凸包(Convex Hull)是包含给定点集合的最小凸多边形。凸包算法有多种实现方法,其中包括基于递增极角排序、Graham扫描、Jarvis步进法等。下面,我将提供一个简单的凸包算法实现,基于Graham扫描算法。
Graham扫描算法是一种用于求解平面点集的凸包问题的常见算法。凸包是包含给定点集合的最小凸多边形。Graham扫描算法的基本思想是通过选择一个特殊的起点,将点集按照极角排序,然后通过栈的操作来逐步构建凸包。
以下是Graham扫描算法的基本步骤:
-
选择极点: 从给定的点集中选择一个极点作为起始点。通常选择最下面且最左边的点,以确保算法的稳定性。
-
极角排序: 将其他所有点按照相对于极点的极角进行排序。极角可以使用反正切函数(atan2)计算。排序后的点集顺序将确定扫描过程中点的访问顺序。
-
扫描过程: 从第三个点开始,按照排序后的顺序逐个处理每个点。对于每个点,检查它与栈顶两个点的转向关系(顺时针、逆时针或平行)。如果是逆时针,将该点压入栈;如果是顺时针或平行,则出栈,直到找到逆时针为止。这确保了最终栈中的点构成凸包。
-
构建凸包: 扫描完成后,栈中的点就是凸包的顶点,它们按照逆时针方向排列。
Graham扫描算法的时间复杂度主要取决于对点的排序操作,通常为 O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn),其中n是点的数量。该算法的优势在于其相对简单的实现和较好的性能。然而,需要注意的是,在特定情况下,例如存在大量共线点的情况下,算法的性能可能会有所下降。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math# 定义二维点的类
class Point:def __init__(self, x, y):self.x = xself.y = y# 计算极角
def polar_angle(p0, p):dx = p.x - p0.xdy = p.y - p0.yreturn math.atan2(dy, dx)# 判断三个点的转向关系
def orientation(p, q, r):val = (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x) - (q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y)if val == 0:return 0 # 平行return 1 if val > 0 else 2 # 顺时针或逆时针# Graham扫描算法
def convex_hull(points):n = len(points)if n < 3:print("Convex Hull requires at least 3 points.")return []# 寻找最下面且最左边的点作为极点pivot = min(range(n), key=lambda i: (points[i].y, points[i].x))points[0], points[pivot] = points[pivot], points[0]# 根据极角对其余点进行排序points[1:] = sorted(points[1:], key=lambda p: (polar_angle(points[0], p), p.x, p.y))# 构建凸包hull = [points[0], points[1]]for i in range(2, n):while len(hull) > 1 and orientation(hull[-2], hull[-1], points[i]) != 2:hull.pop()hull.append(points[i])return hull# 示例点集
points = [Point(0, 3), Point(1, 1), Point(2, 2), Point(4, 4), Point(0, 0), Point(1, 2), Point(3, 1), Point(3, 3)]# 计算凸包
convex_hull_points = convex_hull(points)# 绘制原始离散点
x_values = [point.x for point in points]
y_values = [point.y for point in points]
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, color='blue', label='Original Points')# 绘制凸包
hull_x = [point.x for point in convex_hull_points]
hull_y = [point.y for point in convex_hull_points]
hull_x.append(convex_hull_points[0].x) # 闭合凸包
hull_y.append(convex_hull_points[0].y)
plt.plot(hull_x, hull_y, color='red', linestyle='-', linewidth=2, label='Convex Hull')# 显示图例和图形
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title('Convex Hull')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()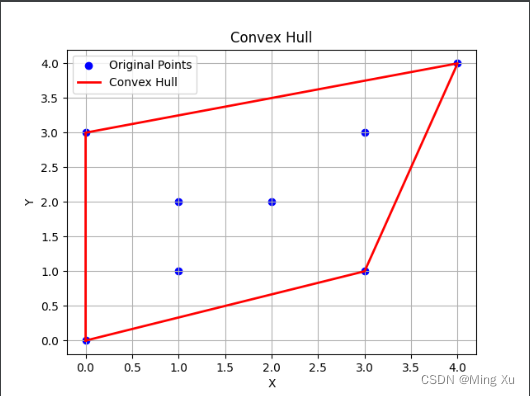
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>// 定义二维点的结构体
struct Point {double x, y;// 构造函数Point(double _x, double _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}// 用于排序的比较函数static bool compare(const Point& a, const Point& b) {return (a.y < b.y) || (a.y == b.y && a.x < b.x);}
};// 计算极角
double polarAngle(const Point& p0, const Point& p) {double dx = p.x - p0.x;double dy = p.y - p0.y;return atan2(dy, dx);
}// 判断三个点的转向关系
int orientation(const Point& p, const Point& q, const Point& r) {double val = (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x) - (q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y);if (val == 0) return 0; // 平行return (val > 0) ? 1 : 2; // 顺时针或逆时针
}// Graham扫描算法
std::vector<Point> convexHull(std::vector<Point>& points) {size_t n = points.size();if (n < 3) {std::cerr << "Convex Hull requires at least 3 points." << std::endl;return std::vector<Point>();}// 寻找最下面且最左边的点作为极点size_t pivot = 0;for (size_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {if (points[i].y < points[pivot].y || (points[i].y == points[pivot].y && points[i].x < points[pivot].x)) {pivot = i;}}// 将极点移到数组的第一个位置std::swap(points[0], points[pivot]);// 根据极角对其余点进行排序std::sort(points.begin() + 1, points.end(), [&points](const Point& a, const Point& b) {double angleA = polarAngle(points[0], a);double angleB = polarAngle(points[0], b);return (angleA < angleB) || (angleA == angleB && (a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.y < b.y)));});// 构建凸包std::vector<Point> hull;hull.push_back(points[0]);hull.push_back(points[1]);for (size_t i = 2; i < n; i++) {while (hull.size() > 1 && orientation(hull[hull.size() - 2], hull[hull.size() - 1], points[i]) != 2) {hull.pop_back();}hull.push_back(points[i]);}return hull;
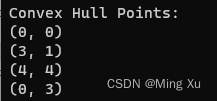
}int main() {// 示例点集std::vector<Point> points = { {0, 3}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {4, 4}, {0, 0}, {1, 2}, {3, 1}, {3, 3} };// 计算凸包std::vector<Point> convexHullPoints = convexHull(points);// 输出凸包的点std::cout << "Convex Hull Points:" << std::endl;for (const auto& point : convexHullPoints) {std::cout << "(" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ")" << std::endl;}return 0;
}
项目初始化)
)

开展某品牌家纺神秘顾客调研)


)









文件系统(六))


