目录
2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
2.2队列的实现
2.2.1初始化队列
2.2.2队尾入队列
2.2.3队头出队列
2.2.4获取队列头部元素
2.2.5 销毁队列
3.栈和队列面试题
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
编辑
622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
编辑
2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
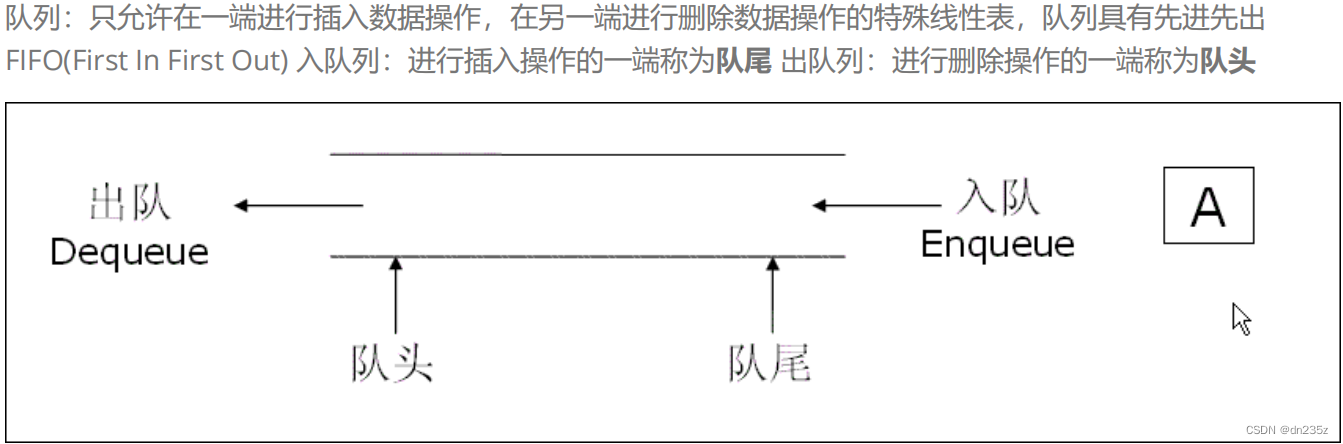
将队列运用于抽号机能够计算出排队需要的等待的时间,需要等待前面的人数等信息,也能实现叫号(取队头)操作,能够实现绝对的公平,不存在插队现象。
2.2队列的实现
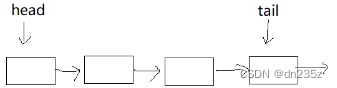
2.2.1初始化队列
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}2.2.2队尾入队列
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//开辟新节点QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}//初始化新节点newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;//判断队列是否为空if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}//不为空尾插else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}2.2.3队头出队列
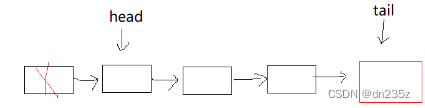
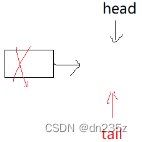
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//列表不能为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//如果列表只剩一个成员if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}//正常头删else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}2.2.4获取队列头部元素
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//检查列表不为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//列表为空返回1,不为空返回0return pq->head == NULL;
}2.2.5 销毁队列
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}2.2.6 探空
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//列表为空返回1,不为空返回0return pq->head == NULL;
}3.栈和队列面试题
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

分析:创建两个队列入队列:入不为空的队列出队列:出不为空的前n-1个元素,插入到空队列,删除剩余元素




typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{QDataType data;struct QueueNode* next;}QNode;
typedef struct Que
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
//队列节点数
int QueueSize(Que* pq);// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//开辟新节点QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}//初始化新节点newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;//判断队列是否为空if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;pq->size++;}//不为空尾插else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;pq->size++;}
}// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//列表不能为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//如果列表只剩一个成员if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}//正常头删else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//检查列表不为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}// 获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//检查列表不为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//列表为空返回1,不为空返回0return pq->head == NULL;
}
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//队列节点数
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}//定义列表的结构体
typedef struct {Que q1;Que q2;
} MyStack;
//列表初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate() {//不能直接初始化,临时变量,出函数销毁,需要开辟空间MyStack* pst=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));//参数为队列的指针QueueInit(&pst->q1);QueueInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {//谁不为空push到谁if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}
//出栈
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {//随便假设一个为空队列,一个为非空Que* empty=&obj->q1;Que* nonempty=&obj->q2;//如果假设错误,就交换if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){nonempty=&obj->q1;empty=&obj->q2;}//将非空栈出到剩尾元素为止while(QueueSize(nonempty)>1){//非空栈入到空栈QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonempty));//入一个出一个QueuePop(nonempty);}//保存尾元素int top=QueueFront(nonempty);//出掉尾元素QueuePop(nonempty);return top;}
//取栈顶
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {//谁不为空取谁的队尾if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}
//探空
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {//两个列表都空才为空return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{//结构体指针下创建了两个列表,需要先释放列表QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();* myStackPush(obj, x);* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);* myStackFree(obj);
*/232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
栈的特性是先后进先出,队列的特性是先进先出;若想用栈实现先进先出,就需要另创建一个栈,将原栈中的数据倒过去就能够轻松实现。
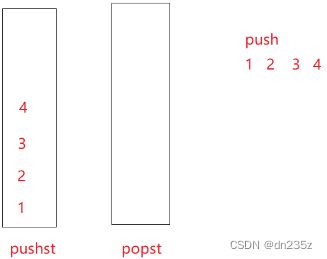
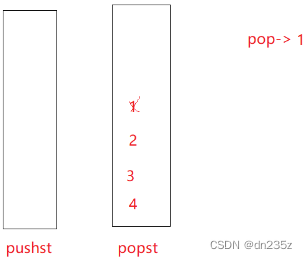
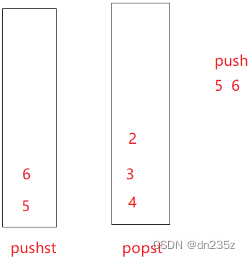
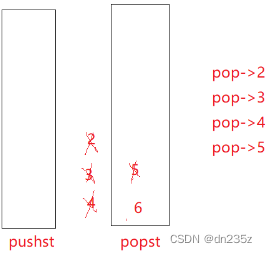
原栈中的数据倒过去之后,此时插入数据,直接插入到原栈中,用原栈专门用来接收数据,如果再出栈,用一个栈专门出栈,当专门出栈的栈出空之后,再从原栈倒数据过来;而不用每次出栈都把数据倒出去又倒回来,很麻烦。
typedef int STDataType;
//支持动态增长的栈
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;//栈顶int capacity;//容量
}ST;// 初始化栈
void STInit(ST* ps);
// 入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
// 出栈
void STPop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int STSize(ST* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
// 销毁栈
void STDestroy(ST* ps);void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);// 11:40if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);// assert(ps->top > 0);--ps->top;
}STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);// assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}//定义两个栈类型
typedef struct {ST pushst;ST popst;
} MyQueue;//开辟并初始化结构体变量
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&obj->pushst);STInit(&obj->popst);return obj;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {//始终往push栈上面pushSTPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
//出队列
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {int front=myQueuePeek(obj);//与peek唯一不同之处就是取得队头后删掉STPop(&obj->popst);return front;
}
//取队头数据
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if(STEmpty(&obj->popst)){//pop为空,从push倒数据while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst)){//pop入一个STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));//push出一个STPop(&obj->pushst);}}//不为空,直出return STTop(&obj->popst);
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {//两个栈都为空才为空return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {STDestroy(&obj->pushst);STDestroy(&obj->popst);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();* myQueuePush(obj, x);* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);* myQueueFree(obj);
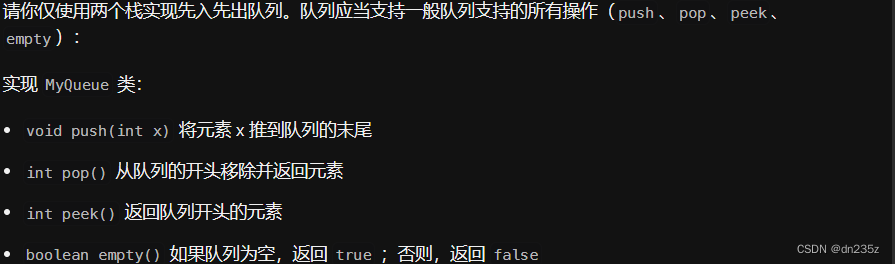
*/622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
我们用数组来实现,给数组多开一个 rear 空间(不存数据)用来解决探空和探满的问题
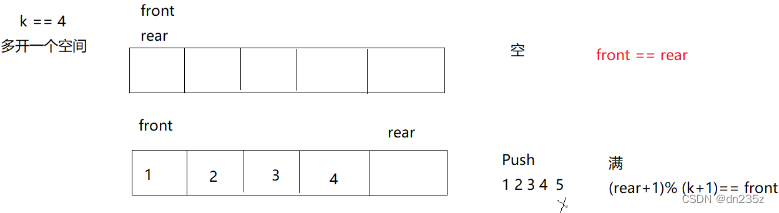
front 为列表头节点的下标,rear 为为尾节点的下一个节点的下标;front 和rear 初始值为0,push 一次 rear ++一次,由于列表是定长的,因此当push 了k个数据时,列表就放满了,不能再入数据。放满的标志为此时列表的实际长度(包括 rear节点)对理论长度 k+1 取余的结果等于 front 。

pop操作,我们直接让 front ++,遵循先进先出的原则。

push 操作,push 一次,rear 向后移动一次,直到 rear 的下一个为 front ,则代表放满,标志依然为(rear+1)%(k+1)=front ,当rear<k,就等于 rear +1= front。
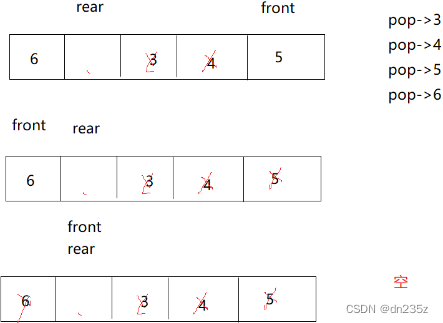
此时再 pop 到 front 处于数组末尾,继续 pop,front 就转到数组开头,当 rear 和 front 重合且为空时,数组就为空。
//定义队列
typedef struct {//数组int *a;//头int front;//尾int rear;//数组长度(不包含rear)int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
//初始化队列
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {//为队列开空间MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));//为数组开空间,多开一个rear用于探空(满)obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));obj->front=obj->rear=0;obj->k=k;return obj;
}
//探空(非0为空,0为非空)
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {//front和rear相等就是空return obj->front==obj->rear;}
//探满(非0为满,0为未满)
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {//rear的下一个为front为满;rear在队尾,front在对头为满。return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;}
//插入
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {//先探满if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}//正常情况下往rear位置放数据,放完后移obj->a[obj->rear]=value;obj->rear++;//如果rear走到队尾之后(++之后等于k),那么++之后应该挪到队头(归0,因此取模)//取模操作在走过队尾之前无效obj->rear%=(obj->k+1);return true;
}
//删除
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {//先探空if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}//正常情况下front后移obj->front++;//如果front走到队尾之后(++之后等于k),那么++之后应该挪到队头(归0,因此取模)obj->front%=(obj->k+1);return true;
}
//取头
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {//探空if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}else{return obj->a[obj->front];}
}
//取尾(取rear的上一个节点)
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {//探空if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}else{//+k并对k+1取余,当rear在队头,上一个节点就在队尾//不在队头时取余结果刚好为上一个节点return obj->a[(obj->rear+obj->k)%(obj->k+1)];}}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {free(obj->a);free(obj);}/*** Your MyCircularQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyCircularQueue* obj = myCircularQueueCreate(k);* bool param_1 = myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, value);* bool param_2 = myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);* int param_3 = myCircularQueueFront(obj);* int param_4 = myCircularQueueRear(obj);* bool param_5 = myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj);* bool param_6 = myCircularQueueIsFull(obj);* myCircularQueueFree(obj);
*/



)











)
:特殊矩阵的压缩存储:稀疏矩阵——压缩稀疏行(CSR))

总结)

)