1. 插入排序 (⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
直接插入排序是一种简单的插入排序法,思想是是把待排序的数据按照下标从小到大,依次插入到一个已经排好的序列中,直至全部插入,得到一个新的有序序列。例如:我们玩扑克牌的时候,每次摸进一张的新的牌我们会将其插入到合适的位置。
思路: 我们假设第一个数据有序,从第二个元素开始进行插入(最开始把前面第一个数据看作一个有序的区间),从后向前依次寻找合适位置,每次插入的时候如果当前位置不合适将当前位置向后移动一位。
InsertSort 实现:
// 插入排序
void InsertSort(int * nums , int size) {for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {// 把 [0 , end] 看作有序区间int end = i;// nums[end + 1]为需要插入的元素 使用 temp 保存int temp = nums[end + 1];// 找插入位置while (end >= 0 && temp < nums[end]) {// 把当前元素向后移动nums[end + 1] = nums[end];end--;}// 来到这里说明 temp >= nums[end] 找到插入位置// 插入nums[end + 1] = temp;}
}
我们可以思考一下极端情况:
- 假设数据为
3 5 7,end为1,temp = 7,所以temp < nums[end]为false循环结束,执行nums[end + 1] = temp,相当于nums[2] = 7而当前位置本来就是7,不会有影响。 - 假设数据为
3 5 1,end为1,temp = 1,当前temp < nums[end]将数据向后移动直至3 3 5,当end = -1循环结束,nums[end + 1] = temp相当于nums[0] = temp,所以最终结果为1 3 5。
总结:
- 元素结合越接近有序,直接插入排序算法的时间效率就越高。
- 最坏时间复杂度: O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)
- 接近有序或已经有序时间复杂度: O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
2.希尔排序 (⭐️⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
希尔排序又称缩小增量法。希尔排序的基本思想是:先选定一个 gap (整数),把待排序中的数据分成 gap 组(gap 距离的为同一组),并对每一组内的的数据进行插入排序。
假设 gap = 3 将下面的 10 个数分成 3 组。 {9 , 5 , 8 , 5}、{1 , 7 , 6}、{2 , 4 , 3}分别进行插入排序。当 gap 不为 1 时都是预排序,当 gap = 1时是插入排序,因为当数据接近有序的时候,插入排序的效率很高。

1️⃣ gap 组希尔排序: 这是希尔排序的 gap 组的一种写法,按上面的图来说,这样的写法是先走完红色组,再走蓝色组……
void ShellSort (int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);// 假设 gap = 3int gap = 3;for (int j = 0; j < gap; j++) {for (int i = j; i < size - gap; i+=gap) {int end = i;int temp = nums[end + gap];while (end >= 0 && temp < nums[end]) {nums[end + gap] = nums[end];end -= gap;}nums[end + gap] = temp;}}
}
2️⃣ gap 组希尔排序:第二种在上一种写法上进行了优化,原来是一组走完再走下一组,现在是一组一组间交替的去插入排序。
void ShellSort (int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);// 假设 gap = 3int gap = 3;for (int i = 0; i < size - gap; i++) {int end = i;int temp = nums[end + gap];while (end >= 0 && temp < nums[end]) {nums[end + gap] = nums[end];end -= gap;}nums[end + gap] = temp;}
}
ShellSort 实现:当 gap > 1 的时候都是预排序(是为了让数据更接近有序,因为直接插入排序当数据接近有序的时候是 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)),而这里 gap / 3 + 1 是为了最后一次让 gap = 1。 当 gap 越大的时候大的数会越快的到后面,但是数组越不接近有序。当 gap 越小的时候,数组越接近有序。当 gap = 1 就是直接插入排序。
void ShellSort (int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);int gap = size;while (gap > 1) {gap = gap / 3 + 1;for (int i = 0; i < size - gap; i++) {int end = i;int temp = nums[end + gap];while (end >= 0 && temp < nums[end]) {nums[end + gap] = nums[end];end -= gap;}nums[end + gap] = temp;}}
}
总结:
- 时间复杂度 ~ O ( N 1.3 ) O(N^{1.3}) O(N1.3)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
- 希尔排序是插入排序的优化
3. 选择排序 (⭐️)
🌟 思想:
每一次从待排序的数据种选出最小或者最大的元素下标,存放在当前序列的起始位置,直到排序结束。
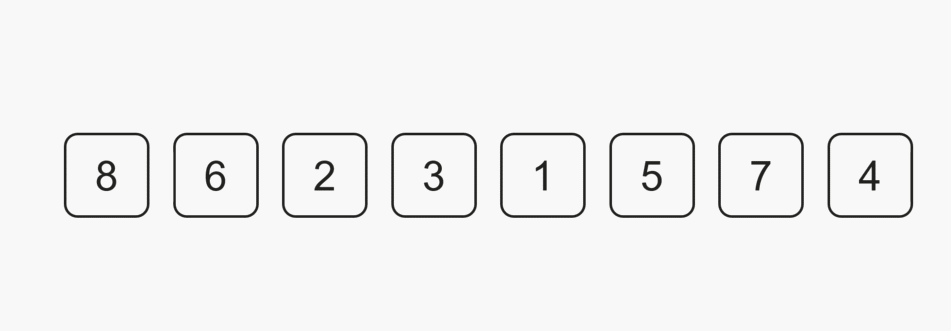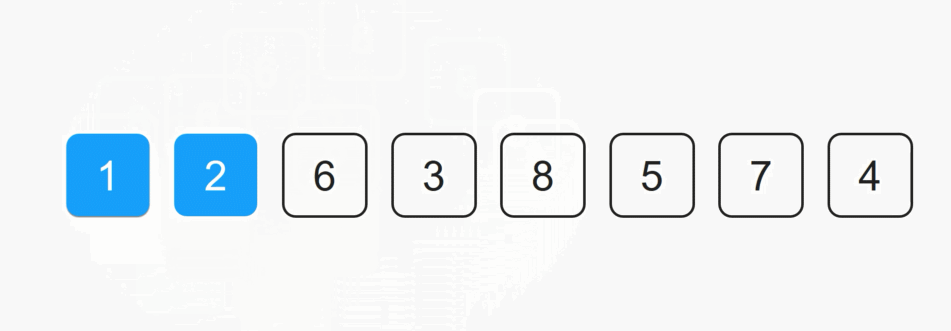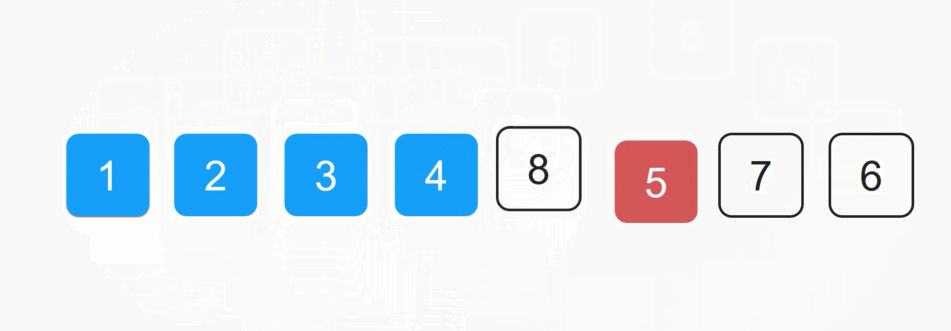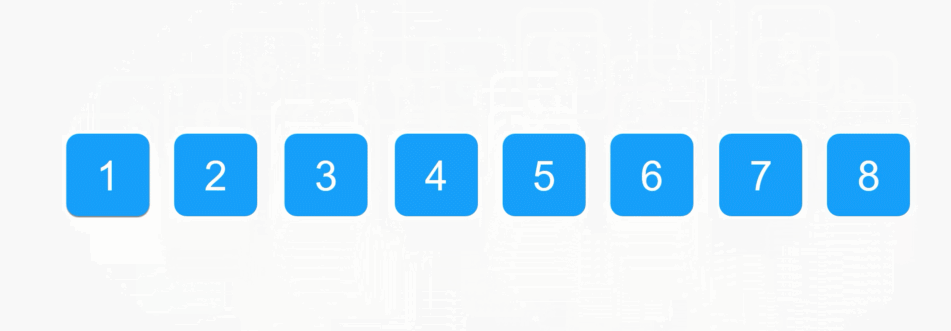
1️⃣SelectSort 实现:
// 选择排序
void SelectSort(int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {int minIndex = i + 1;// 选数for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {if (nums[j] < nums[minIndex ]) {minIndex = j;}}// 交换int temp = nums[minIndex];nums[minIndex] = nums[i];nums[i] = temp;}
}
2️⃣ SelectSort 优化: 我们可以同时选出两个数一个最大一个最小,把最小的组交换到当前区间的左边,最大的交换到区间的右边。
void SelectSort(int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);int left = 0;int right = size - 1;while (left < right) {// 最小值下标默认从左区间开始int maxIndex = left;int minIndex = left;for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) {if (nums[i] > nums[maxIndex]) {maxIndex = i;}if (nums[i] < nums[minIndex]) {minIndex = i;}}// 交换Swap(&nums[left] , &nums[minIndex]);// 特殊情况:假设第一个位置就是最大值 那么做完第一次交换最小的值到最左边// 而最大值被交换到了原来最小值的位置if (left == maxIndex) {maxIndex = minIndex;}Swap(&nums[right] , &nums[maxIndex]);left++;right--;}
}
Swap 实现:
// 交换
void Swap(int* val1, int* val2) {int temp = *val1;*val1 = *val2;*val2 = temp;
}
总结:
- 选择排序比较好理解,但是效率很低,实际种很少使用。
- 时间复杂度 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)
4. 堆排序 (⭐️⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
堆排序是指用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序思想,它是选择排序的一种,它是用堆来进行选数。升序需要建大堆,降序需要建小堆。
拿升序来举例,因为大堆的堆顶是最大的数,此时我们可以让堆顶和末尾元素交换。再让堆顶的元素向下调整(只不过此时向下调整,我们先让数组的长度减 1,因为最大的数已经到末尾的位置了,不必算入堆内)
AdjustDown 实现(大堆举例):
// 堆的向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(int * nums , int size , int parent) {assert(nums);// 默认左孩子最大int child = 2 * parent + 1;while (child < size) {// 选出左右孩子最大的孩子if (child + 1 < size && nums[child + 1] > nums[child]) {child++;}// 最大的孩子比父亲还大则调整if (nums[child] > nums[parent]) {Swap(&nums[child] , &nums[parent]);// 继续向下搜索parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;} else {break;}}
}
AdjustUp 实现(大堆举例):
// 堆的向上调整算法
void AdjustUp (int * nums , int child) {int parent = (child - 1) / 2;// 当孩子 = 0的时候已经没有父亲节点了while (child > 0) {if (nums[child] > nums[parent]) {Swap(&nums[child] , &nums[parent]);// 继续向上搜索child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;} else {break;}}
}
HeapSort 实现:
// 堆排序
void HeapSort(int * nums , int size) {assert(nums);// 先建堆// 向上调整算法建堆// for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {// AdjustUp(nums , i);// }// 向下调整算法建堆// 向下调整的前提是:左右子树必须都是堆// 所以大堆从第一个非叶子节点开始向下调整for (int parent = (size - 1 - 1) / 2; parent >= 0; parent--) {AdjustDown(nums , size , parent);}// 排序int end = size - 1;while (end > 0) {// 堆顶元素和末尾元素交换Swap(&nums[0] , &nums[end]); AdjustDown(nums , end , 0);end--;}
}
总结:
- 堆排序的时间复杂度 O ( N ∗ l o g N ) O(N*logN) O(N∗logN)
- 向上调整算法建堆的时间复杂度是 O ( N ∗ l o g N ) O(N * logN) O(N∗logN),向下调整算法建堆的时间复杂度是 O ( N ) O(N) O(N),但是向下调整算法建堆的前提是:当前左右子树必须是堆。所以向下调整算法要从非叶子节点开始向下调整,最后一个非叶子节点就是最后一个元素的父节点
(size - 1 - 1) / 2。
5. 冒泡排序 (⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
冒泡排序是交换排序的一种。所谓交换就是根据序列中两个记录下标值的比较结果来对这一对数据进行交换,当第一躺冒泡排序结束后,若是升序会把最大的数冒到最后末尾,以此类推。
BubbleSort 实现:
// 冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* nums, int size) {assert(nums);for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) {if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {Swap(&nums[j] , &nums[j + 1]);}}}
}
BubbleSort 优化:当数组为有序的时候,我们用 enchage 来记录,若当前这一趟一次都没有交换,则数组已经有序。
// 冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* nums, int size) {assert(nums);for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {int exchage = 1;for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) {if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {exchage = 0;Swap(&nums[j] , &nums[j + 1]);}}if (exchage) {break;}}
}
总结:
- 冒泡排序是非常经典的排序
- 时间复杂度 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)
6. 快速排序 (⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
快速排序是 Hoare于1962年提出的一种二叉树结构的交换排序方法。基本思想是:从待排序序列中选一个 key(通常为最左边或者最右边),按照 key 把待排序序列分成两个子序列,左序列中的元素都 < key,右序列的元素都 > key,然后左右序列重复该过程,直到所有元素都排列在对应的位置上。

1.hoare版本:
思路和结论:假设 key 为最左边的数,那么就要先从右边走,再走左边。假设 key 为最右边的数,那么就要从左边先走,再走右边。这样做的目的是:当 left 与 right 相遇结束的时候,让 key 位置的元素与当前相遇位置交换,而当前相遇位置一定能保证比 key 要小(或大)。 第一次快速排序相当于处理好了第一个区间,因为 key 找到了合适的位置左面的数都比 key 小,右面的数都比 key 要大,此时只需要让左右区间重复上面的过程。左右区间划分为了 [begin , keyIndex - 1] keyIndex [keyIndex + 1 , end]。递归处理即可,当左右区间只剩一个数(begin == end)或者区间不存在(begin > end)的时候为递归结束条件。
QucikSort实现:
void QuickSort(int * nums , int begin , int end) {// 只剩一个数或者区间不存在不需要处理if (begin >= end) {return;}int left = begin;int right = end;// key 默认为最左边的数字int keyIndex = left;while (left < right) {// 右边先走,找小while (left < right && nums[right] >= nums[keyIndex]) {right--;}// 左边找大while (left < right && nums[left] <= nums[keyIndex]) {left++;}// 交换Swap(&nums[left] , &nums[right]);}// 相遇位置和 keyIndex 交换Swap(&nums[keyIndex] , &nums[left]);// 更改 keyIndexkeyIndex = left;QuickSort(nums , begin , keyIndex - 1);QuickSort(nums , keyIndex + 1, end);
}
💬 思考问题:
-
nums[left] <= nums[keyIndex]和nums[right] >= nums[keyIndex]这里为什么要使用=,不使用=可以吗?结论是不可以。
- 为什么右边和左边走的时候要加上
left < right?

- 为什么
key如果是左边的数就要先从右边走呢?左边先走可以吗?结论是不可以。

2.挖坑版本:
思路:先将最左面的数据存在一个临时变量 key 中,这样当前 key 这个位置就是一个坑位。右面 right 找小,找到之后把小的数填到当前坑中 nums[keyIndex] = nums[right],此时更换坑的位置 keyIndex = right。左面 left 找大,找到之后把大的数继续填到当前坑中 nums[keyIndex] = nums[left],此时继续更换坑的位置 keyIndex = left。当 left 与 right 相遇时在把 key 填入相遇(坑位)位置。
QucikSort实现:
void QuickSort(int * nums , int begin , int end) {// 只剩一个数或者区间不存在不需要处理if (begin >= end) {return;}int left = begin;int right = end;// 保存当前坑的元素int key= nums[left];// 坑位int keyIndex = left;while (left < right) {while (left < right && nums[right] >= key) {right--;}// 填坑nums[keyIndex] = nums[right];// 更换坑的位置keyIndex = right;while (left < right && nums[left] <= key) {left++;}// 填坑nums[keyIndex] = nums[left];// 更换坑的位置keyIndex = left;}// 循环结束填入当前坑位nums[keyIndex] = key;QuickSort(nums , begin , keyIndex - 1);QuickSort(nums , keyIndex + 1, end);
}
注:同样一组数,使用 hoare 思想和挖坑法思想进行一轮快排的结果是不同的。
例如:{6 , 1 , 2 , 7 , 9 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 10 , 8}
-
hoare:第一次交换{6 , 1 , 2 , 5 , 9 , 3 , 4 , 7 , 10 , 8}、第二次交换{6 , 1 , 2 , 5 , 4 , 3 , 9 , 7 , 10 , 8}、循环结束相遇位置与keyIndex位置交换{3 , 1 , 2 , 5 , 4 , 6 , 9 , 7 , 10 , 8}最终结果。 -
挖坑法:第一次挖坑{5 , 1 , 2 , 7 , 9 , 3 , 4 , (5) , 10 , 8}、第二次{5 , 1 , 2 , (7) , 9 , 3 , 4 , 7 , 10 , 8}、第三次{5 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 9 , 3 , (4) , 7 , 10 , 8}、第四次{5 , 1 , 2 , 4 , (9) , 3 , 9 , 7 , 10 , 8}、第五次{5 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 3 , (3) , 9 , 7 , 10 , 8}、循环结束把当前坑位填入key最终结果是{5 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 3 , 6 , 9 , 7 , 10 , 8}。
3.前后指针版本:
思路: 定义一个 prev 和 cur,cur 找比 key 要小的数,若找到则 ++prev 和 cur 当前下标的元素进行交换,这样做有一种把小的数翻到前面来,大的往后推。而 prev 后面的数都要比 key 大,最终 cur 越界循环结束,再把 keyIndex 位置和 prev 位置的元素进行交换。
QucikSort 实现:
void QuickSort(int * nums , int begin , int end) {// 只剩一个数或者区间不存在不需要处理if (begin >= end) {return;}int prev = begin;int cur = prev + 1;int keyIndex = begin;while (cur <= end) {if (nums[cur] < nums[keyIndex] && ++prev != cur) {Swap(&nums[prev] , &nums[cur]);}cur++;}Swap(&nums[prev] , &nums[keyIndex]);keyIndex = prev;QuickSort(nums , begin , keyIndex - 1);QuickSort(nums , keyIndex + 1, end);
}
🌟 快排优化
💬 为什么要优化?
因为 key 会影响快排的效率,如果每次的 key 都是中间那个值那么每次都是二分,若每次的 key 都是最小的,最坏情况下快排的时间复杂度 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)。最大的问题是会引起 栈溢出。
1.三数取中优化:
思路: 第一个数和中间还有最后的数,选不是最大也不是最小的数。三数取中主要体现在数据已经有序的情况下。
getMidIndex 实现:
int getMidIndex(int* nums, int begin, int end) {int midIndex = (begin + end) / 2;if (nums[begin] > nums[midIndex]) {// nums[begin] > nums[minIndex]if (nums[midIndex] > nums[end]) {// nums[begin] > nums[minIndex] > nums[end]return midIndex;}else if (nums[begin] > nums[end]) {// nums[begin] > nums[minIndex]// nums[end] >= nums[minIndex]// nums[begin] > nums[end]return end;}else {// nums[begin] > nums[minIndex]// nums[end] >= nums[minIndex]// nums[begin] <= nums[end]return begin;}}else {// nums[begin] <= nums[minIndex]if (nums[begin] > nums[end]) {// nums[begin] <= nums[minIndex]// nums[begin] > nums[end]return begin;}else if (nums[midIndex] > nums[end]) {// nums[begin] <= nums[minIndex]// nums[begin] <= nums[end]// nums[minIndex] > nums[end]return end;}else {// nums[begin] <= nums[minIndex]// nums[begin] <= nums[end]// nums[minIndex] <= nums[end]return midIndex;}}
}
2.小区间优化:
思路: 若只剩最后 10 - 20 个数,还使用快速排序的递归就有点不太划算了。所以当区间较小的时候,就不再使用递归继续划分小区间。考虑直接用其他排序对小区间处理,而希尔排序和堆排序对于数据量小的时候也不太优,所以在简单排序中,插入排序适应性最强。 小区间优化体现在减少递归的调用次数。
QuickSort 优化实现:
void QuickSort(int* nums, int begin, int end) {// 只剩一个数或者区间不存在不需要处理if (begin >= end) {return;}if (end - begin > 15) {int prev = begin;int cur = prev + 1;int keyIndex = begin;// 三数取中优化int midIndex = getMidIndex(nums, begin, end);Swap(&nums[keyIndex], &nums[midIndex]);while (cur <= end) {if (nums[cur] < nums[keyIndex] && ++prev != cur) {Swap(&nums[prev], &nums[cur]);}cur++;}Swap(&nums[prev], &nums[keyIndex]);keyIndex = prev;QuickSort(nums, begin, keyIndex - 1);QuickSort(nums, keyIndex + 1, end);} else {// 小区间优化// 插入排序InsertSort(nums + begin , end - begin + 1);}
}
🌟 快排非递归
QuickSortNoneR 非递归实现:
// 快排非递归(使用栈)
void QucikSortNoneR(int* nums, int begin, int end) {assert(nums);Stack stack;StackInit(&stack);// 区间进栈StackPush(&stack , end);StackPush(&stack, begin);while (!StackEmpty(&stack)) {// 取出左右区间int left = StackTop(&stack);StackPop(&stack);int right = StackTop(&stack);StackPop(&stack);// 快排int keyIndex = left;int prev = left;int cur = prev + 1;while (cur <= right) {if (nums[cur] < nums[keyIndex] && ++prev != cur) {Swap(&nums[prev], &nums[cur]);}cur++;}Swap(&nums[prev], &nums[keyIndex]);keyIndex = prev;// [left , keyIndex - 1] keyIndex [keyIndex + 1 , right]if (keyIndex + 1 < right) {// 区间存在 入栈StackPush(&stack, right);StackPush(&stack, keyIndex + 1);}if (left < keyIndex - 1) {// 区间存在 入栈StackPush(&stack, keyIndex - 1);StackPush(&stack, left);}}StackDestroy(&stack);
}
总结:
- 时间复杂度 O ( N ∗ l o g N ) O(N*logN) O(N∗logN)
- 空间复杂度 O ( l o g N ) O(logN) O(logN)
7. 归并排序 (⭐️⭐️⭐️)
🌟 思想:
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,是分治的一个典型的应用。将两个有序的子序列归并得到完全有序的序列。归并排序要借助额外的空间。
MergeSort 递归实现:
void merge(int* nums, int begin, int end, int* temp) {// 区间只有一个数或者不存在if (begin >= end) {return;}int midIndex = (begin + end) / 2;// [begin , midIndex] [minIndex + 1 , end]merge(nums , begin , midIndex , temp);merge(nums , midIndex + 1 , end , temp);// 归并int leftBegin = begin;int leftEnd = midIndex;int rightBegin = midIndex + 1;int rightEnd = end;int i = leftBegin;while (leftBegin <= leftEnd && rightBegin <= rightEnd) {if (nums[leftBegin] < nums[rightBegin]) {temp[i++] = nums[leftBegin++];}else {temp[i++] = nums[rightBegin++];}}// 左区间还存在while (leftBegin <= leftEnd) {temp[i++] = nums[leftBegin++];}// 右区间还存在while (rightBegin <= rightEnd) {temp[i++] = nums[rightBegin++];}// 拷贝回原数组memcpy(nums + begin , temp + begin, (end - begin + 1) * sizeof(int));
}// 归并排序
void MergeSort(int* nums, int size) {assert(nums);int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);assert(temp);merge(nums , 0 , size - 1 , temp);free(temp);
}
🌟 归并非递归
MergeSort 非递归实现:
// 归并排序非递归
void MergeSortNoneR(int* nums, int size) {assert(nums);int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);assert(temp);int gap = 1;while (gap < size) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i += 2 * gap) {int leftBegin = i;int leftEnd = i + gap - 1;int rightBegin = i + gap;int rightEnd = i + 2 * gap - 1;// 检查边界if (leftEnd >= size) {// 修正左区间leftEnd = size - 1;// 让右区间不存在rightBegin = size + 1;rightEnd = size;}else if (rightBegin >= size) {rightBegin = size + 1;rightEnd = size;}else if (rightEnd >= size) {rightEnd = size - 1;}// 归并int j = leftBegin;while (leftBegin <= leftEnd && rightBegin <= rightEnd) {if (nums[leftBegin] < nums[rightBegin]) {temp[j++] = nums[leftBegin++];}else {temp[j++] = nums[rightBegin++];}}// 左区间还存在while (leftBegin <= leftEnd) {temp[j++] = nums[leftBegin++];}// 右区间还存在while (rightBegin <= rightEnd) {temp[j++] = nums[rightBegin++];}}memcpy(nums, temp, sizeof(int) * size);gap *= 2;}free(temp);
}
总结:
- 时间复杂度 O ( N ∗ l o g N ) O(N*logN) O(N∗logN)
- 空间复杂度 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)





传播常数β的matlab计算(验证了是对的))


:Streaming DataFrame 和 Streaming DataSet 创建)










