引言
结合前面所学
http://ELK日志分析系统
一、为什么要做日志分析平台
随着业务量的增长,每天业务服务器将会产生上亿条的日志,单个日志文件达几个GB,这时我们发现用Linux自带工具,cat grep awk 分析越来越力不从心了,而且除了服务器日志,还有程序报错日志,分布在不同的服务器,查阅繁琐。
待解决的痛点:
- 大量不同种类的日志成为了运维人员的负担,不方便管理;
- 单个日志文件巨大,无法使用常用的文本工具分析,检索困难;
- 日志分布在多台不同的服务器上,业务一旦出现故障,需要一台台查看日志。
二、ELK+Filebeat+Zookeeper+Kafka架构
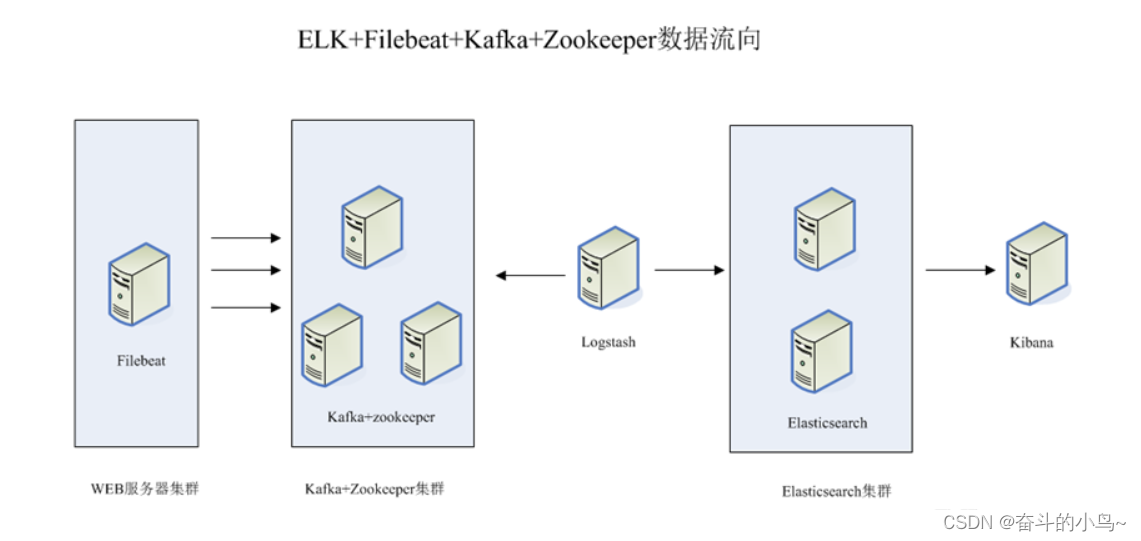
整体的架构如上图所示
这个架构图从左到右,总共分为5层,每层实现的功能和含义分别介绍如下:
第一层、数据采集层
- 数据采集层位于最左边的业务服务器集群上,在每个业务服务器上面安装了filebeat做日志收集,然后把采集到的原始日志发送到Kafka+zookeeper集群上。
第二层、消息队列层
- 原始日志发送到Kafka+zookeeper集群上后,会进行集中存储,此时,filbeat是消息的生产者,存储的消息可以随时被消费。
第三层、数据分析层
- Logstash作为消费者,会去Kafka+zookeeper集群节点实时拉取原始日志,然后将获取到的原始日志根据规则进行分析、清洗、过滤,最后将清洗好的日志转发至Elasticsearch集群。
第四层、数据持久化存储
- Elasticsearch集群在接收到logstash发送过来的数据后,执行写磁盘,建索引库等操作,最后将结构化的数据存储到Elasticsearch集群上。
第五层、数据查询、展示层
- Kibana是一个可视化的数据展示平台,当有数据检索请求时,它从Elasticsearch集群上读取数据,然后进行可视化出图和多维度分析。
三、搭建ELK+Filebeat+Zookeeper+Kafka
1、环境准备
| 服务器ip地址 | 节点名称 | 安装组件 |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.10.100 | node1 | Elasticsearch 、Kibana |
| 192.168.10.101 | node2 | Elasticsearch |
| 192.168.10.102 | logstash | logstash、Apache |
| 192.168.10.103 | filebeat | filebeat |
| 192.168.10.104 | zk+kfk1 | zookeeper、Kafka |
| 192.168.10.105 | zk+kfk2 | zookeeper、Kafka |
所有服务器关闭防火墙以及核心防护
systemctl stop firewalld
setenforce 0修改主机名
##第一台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname node1
[root@localhost ~]#bash##第二台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname node2
[root@localhost ~]#bash##第三台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname logstash
[root@localhost ~]#bash##第四台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname filebeat
[root@localhost ~]#bash##第五台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname zk-kfk1
[root@localhost ~]#bash##第六台
[root@localhost ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname zk-kfk2
[root@localhost ~]#bash配置域名解析
echo "192.168.10.100 node1" > /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.10.101 node2" > /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.10.102 logstash" > /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.10.103 filebeat" > /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.10.104 zk-kfk1" > /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.10.105 zk-kfk2" > /etc/hosts查看java环境
##java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_131"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode)2、部署ElasticSearch(在node1、node2节点上)
两台同时操作
1.安装ElasticSearch的rpm包,并解压
#上传elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm到/opt目录下
cd /opt
rz -E
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm ##解压2.加载服务系统并开启开机自启
systemctl daemon-reload ##加载服务
systemctl enable elasticsearch.service ##设置开机自启服务3.修改ElasticSearch主配置文件
[root@node1 opt]#cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak ##先进性备份
[root@node1 opt]#vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml ###修改elasticsearch主配置文件cluster.name: my-elk-cluster ##第17行, 取消注释,指定集群名字
node.name: node1 ##第23行, 取消注释,指定节点名字:Node1节点为node1,Node2节点为node2
path.data: /data/elk_data ##第33行, 取消注释,指定数据存放路径
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/ ##第37行, 取消注释,指定日志存放路径
bootstrap.memory_lock: false ##第43行, 取消注释,改为在启动的时候不锁定内存
network.host: 0.0.0.0 ##第55行, 取消注释,设置监听地址,0.0.0.0代表所有地址
http.port: 9200 ##第59行, 取消注释,ES 服务的默认监听端口为9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"] ##第68行, 集群发现通过单播实现,指定要发现的节点 node1、node2[root@node1 opt]#grep -v "^#" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
node.name: node1
path.data: /data/elk_data
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"]4.创建数据存放路径并授权,启动服务并查看端口是否开启
mkdir -p /data/elk_data ##创建数据存放路径
chown elasticsearch:elasticsearch /data/elk_data/ ##给数据存放路径赋予权限
systemctl start elasticsearch.service ##启动比较慢,需要等待
netstat -natp | grep 9200 ##过滤端口
tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 37606/java5.查看节点信息
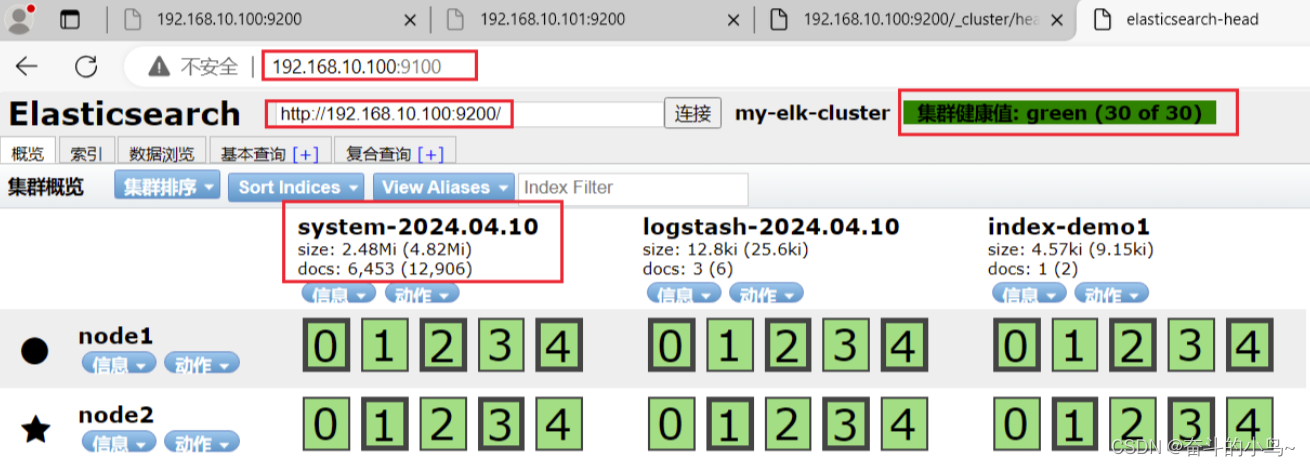
浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:9200 、 http://192.168.10.101:9200 查看节点 Node1、Node2 的信息。浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:9200/_cluster/health?pretty 、 http://192.168.10.101:9200/_cluster/health?pretty查看群集的健康情况,可以看到 status 值为 green(绿色), 表示节点健康运行。#使用上述方式查看群集的状态对用户并不友好,可以通过安装 Elasticsearch-head 插件,可以更方便地管理群集。绿色:健康 数据和副本 全都没有问题
红色:数据都不完整
黄色:数据完整,但副本有问题3、安装ElasticSearch-head插件(在node1节点上操作)
1.编译安装node1
#上传软件包 node-v8.2.1.tar.gz 到/opt
yum install gcc gcc-c++ make -y
cd /opt
rz -E
tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
cd node-v8.2.1/
./configure
make -j4 && make install2.安装phantomjs(前端框架)
[root@node1 opt]#ls
elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm node-v8.2.1.tar.gz rh
elasticsearch-head.tar.gz node-v8.2.1 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@node1 opt]#tar jxf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 -C /usr/local/src/
[root@node1 opt]#cd /usr/local/src/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin/
[root@node1 bin]#ls
phantomjs
[root@node1 bin]#cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin/3.安装ElasticSearch-head数据可视化工具
[root@node1 opt]#ls
elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm node-v8.2.1.tar.gz rh
elasticsearch-head.tar.gz node-v8.2.1 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@node1 opt]#tar xf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@node1 opt]#cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]#ls
Dockerfile Gruntfile.js LICENCE package-lock.json README.textile test
Dockerfile-alpine grunt_fileSets.js node_modules plugin-descriptor.properties _site
elasticsearch-head.sublime-project index.html package.json proxy src
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]#npm install
npm WARN deprecated fsevents@1.2.13: The v1 package contains DANGEROUS / INSECURE binaries. Upgrade to safe fsevents v2
npm WARN optional SKIPPING OPTIONAL DEPENDENCY: fsevents@^1.0.0 (node_modules/karma/node_modules/chokidar/node_modules/fsevents):
npm WARN notsup SKIPPING OPTIONAL DEPENDENCY: Unsupported platform for fsevents@1.2.13: wanted {"os":"darwin","arch":"any"} (current: {"os":"linux","arch":"x64"})
npm WARN elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 license should be a valid SPDX license expressionup to date in 5.63s4.修改ElasticSearch主配置文件
[root@node1 opt]#vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml ##修改 Elasticsearch 主配置文件--末尾添加以下内容--
http.cors.enabled: true #开启跨域访问支持,默认为 false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #指定跨域访问允许的域名地址为所有systemctl restart elasticsearch ##重启elasticsearch服务5.启动ElasticSearch-head服务
#必须在解压后的 elasticsearch-head 目录下启动服务,进程会读取该目录下的 gruntfile.js 文件,否则可能启动失败。
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
npm run start &> elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head
> grunt serverRunning "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100#elasticsearch-head 监听的端口是 9100
ss -natp |grep 91006.通过ELasticSearch-head查看ElasticSearch信息
通过浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:9100/ 地址并连接群集。
如果看到群集健康值为 green 绿色,代表群集很健康。
注意:有的时候显示未连接,这时将 localhost 改成 IP 地址即可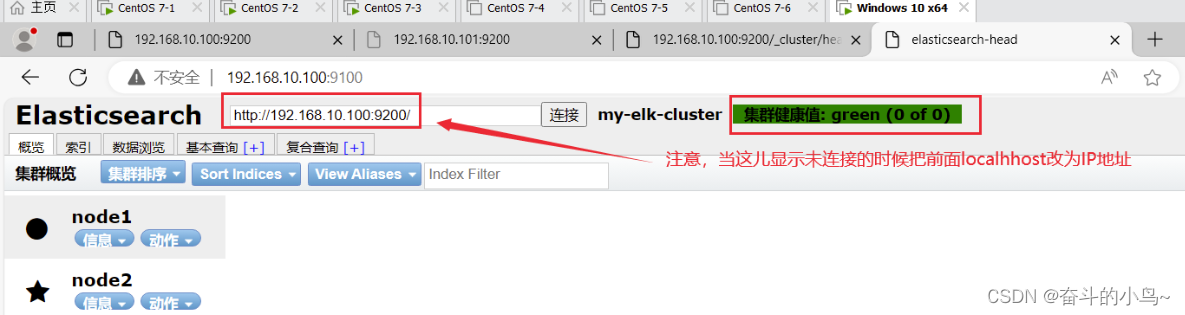
7.插入索引
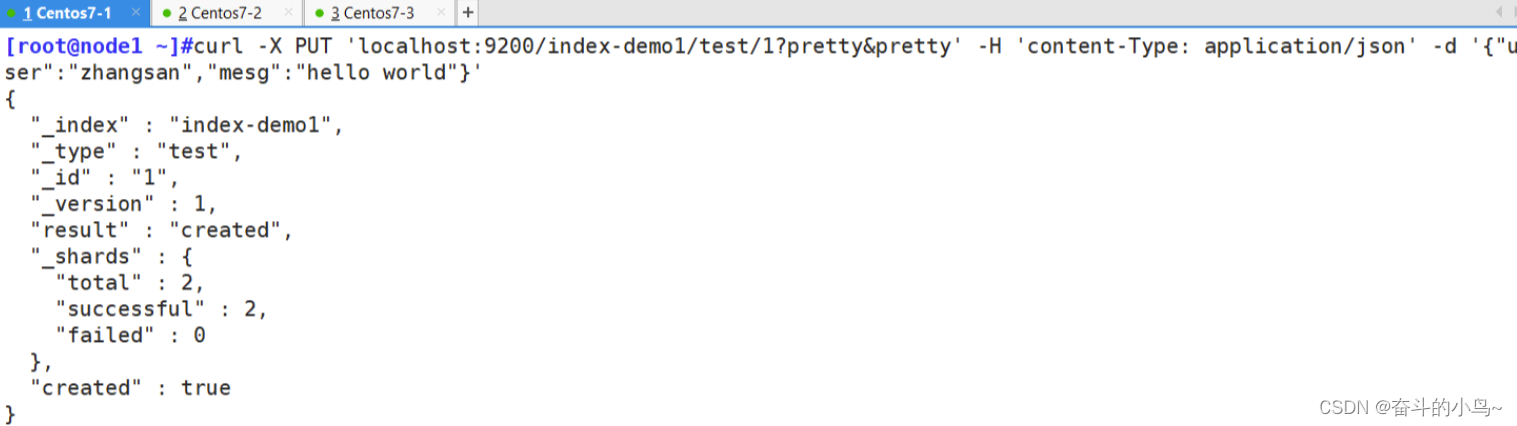
#通过命令插入一个测试索引,索引为 index-demo,类型为 test。
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo1/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'//输出结果如下:
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"created" : true
}
8.浏览器查看索引信息
浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:9100/ 查看索引信息,
可以看见索引默认被分片5个,并且有一个副本。
点击“数据浏览”,会发现在node1上创建的索引为 index-demo,类型为 test 的相关信息。4、ELK Logstash部署(在APache节点上操作)
1.安装Apache服务(httpd)
yum install httpd -y ##安装Apache服务2.安装java环境
[root@logstash opt]#java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_131"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode)3.安装Logstash
[root@logstash ~]#cd /opt/
[root@logstash opt]#rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@logstash opt]#ls
logstash-5.5.1.rpm rh
[root@logstash opt]#rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm
警告:logstash-5.5.1.rpm: 头V4 RSA/SHA512 Signature, 密钥 ID d88e42b4: NOKEY
准备中... ################################# [100%]
正在升级/安装...1:logstash-1:5.5.1-1 ################################# [100%]
Using provided startup.options file: /etc/logstash/startup.options
Successfully created system startup script for Logstash[root@logstash opt]#ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/ ##做软链接4.测试Logstash
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl start logstash.service ##首先开启服务
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl enable logstash.service
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl status logstash.service
● logstash.service - logstashLoaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/logstash.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)Active: active (running) since 三 2024-04-10 22:42:12 CST; 3s agoMain PID: 5783 (java)CGroup: /system.slice/logstash.service└─5783 /usr/bin/java -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=75 -XX:+U...4月 10 22:42:12 logstash systemd[1]: Started logstash.
4月 10 22:42:12 logstash systemd[1]: Starting logstash...##定义输入和输出流:
##输入采用标准输入,输出采用标准输出(类似管道)
##logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'[root@logstash ~]#logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
ERROR StatusLogger No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path //usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs to console
22:45:31.013 [main] INFO logstash.setting.writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/queue"}
22:45:31.016 [main] INFO logstash.setting.writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.dead_letter_queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/dead_letter_queue"}
22:45:31.043 [LogStash::Runner] INFO logstash.agent - No persistent UUID file found. Generating new UUID {:uuid=>"c93492d0-eb1a-4fb2-a962-69e4952cbc77", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/uuid"}
22:45:31.203 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>4, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>500}
22:45:31.259 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
22:45:31.328 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}www.baidu.com
2024-04-10T14:47:32.349Z logstash www.baidu.comrubydebug 输出:
#使用 rubydebug 输出详细格式显示,codec 为一种编解码器
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'[root@logstash ~]#logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
ERROR StatusLogger No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path //usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs to console
22:55:57.519 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>4, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>500}
22:55:57.538 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
22:55:57.621 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
www.baidu.com
{"@timestamp" => 2024-04-10T14:56:14.400Z,"@version" => "1","host" => "logstash","message" => "www.baidu.com"
}输出到 ES:
#使用 Logstash 将信息写入 Elasticsearch 中
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.10.100:9200"] } }'[root@logstash ~]#logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.10.100:9200"] } }'
ERROR StatusLogger No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path //usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs to console
23:13:22.928 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Elasticsearch pool URLs updated {:changes=>{:removed=>[], :added=>[http://192.168.10.100:9200/]}}
23:13:22.931 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Running health check to see if an Elasticsearch connection is working {:healthcheck_url=>http://192.168.10.100:9200/, :path=>"/"}
23:13:23.004 [[main]-pipeline-manager] WARN logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>#<Java::JavaNet::URI:0x65334761>}
23:13:23.005 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Using mapping template from {:path=>nil}
23:13:23.238 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Attempting to install template {:manage_template=>{"template"=>"logstash-*", "version"=>50001, "settings"=>{"index.refresh_interval"=>"5s"}, "mappings"=>{"_default_"=>{"_all"=>{"enabled"=>true, "norms"=>false}, "dynamic_templates"=>[{"message_field"=>{"path_match"=>"message", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false}}}, {"string_fields"=>{"match"=>"*", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false, "fields"=>{"keyword"=>{"type"=>"keyword", "ignore_above"=>256}}}}}], "properties"=>{"@timestamp"=>{"type"=>"date", "include_in_all"=>false}, "@version"=>{"type"=>"keyword", "include_in_all"=>false}, "geoip"=>{"dynamic"=>true, "properties"=>{"ip"=>{"type"=>"ip"}, "location"=>{"type"=>"geo_point"}, "latitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}, "longitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}}}}}}}}
23:13:23.253 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - New Elasticsearch output {:class=>"LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch", :hosts=>[#<Java::JavaNet::URI:0x67ed24a3>]}
23:13:23.285 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>4, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>500}
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
23:13:23.420 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
23:13:23.541 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
5.定义Logstash配置文件
#修改 Logstash 配置文件,让其收集系统日志/var/log/messages,并将其输出到 elasticsearch 中。
chmod +r /var/log/messages #让 Logstash 可以读取日志vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf #该文件需自行创建,文件名可自定义
input {file{path =>"/var/log/messages" #指定要收集的日志的位置type =>"system" #自定义日志类型标识start_position =>"beginning" #表示从开始处收集}
}
output {elasticsearch { #输出到 elasticsearchhosts => [ "192.168.10.100:9200" ] #指定 elasticsearch 服务器的地址和端口index =>"system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" #指定输出到 elasticsearch 的索引格式}
}systemctl restart logstash 6.浏览器访问查看索引信息
浏览器访问 http://192.168.79.26:9100 查看索引信息
5、ELK Kibana部署(在node1节点上操作)
1.安装Kibana
下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases/kibana-5-5-1[root@node1 ~]#cd /opt/
[root@node1 opt]#ls
elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm node-v8.2.1.tar.gz rh
elasticsearch-head.tar.gz node-v8.2.1 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@node1 opt]#rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
警告:kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm: 头V4 RSA/SHA512 Signature, 密钥 ID d88e42b4: NOKEY
准备中... ################################# [100%]
正在升级/安装...1:kibana-5.5.1-1 ################################# [100%]2.设置Kibana的主配置文件
cp /etc/kibana/kibana.yml /etc/kibana/kibana.yml.bak ##给匹配值文件做备份
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml ##设置 Kibana 的主配置文件
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
server.port: 5601 ##第2行, 取消注释,Kiabana 服务的默认监听端口为5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0" ##第7行, 取消注释,设置 Kiabana 的监听地址,0.0.0.0代表所有地址
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.10.100:9200" ##第21行,取消注释,设置和 Elasticsearch 建立连接的地址和端口
kibana.index: ".kibana" ##第30行,取消注释,设置在 elasticsearch 中添加.kibana索引3.启动Kibana服务
[root@node1 opt]#systemctl start kibana.service
[root@node1 opt]#systemctl enable kibana.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kibana.service to /etc/systemd/system/kibana.service.
[root@node1 opt]#lsof -i:5601
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
node 2332 kibana 11u IPv4 32050 0t0 TCP *:esmagent (LISTEN)
[root@node1 opt]#netstat -natp | grep 5601
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5601 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2332/node4.验证Kibana
浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:5601
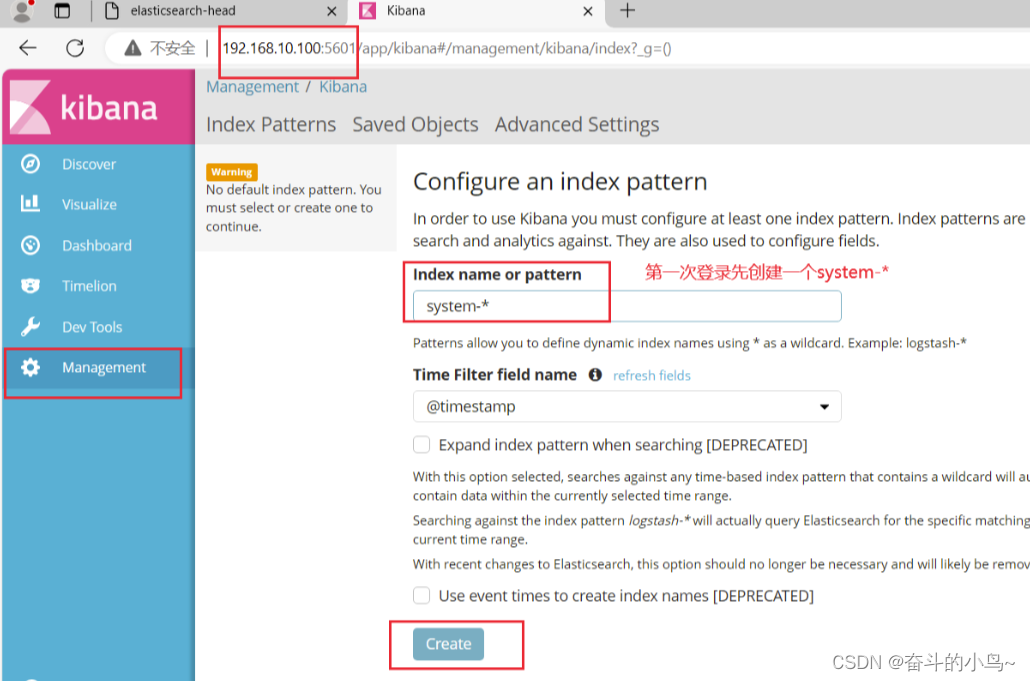
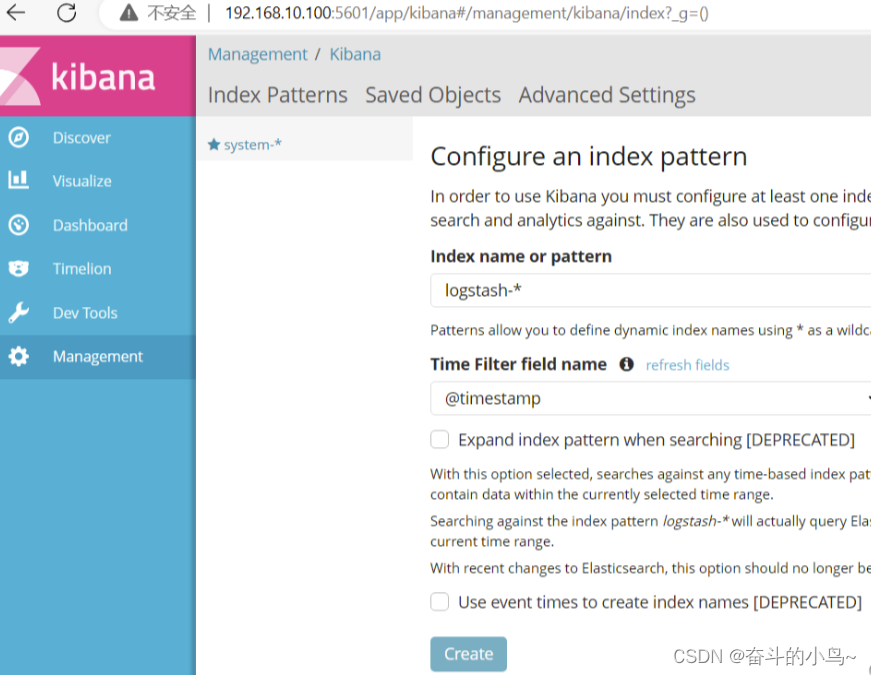
5.将Apache服务器的日志(访问的、错误的)添加到ES并通过Kibana显示
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl status httpd.service
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl start httpd.service
[root@logstash ~]#systemctl status httpd.service[root@logstash conf.d]#vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/apache_log.conffile {path => "/etc/httpd/logs/access_log"type => "access"start_position => "beginning"} file {path => "/etc/httpd/logs/error_log"type => "error"start_position => "beginning"}
} output {if [type] == "access" {elasticsearch {hosts => ["192.168.10.100:9200"]index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"} } if [type] == "error" {elasticsearch {hosts => ["192.168.10.100:9200"]index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"} }
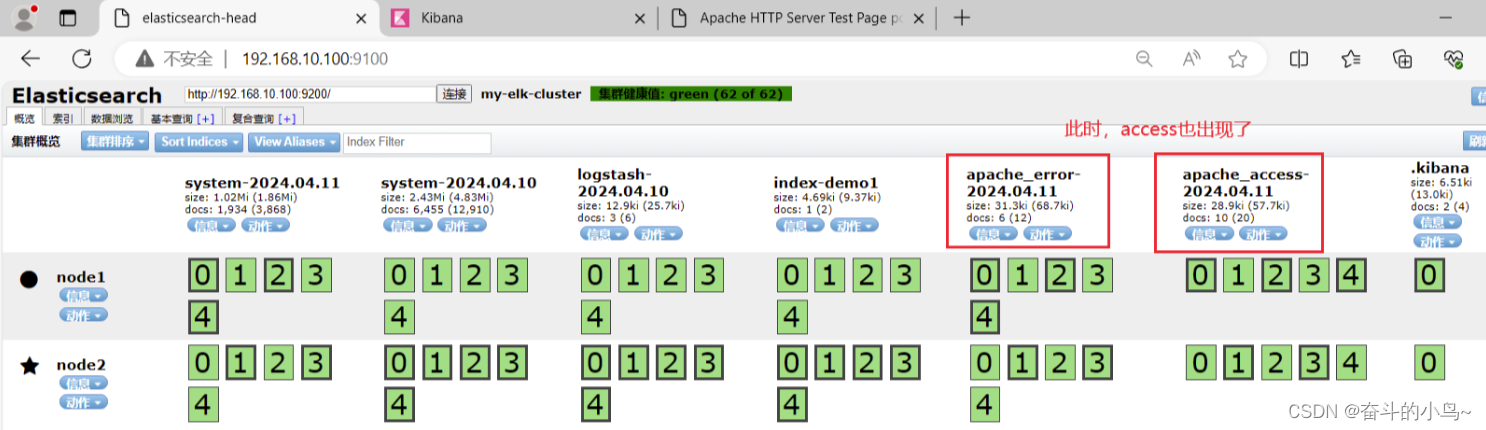
} cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf6.浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:9100 查看索引是否创建
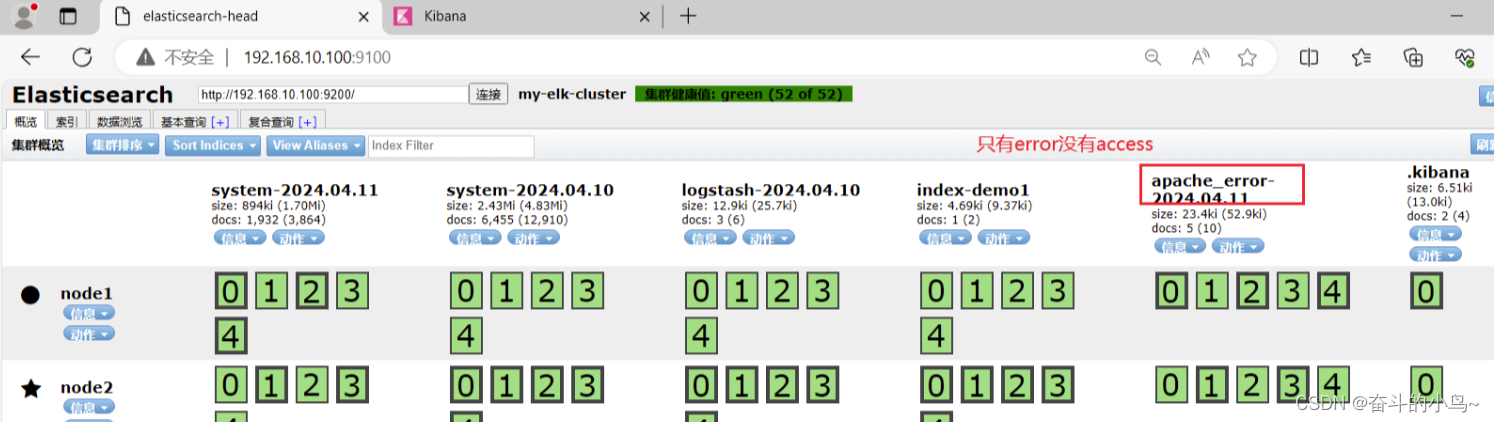
需要访问Apache页面,才会出现access
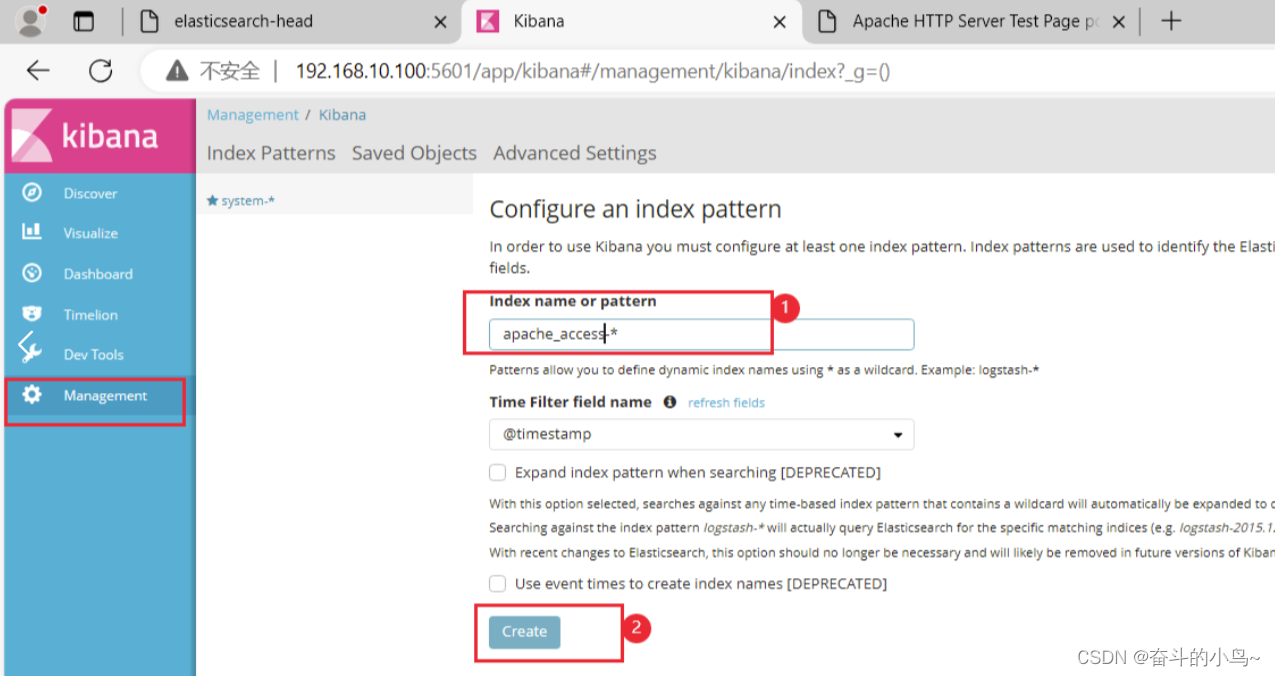
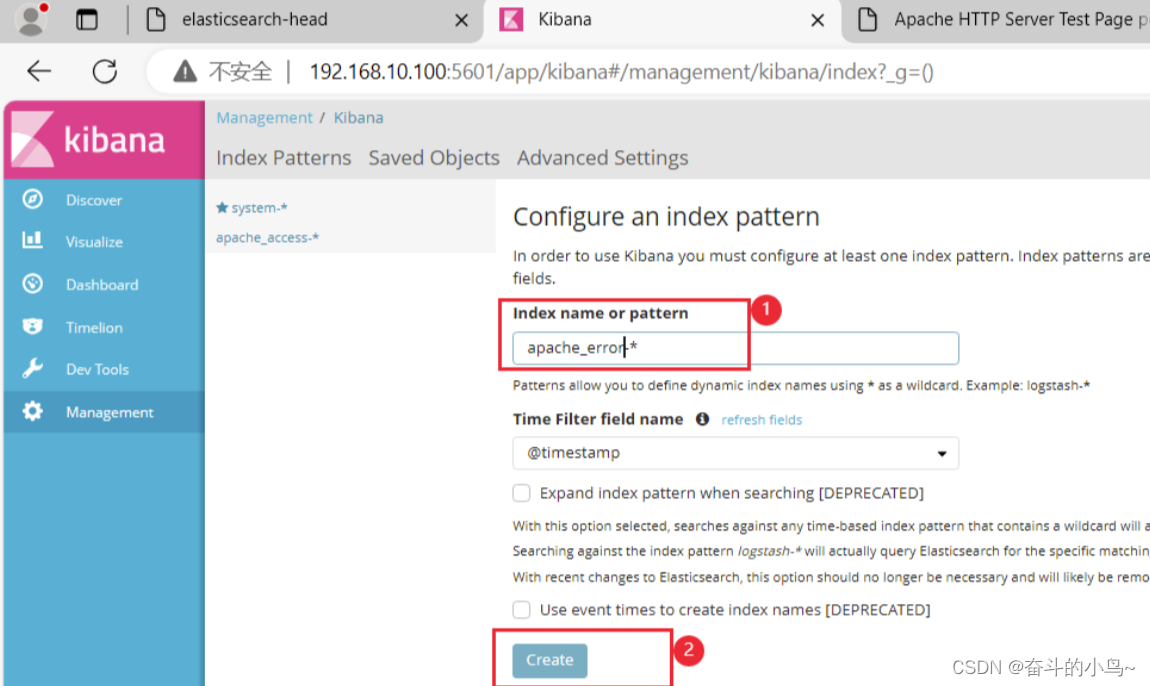
7.浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.100:5601 登录 Kibana
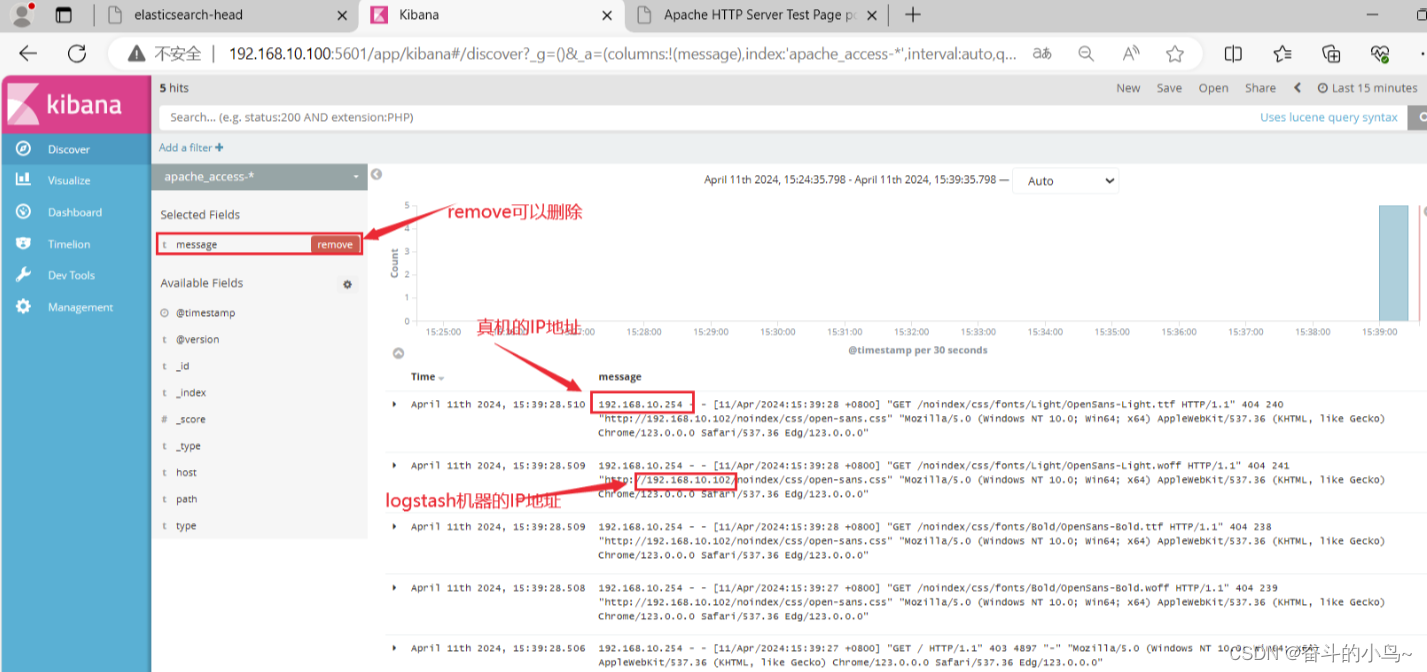
敬请期待后续



)


)




)






FineBI FCP模拟试卷-股票收盘价分析】)
