后端杂七杂八系列篇三
- ① Spring Event用法
- ① 同步代码的用法
- ① 自定义事件
- ② 定义监听器
- ③ 定义发布者
- ④ 发布消息后,接口收到消息
- ② 异步代码的用法
- ① `开启异步`
- ② 自定义事件
- ③ 自定义监听器(推荐使用 @EventListener 注解),`使用@Async注解`
- ④ 定义发布者
- ⑤ 发布消息后,`观察同步与异步消息`
- ② SpringBoot+Redis BitMap 实现签到与统计功能
- ① 什么是Redis BitMap ?
- ② SpringBoot 整合 Redis 实现签到 功能
- ① 设计思路
- ② 如何连续签到天数?
- ③ 如何得到本月到今天为止的所有签到数据?
- ④ 如何从后向前遍历每个Bit位?
- ⑤ 代码Demo
- ③ 基于Redis实现分布式锁(使用Redisson)
- ⑤ redis 缓存穿透
① Spring Event用法
实际业务开发过程中,业务逻辑可能非常复杂,核心业务 + N个子业务。如果都放到一块儿去做,代码可能会很长,耦合度也会很高。
MQ解决这个问题,但是在业务不是特别复杂的情况下,我们可以使用观察者设计模式来完成。Spring Event(Application Event)其实就是一个观察者设计模式。

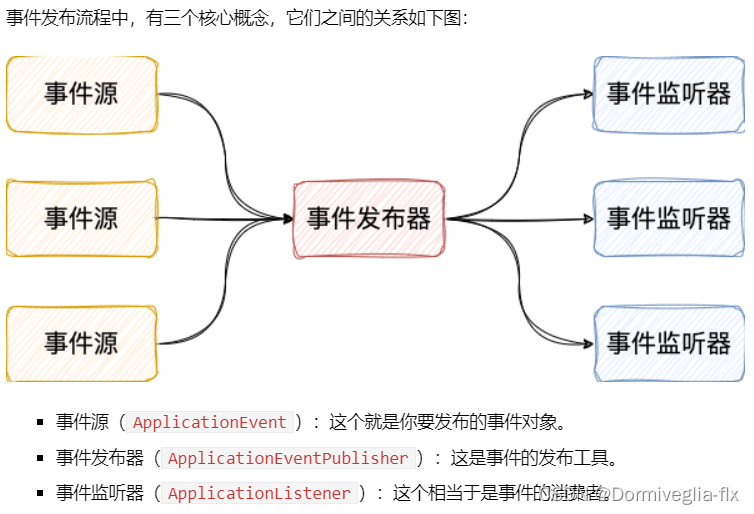
① 同步代码的用法
① 自定义事件
// 定义事件,继承 ApplicationEvent 的类成为一个事件类@Data
@ToString
public class OrderProductEvent extends ApplicationEvent {/** 该类型事件携带的信息 */private String orderId;public OrderProductEvent(Object source, String orderId) {super(source);this.orderId = orderId;}
}
② 定义监听器
// 监听并处理事件,实现 ApplicationListener 接口或者使用 @EventListener 注解@Slf4j
@Component
public class OrderProductListener implements ApplicationListener<OrderProductEvent> {/** 使用 onApplicationEvent 方法对消息进行接收处理 */@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(OrderProductEvent event) {String orderId = event.getOrderId();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Thread.sleep(2000);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("{}:校验订单商品价格耗时:({})毫秒", orderId, (end - start));}}
③ 定义发布者
// 发布事件,通过 ApplicationEventPublisher 发布事件@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
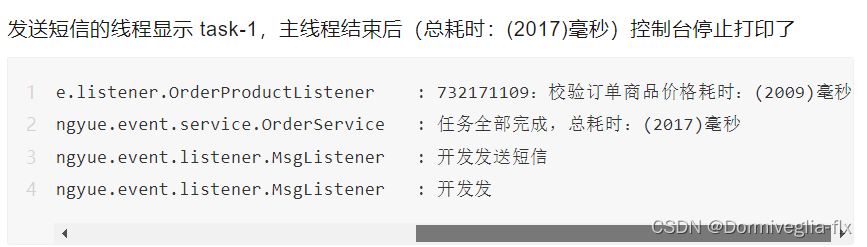
public class OrderService {/** 注入ApplicationContext用来发布事件 */private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;/*** 下单** @param orderId 订单ID*/public String buyOrder(String orderId) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 1.查询订单详情// 2.检验订单价格 (同步处理)applicationContext.publishEvent(new OrderProductEvent(this, orderId));// 3.短信通知(异步处理)long end = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("任务全部完成,总耗时:({})毫秒", end - start);return "购买成功";}}
④ 发布消息后,接口收到消息
// 发布消息后,接口收到消息@SpringBootTest
public class OrderServiceTest {@Autowired private OrderService orderService;@Testpublic void buyOrderTest() {orderService.buyOrder("732171109");}
}

② 异步代码的用法
有些业务场景不需要在一次请求中同步完成,比如邮件发送、短信发送等。
① 开启异步
// 新增@EnableAsync注解@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class MingYueSpringbootEventApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(MingYueSpringbootEventApplication.class, args);}
}
② 自定义事件
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MsgEvent {/** 该类型事件携带的信息 */public String orderId;
}
③ 自定义监听器(推荐使用 @EventListener 注解),使用@Async注解
// 使用@EventListener 注解@Slf4j
@Component
public class MsgListener {@Async@SneakyThrows@EventListener(MsgEvent.class)public void sendMsg(MsgEvent event) {String orderId = event.getOrderId();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("开发发送短信");log.info("开发发送邮件");Thread.sleep(4000);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("{}:发送短信、邮件耗时:({})毫秒", orderId, (end - start));}
}
④ 定义发布者
public String buyOrder(String orderId) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 1.查询订单详情// 2.检验订单价格 (同步处理)applicationContext.publishEvent(new OrderProductEvent(this, orderId));// 3.短信通知(异步处理)applicationContext.publishEvent(new MsgEvent(orderId));long end = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("任务全部完成,总耗时:({})毫秒", end - start);return "购买成功";
}
⑤ 发布消息后,观察同步与异步消息
@Test
public void buyOrderTest() {orderService.buyOrder("732171109");
}
② SpringBoot+Redis BitMap 实现签到与统计功能
① 什么是Redis BitMap ?
在数据处理和分析中,常常需要对大量的数据进行统计和计算。
当数据量达到亿级别时,传统的数据结构和算法已经无法胜任这个任务。Bitmap(位图)是一种适合于大规模数据统计的数据结构,能够以较低的空间复杂度存储大规模数据,并且支持高效的位运算操作。本文将介绍 Bitmap 的基本概念、实现方式和在亿级数据计算中的应用。

② SpringBoot 整合 Redis 实现签到 功能
① 设计思路
我们可以把年和月作为BitMap的key,然后保存到一个BitMap中,每次签到就到对应的位上把数字从0 变为1,只要是1,就代表是这一天签到了,反之咋没有签到。
比如 2024年1月1日的签到:
Key(202401) Value:1
比如 2024年1月2日的签到:
Key(202401) Value:1
比如 2024年1月3日的未签到:
Key(202401) Value:0
所以2024年一月份的签到状态可以表示为:
Key(202401) Value:1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1
为了区分用户,我们可以加一个用户标识。比如 202401:24ewe89 后面的这个24ewe89是用户的token
② 如何连续签到天数?

③ 如何得到本月到今天为止的所有签到数据?

④ 如何从后向前遍历每个Bit位?

br>
⑤ 代码Demo
// controller@GetMapping("/signCount")
public Result signCount() {return userService.signCount();
}
// servicepublic Result signCount() {//1. 获取登录用户Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();//2. 获取日期LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();//3. 拼接keyString keySuffix = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(":yyyyMM"));String key = RedisConstants.USER_SIGN_KEY + userId + keySuffix;//4. 获取今天是本月的第几天int dayOfMonth = now.getDayOfMonth();//5. 获取本月截至今天为止的所有的签到记录,返回的是一个十进制的数字 BITFIELD sign:5:202301 GET u3 0List<Long> result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().bitField(key,BitFieldSubCommands.create().get(BitFieldSubCommands.BitFieldType.unsigned(dayOfMonth)).valueAt(0));//没有任务签到结果if (result == null || result.isEmpty()) {return Result.ok(0);}Long num = result.get(0);if (num == null || num == 0) {return Result.ok(0);}//6. 循环遍历int count = 0;while (true) {//6.1 让这个数字与1 做与运算,得到数字的最后一个bit位 判断这个数字是否为0if ((num & 1) == 0) {//如果为0,签到结束break;} else {count ++;}num >>>= 1;}return Result.ok(count);
}
③ 基于Redis实现分布式锁(使用Redisson)
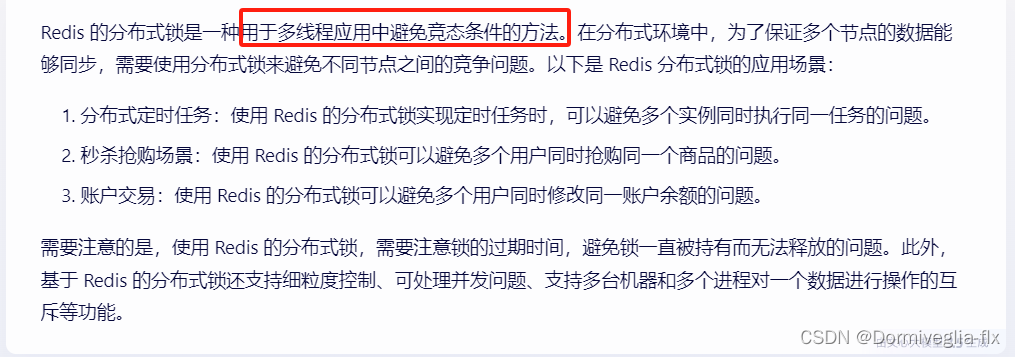
用法
1. pom文件
<dependency><groupId>org.redisson</groupId><artifactId>redisson</artifactId><version>3.13.6</version></dependency>
- 配置 Redisson 客户端
@Configuration
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RedissonConfig {@Beanpublic RedissonClient redissonClient() {Config config = new Config();config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.88.130:6379").setPassword("root");return Redisson.create(config);}}
- Redisson 的可重入锁
@Testpublic void tesRedisson() throws InterruptedException {// 获取可重入锁, 指定锁的名称RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("anLock");// 尝试获取锁// 参数1:获取锁的最大等待时间(期间会多次重试获取锁)// 参数2:锁自动释放时间// 参数3:时间单位boolean isGetLock = lock.tryLock(1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (isGetLock) {try {System.out.println("执行业务");} finally {lock.unlock();}}}⑤ redis 缓存穿透
什么是缓存穿透?
redis已经没有了,还查询mysql

解决方案:布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器主要是用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中
—主要是nfs方式挂载)



(四))
)






:阻塞/非阻塞 IO)



)


)