✨MyShell实现✨
c++并发编程(书籍)
✨进程等待
✨wait/waitpid
✨代码示例
✨coredump
✨什么是coredump
✨开启coredump功能
✨示例代码
✨退出码
✨进程替换
✨原理
✨进程替换接口一览
✨实现一个shell
✨myshell反思
✨参考文章

✨进程等待
✨wait/waitpid
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *stat_loc);
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *stat_loc, int options);
pid = -1, 表示等待任意进程退出
pid > 0,和wait等价,等待子进程stat_loc :保存退出状态;可以传入nullptr,表示不保存退出状态options = 0,阻塞等待
WONHANG,如果子进程没有退出,不进行阻塞等待直接返回0
子进程结束,返回子进程pidWIFEXITED(status): 若为正常终止子进程返回的状态,则为真。
进程调用exit/ _exit函数退出——正常终止
信号退出——不正常终止
WEXITSTATUS(status): 若WIFEXITED非零(进程退出),提取子进程退出码。
WTERMSIG(status):不正常退出时获取退出信号
✨代码示例
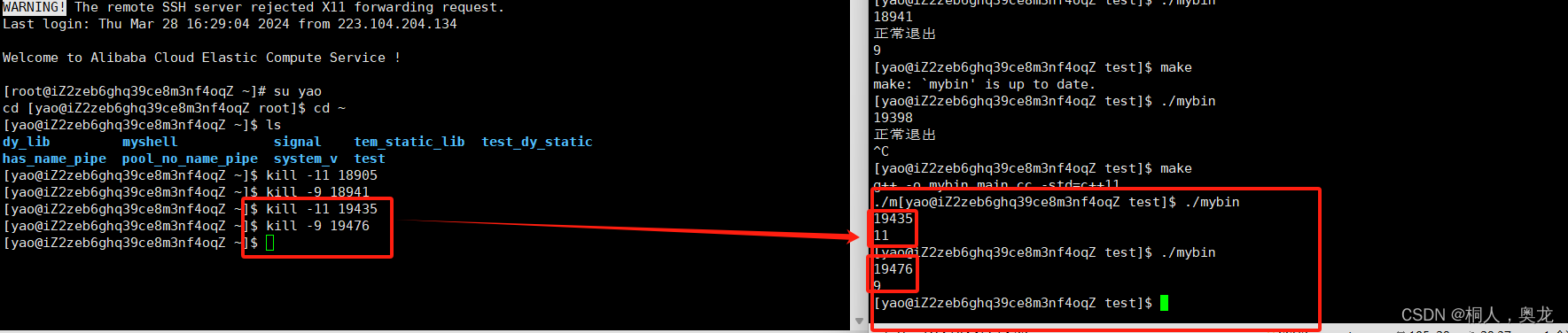
此处只分析不正常退出的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;int main()
{int id = fork();if(id==0){// 子进程// puts("正常退出");// exit(0);while(1) ;}else{// 父进程cout<< id <<endl;int status=0;waitpid(id,&status,0);if(WIFEXITED(status)==0){// 不正常退出cout<< WTERMSIG(status)<<endl;}else{cout << WEXITSTATUS(status)<<endl;}}return 0;
}
✨coredump
✨什么是coredump
我们知道所有的程序最终运行起来,都会变成进程,进程在运行时可能会异常终止或崩溃,而Linux操作系统会将程序当时的内存状态记录下来,保存在一个文件中,这种行为就叫做Core Dump(中文有的翻译成核心转储)。(信号也是异常终止)
✨开启coredump功能
在没有开启之前计算机是无法使用这个功能的
配置信息——只介绍只能使用一次的配置
ulimit -c 1024 设置写入的文件大小
sudo sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=/tmp/core-%e-%s-%u-%g-%p-%t 配置文件存放路径
生成的文件在/tem下的以core开头的文件
sudo sysctl -p 使配置立即生效
✨示例代码
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;int main()
{int id = fork();if(id==0){// 子进程// puts("正常退出");// exit(0);// while(1) ;int* p=nullptr;*p=8;}else{// 父进程cout<< id <<endl;waitpid(id,&status,0);}return 0;
}

✨退出码
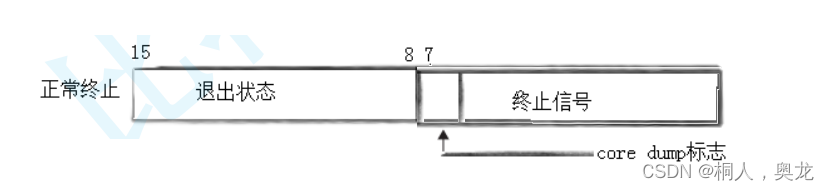
对于waitpid的status并不是我们认为的int32位,存储的数据只有16位
开启coredump功能,异常终止coredump会置为1;不开启什么也看不到
✨进程替换
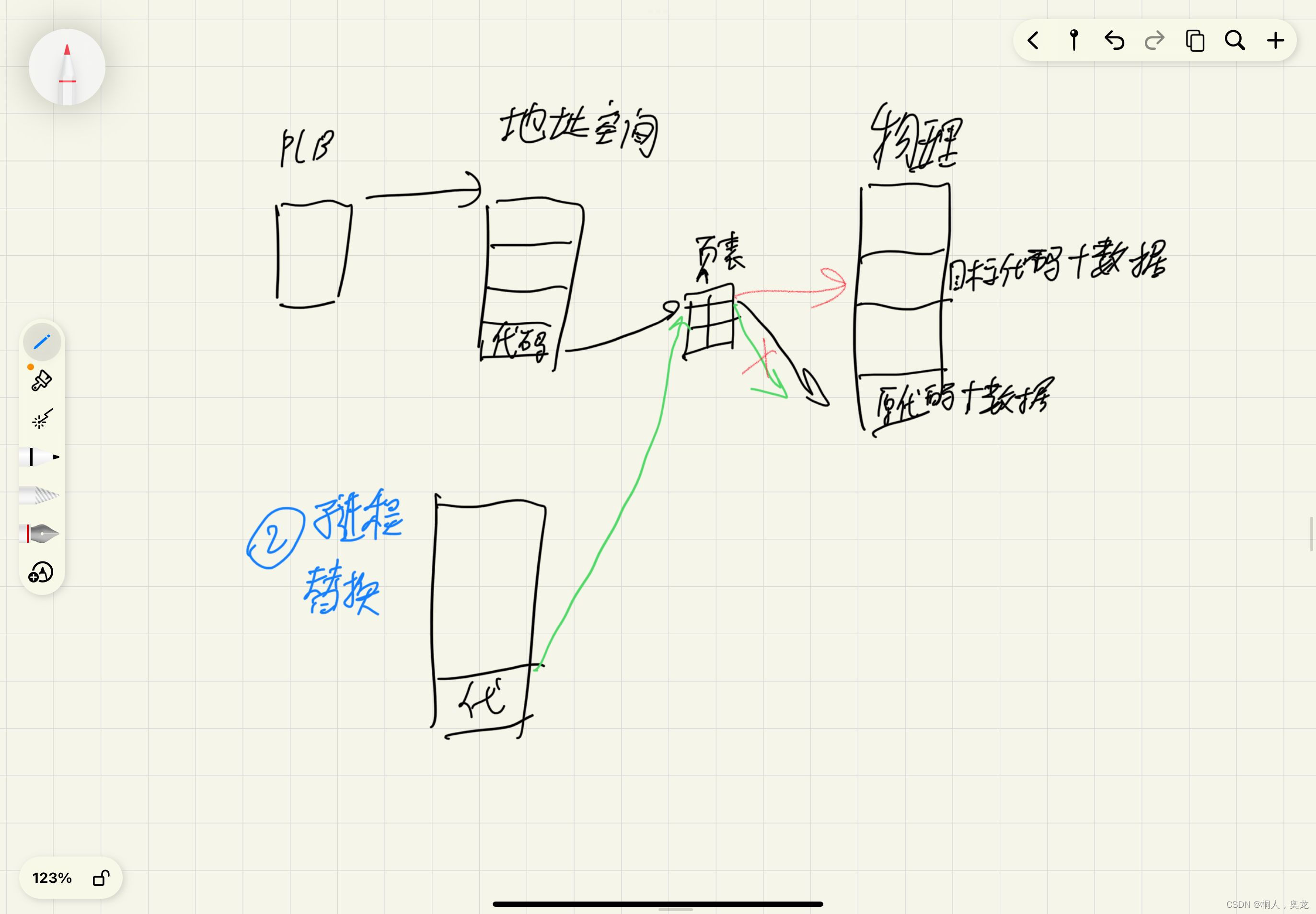
✨原理
子进程会继承父进程的环境变量
主进程替换
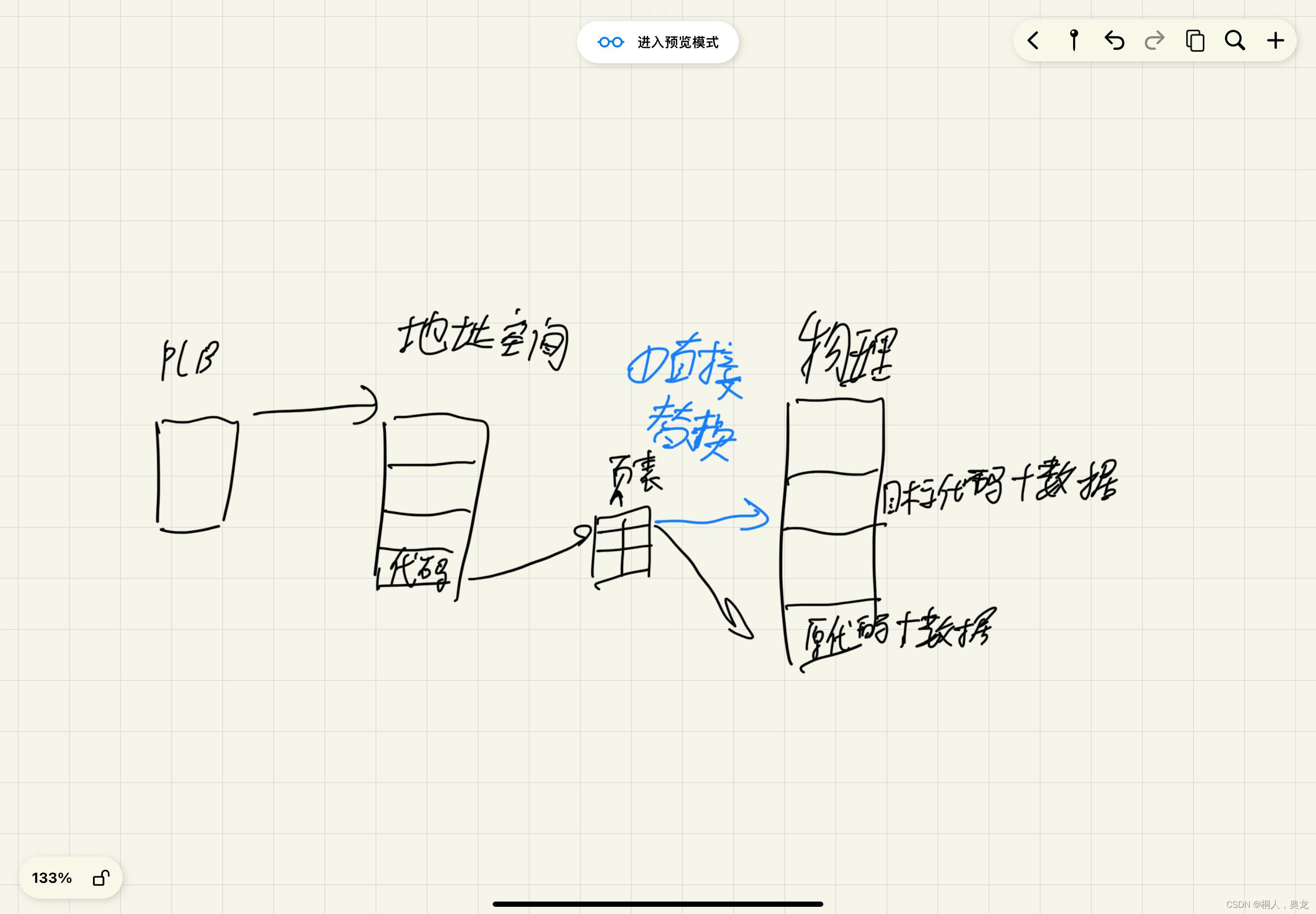
子进程替换
✨进程替换接口一览
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg,... , char* const envp[]);int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
arg——如何使用命令如何传参
l ——列表形式传参,path:目标替换文件的具体文件路径,一定是以NULL结尾
p——不需要指明路径,file:目标替换文件的文件名
e——可以传递环境变量
v——将命令使用参数以数组的形式传参,一定是以NULL结尾
✨ 实现一个shell
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>using namespace std;
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>// string op;
char* command[30];
char s[100];// 接收输入,防止strtok返回局部变量地址void GetUserOp()
{// getline(cin,op);// puts("读取成功");// cout<<op<<endl;// char s[100];fgets(s,sizeof(s),stdin);// 会将\n读入s[strlen(s)-1]='\0';int cnt=0;memset(command,0,sizeof(command));// char* str = (char*)op.c_str();command[cnt++] = strtok(s ," ");while(command[cnt++] = strtok(NULL," ")) ;// command 数据类型存的是指针,如果是局部的s进行接收输入的话// strtok返回的是这个接收数据的字符位置的指针// 如果是局部的话,就会造成数据丢失// printf("%p\n",s); // printf("%p\n",command[0]);// command[cnt-1]=NULL;// cout<< &command[0]<<endl;// while(i<op.size())// {// // string tem;// // while(i<op.size() && op[i]!=' ')// // {// // tem+=op[i++];// // }// // i++;// // if(cnt == 0)// // {// // tem = string("/usr/bin/") + tem;// // }// // command[cnt++] = tem.c_str();// // strcpy(command[cnt++],tem.c_str());// // cout<<command<<endl;// // cout<<cnt-1 << "-->" << command[cnt-1]<<endl;// }
}
void DoCommand()
{if(!strcmp(command[0],"ls")){execvp(command[0],command);}else if(!strcmp(command[0],"cd")){chdir(command[1]);char* pwd;// char* cwd;char cwd[100];getcwd(cwd,sizeof(cwd));sprintf(pwd,"PWD=%s",cwd);// 必须要使用pwd将环境变量进行改变,不能多加空格// 必须和环境变量格式完全一致// cout<<pwd<<endl;putenv(pwd);// 将环境变量的路径设置完美}else if(!strcmp(command[0],"env")){int cnt=0;while(environ[cnt])cout<<environ[cnt++]<<endl;}else if(!strcmp(command[0],"echo")){if(command[1]==NULL) {puts("");return;}else if(command[1][0]=='$'){char* val = command[1]+1;if(!strcmp(val,"?")){// 上次程序的返回值需要记录}else{char* ret = getenv(val);cout<<ret<<endl;}}else cout<<command[1]<<endl;}else if(!strcmp(command[0],"export")){if(command[1] == NULL) return;putenv(command[1]);}else{execvp(command[0],command);}// puts("..");// 进程替换之后,他不可能运行出来的
}
int main()
{while(1){pid_t id = fork();if(id==0){GetUserOp();// cout<<command[0]<<endl;// puts("--");DoCommand();}else{// 主进程waitpid(id,nullptr,0);}}// 不能在子进程中只读取一次,虽然你有个循环// 但是你的子进程替换完之后就回不来了,就没有循环了// pid_t id = fork();// if(id==0)// {// puts("进程替换开始");// // chdir("/usr/bin");// 更换工作路径// while(1)// {// GetUserOp();// puts("**");// DoCommand();// }return 0;
}
✨ myshell实现反思
- 不能先fork然后子进程中添加一个while循环进行替换,这样子好像是进行可以替换完一次再回来替换第二次,事实上是替换会将子进程的代码替换掉,也就是while没有了,替换完结束后直接被主进程捕获,终止程序
错误代码
// 不能在子进程中只读取一次,虽然你有个循环// 但是你的子进程替换完之后就回不来了,就没有循环了// pid_t id = fork();// if(id==0)// {// puts("进程替换开始");// // chdir("/usr/bin");// 更换工作路径// while(1)// {// GetUserOp();// puts("**");// DoCommand();// }
正确代码
while(1){pid_t id = fork();if(id==0){GetUserOp();// cout<<command[0]<<endl;// puts("--");DoCommand();}else{// 主进程waitpid(id,nullptr,0);}}
- strtok函数
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);
他能将字符串进行按照指定的方式切割,并且返回char*(也就是切割出来的字符串)
当完全被切割完的时候就会返回NULL,这个刚好可以被接收当列表中的最后一个参数
错误代码分析
// char s[100];fgets(s,sizeof(s),stdin);// 会将\n读入s[strlen(s)-1]='\0';int cnt=0;memset(command,0,sizeof(command));// char* str = (char*)op.c_str();command[cnt++] = strtok(s ," ");while(command[cnt++] = strtok(NULL," ")) ;
如果使用局部变量进行接收输入,再切割出字符串进行返回时,他返回的也是局部的字符串中的字符所对应的地址,这样一来就出现问题了,command存的是局部变量的地址,局部变量出了作用域就销毁了,这样一来就找不到切割好的字符串了——不能返回局部变量的地址/引用
正确代码
将s设置为全局变量
char* command[30];
char s[100];// 接收输入,防止strtok返回局部变量地址void GetUserOp()
{// getline(cin,op);// puts("读取成功");// cout<<op<<endl;// char s[100];fgets(s,sizeof(s),stdin);// 会将\n读入s[strlen(s)-1]='\0';int cnt=0;memset(command,0,sizeof(command));// char* str = (char*)op.c_str();command[cnt++] = strtok(s ," ");while(command[cnt++] = strtok(NULL," ")) ;
}
- chdir函数——更待工作路径
#include<unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);
getenv函数——获得当前环境的环境变量
putenv函数——设置当前环境的环境变量
#include<stdlib.h>
char *getenv(const char *name);
int putenv(char *string);
错误代码
子进程会继承父进程的环境变量
else if(!strcmp(command[0],"cd")){chdir(command[1]);}
如果只写这一句,虽然他的工作路径已经更改了,但是环境变量并没有一同改变,就会出现一个很神奇的现象,你的pwd路径和环境变量路径不一致的问题
正确代码
else if(!strcmp(command[0],"cd")){chdir(command[1]);char* pwd;// char* cwd;char cwd[100];getcwd(cwd,sizeof(cwd));sprintf(pwd,"PWD=%s",cwd);// 必须要使用pwd将环境变量进行改变,不能多加空格// 必须和环境变量格式完全一致// cout<<pwd<<endl;putenv(pwd);// 将环境变量的路径设置完美}
- 补充
当我们需要输出环境变量的时候,可以使用extern char **environ;进行输出
✨参考文章
开启coredump功能


)




的介绍以及使用)






)
)


【附代码文档】)