到第零层建堆,虽然两种方法的层数一样,但是涉及的元素个数相差很多for(int i=(n-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(a, n, i);}int end=n-1;while(end>0){//因为是大堆,所以第一个元素始终是最大的,我们让最后一个元素和第一个交换,然后再调整一下,让调整后的第一个元素是最大的,注意这次调整的元素个数要减一,然后循环直到 end(每次调整的元素个数) 为一就不用交换调整了。Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);AdjustDown(a, end, 0);end--;} }
快速排序
概念
快速排序是Hoare于1962年提出的一种二叉树结构的交换排序方法,其基本思想为:任取待排序元素序列中的某元素作为基准值,按照该排序码将待排序集合分割成两子序列,左子序列中所有元素均小于基准值,右子序列中所有元素均大于基准值,然后最左右子序列重复该过程,直到所有元素都排列在相应位置上为止时间复杂度
O(N*logN)空间复杂度
O(logN~N)算法分析
hoare 版
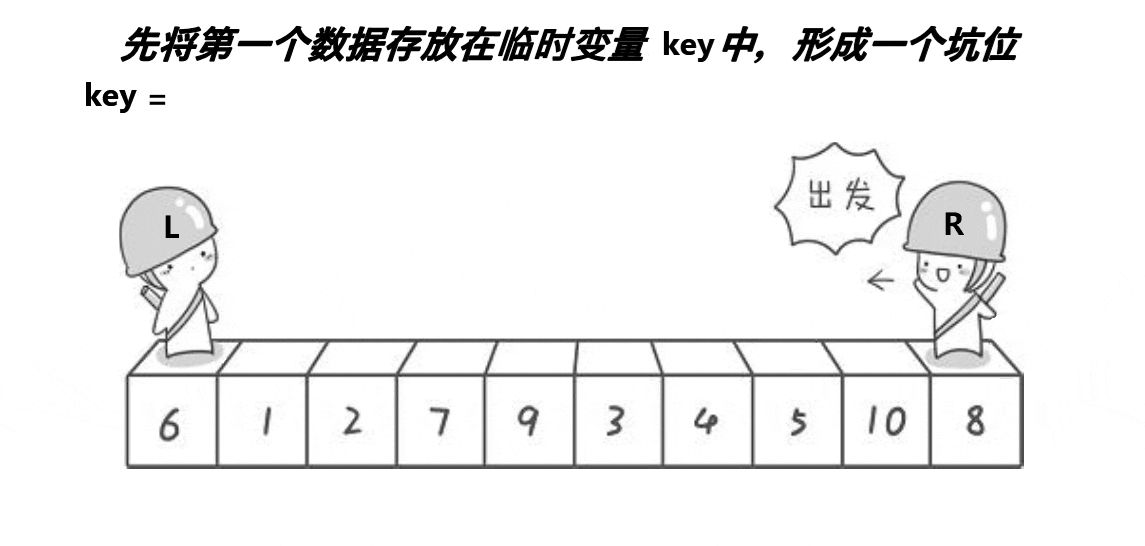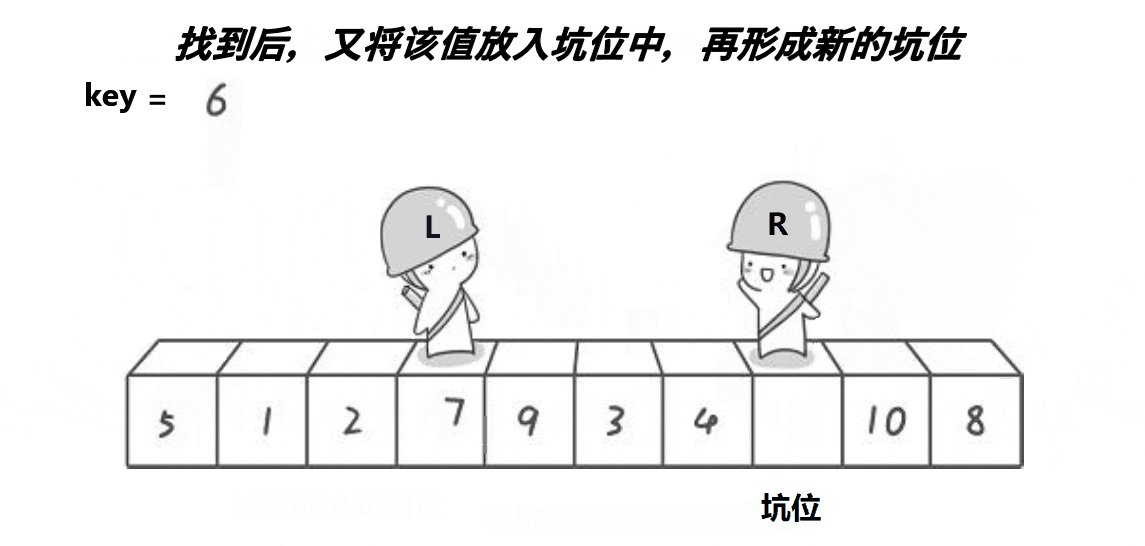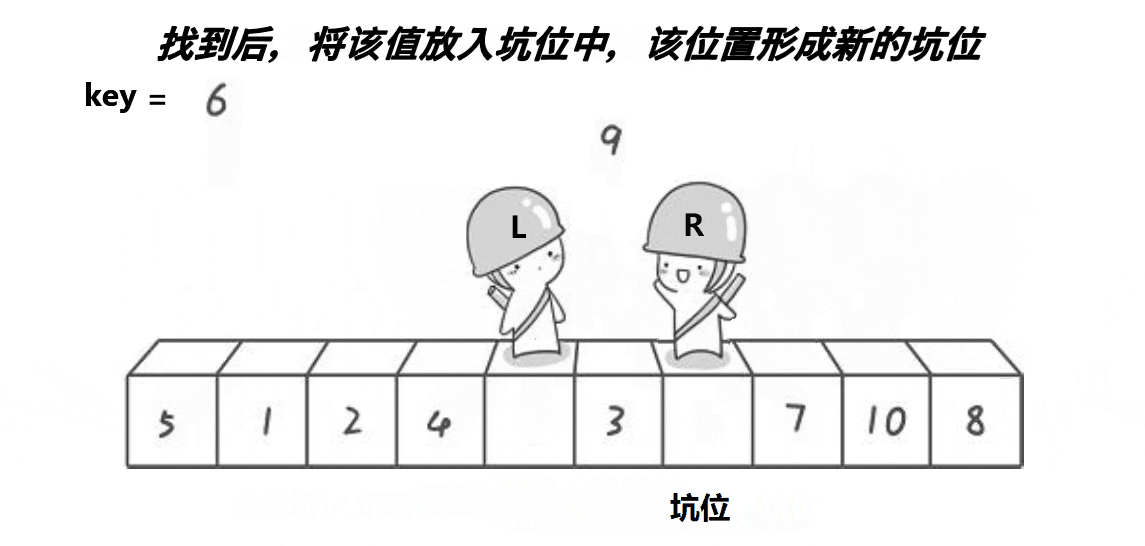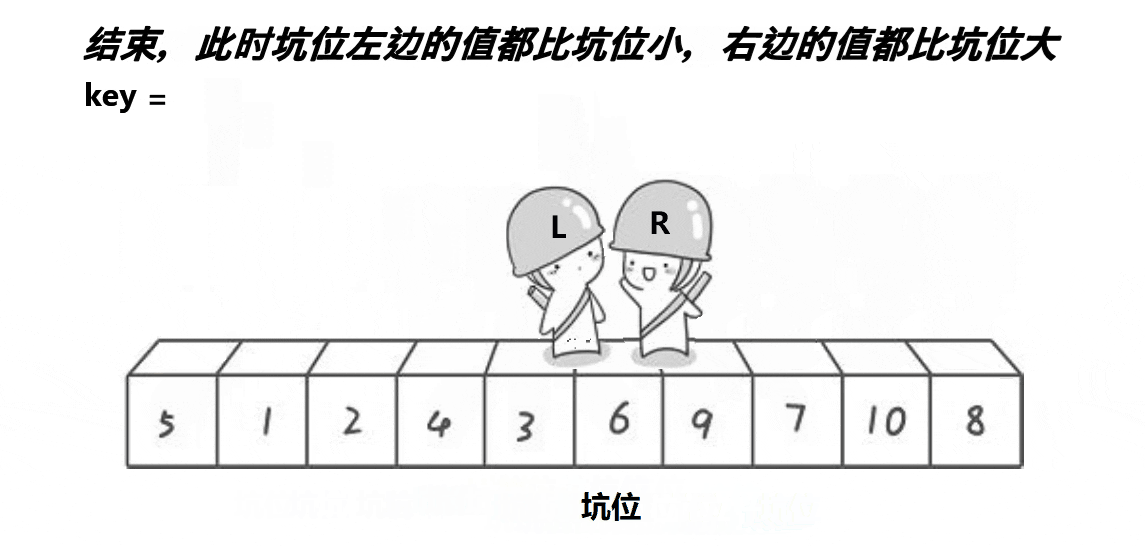
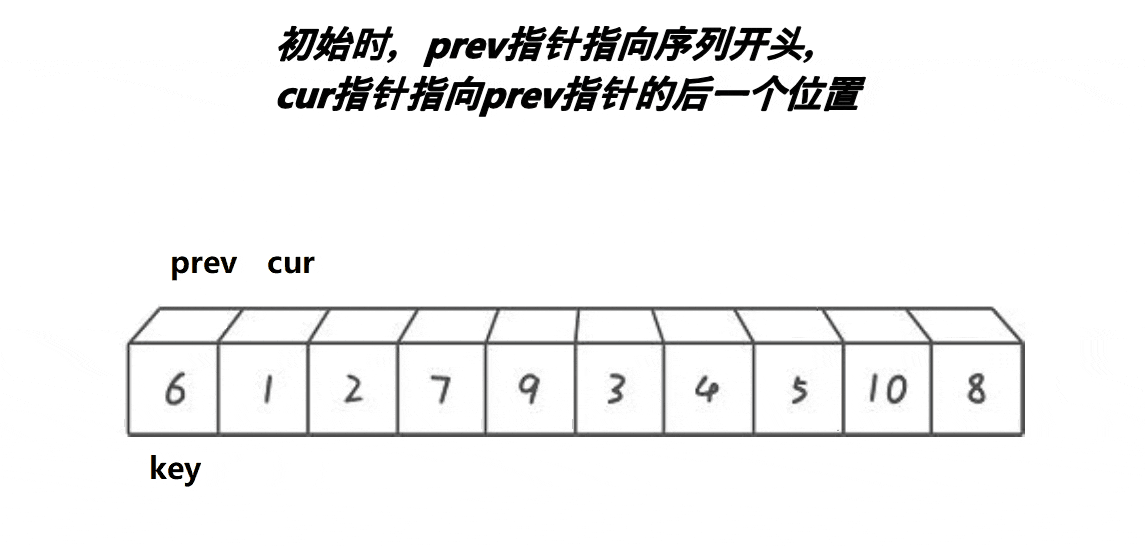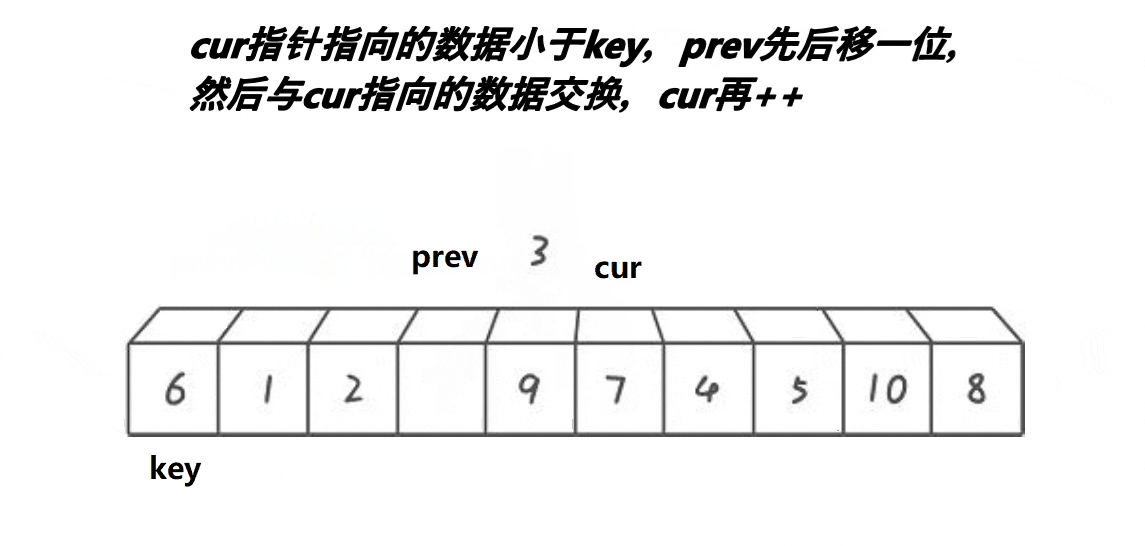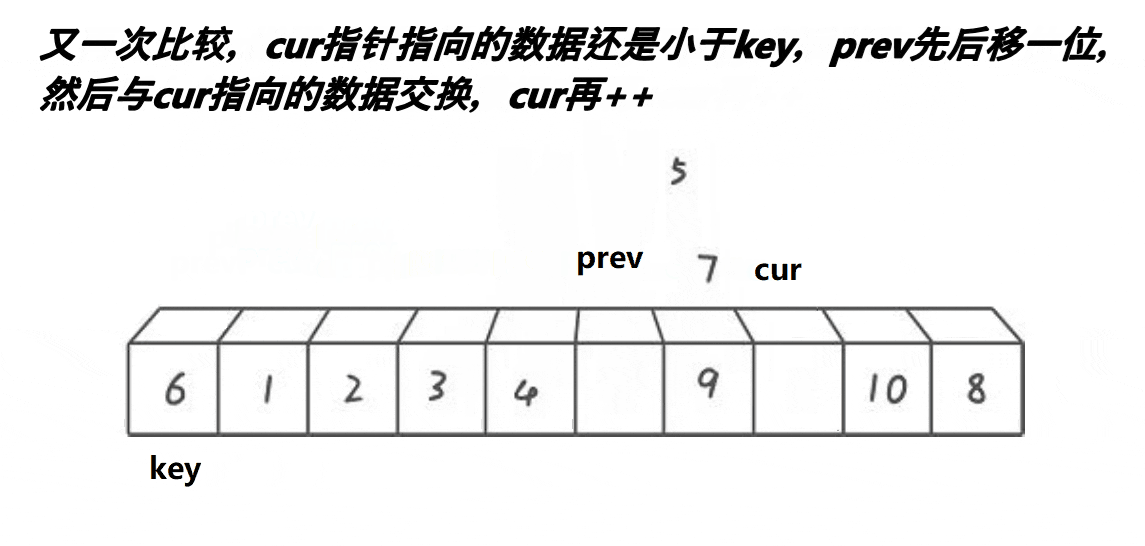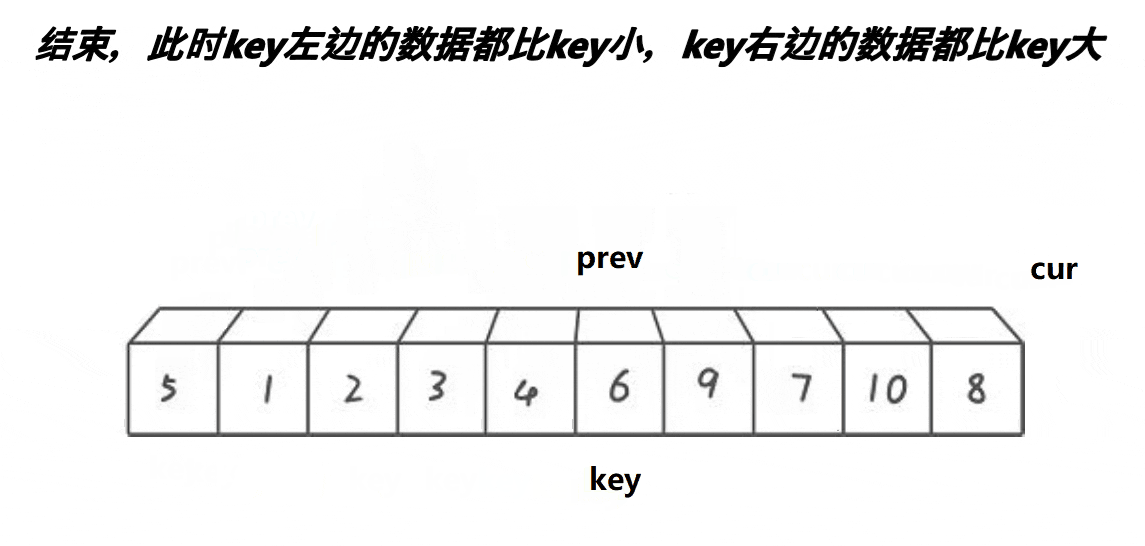
int partsort_hoare(int* a,int begin,int end) {int keyi=begin;while(begin<end){//右边找小while(begin<end&&a[end]>a[keyi]){end--;}//左边找大while(begin<end&&a[begin]<a[keyi]){begin++;}Swap(&a[begin], &a[end]);}Swap(&a[begin], &a[keyi]);keyi=begin;return keyi; } void QuickSort_1(int* a,int begin,int end) {if(begin>=end)return;int ret=partsort_hoare(a, begin,end);//[begin,ret-1][ret][ret+1,end]int begin1=begin,end1=ret-1;int begin2=ret+1,end2=end;QuickSort_1(a, begin1, end1);QuickSort_1(a, begin2, end2); } //这里所以添加这个函数,是为了和其他排序函数参数保持一致 void QuickSort(int* a,int n) {QuickSort_1(a, 0, n-1); }除了 hoare 版还有两个版本。
挖坑版
int partsort_hole(int* a,int begin,int end) {int key=a[begin];int hole=begin;while(begin<end){//右边找小while(begin<end&&a[end]>key){end--;}Swap(&a[hole], &a[end]);hole=end;//左边找大while(begin<end&&a[begin]<key){begin++;}Swap(&a[hole], &a[begin]);hole=begin;}a[hole]=key;return hole; }前后指针版
int partsort_prev_cur(int* a,int begin,int end) {int keyi=begin;int prev=begin;int cur=begin+1;while(cur<=end){//思路:让 prev 指向的值始终小于a[keyi],让 cur 指向大于a[keyi]//1.最开始的 prev 和 cur 相邻//2.当 cur 遇到比a[keyi]的大的值以后,他们 1 以后,他们之间的值都是比a[keyi]大的值//3.cur找小,找到小以后,跟++prev位置的值交换,相当于大的翻滚似的右边推,同时把小的换到左边if(a[cur]<a[keyi]&&++prev!=cur){Swap(&a[prev], &a[cur]);}cur++;}Swap(&a[prev], &a[keyi]);return prev; }拓展延伸
快速排序的非递归
之所以会有非递归版本,因为递归需要开辟栈帧,开辟栈帧是在栈进行的,栈内存较小,如果递归很深会导致栈溢出,而非递归是通过循环实现的,是在堆上实现的,堆内存较大,不会出现溢出。
算法:
这里使用了栈这种数据结构
void QuickSortNonR(int* a,int n) {int begin=0,end=n-1;ST st;STInit(&st);STPush(&st, end);STPush(&st, begin);while(!STEmpty(&st)){int left=STTop(&st);STPop(&st);int right=STTop(&st);STPop(&st);int keyi=partsort_hoare(a, left, right);if(keyi+1<right){STPush(&st, right);STPush(&st, keyi+1);}if(keyi-1>left){STPush(&st, keyi-1);STPush(&st, left);}} }栈的实现:C语言中数据结构——栈_ᰔᩚ. 一怀明月ꦿ的博客-CSDN博客
快速排序的优化
1.三数取中
如果排序的元素是有序的,这将对快速排序非常不友好,所以采用三数取中。
算法:
int GetMidIndex(int* a,int left,int right) {int mid=(left+right)/2;if(a[left]<a[mid]){if(a[mid]<a[right])return mid;else if(a[left]<a[right])return right;elsereturn left;}else{if(a[mid]>a[right])return mid;else if(a[left]>a[right])return right;elsereturn left;} } 使用方法: 在 partsort_hoare/ partsort_hole/ partsort_prev_cur中加入int midi=GetMidIndex(a, begin, end);Swap(&a[begin], &a[midi]);2.三路划分
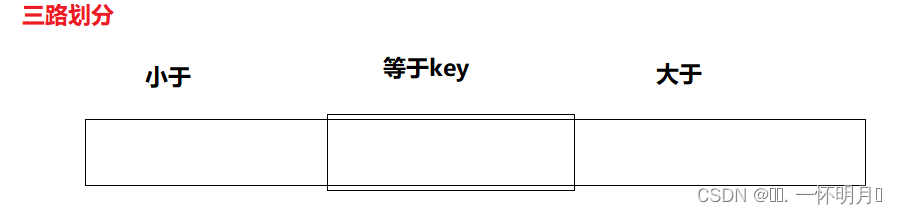
因为快速排序的效率和排序的数列有关系,快速排序的时间效率O(N*lgN~N^2),如果数列如果全是一样的数,就会导致效率为O(N^2),所以需要对现有的结构进行优化,例如三路划分
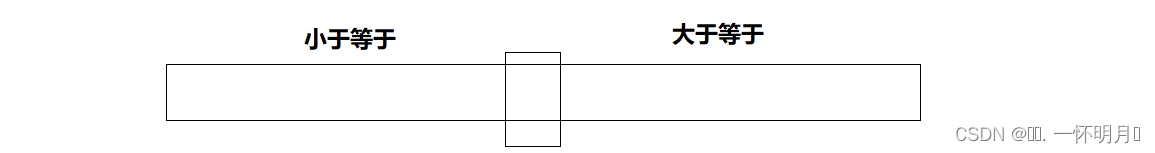
以前的快速排序结构划分的区间只有两个【小于等于key】【大于等于key】
我们将数列划分为三个区间【小于key】【等于key】【大于key】
三路划分的整体方法是hoare版和前后指针版的结合
cur=left key=a[left]
1.a[cur]<key 交换a[left]和a[cur] ++left,++cur
2.a[cur]>key 交换a[right和a[cur] --right
3.a[cur]==key ++cur
实际上:
1.小的放到左边,大的放到右边
2.跟key相等的值放到中间
这里针对于递归版本
算法:
void QuickSort(int* a,int begin,int end) {if(begin>=end)return;int left=begin;int right=end;int cur=left+1;int midi=GetMidIndex(a, left, right);Swap(&a[left], &a[midi]);int key=a[left];while(cur<=right){if(a[cur]<key){Swap(&a[left], &a[cur]);left++;cur++;}else if(a[cur]>key){Swap(&a[cur], &a[right]);right--;}else{cur++;}}//[begin,left-1][left,right][right+1,end]QuickSort(a, begin, left-1);QuickSort(a, right+1, end); }
归并排序
概念
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效,稳定的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。时间复杂度
O(N*logN)空间复杂度
O(N)算法分析
排序详情:秒懂百科
void _MergeSort(int* a,int begin,int end,int* temp) {if(begin==end)return;int midi=(begin+end)/2;//[begin,midi][midi+1,end]int begin1=begin,end1=midi;int begin2=midi+1,end2=end;_MergeSort(a, begin1, end1, temp);_MergeSort(a, begin2, end2, temp);int j=begin;while(begin1<=end1&&begin2<=end2){if(a[begin1]<a[begin2]){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}else{temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}}while(begin1<=end1){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}while(begin2<=end2){temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}memcpy(a+begin,temp+begin,sizeof(int)*(end-begin+1)); } void MergeSort(int* a,int n) {//归并两个区间,做不到在原数组中操作,需要一个数组作为媒介,temp就是媒介int* temp=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);_MergeSort(a,0,n-1,temp);free(temp); }拓展延伸
归并非递归
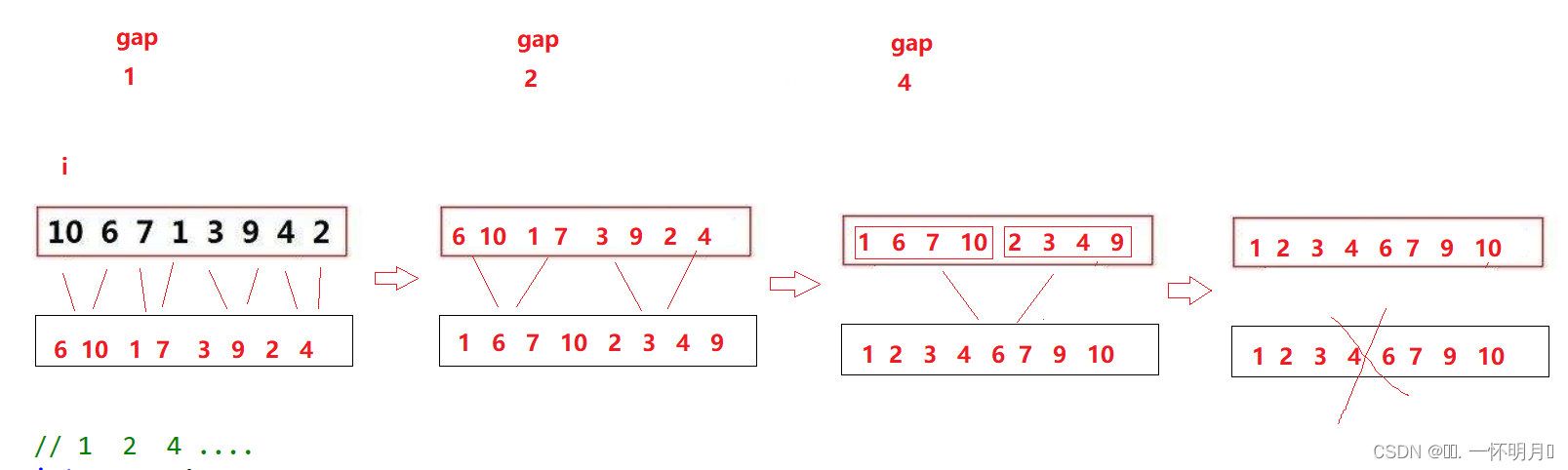
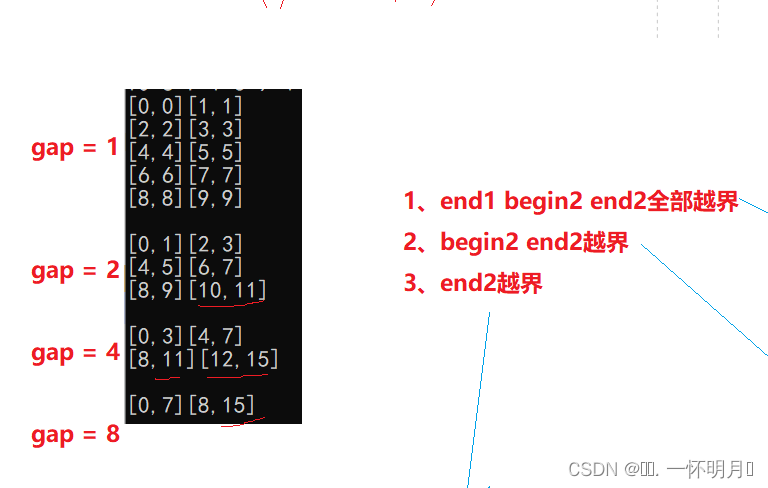
归并排序的非递归结构是通过循环实现的,递归是将整个区间划分为一个个小区间进行归并,而非递归是将一个个小区间归并,通过变量gap控制每次归并区间的大小,如图
非递归的结构,通常会有越界的可能
1.将一二种越界跳出循环,第三种采用修正的方法
void MergeSortNonR(int* a,int n) {int* temp=(int* )malloc(sizeof(int)*n);int gap=1;while(gap<n){int j=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i+=2*gap){int begin1=i,end1=i+gap-1;int begin2=i+gap,end2=i+2*gap-1;if(end1>=n||begin2>=n)break;if(end2>=n){end2=n-1;}while(begin1<=end1&&begin2<=end2){if(a[begin1]<a[begin2]){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}else{temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}}while(begin1<=end1){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}while(begin2<=end2){temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}//归并一段,拷贝一段memcpy(a+i,temp+i,sizeof(int)*(end2-i+1));}gap*=2;}free(temp); }2.全按修正方法
void MergeSortNonR_1(int* a,int n) {int* temp=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);int gap=1;while(gap<n){int j=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i+=2*gap){int begin1=i,end1=i+gap-1;int begin2=i+gap,end2=i+2*gap-1;if(end1>=n){end1=n-1;//修成不存在的区间begin2=n;end2=n-1;}else if(begin2>=n){//修成不存在的区间begin2=n;end2=n-1;}else if(end2>=n){end2=n-1;}while(begin1<=end1&&begin2<=end2){if(a[begin1]<a[begin2]){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}else{temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}}while(begin1<=end1){temp[j++]=a[begin1++];}while(begin2<=end2){temp[j++]=a[begin2++];}memcpy(a+i,temp+i,sizeof(int)*(end2-i+1));}gap*=2;}free(temp); }
基数排序
概念
基数排序(radix sort)属于“分配式排序”(distribution sort),又称“桶子法”(bucket sort)或bin sort,顾名思义,它是透过键值的部份资讯,将要排序的元素至某些“桶”中,藉以达到排序的作用,基数排序法是属于稳定性的排序,在某些时候,基数排序法的效率高于其它的稳定性排序法。
时间复杂度
O(N+range)
空间复杂度
O(range)
算法分析
void CountSort(int* a,int n) {//计算范围int min=a[0],max=a[0];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(a[i]<min)min=a[i];if(a[i]>max)max=a[i];}int range=max-min+1;//统计次数int* temp=(int* )malloc(sizeof(int)*range);memset(temp, 0, sizeof(int)*range);for(int i=0;i<n;i++){temp[a[i]-min]++;}//排序int j=0;for(int i=0;i<range;i++){while(temp[i]--){a[j++]=i+min;}} }
排序算法对比
排序10000个,统计所需要的时间
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include<time.h> //打印函数 void Print(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n;i++){printf("%d ",a[i]);}printf("\n"); } //交换函数 void Swap(int* e1,int* e2) {int temp=*e1;*e1=*e2;*e2=temp; } //向下调整 //大根堆 void AdjustDown(int* a,int n,int parent) {int child=parent*2+1;while(child<n){if(child+1<n&&a[child]>a[child+1]){child++;}if(a[child]<a[parent]){Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent=child;child=parent*2+1;}else{break;}} } //建大堆排序 void AdjustDownSort(int*a,int n) {for(int i=(n-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(a, n, i);}int end=n-1;while(end>0){Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);AdjustDown(a, end, 0);end--;} } //冒泡排序 void BubbleSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){if(a[j]>a[j+1])Swap(&a[j], &a[j+1]);}} } //选择排序 void SelectSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){if(a[i]>a[j])Swap(&a[i], &a[j]);}} } //插入排序 void InsertSort(int* a,int n) {for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int end=i;int temp=a[i+1];while(end>=0){if(a[end]>temp){a[end+1]=a[end];end--;}else{break;}}a[end+1]=temp;} } //希尔排序 void SellSort(int* a,int n) {int gap=n;while(gap>1){gap=gap/3+1;for(int i=0;i<n-gap;i++){int end=i;int temp=a[end+gap];while(end>=0){if(a[end]>temp){a[end+gap]=a[end];end-=gap;}else{break;}}a[end+gap]=temp;}} } //系统自带的快排 int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2) {return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2; } //快速排序 hoare 版本 int GetMidIndex(int* a,int left,int right) {int mid=(left+right)/2;if(a[left]<a[mid]){if(a[mid]<a[right])return mid;else if(a[left]<a[right])return right;elsereturn left;}else{if(a[mid]>a[right])return mid;else if(a[left]>a[right])return right;elsereturn left;} } int partSort(int* a,int left,int right) {int midi=GetMidIndex(a, left, right);Swap(&a[left], &a[midi]);int keyi=left;while(left<right){//右边找小while(left<right&&a[right]>=a[keyi]){--right;}//左边找大while(left<right&&a[left]<=a[keyi]){++left;}Swap(&a[right], &a[left]);}Swap(&a[right], &a[keyi]);return left; } void QuickSort(int* a,int begin,int end) {if(begin>=end)return;int key=partSort(a, begin, end);QuickSort(a, begin, key-1);QuickSort(a, key+1, end); } void QuickSort_1(int* a,int begin,int end) {if(begin>=end)return;if(end-begin+1<10){InsertSort(a+begin, end-begin+1);return;}int key=partSort(a, begin, end);QuickSort(a, begin, key-1);QuickSort(a, key+1, end); } //归并排序 void _MergeSort(int *a,int begin,int end,int *temp) {if(begin==end)return;int mid=(begin+end)/2;//[begin,mid][mid+1,end]_MergeSort(a, begin, mid, temp);_MergeSort(a, mid+1, end, temp);int begin1=begin,end1=mid;int begin2=mid+1,end2=end;int i=begin;while(begin1<=end1&&begin2<=end2){if(a[begin1]<a[begin2]){temp[i++]=a[begin1++];}else{temp[i++]=a[begin2++];}}while(begin1<=end1){temp[i++]=a[begin1++];}while(begin2<=end2){temp[i++]=a[begin2++];}memcpy(a+begin,temp+begin,sizeof(int)*(end-begin+1)); } void MergeSort(int *a,int n) {int* temp=malloc(sizeof(int)*n);_MergeSort(a, 0,n-1,temp);free(temp); } void _MergeSort_1(int *a,int begin,int end,int *temp) {if(begin==end)return;if(end-begin+1<10){InsertSort(a+begin, end-begin+1);return;}int mid=(begin+end)/2;//[begin,mid][mid+1,end]_MergeSort(a, begin, mid, temp);_MergeSort(a, mid+1, end, temp);int begin1=begin,end1=mid;int begin2=mid+1,end2=end;int i=begin;while(begin1<=end1&&begin2<=end2){if(a[begin1]<=a[begin2]){temp[i++]=a[begin1++];}else{temp[i++]=a[begin2++];}}while(begin1<=end1){temp[i++]=a[begin1++];}while(begin2<=end2){temp[i++]=a[begin2++];}memcpy(a+begin,temp+begin,sizeof(int)*(end-begin+1)); } void MergeSort_1(int *a,int n) {int* temp=malloc(sizeof(int)*n);_MergeSort_1(a, 0,n-1,temp);free(temp); } void CountSort(int* a,int n) {int min=a[0],max=a[0];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(a[i]<min)min=a[i];if(a[i]>max)max=a[i];}int range=max-min+1;int* countA=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*range);memset(countA,0,sizeof(int)*range);//统计次数for(int i=0;i<n;i++){countA[a[i]-min]++;}//排序int k=0;for(int j=0;j<range;j++){while(countA[j]--){a[k++]=j+min;}} } void test1(void) {srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));const int N=10000;int* a1=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a2=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a3=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a4=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a5=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a6=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a7=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a8=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a9=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a10=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);int* a11=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);for(int i=0;i<N;i++){a1[i]=rand()%10000;a2[i]=a1[i];a3[i]=a1[i];a4[i]=a1[i];a5[i]=a1[i];a6[i]=a1[i];a7[i]=a1[i];a8[i]=a1[i];a9[i]=a1[i];a10[i]=a1[i];a11[i]=a1[i];}int begin1=(int)clock();BubbleSort(a1, N);int end1=(int)clock();printf("冒泡排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end1-begin1);int begin2=(int)clock();SelectSort(a2, N);int end2=(int)clock();printf("选择排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end2-begin2);int begin3=(int)clock();AdjustDownSort(a3, N);int end3=(int)clock();printf("堆排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end3-begin3);int begin4=(int)clock();InsertSort(a4, N);int end4=(int)clock();printf("插入排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end4-begin4);int begin5=(int)clock();SellSort(a5, N);int end5=(int)clock();printf("希尔排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end5-begin5);int begin6=(int)clock();qsort(a6, N, 4, cmp_int);int end6=(int)clock();printf("快排排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end6-begin6);int begin7=(int)clock();QuickSort(a7, 0, N-1);int end7=(int)clock();printf("Quick排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end7-begin7);int begin10=(int)clock();QuickSort_1(a10, 0, N-1);int end10=(int)clock();printf("Quick+插入排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end10-begin10);int begin8=(int)clock();MergeSort(a8, N);int end8=(int)clock();printf("归并排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end8-begin8);int begin9=(int)clock();MergeSort_1(a9, N);int end9=(int)clock();printf("归并+插入排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end9-begin9);int begin11=(int)clock();CountSort(a11, N);int end11=(int)clock();printf("计数排序所需的时间:%d(10^-3ms)\n",end11-begin11); } int main() {test1();return 0; }结果
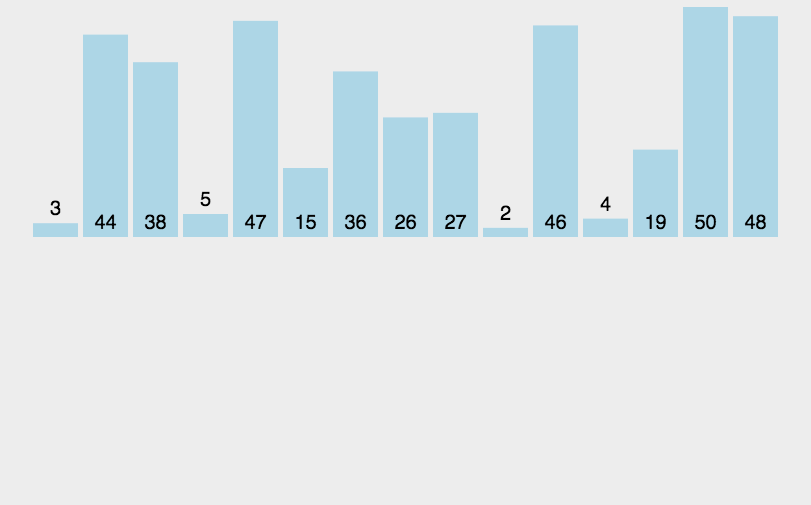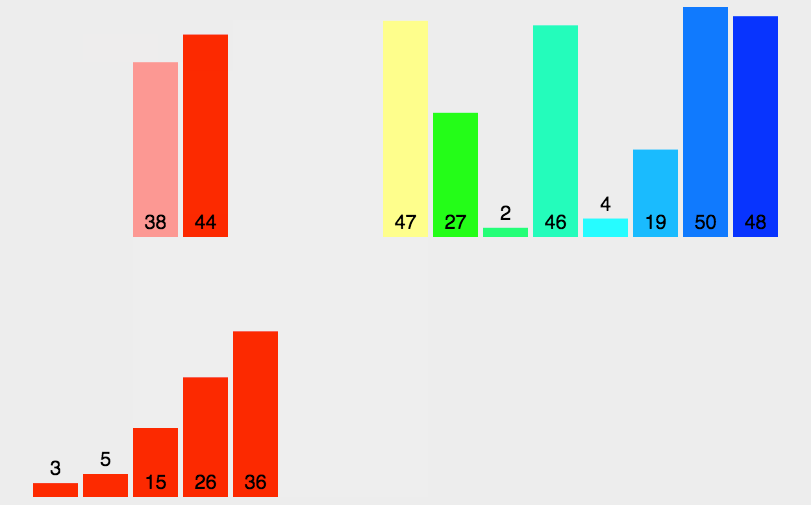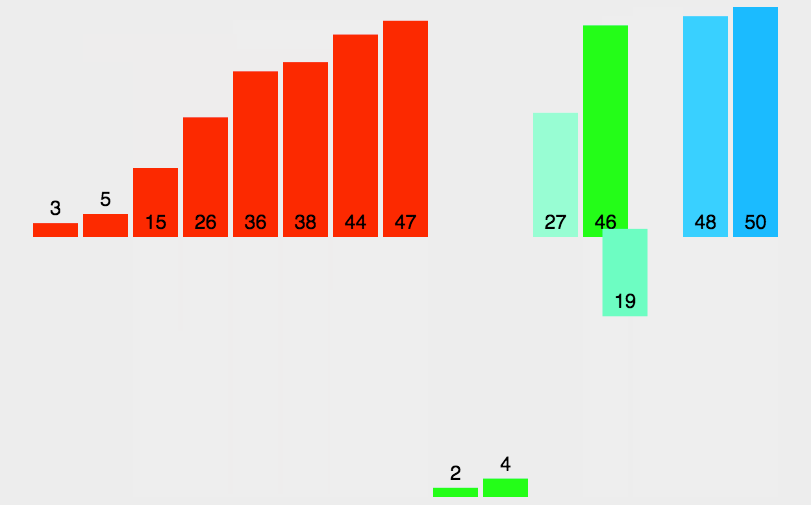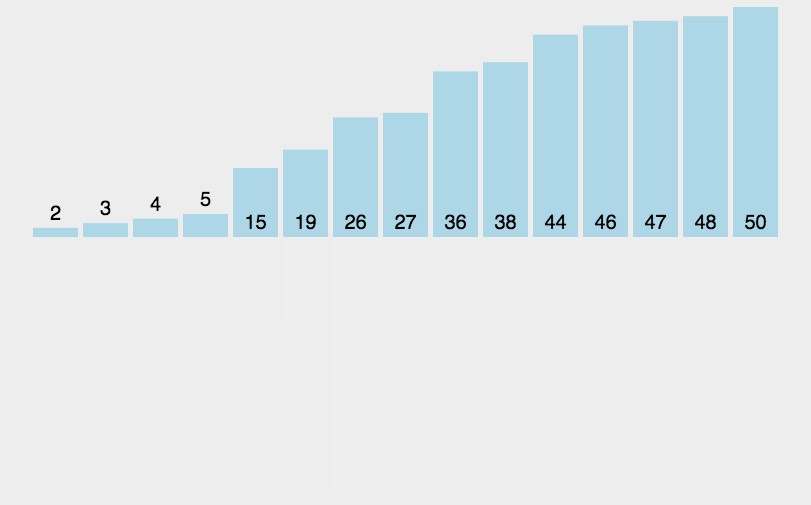
冒泡排序所需的时间:256675(10^-3ms)
选择排序所需的时间:306183(10^-3ms)
堆排序所需的时间:1534(10^-3ms)
插入排序所需的时间:51008(10^-3ms)
希尔排序所需的时间:1690(10^-3ms)
快排排序所需的时间:955(10^-3ms)
Quick排序所需的时间:1235(10^-3ms)
Quick+插入排序所需的时间:1285(10^-3ms)
归并排序所需的时间:1261(10^-3ms)
归并+插入排序所需的时间:1207(10^-3ms)
计数排序所需的时间:204(10^-3ms)
🌸🌸🌸如果大家还有不懂或者建议都可以发在评论区,我们共同探讨,共同学习,共同进步。谢谢大家! 🌸🌸🌸




)


)
)












