一 lseek 函数
函数说明:此函数用于文件偏移
Linux中可使用系统函数lseek来修改文件偏移量(读写位置)
每个打开的文件都记录着当前读写位置,打开文件时读写位置是0,表示文件开头,通常读写多少个字节就会将读写位置往后移多少个字节。但是有一个例外,如果以O_APPEND方式打开,每次写操作都会在文件末尾追加数据,然后将读写位置移到新的文件末尾。lseek和标准I/O库的fseek函数类似,可以移动当前读写位置(或者叫偏移量)。
回忆fseek的作用及常用参数。 SEEK_SET、SEEK_CUR、SEEK_END
int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); 成功返回0;失败返回-1
特别的:超出文件末尾位置返回0;往回超出文件头位置,返回-1
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence); 失败返回-1;成功:返回的值是较文件起始位置向后的偏移量。
特别的:lseek允许超过文件结尾设置偏移量,文件会因此被拓展。
注意文件“读”和“写”使用同一偏移位置。
也就是说:当我们先写了一段数据后,如果没有close(fd),则这时候文件中的位置,在写入数据的最后一位,这时候再去读,是读不到刚才写的哪些数据的,要移动数据到开始写的位置。
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
DESCRIPTION
The lseek() function repositions the offset of the open file associated
with the file descriptor fd to the argument offset according to the
directive whence as follows:
SEEK_SET
The offset is set to offset bytes.
SEEK_CUR
The offset is set to its current location plus offset bytes.
SEEK_END
The offset is set to the size of the file plus offset bytes.
参数:
int fd, 指向文件的fd
off_t offset, off_t 的本质是 long int: 偏移量
int whence 从哪里开始偏移SEEK_SET,SEEK_CUR, SEEK_END
SEEK_SET,从开始位置
SEEK_CUR,从当前位置
SEEK_END 从文件最后位置
返回值:
失败返回-1;errno 被设置
成功:返回的值是较文件起始位置向后的偏移量。
lseek常用应用:
1. 使用lseek拓展文件:write操作才能实质性的拓展文件。单lseek是不能进行拓展的。
一般:write(fd, "\0", 1);

2. 通过lseek获取文件的大小:lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); 【lseek_test.c】
【最后注意】:lseek函数返回的偏移量总是相对于文件头而言。
二 查看文件的表示形式
od -tcx filename 查看文件的16进制表示形式
od -tcd filename 查看文件的10进制表示形式
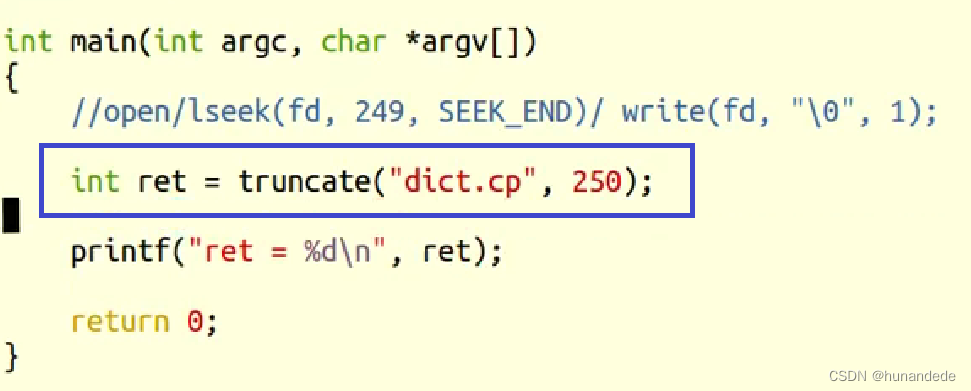
三 truncate 函数 ,真正的改变文件大小的函数
函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
函数参数
第一个:要改变的文件的路径,
第二个:要将文件改成多大。
如果length小于原来的文件,则原来的文件会被截断
如果length 大于原来的文件,则原来的文件会被扩展
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回-1, errno 被设置




)


)



 | @Prop装饰器)







)