1.线性表
线性表 ( linear list ) 是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使 用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串... 线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的, 线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2、顺序表
2.1概念及结构
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存 储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1. 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
2. 动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
2.2 顺序表的实现
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空 间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间 大小,所以下面实现动态顺序表。
//SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>typedef int SLDataType;
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4typedef struct SeqList
{SLDataType* arr;int size;int capacity;
}SL;void SLInit(SL* ps);
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
void SLPushBack(SL* ps);
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"void SLInit(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->arr = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * INIT_CAPACITY);if (ps->arr == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY;
}void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->arr);ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void CheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (NULL == tmp){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}
}void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{//assert(ps);//CheckCapacity(ps);//ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{//assert(ps);//assert(ps->size > 0);//ps->size--;SLErase(ps, ps->size-1);
}void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{//assert(ps);//CheckCapacity(ps);//SLDataType end = ps->size - 1;//while (end >= 0)//{// ps->arr[end + 1] = ps->arr[end];// end--;//}//ps->arr[0] = x;//ps->size++;SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
}void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{//assert(ps);//assert(ps->size > 0);//SLDataType begin = 1;//while (begin < ps->size)//{// ps->arr[begin - 1] = ps->arr[begin];// begin++;//}//ps->size--;SLErase(ps, 0);
}void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);CheckCapacity(ps);SLDataType end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->arr[end + 1] = ps->arr[end];end--;}ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);SLDataType begin = pos + 1;while (begin < ps->size){ps->arr[begin - 1] = ps->arr[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;
}int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){if (ps->arr[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}2.4 顺序表的问题及思考
问题:
1. 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到 200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
思考:
如何解决以上问题呢?试试链表。
3.链表
3.1 链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表 中的指针链接次序实现的 。
3.2 链表的分类
1. 单向或者双向
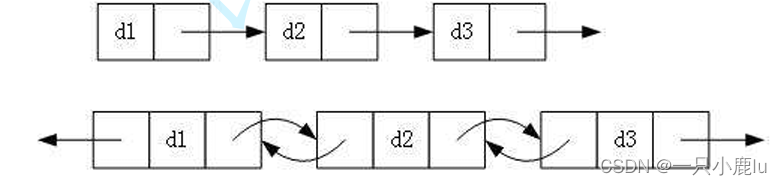
2. 带头或者不带头
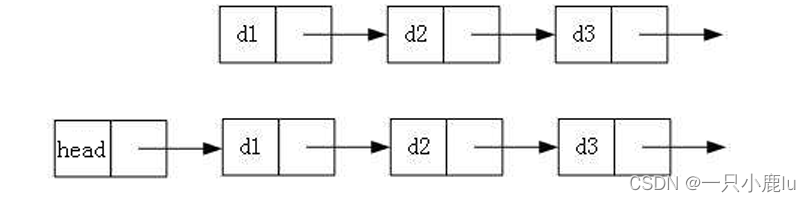
3. 循环或者非循环

虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:
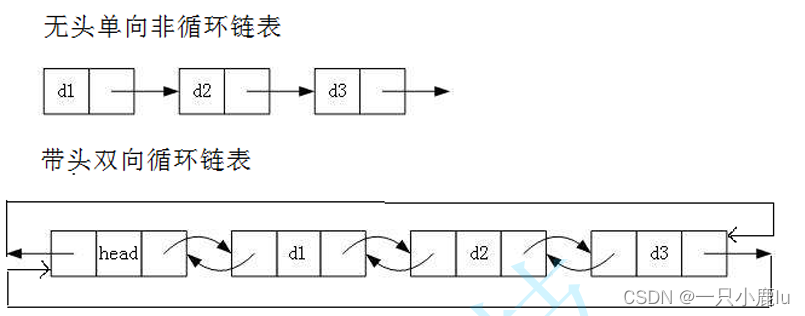
1. 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2. 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了。
3.3 链表的实现
3.3.1无头单向非循环链表
//SList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int DataType;typedef struct SListNode
{DataType data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
SLTNode* BuyNode(DataType x);
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, DataType x);
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, DataType x);//在pos之前插入
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, DataType x);//在pos之后插入
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);//pos位置删除
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);//pos位置之后删除
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);//SList.c
#include"SList.h"void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULLL");
}SLTNode* BuyNode(DataType x)
{SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("maloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);//只有一个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}//多个节点else {SLTNode* pre = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){pre = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;pre->next = NULL;//or//SLTNode* tail = *pphead;//while (tail->next->next != NULL)//{// tail = tail->next;//}//free(tail->next);//tail->next = NULL;}
}void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* first = *pphead;*pphead = (first)->next;free(first);first = NULL;}SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead,DataType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, DataType x)
{assert(pos);assert(pphead);if (pos==*pphead){SLTPushFront(pphead,x);}else{SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != pos){cur = cur->next;}SLTNode* newnode=BuyNode(x);newnode->next = pos;cur->next = newnode;}
}void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, DataType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pphead);if (*pphead == pos){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != pos){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);SLTNode* del = pos->next;pos->next = del->next;free(del);del = NULL;
}void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur) {SLTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}3.3.2带头双向循环链表
//List.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int DataType;typedef struct ListNode
{DataType data;struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;
}LTNode;LTNode* BuyNode(DataType x);
LTNode* LTInit();
void LTDestroy(LTNode* phead);
void LTPrint(LTNode* phead);
bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead);
void LTPushBack(LTNode* phead, DataType x);
void LTPopBack(LTNode* phead);
void LTPushFront(LTNode* phead, DataType x);
void LTPopFront(LTNode* phead);
void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, DataType x);//在pos之前插入
void LTErase(LTNode* pos);//删除pos位置的节点
LTNode* LTFind(LTNode* phead, DataType x);//List.c
#include"List.h"LTNode* BuyNode(DataType x) {LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;
}LTNode* LTInit()
{LTNode* phead = BuyNode(-1);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;
}void LTDestroy(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){LTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);//phead = NULL;
}void LTPrint(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);printf("<=>head<=>");LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){printf("%d<=>", cur);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);return phead->next == phead;
}void LTPushBack(LTNode* phead, DataType x)
{//assert(phead);//LTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;//tail->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = tail;//newnode->next = phead;//phead->prev = newnode;LTInsert(phead, x);
}void LTPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{//assert(phead);//assert(!LTEmpty(phead));//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;//LTNode* tail_prev = tail->prev;//tail_prev->next = phead;//phead->prev = tail_prev;//free(tail);//tail = NULL;LTErase(phead->prev);
}void LTPushFront(LTNode* phead, DataType x)
{//assert(phead);//LTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);//LTNode* first = phead->next;//newnode->next = first;//first->prev = newnode;//phead->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = phead;LTInsert(phead->next, x);
}void LTPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{//assert(phead);//assert(!LTEmpty(phead));//LTNode* first = phead->next;//LTNode* first_next = first->next;//phead->next = first_next;//first_next->prev = phead;//free(first);//first = NULL;LTErase(phead->next);
}void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, DataType x)
{assert(pos);LTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);LTNode* pos_prev = pos->prev;pos_prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = pos_prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;
}void LTErase(LTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);LTNode* pos_prev = pos->prev;LTNode* pos_next = pos->next;pos_prev->next = pos_next;pos_next->prev = pos_prev;free(pos);pos=NULL;
}LTNode* LTFind(LTNode* phead, DataType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}3.4顺序表和链表的区别
1、存储空间上
顺序表:物理上一定连续;链表:逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续。
2、随机访问
顺序表支持随机访问O(1),链表不支持随机访问O(n)。
3、任意位置插入或删除元素
顺序表:可能需要搬移元素,效率低O(n);链表:只需修改指针指向。
4、插入
顺序表是动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容;链表没有容量的概念。
5、应用场景
顺序表:元素高效存储+频繁访问;链表:任意位置插入和删除频繁。
6、缓存利用率
顺序表:高;链表:低。
4、链表面试题
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点。203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
// 方法一
// struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
// struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
// struct ListNode* cur = head;// while (cur) {
// if (cur->val == val) {
// if (pre == NULL) {
// head = cur->next;
// free(cur);
// cur = head;
// } else {
// pre->next = cur->next;
// free(cur);
// cur = pre->next;
// }
// } else {
// pre = cur;
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// }
// return head;
// }// 方法2
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while (cur) {if (cur->val != val) {if (tail == NULL) {newhead = tail = cur;} else {tail->next = cur;tail = tail->next;}cur = cur->next;} else {struct ListNode* next=cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}}if(tail)tail->next=NULL;return newhead;
}方法1:直接在原链表上删除等于val的结点
方法2:把不等于val的结点尾插到新链表
2. 反转一个单链表。 206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/// 原链表上改变链表指向
// struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
// if(head==NULL)
// return NULL;
// struct ListNode *prev, *cur, *next;
// prev = NULL;
// cur = head;
// next = cur->next;
// while (cur) {
// cur->next = prev;
// prev = cur;
// cur = next;
// if (next) {
// next = next->next;
// }
// }
// return prev;
// }// 在新链表头插
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while (cur) {struct ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newhead;newhead = cur;cur = next;}return newhead;
}方法1:在原链表上翻转链表指向
方法2:给一个新结点,一个个头插
3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。 876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}快慢指针,一个走一步,一个走两步,fast->next==NULL或者fast==NULL结束。
4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。输出单向链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int DataType;typedef struct SListNode {DataType data;struct SListNode* next;
} SLTNode;SLTNode* BuyNode(DataType x) {SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));if (newnode == NULL) {perror("maloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x) {SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL) {*pphead = newnode;} else {SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL) {tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead) {SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur) {SLTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}
}int Find(SLTNode* phead, int k) {SLTNode* fast, *slow;fast = slow = phead;while (k--) {fast = fast->next;}while (fast) {fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow->data;
}int main() {int count = 0;while (scanf("%d", &count) != EOF) {SLTNode* phead = NULL;while (count--) {int x = 0;scanf("%d", &x);SLTPushBack(&phead, x);}int k = 0;scanf("%d", &k);int ret = Find(phead, k);printf("%d\n", ret);SLTDestroy(phead);phead = NULL;}return 0;
}快慢指针,fast先走k步,然后fast和slow再一起走,fast==NULL结束。
或者fast先走k-1步,然后fast和slow再一起走,fas->nextt==NULL结束。
(上面代码用第一种)
5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有 结点组成的。 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {struct ListNode* c1 = list1;struct ListNode* c2 = list2;struct ListNode *gurad = NULL, *tail = NULL;gurad = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));tail->next = NULL;while (c1 && c2) {if (c1->val <= c2->val) {tail->next = c1;tail = tail->next;c1 = c1->next;} else {tail->next = c2;tail = tail->next;c2 = c2->next;}}if (c1) {tail->next = c1;}if (c2) {tail->next = c2;}struct ListNode* head=gurad->next;free(gurad);return head;
}遍历两个链表,取小的尾插到新链表(尾插带哨兵位的头结点可以减少很多情况)
6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结 点之前 。链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
#include <cstdlib>
class Partition {public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {ListNode* lguard, *gguard, *ltail, *gtail;lguard =ltail= (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));gguard =gtail= (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ltail->next = gtail->next = nullptr;ListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur != nullptr) {if (cur->val < x) {ltail->next = cur;ltail = ltail->next;} else {gtail->next = cur;gtail = gtail->next;}cur = cur->next;}ltail->next = gguard->next;gtail->next = nullptr;pHead = lguard->next;free(lguard);free(gguard);return pHead;}
};将小于x的尾插到一个链表,将大于等于x的尾插到另一个链表,再将两个链表链接起来。(带哨兵位头结点)
7. 链表的回文结构。 链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;struct ListNode* prev, *cur, *next;prev = NULL;cur = head;next = cur->next;while (cur) {cur->next = prev;prev = cur;cur = next;if (next) {next = next->next;}}return prev;
}class PalindromeList {public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) {ListNode* mid = middleNode(head);ListNode* rhead = reverseList(mid);while (head && rhead) {if (head->val != rhead->val) {return false;}head = head->next;rhead = rhead->next;}return true;}
};1、找中间结点
2、从中间结点开始对后半段逆置
3、前半段和后半段比较即可
8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA,struct ListNode* headB) {struct ListNode *tail1 = headA, *tail2 = headB;int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;while (tail1) {tail1 = tail1->next;len1++;}while (tail2) {tail2 = tail2->next;len2++;}if(tail1!=tail2){return NULL;}int gap = abs(len1 - len2);struct ListNode *shortList = headA, *longList = headB;if (len1 > len2) {shortList = headB;longList = headA;}while (gap--) {longList = longList->next;}while (longList != shortList) {longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}return longList;
}1、求出两个链表的长度
2、长的先走差距步
3、再同时走,两个地址相同就是交点
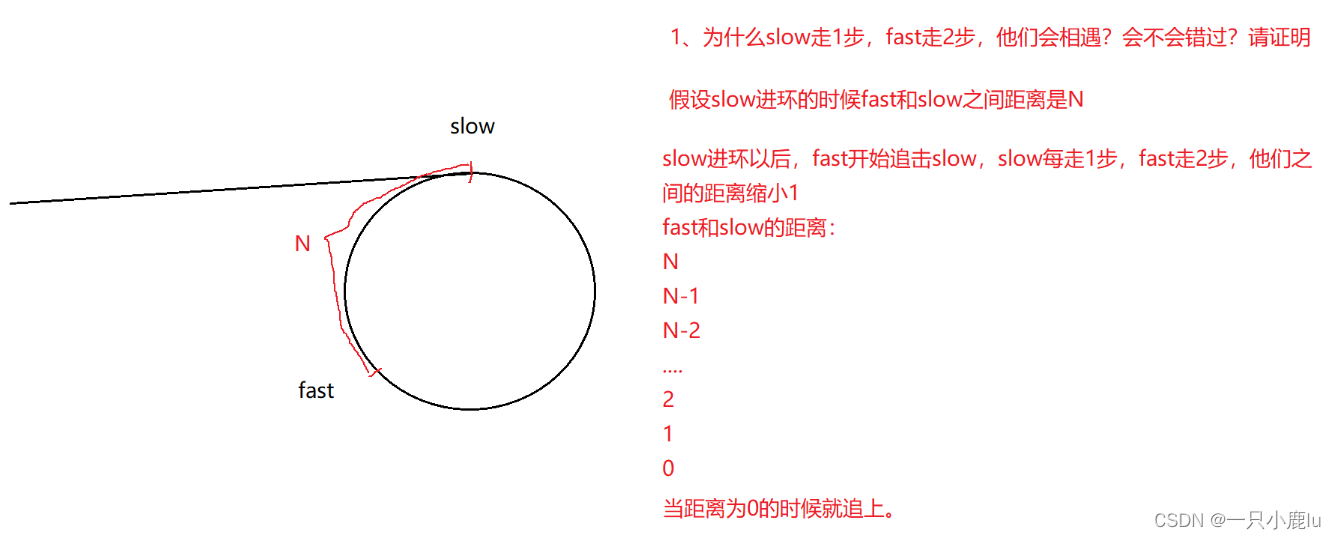
9. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode *fast, *slow;fast = slow = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {return true;}}return false;
}
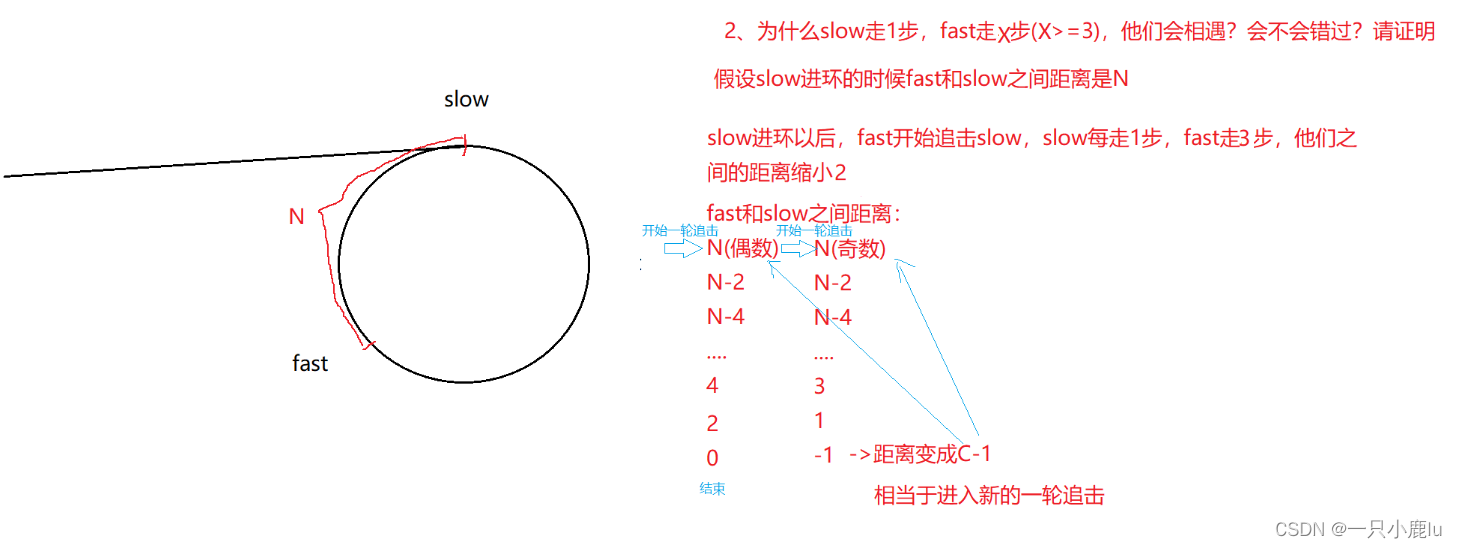
10. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
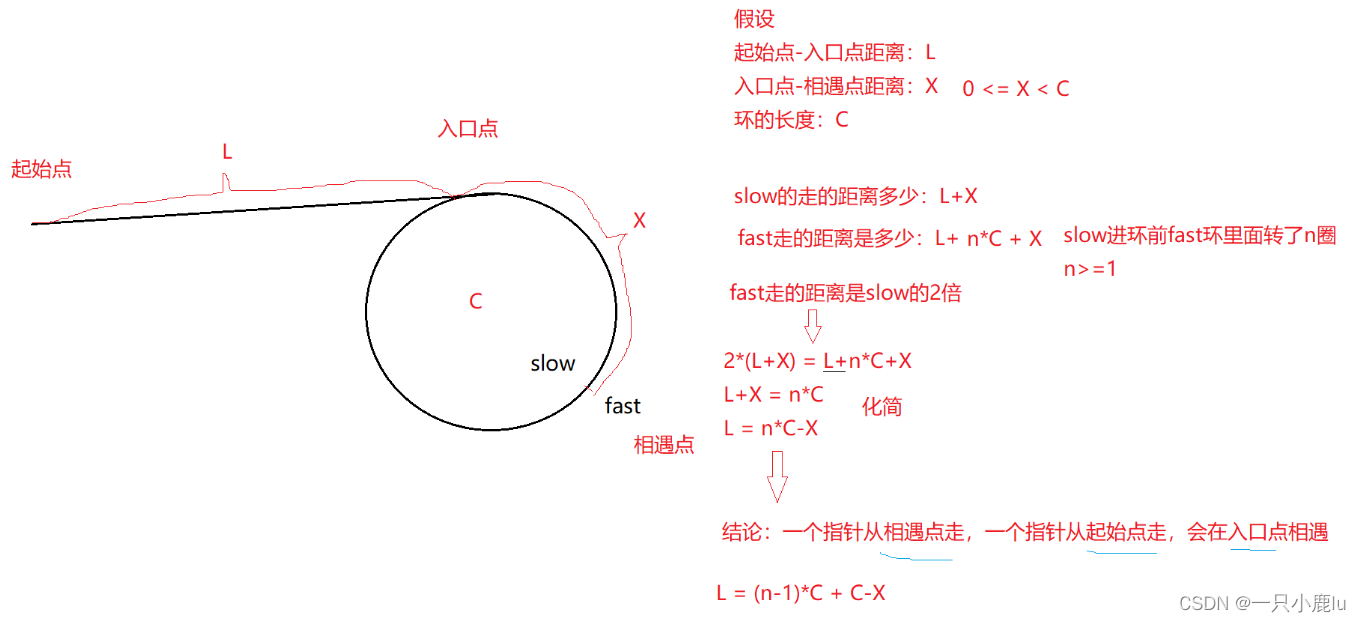
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode *fast, *slow;fast = slow = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {struct ListNode* meet=slow;struct ListNode* start=head;while(meet!=start){meet=meet->next;start=start->next;}return meet;}}return NULL;
}
11. 给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何结点 或空结点。 要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝。138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {// 1、把拷贝结点链接在原结点的后面struct Node* cur = head;while (cur) {struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val = cur->val;struct Node* next = cur->next;cur->next = copy;copy->next = next;cur = next;}// 2、拷贝结点的random是原结点random->nextcur = head;while (cur) {struct Node* copy = cur->next;if (cur->random == NULL) {copy->random = NULL;} else {copy->random = cur->random->next;}cur = cur->next->next;}// 3、拷贝结点解下来链成一个新链表,原链表恢复struct Node* copyhead = NULL;struct Node* copytail = NULL;cur = head;while (cur) {struct Node* copy = cur->next;struct Node* next = copy->next;// copy尾插if (copyhead == NULL) {copyhead = copytail = copy;} else {copytail->next = copy;copytail = copytail->next;}// 恢复原链表cur->next = next;cur = next;}return copyhead;
}1、把拷贝结点链接在原结点的后面
2、拷贝结点的random是原结点random->next
3、拷贝结点解下来链成一个新链表,原链表恢复
5、栈
5.1栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
5.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。
//Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int DataType;
#define InitCapacity 4typedef struct Stack
{DataType* a;int top;//栈顶int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, DataType x);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
void STPop(ST* ps);
DataType STTop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素
int STSize(ST* ps);//获取有效元素个数//Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * InitCapacity);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}ps->capacity = InitCapacity;ps->top = 0;//top是栈顶元素的下一个位置//ps->top = -1;//top是栈顶元素位置
}void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void STPush(ST* ps, DataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){DataType* tmp = (DataType*)realloc(ps, sizeof(DataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = 2;ps->top++;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}DataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}6、队列
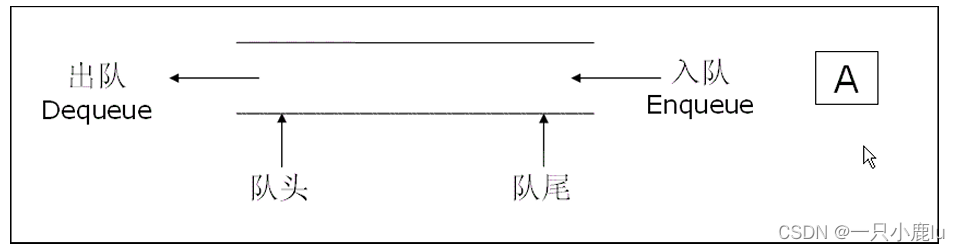
6.1队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
6.2队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
//Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int DataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;DataType data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;DataType size;
}Queue;void QInit(Queue* pq);
void QDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QPush(Queue* pq, DataType x);
void QPop(Queue* pq);
bool QEmpty(Queue* pq);
DataType QFront(Queue* pq);
DataType QBack(Queue* pq);
int QSize(Queue* pq);
//Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"void QInit(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QPush(Queue* pq, DataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){assert(pq->tail==NULL);pq->head = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QPop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head!=NULL);if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}bool QEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}DataType QFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}DataType QBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}int QSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}7.栈和队列面试题
1. 括号匹配问题。20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)
2. 用队列实现栈。225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
3. 用栈实现队列。232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
4. 设计循环队列。622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)



- c++)
和super(props))


、国家域名、经纬度)

)
)

)






)