目录
- 4.4 Divide and Conquer
- 1) 概述
- 二分查找
- 快速排序
- 归并排序
- 合并K个排序链表 - LeetCode 23
- 对比动态规划
- 2) 快速选择算法
- 数组中第k个最大元素-Leetcode 215
- 数组中位数
- 3) 快速幂-Leetcode 50
- 4) 平方根整数部分-Leetcode 69
- 5) 至少k个重复字符的最长子串-Leetcode 395

4.4 Divide and Conquer
1) 概述
分治思想
- 将大问题划分为两个到多个子问题
- 子问题可以继续拆分成更小的子问题,直到能够简单求解
- 如有必要,将子问题的解进行合并,得到原始问题的解
之前学过的一些经典分而治之的例子
- 二分查找
- 快速排序
- 归并排序
- 合并K个排序链表 - LeetCode 23
二分查找
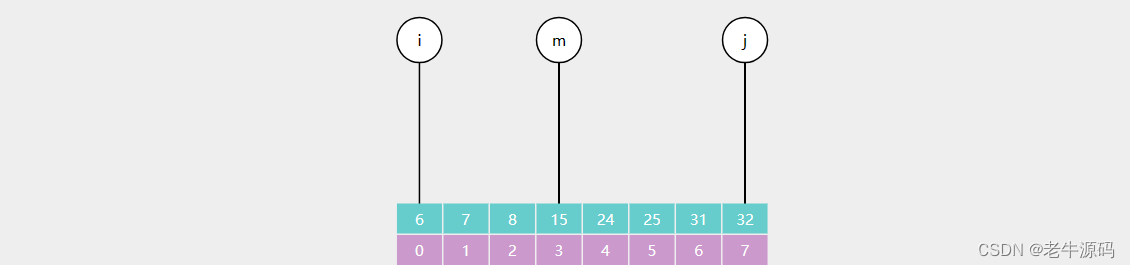
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int target) {return recursion(a, target, 0, a.length - 1);
}public static int recursion(int[] a, int target, int i, int j) {if (i > j) {return -1;}int m = (i + j) >>> 1;if (target < a[m]) {return recursion(a, target, i, m - 1);} else if (a[m] < target) {return recursion(a, target, m + 1, j);} else {return m;}
}
减而治之,每次搜索范围内元素减少一半
快速排序
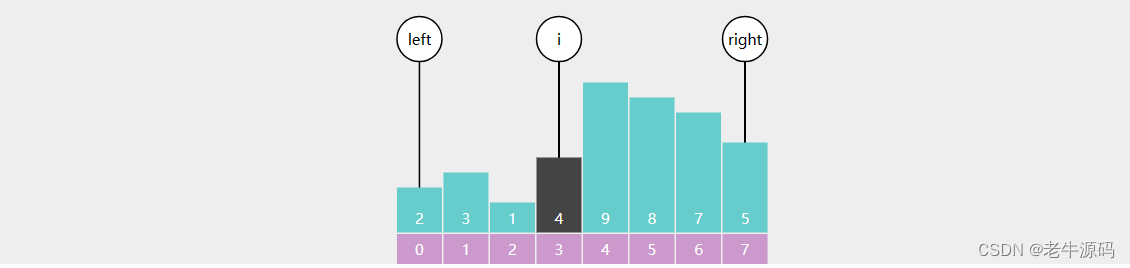
public static void sort(int[] a) {quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) {return;}int p = partition(a, left, right);quick(a, left, p - 1);quick(a, p + 1, right);
}
分而治之,这次分区基准点,在划分后两个区域分别进行下次分区
归并排序

public static void sort(int[] a1) {int[] a2 = new int[a1.length];split(a1, 0, a1.length - 1, a2);
}private static void split(int[] a1, int left, int right, int[] a2) {int[] array = Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, left, right + 1);// 2. 治if (left == right) {return;}// 1. 分int m = (left + right) >>> 1;split(a1, left, m, a2); split(a1, m + 1, right, a2); // 3. 合merge(a1, left, m, m + 1, right, a2);System.arraycopy(a2, left, a1, left, right - left + 1);
}
分而治之,分到区间内只有一个元素,合并区间
合并K个排序链表 - LeetCode 23
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if (lists.length == 0) {return null;}return split(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}public ListNode split(ListNode[] lists, int i, int j) {System.out.println(i + " " + j);if (j == i) {return lists[i];}int m = (i + j) >>> 1;return mergeTwoLists(split(lists, i, m),split(lists, m + 1, j));
}
分而治之,分到区间内只有一个链表,合并区间
对比动态规划
- 都需要拆分子问题
- 动态规划的子问题有重叠、因此需要记录之前子问题解,避免重复运算
- 分而治之的子问题无重叠
2) 快速选择算法
public class Utils {static int quick(int[] a, int left, int right, int index) {int p = partition(a, left, right);if (p == index) {return a[p];}if (p < index) {return quick(a, p + 1, right, index);} else {return quick(a, left, p - 1, index);}}static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(right - left + 1) + left;swap(a, left, idx);int pv = a[left];int i = left + 1;int j = right;while (i <= j) {// i 从左向右找大的或者相等的while (i <= j && a[i] < pv) {i++;}// j 从右向左找小的或者相等的while (i <= j && a[j] > pv) {j--;}if (i <= j) {swap(a, i, j);i++;j--;}}swap(a, j, left);return j;}static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {int t = a[i];a[i] = a[j];a[j] = t;}
}
数组中第k个最大元素-Leetcode 215
public class FindKthLargestLeetcode215 {/*目标 index = 43 2 1 5 6 4=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (3)=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (5)=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (4)*/public int findKthLargest(int[] a, int k) {return Utils.quick(a, 0, a.length - 1, a.length - k);}public static void main(String[] args) {// 应为5FindKthLargestLeetcode215 code = new FindKthLargestLeetcode215();System.out.println(code.findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 2));// 应为4System.out.println(code.findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5, 5, 6}, 4));}
}
数组中位数
public class FindMedian {/*偶数个3 1 5 4奇数个4 5 14 5 1 6 3*/public static double findMedian(int[] nums) {if (nums.length % 2 != 0) {return findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2);} else {System.out.println((nums.length / 2 - 1) + "," + (nums.length / 2));int a = findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2);int b = findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2 - 1);return (a + b) / 2.0;}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{3, 1, 5, 4}));System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{3, 1, 5, 4, 7, 8}));System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{4, 5, 1}));System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{4, 5, 1, 6, 3}));}static int findIndex(int[] a, int index) {return Utils.quick(a, 0, a.length - 1, index);}}
3) 快速幂-Leetcode 50
public class QuickPowLeetcode50 {/*2^10/ \2^5 2^5/ \ / \2 2^2 2^2 2 2^2 2^2/ \ / \ / \ / \2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2256 n=1 x=65536 mul=1024/ \16 16 n=2 x=256 mul=4/ \ / \2 4 4 2 4 4 n=5 x=16 mul=4/ \ / \ / \ / \2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 n=10 x=4 mul=1*/static double myPow(double x, int n) {if (n == 0) {return 1;}double mul = 1;long N = n;if (n < 0) {N = -N;}while (N > 0) {if ((N & 1) == 1) {mul *= x;}x = x * x;N = N >> 1;}return n > 0 ? mul : 1 / mul;}static double myPow1(double x, int n) {long N = n;if (N < 0) {return 1.0 / rec(x, -N);}return rec(x, n);}static double rec(double x, long n) {if (n == 0) {return 1;}if (n == 1) {return x;}double y = rec(x, n / 2);if ((n & 1) == 1) {return x * y * y;}return y * y;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(myPow(2, 10)); // 1024.0System.out.println(myPow(2.1, 3)); // 9.261System.out.println(myPow(2, -2)); // 0.25System.out.println(myPow(2, 0)); // 1.0System.out.println(myPow(2, -2147483648)); // 1.0}
}
4) 平方根整数部分-Leetcode 69
public class SqrtLeetcode69 {static int mySqrt(int x) {int i = 1, j = x;int r = 0;while (i <= j) {int m = (i + j) >>> 1;if (x / m >= m) {r = m;i = m+1;} else {j = m-1;}}return r;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(mySqrt(1));System.out.println(mySqrt(2));System.out.println(mySqrt(4));System.out.println(mySqrt(8));System.out.println(mySqrt(9));}
}
- while(i <= j) 含义是在此区间内,只要有数字还未尝试,就不算结束
- r 的作用是保留最近一次当 m 2 < = x m^2 <= x m2<=x 的 m 的值
- 使用除法而非乘法,避免大数相乘越界
5) 至少k个重复字符的最长子串-Leetcode 395
public class LongestSubstringLeetcode395 {static int longestSubstring(String s, int k) {// 子串落选情况if (s.length() < k) {return 0;}int[] counts = new int[26]; // 索引对应字符 值用来存储该字符出现了几次char[] chars = s.toCharArray();for (char c : chars) { // 'a' -> 0 'b' -> 1 ....counts[c - 'a']++;}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(counts));for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {char c = chars[i];int count = counts[c - 'a']; // i字符出现次数if (count > 0 && count < k) {int j = i + 1;while(j < s.length() && counts[chars[j] - 'a'] < k) {j++;}System.out.println(s.substring(0, i) + "\t" + s.substring(j));return Integer.max(longestSubstring(s.substring(0, i), k),longestSubstring(s.substring(j), k));}}// 子串入选情况return s.length();}public static void main(String[] args) {// i jSystem.out.println(longestSubstring("aaaccbbb", 3)); // ababbSystem.out.println(longestSubstring("dddxaabaaabaacciiiiefbff", 3));
// System.out.println(longestSubstring("ababbc", 3)); // ababb
// System.out.println(longestSubstring("ababbc", 2)); // ababb/*ddd aabaaabaa iiii fbffaa aaa aa f ff统计字符串中每个字符的出现次数,移除哪些出现次数 < k 的字符剩余的子串,递归做此处理,直至- 整个子串长度 < k (排除)- 子串中没有出现次数 < k 的字符*/}
}



 + 写时复制 + AOF(Append Only File)+混合持久化))

——创建(create)角色脚本(panel)——静态(static))



和非聚簇索引(二级索引)/什么是回表?)




)




