一、string的构造函数方式:

代码形式:
void Test1()
{string s1(); // 空字符串string s2("Hello World"); // 字符串初始化为 "Hello World" string s3(s2); //拷贝构造: 将s2复制给s3、 输出为: Hello Worldstring s4(s2, 2, 3); // 从 s2 的下标 2 的位置开始复制 3 个值给 s4,输出为: llostring s5(s2, 3); // 从 s2 的下标 3 的位置开始 复制到结尾个字符给 s5,输出为: llo Worldstring s6(5, '#'); // 生成5个字符为 # 的字符串,输出为: #####}二、常用的大小/容量相关操作:
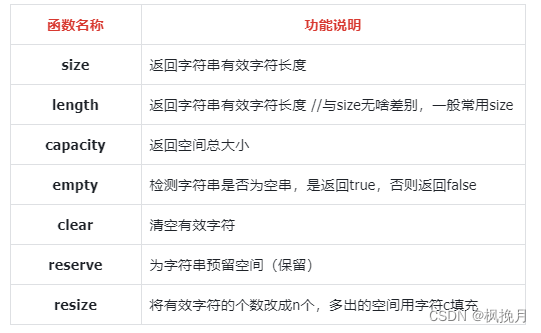
代码形式:
void Test2()
{string s1("Hello World");cout << s1.size() << endl; // 输出为 11cout << s1.length() << endl; // 输出为 11cout << s1.max_size() << endl; // 支持的最大长度cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 输出为 15// clear清除有效数据,但不清除空间(capacity)s1.clear();cout << s1 << endl; // 输出为空,因为clear清除了有效字符// reserve 可以直接开空间,省去字符串追加字符时的自动扩容操作,提高一点效率s1.reserve(100); // 扩容时有效编译器并不一定会只扩到给定值,有可能会多扩容一些空间cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 当 reserev 中的参数小于capacity时并不会进行缩容// 缩容: shrink_to_fit // 缩容到16(显示的是15,但是一般会包含算上\0入内,capacity不算上\0,所以实际是16)s1.shrink_to_fit();cout << s1.capacity() << endl;// 输出16// resize string s2("Hello");s2.resize(7, '#'); // 将 s2 的有效字符个数改成7个,不足7个的用 # 替换// resize 当不指定第二个参数时默认为'\0'// 当resize 给的值大于 capacity 时 resize 会进行相应的扩容 // 当resize 给的值小于 capacity 时 resize 不会进行缩容 cout << s2 << endl; // 输出为: Hello##
}三、string的常用修改操作:
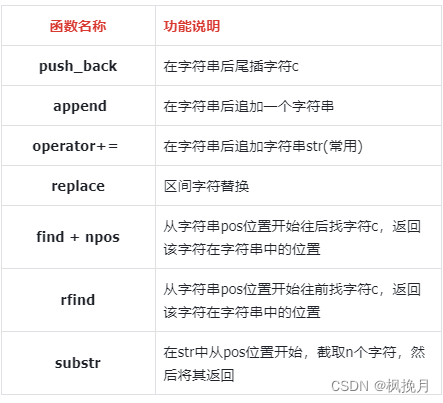
代码形式:
void Test3()
{string s1;string s2("Hello");s1.push_back('c');s1.append("ccccc");s1 += "abcde"; // 一般用 += 比较多,因为可以直接追加字符/字符串s1 += s2;// find(c, n): 从下标 n 位置查找字符 c ,找到返回下标,找不到返回npos// replace(n, m, "c"): 从下标 n 开始的 m 个字符 替换为c:// 以上两个结合使用讲解: 将s3中的空格替换为 ##string s3("Youth gives you light please don't let it down");size_t pos1 = s3.find(' '); // find 不给右参数时默认从 0 开始while (pos1 != string::npos){s3.replace(pos1, 1, "##");pos1 = s3.find(' ');}cout << s3 << endl;// rfind 用法和 find 相似,不同的是 rfind 是从后往前找// rfind(c, n) 从第 n 个位置往前找 c ,找到返回下标,找不到返回npos// rfind不给右参数时默认从字符串最末尾开始// substr(n, m) 主要功能为复制子字符串,从下标 n 开始,复制 m 个字符string s4("Hello World!");string s5 = s4.substr(3, 5); // 输出为: lo Wo// 当substr不给参数时就为直接拷贝构造string s6 = s4.substr(); // 输出为: Hello World!// 当只给定左参数时,就从 n 开始复制到结尾string s7 = s4.substr(3); // 输出为: lo World!}四、string的遍历:
进行字符串的遍历时可以用下标法或者借助迭代器进行遍历。
代码形式:
void Test4()
{string s1("Hello World");// 下标法: C++中重载了 [] 符号,加上对应的下标即可访问for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){cout << s1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// 借助迭代器:// str.begin() 指向字符串的第一个字符位置// str.end() 指向字符串的最后一个字符的下一个位置string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";it1++;}cout << endl;// 反向迭代器:// str.rbegin() 指向字符串的最后一个字符的位置// str.rend() 指向字符串的第一个字符的前一个位置string::reverse_iterator rit1 = s1.rbegin();while (rit1 != s1.rend()){cout << *rit1 << " ";rit1++;}cout << endl;
} 
五、string的任意位置插入 / 删除:
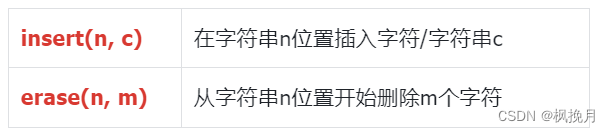
但是在实践中一般很少用到 insert 与 erase 因为要挪动数据,效率很低。
代码形式:
void Test5()
{string s1("Hello World!");s1.insert(2, "##");cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: He##llo World!string s2("Hello World!");s2.erase(4, 6);cout << s2 << endl; // 输出: Helld!}六:补充:
void Test6()
{// compare: 字符串大小比较// 原理: 两个字符串自左向右逐个字符相比(按ASCII值大小相比较),直到出现不同的字符或遇 '\0’为止。string s1("abcd");string s2("aBcd");// s1 与 s2 相比第二个字符 b 的ASCII值大于 Bcout << s1.compare(s2) << endl; // s1 > s2 所以输出1// operator >> 输入运算符重载,可以直接对字符串进行输入// operator << 输出运算符重载,可以直接对字符串进行输出string s3;cin >> s3;cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl;// getline(cin, str) 获取一行字符串// cin 输入时默认空格是作为结束分隔,所以可以用getline将空格输入字符串中string s4;getline(cin, s4);cout << "s4: " << s4 << endl;}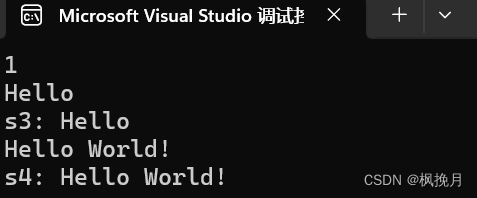
注意事项:
1、cin 与 getline 一起用时注意:
cin只是在缓存区中,把字符读走,会剩余\n在缓存区中,但是getline对\n极度敏感,如果上一个 cin 完立马接 getline 的话会导致getline刚开始读入便遇到/n于是停止读入数据。
解决方法:可以手动清除换行符,cin 后加上 cin.ignore();
![[DevOps云实践] IaaC:通过CloudWatch Agent和自定义Metric监视服务器](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[DevOps云实践] IaaC:通过CloudWatch Agent和自定义Metric监视服务器)

 - 集群操作手册)

)







:AMQP协议)




)
)
)