目录
1. 为什么要有链表?
2. 链表的种类
3. 具体功能实现
(1)节点结构体定义
(2)申请节点
(3)尾插
(4)尾删
(5)头插
(6)头删
(7)查找
(8)指定位置插入
(9)插入指定位置后面
(10)消除指定位置元素
(11)消除指定位置后的数据
(12)打印链表
(13)销毁链表
4. 完整代码
1. slist.c
2. slist.h
3. 测试文件
1. 为什么要有链表?
上篇文章我们介绍了顺序表,顺序表有很多缺陷比如
1. 空间不够需要增容,增容需要付出代价
2. 为了避免频繁扩容,我们满了基本上都是扩2倍,可能会导致一定的空间浪费
3. 要求数据从开始位置连续存储,我们在头部或中间插入删除数据,需要挪动数据,效率不高
那有人就针对顺序表的诸多缺陷,设计出了链表
链表的优缺点如下:
优点:
按需申请空间,不用了就释放空间,头部中间插入删除数据不需要挪动数据,不存在空间浪费。缺点:
每存一个数据都要存一个指针去链接后面的内存节点,不支持随机访问(用下标直接访问第i个)
2. 链表的种类
单向或双向,带头或不带头,循环或不循环
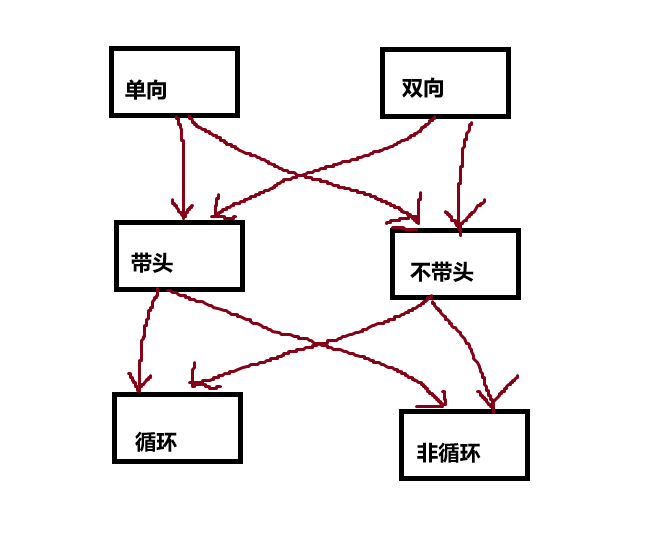
共八种
最常用的为
1. 无头单向非循环链表
结构简单,更多作为其他数据结构的子结构
2. 带头双向循环链表
结构复杂,一般用于单独存储数据,实际使用中结构复杂实现简单
3. 具体功能实现
(1)节点结构体定义
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;data 用来存储数据
next用来存储下一个节点的地址
(2)申请节点
插入数据时节省代码量
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (newnode == NULL){exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}(3)尾插
在链表的末尾链接上一个节点
void SListPushBack(SListNode** phead, SLTDataType x)
{ SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*phead == NULL){*phead = newnode;}else{SListNode* tail = *phead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}}(4)尾删
删除链表最末尾的那个节点
void SListPopBack(SListNode** phead)
{ if (*phead == NULL)return;//assert(*phead!=NULL);if ((*phead)->next == NULL){free(*phead);*phead = NULL;}else{SListNode* tail = *phead;SListNode* t = tail;while (tail->next != NULL){t = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;t->next = NULL;//SListNode* tail = *phead;//while (tail->next->next != NULL)//{// tail = tail->next;//}//free(tail->next);//tail->next = NULL;}}
(5)头插
在链表头部插入数据
void SListPushFront(SListNode** phead, SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *phead;*phead = newnode;
}(6)头删
删除链表头部的数据
void SListPopFront(SListNode** phead)
{if (*phead == NULL)return;SListNode* front=(*phead)->next;free(*phead);*phead = front;
}
(7)查找
查找链表中的某个数据,返回地址,找不到返回空指针
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}else{cur = cur->next;}}return NULL;
}(8)指定位置插入
根据给的地址插入数据(插入到指定位置前面)
void SListInsert(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)//pos配合查找函数
{SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*phead == pos){void SListPopFront(phead);}//找到pos的前一位置else{ SListNode* posPrey = *phead;while (posPrey->next != pos){posPrey = posPrey->next;}posPrey->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}(9)插入指定位置后面
void SListInsertTail(SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}(10)消除指定位置元素
void SListErase(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos)
{assert(head && (*head));assert(pos);if (*phead == pos){*phead = (*phead)->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}else{SListNode* prev = *phead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}(11)消除指定位置后的数据
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);if (pos == NULL){exit(-1);}SListNode* next = pos->next;pos->next = next->next;free(next);next = NULL;
}(12)打印链表
void SListPrint(SListNode* phead)
{SListNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}
(13)销毁链表
使用结束后要销毁
void SListDestroy(SListNode** phead)
{assert(phead && *phead);SListNode* plist = *phead;while (plist->next != NULL){plist = plist->next;free(*phead);*phead = plist;}free(*phead);*phead = NULL;}4. 完整代码
1. slist.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#include"sllist.h"SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (newnode == NULL){exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SListPrint(SListNode* phead)
{SListNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}void SListPushBack(SListNode** phead, SLTDataType x)
{ SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*phead == NULL){*phead = newnode;}else{SListNode* tail = *phead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}}void SListPushFront(SListNode** phead, SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *phead;*phead = newnode;
}void SListPopBack(SListNode** phead)
{ if (*phead == NULL)return;//assert(*phead!=NULL);if ((*phead)->next == NULL){free(*phead);*phead = NULL;}else{SListNode* tail = *phead;SListNode* t = tail;while (tail->next != NULL){t = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;t->next = NULL;//SListNode* tail = *phead;//while (tail->next->next != NULL)//{// tail = tail->next;//}//free(tail->next);//tail->next = NULL;}}void SListPopFront(SListNode** phead)
{if (*phead == NULL)return;SListNode* front=(*phead)->next;free(*phead);*phead = front;
}SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{SListNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}else{cur = cur->next;}}return NULL;
}
void SListInsert(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)//pos配合查找函数
{SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*phead == pos){void SListPopFront(phead);}//找到pos的前一位置else{ SListNode* posPrey = *phead;while (posPrey->next != pos){posPrey = posPrey->next;}posPrey->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}
void SListInsertTail(SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}
void SListErase(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos)
{assert(head && (*head));assert(pos);if (*phead == pos){*phead = (*phead)->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}else{SListNode* prev = *phead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);if (pos == NULL){exit(-1);}SListNode* next = pos->next;pos->next = next->next;free(next);next = NULL;
}
void SListDestroy(SListNode** phead)
{assert(phead && *phead);SListNode* plist = *phead;while (plist->next != NULL){plist = plist->next;free(*phead);*phead = plist;}free(*phead);*phead = NULL;}
2. slist.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;void SListPrint(SListNode* phead);
//打印
void SListPushBack(SListNode** phead, SLTDataType x);
//尾插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** phead,SLTDataType x);
//头插
void SListPopBack(SListNode** phead);
//尾删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** phead);
//头删
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
//找位置
//在pos位置之前去插入一个节点
void SListInsert(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//在pos前面插入//void SListInsert(SListNode* phead, int pos, SLTDataType x);void SListErase(SListNode** phead, SListNode* pos);
//找坐标删除
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos);
//删除坐标后面的值void SListDestroy(SListNode** phead)3. 测试文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#include"sllist.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void TestSList1()
{SListNode* plist = NULL;//初始值SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPushFront(&plist, 5);SListPrint(plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPrint(plist);
}
void TestSList2()
{SListNode* plist = NULL;//初始值SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 2);SListInsert(&plist ,pos,20);SListPrint(plist);//SListDestroy(&plist);//SListPrint(plist);int i = 1;while (pos){printf("第%d个节点%p->%d\n", i++, pos, pos->data);pos = SListFind(pos->next, 2);}pos = SListFind(plist, 3);while(pos){pos->data = 30;pos = SListFind(pos->next, 3);}SListPrint(plist);
}
typedef struct xx
{int* n;
}xx;
int main()
{TestSList2();//xx p;//int a = 0;//p.n = &a;//a = 2;//printf("%d", *(p.n));return 0;
}这篇文章就到这里了,希望可以帮到您
(๑′ᴗ‵๑)I Lᵒᵛᵉᵧₒᵤ❤




)

 此版本的 AutoCAD 安装不正确)

可根据参数名称来指定参数值uccess(data: $list, count: $count))

)



)



 —— 转换流、打印流)
