安装Elasticsearch 7.8.0
官网:Elasticsearch 7.8.0 | Elastic
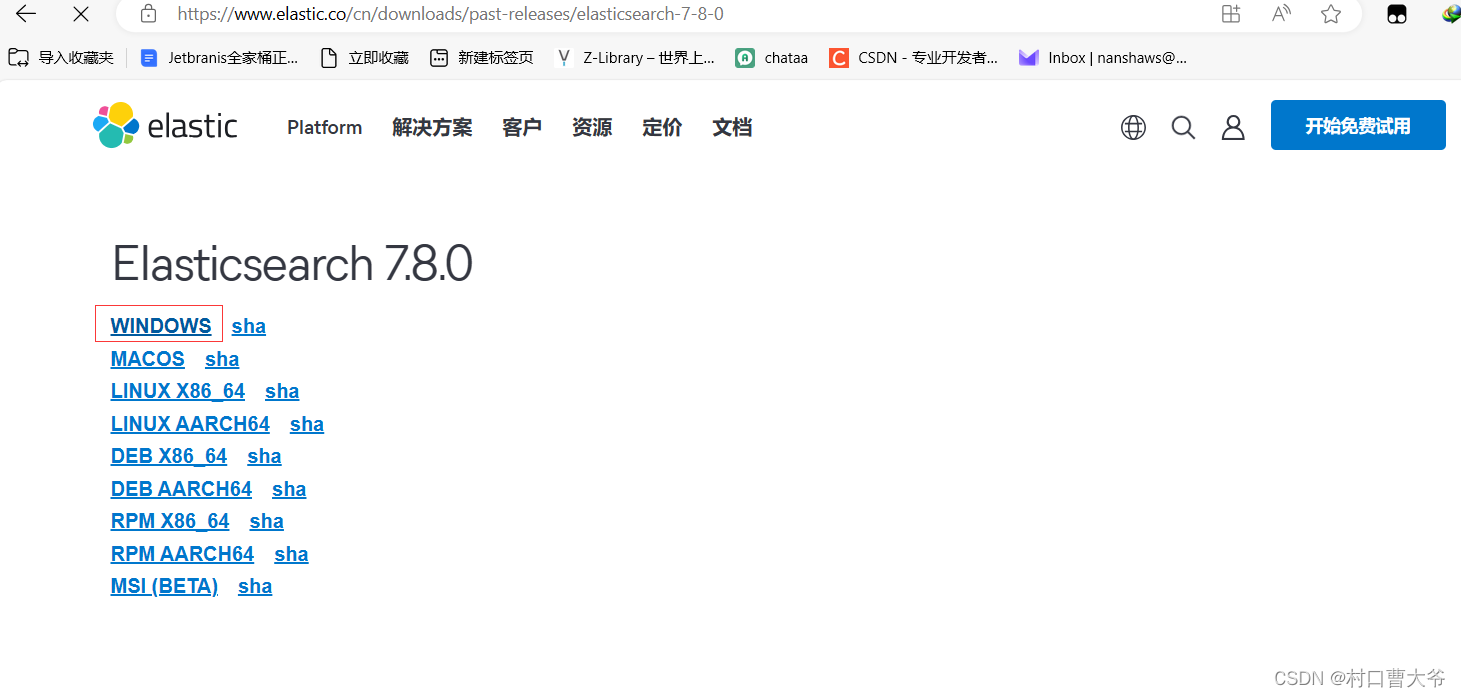
大家下载所需要的安装包即可。然后解压缩:
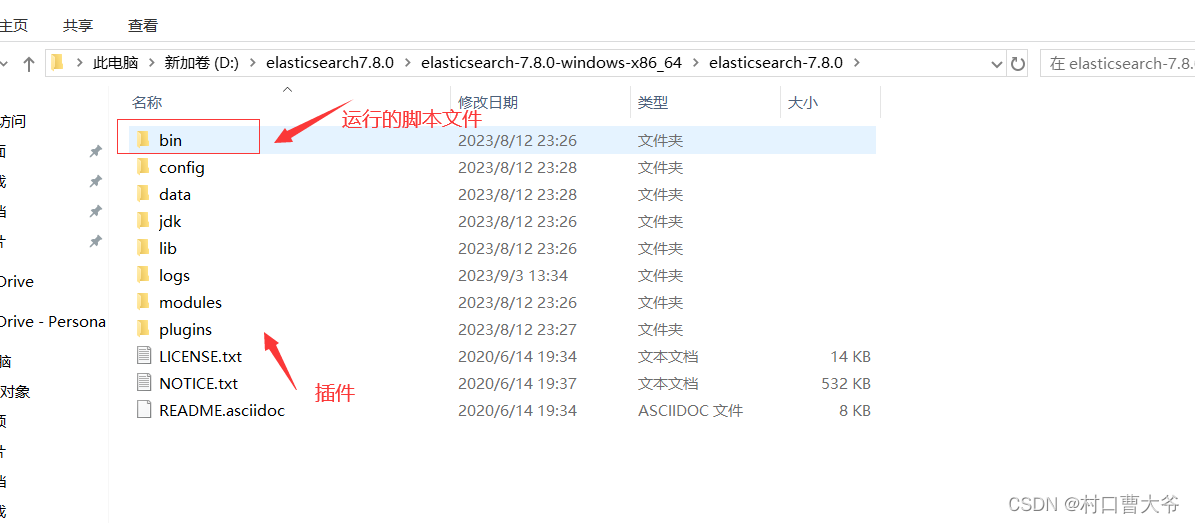
Elasticsearch是通过java编写的,所以自带jdk。多好,下载Elasticsearch赠送jdk 0.0,不过一般我们用自己的jdk。
要启动Elasticsearch服务,就直接进入bin目录,并打开elasticsearch.bat文件。
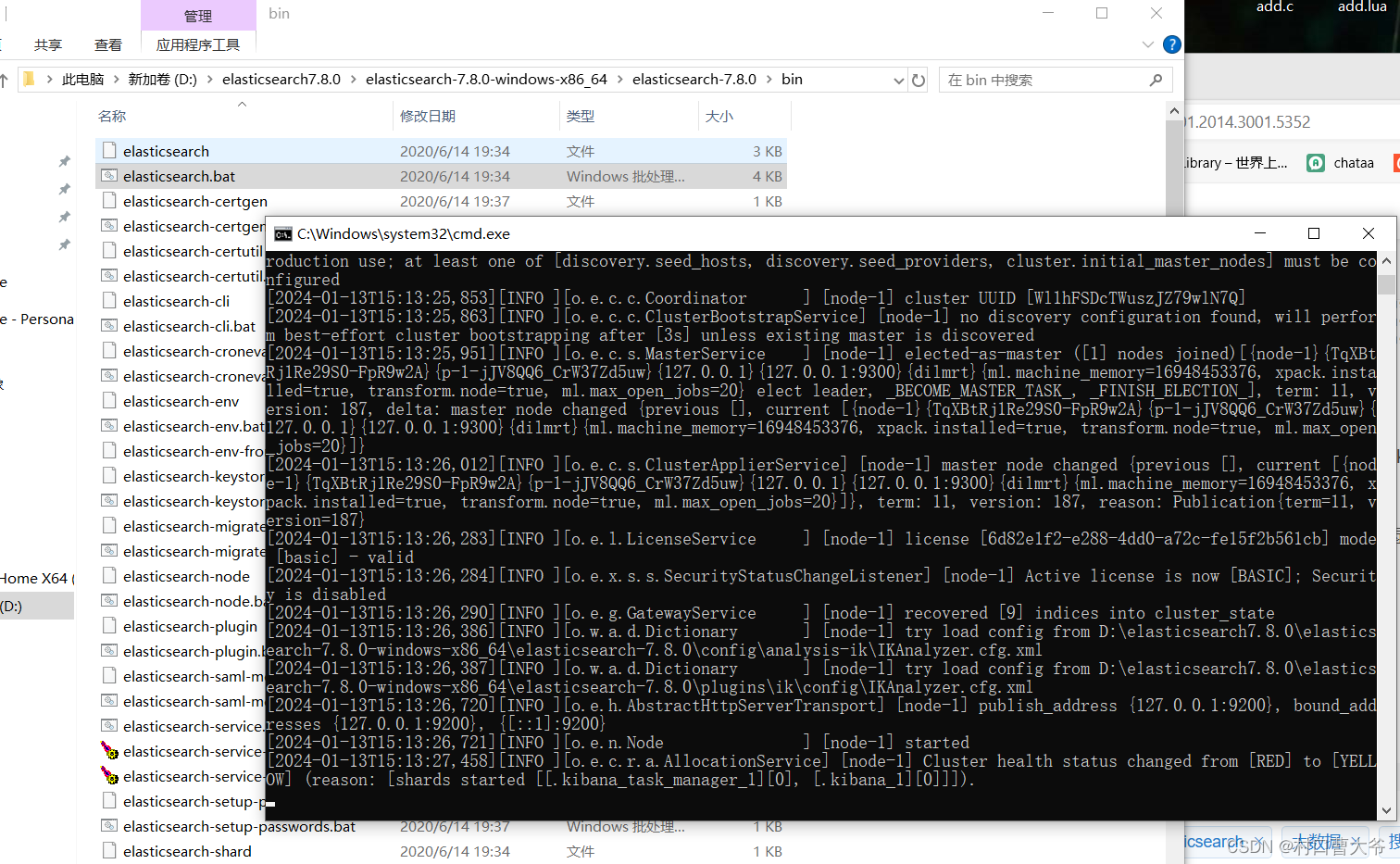
这样就启动好了。
注意:9300端口为Elasticsearch集群间组件的通信端口,9200端口为浏览器访问的http协议RESTful端口。
启动之后,可以打开浏览器:localhost:9200
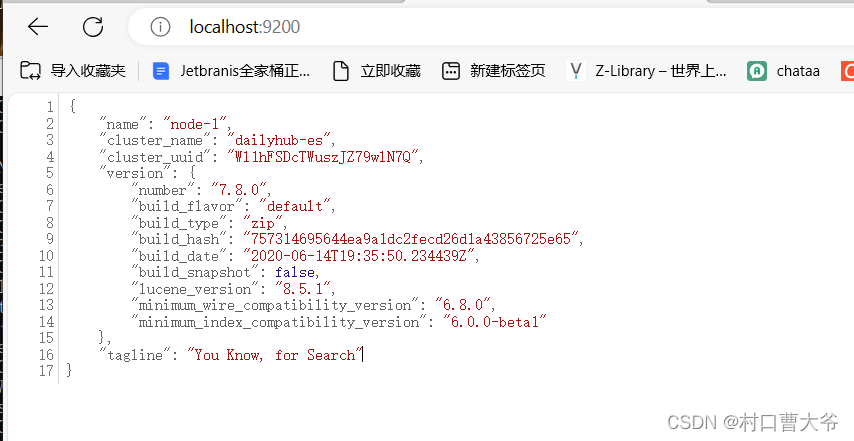
可能你们的和我这个描述不一样,因为我修改了它的配置文件,但是只要出现这种类似的,就说明启动成功了。
注意:在启动的时候,由于版本问题,但凡使用超过java11的版本都有可能出现启动失败问题。
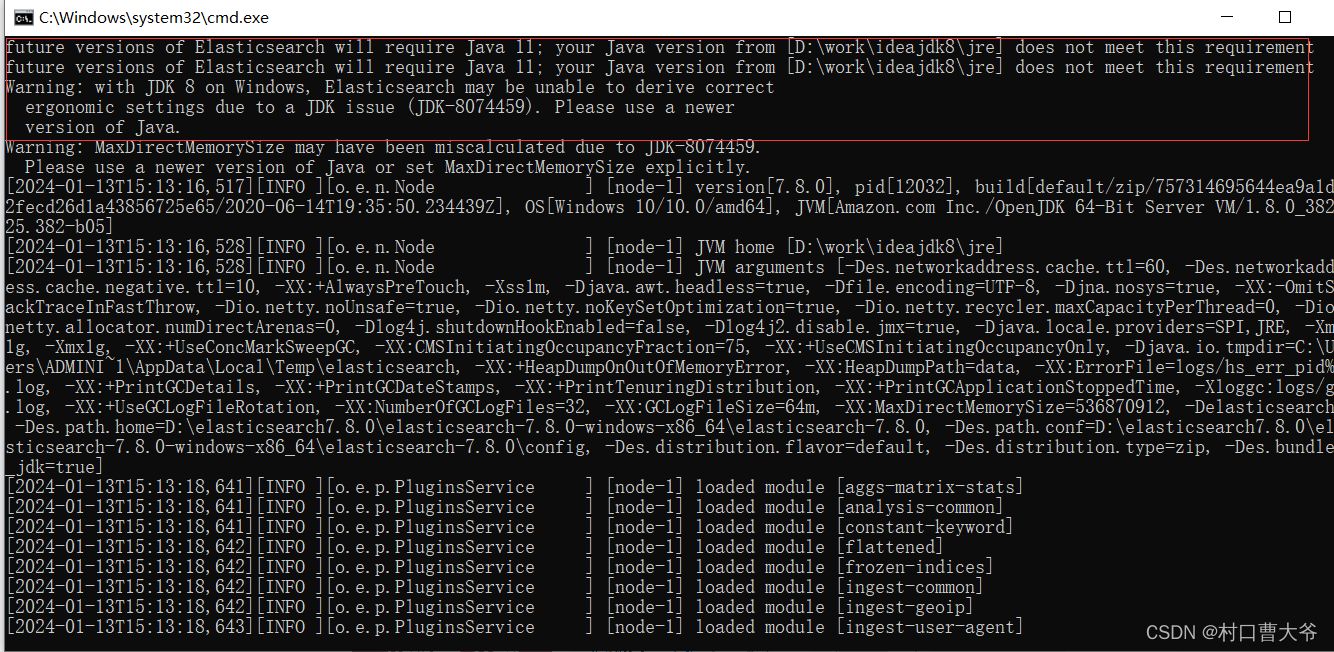
这个东西在启动的时候就有了,意思是这个版本用的是java11,但是我们用java8是完全没有问题的。但到了Java17的时候很多东西都改变了。当然版本小于1.8也会出错。
所以用java17运行Elasticsearch 7.8.0的时候会有很大机率出错。
了解什么是正排索引什么是倒排索引
-
正排索引(Forward Index):
- 正排索引是一种将文档与其对应的词项(terms)列表建立关联的索引结构。
- 对于每篇文档,正排索引会记录文档中的所有词项以及它们的位置信息。
- 通过正排索引,可以直接获取到文档中的内容,而不需要进行复杂的检索操作。
-
倒排索引(Inverted Index):
- 倒排索引是一种将词项与包含这些词项的文档建立关联的索引结构。
- 对于每个词项,倒排索引记录包含该词项的所有文档的标识符或其他相关信息。
- 通过倒排索引,可以快速地找到包含特定词项的所有文档,实现高效的文档检索。
举例说明:
文档1: "机器学习是人工智能的一个重要分支。"
文档2: "深度学习在图像识别领域取得了显著的成果。"
正排索引示例:
文档1: [机器学习, 人工智能, 重要, 分支]
文档2: [深度学习, 图像识别, 显著, 成果]
倒排索引示例:
机器学习: [文档1]
人工智能: [文档1]
重要: [文档1]
分支: [文档1]深度学习: [文档2]
图像识别: [文档2]
显著: [文档2]
成果: [文档2]
而我们的Elasticsearch使用的就是倒排索引
restful风格
RESTful(Representational State Transfer)是一种基于资源的软件架构风格,通常用于设计网络应用程序的 API。以下是一些与RESTful风格相关的主要原则和特征:
-
资源(Resources):
- RESTful 设计强调资源的概念,每个资源都有一个唯一的标识符(URI)。
- 资源可以是任何具体或抽象的实体,如用户、产品、服务等。
-
表现层(Representation):
- 资源的状态通过表现层进行传输,可以是 JSON、XML 等格式。
- 客户端和服务器之间的通信是无状态的。
-
状态转移(State Transfer):
- RESTful 通过对资源的表现层进行操作来实现状态的转移。
- 客户端通过标准的 HTTP 方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等)对资源进行操作。
-
统一接口(Uniform Interface):
- RESTful 鼓励使用统一的接口,使得不同的应用可以通过相同的接口进行通信。
- 统一接口包括标识资源的 URI、通过标准 HTTP 方法对资源进行操作、使用标准的媒体类型(如JSON)等。
-
无状态(Stateless):
- RESTful 架构是无状态的,每个请求都包含了足够的信息以便服务器理解和处理请求。
- 服务器不会存储客户端的状态,每个请求都是独立的。
-
可缓存性(Cacheability):
- RESTful 支持可缓存性,使得客户端可以缓存服务器的响应,提高性能和降低服务器负载。
-
按需扩展性(Layered System):
- RESTful 架构支持按需扩展性,系统可以通过添加新的层来扩展功能。
-
无连接(Stateless Communication):
- RESTful 通信是无连接的,每个请求从客户端到服务器都包含了所有的信息。
RESTful 风格的设计使得系统更具可伸缩性、可维护性,同时提供了清晰的接口,使得不同系统能够有效地协同工作。这种风格通常用于构建 Web 服务和 API。
注意:Elasticsearch 允许GET、PUT、HEAD、DELETE请求。而post和put是针对文档的,但是put要求幂等性,而post并不要求,如果没有定义主键,Elasticsearch的文档创建的时候每次返回的主键都是不一样的,所以用put会报错
Elasticsearch的使用:索引操作
1、 创建索引
对比关系型数据库,创建索引就等同于创建数据库。
在Postman中,向ES服务器发出Put请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl
哦对了,这个工具用的是postman
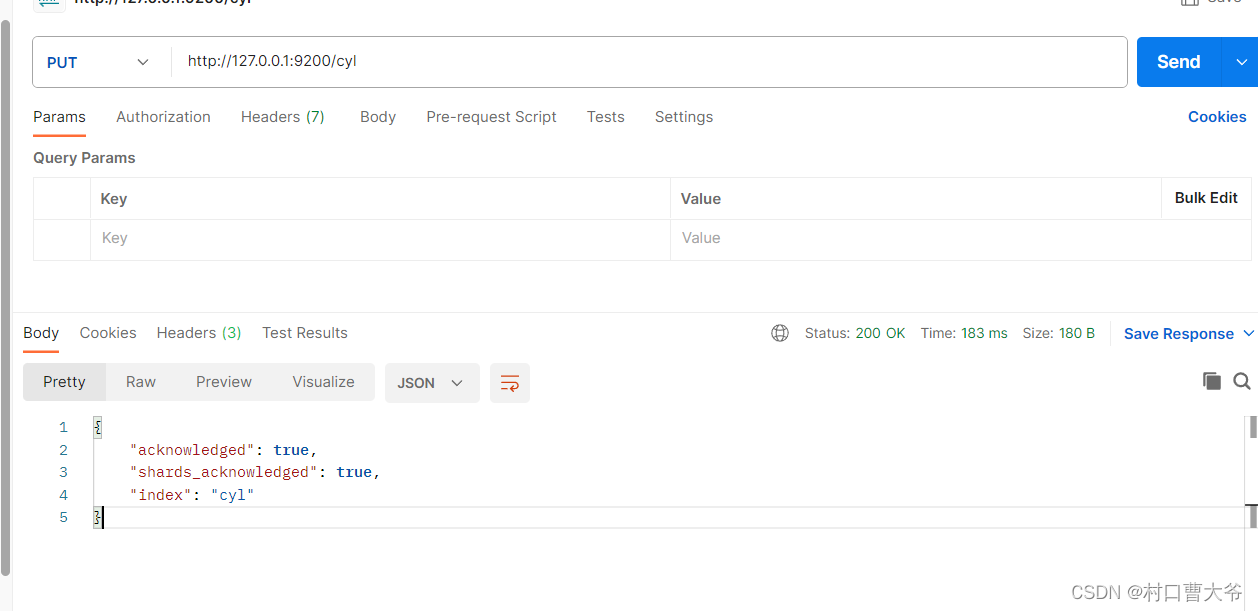
2、 查询索引
在Postman中,向ES服务器发出GET请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl
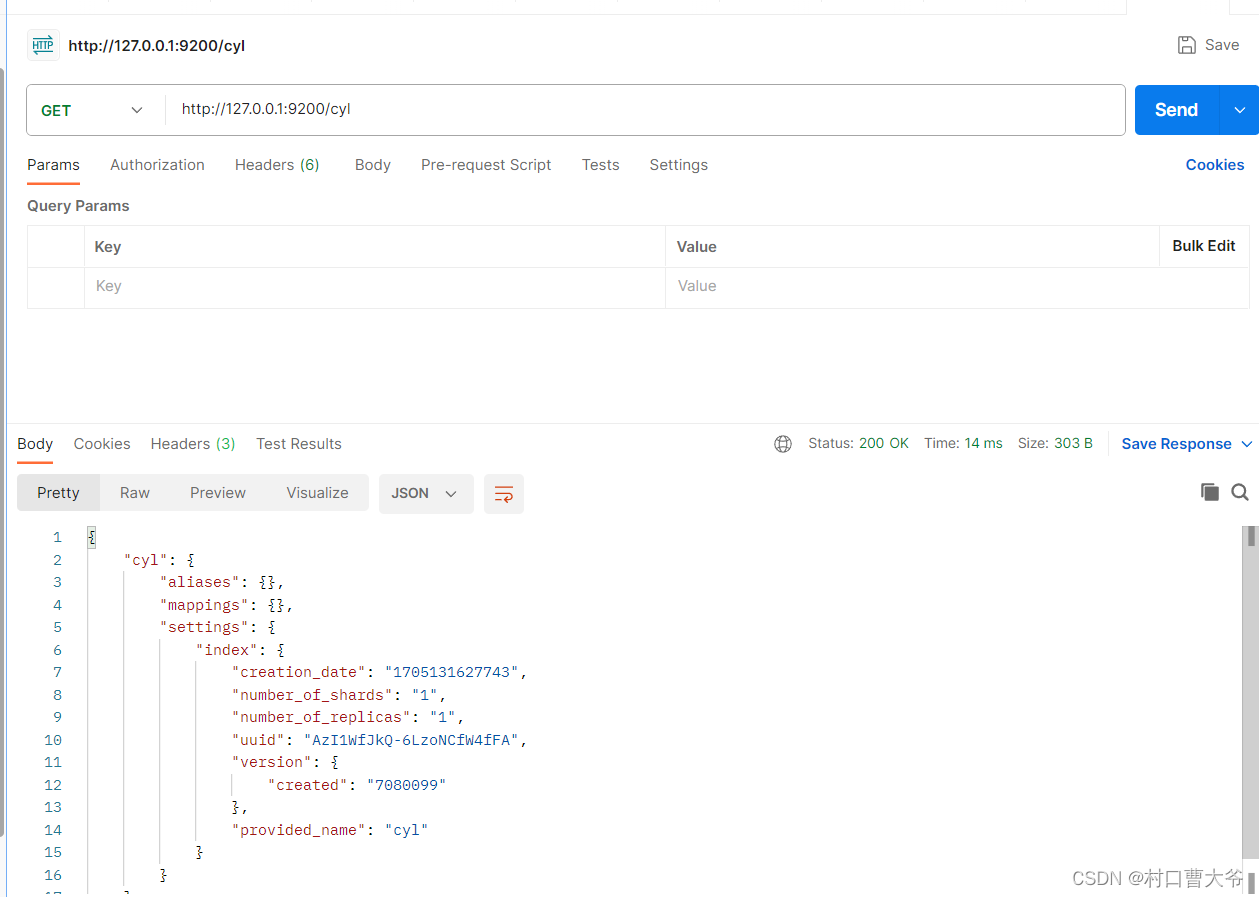
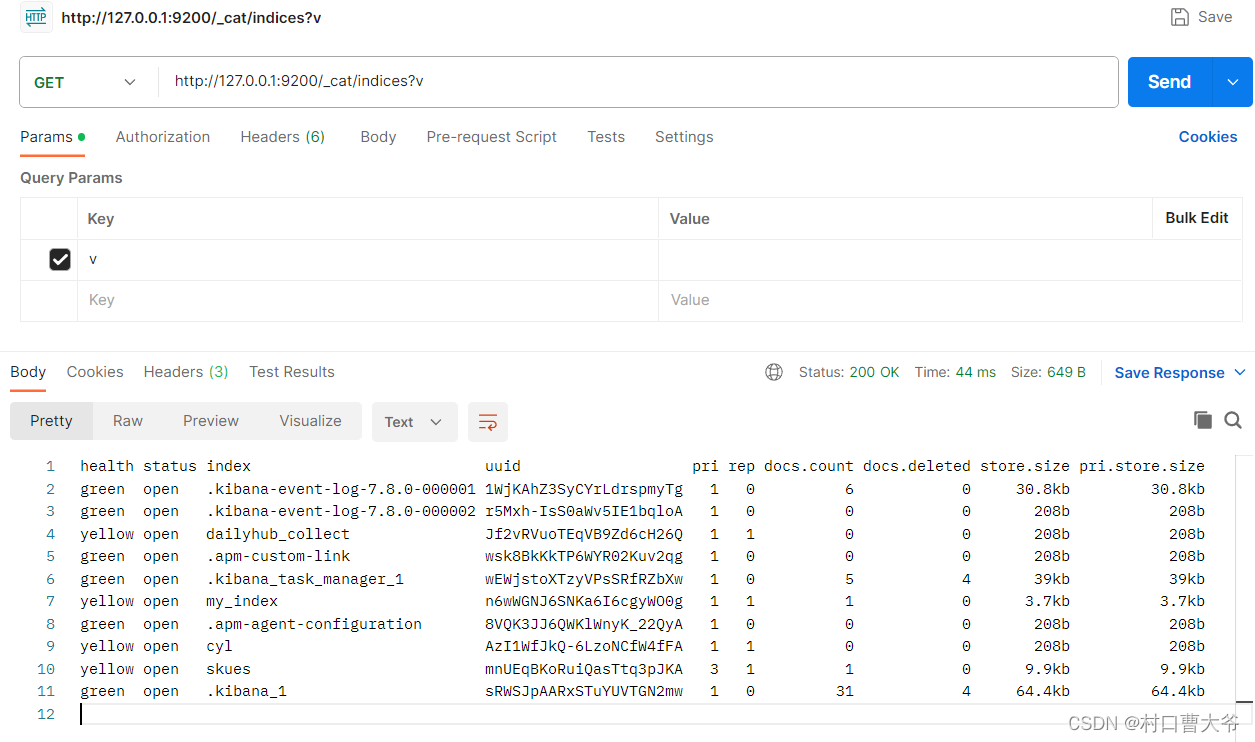
如果想查询所有的索引:GET下面命令
http://127.0.0.1:9200/_cat/indices?v
3、 删除索引
在Postman中,向ES服务器发出DELETE请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl
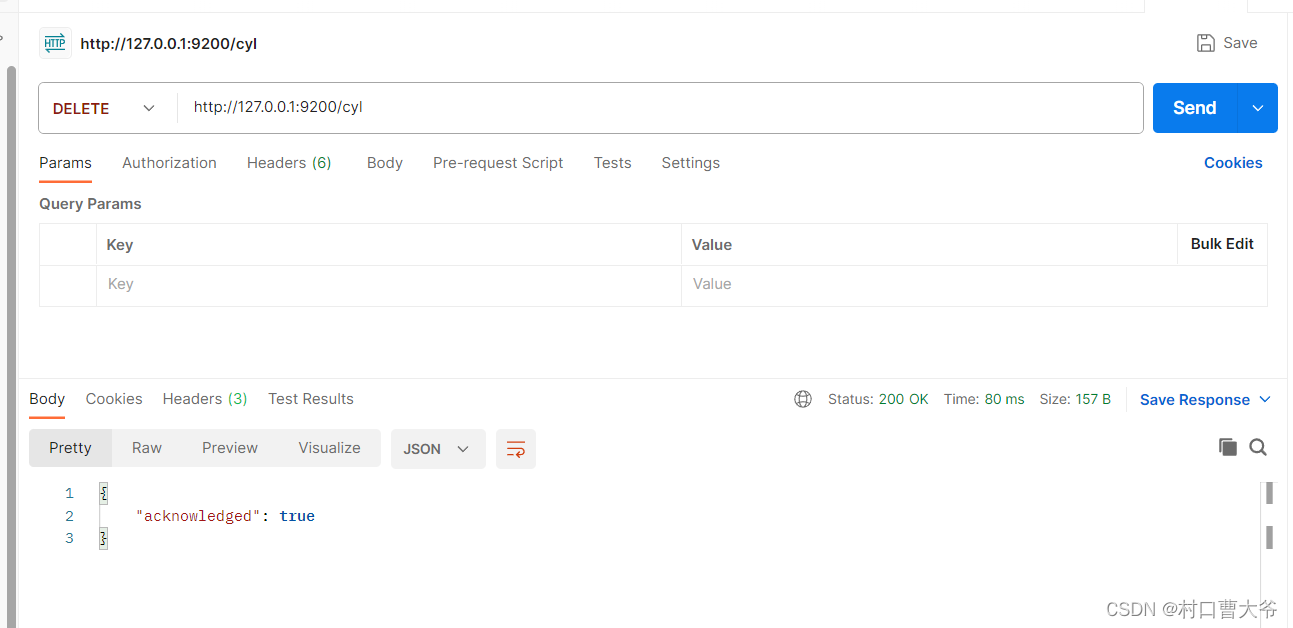
删除成功。
Elasticsearch的使用:文档操作
创建文档
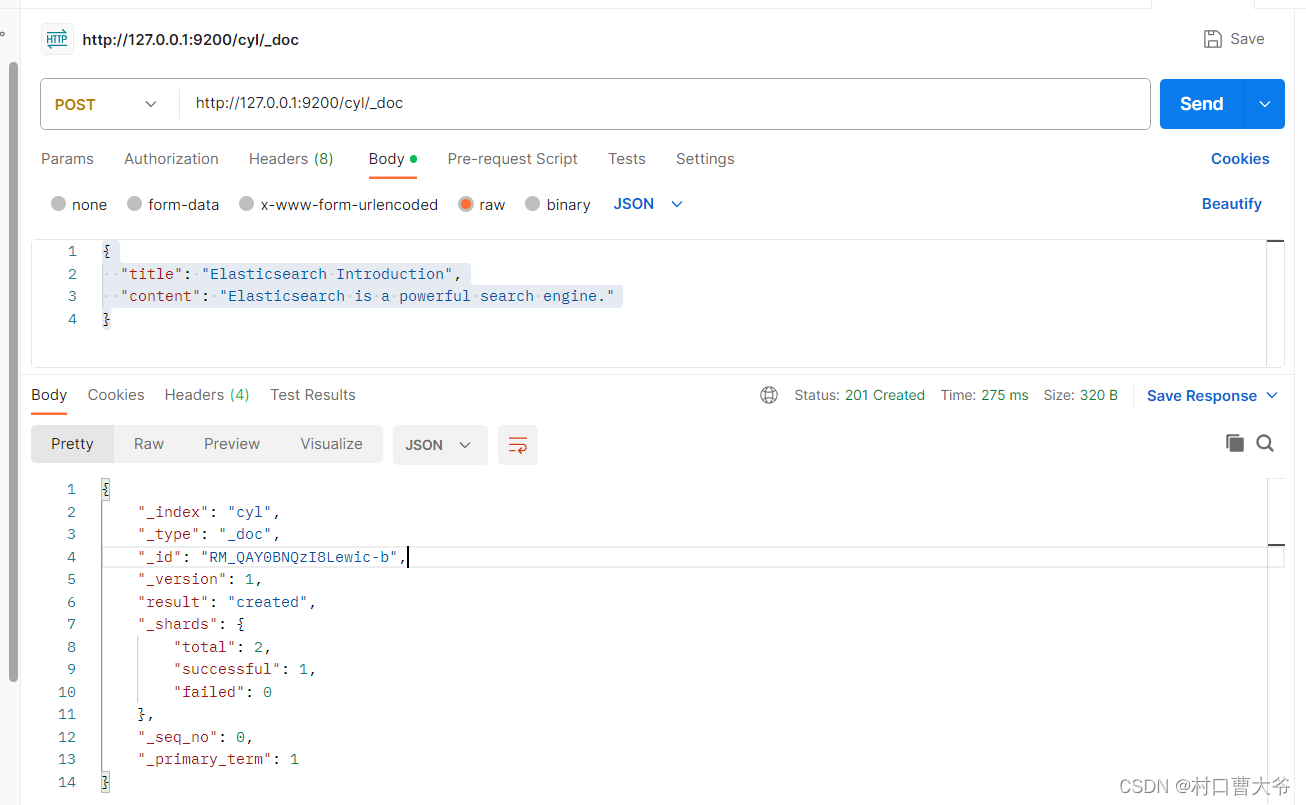
Post 请求http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_doc
{"title": "Elasticsearch Introduction","content": "Elasticsearch is a powerful search engine."
}
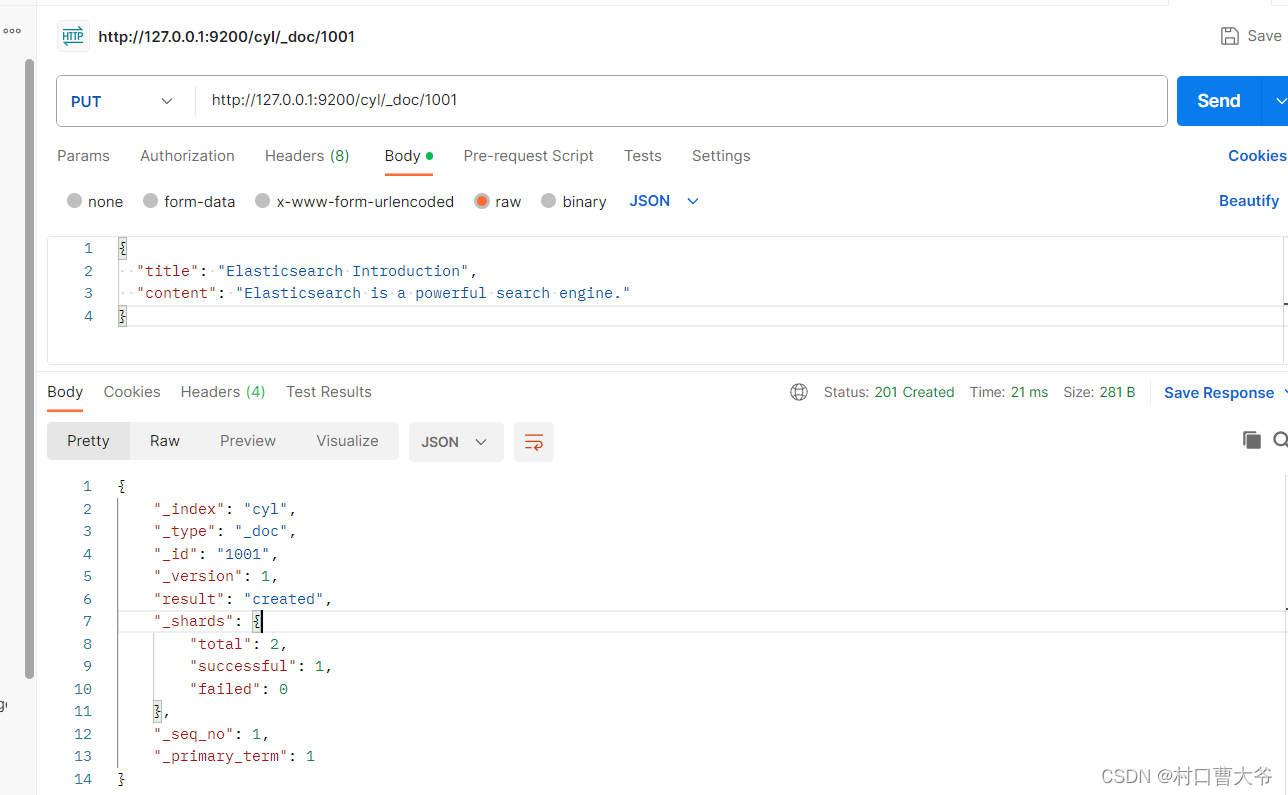
由于幂等性原因,我加了个自定义主键,就可以用put了。
PUT 请求http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_doc/1001
查询文档
GET请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_doc/1001
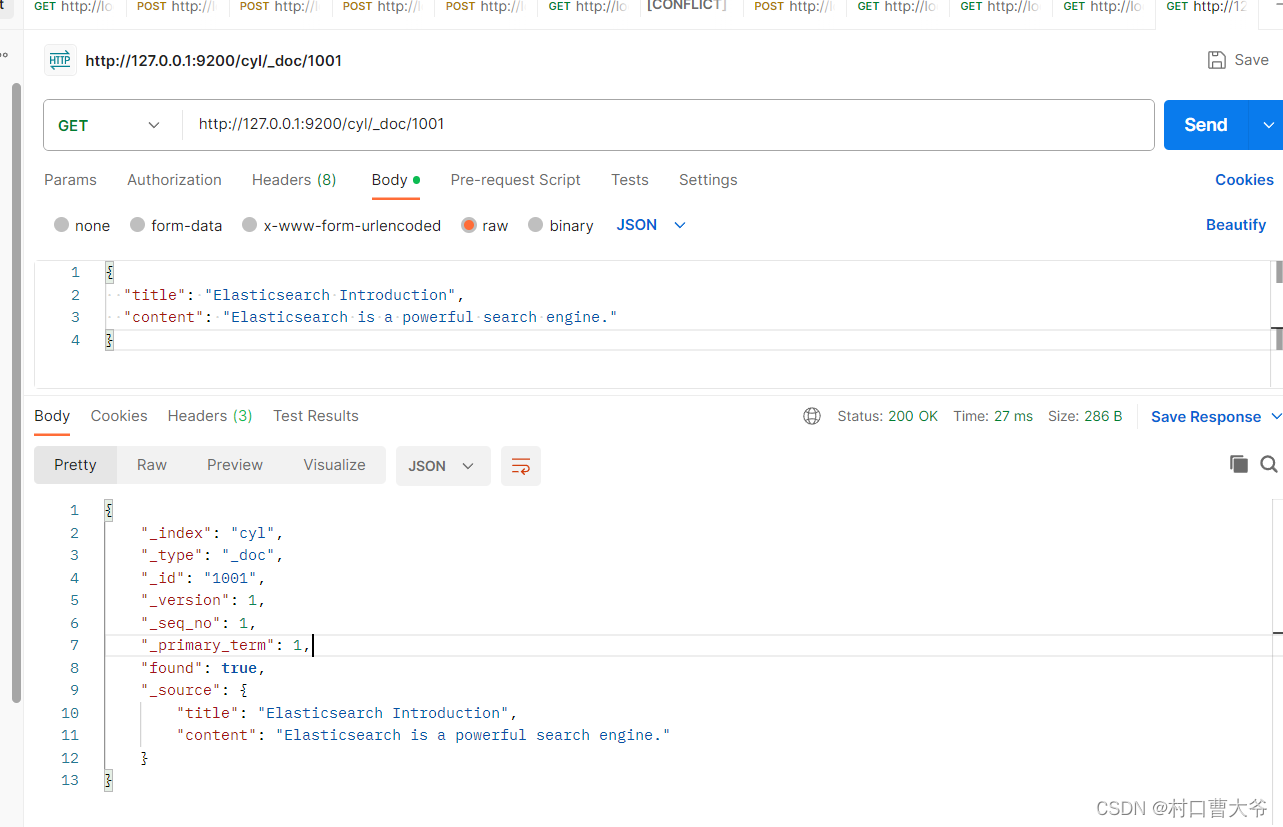
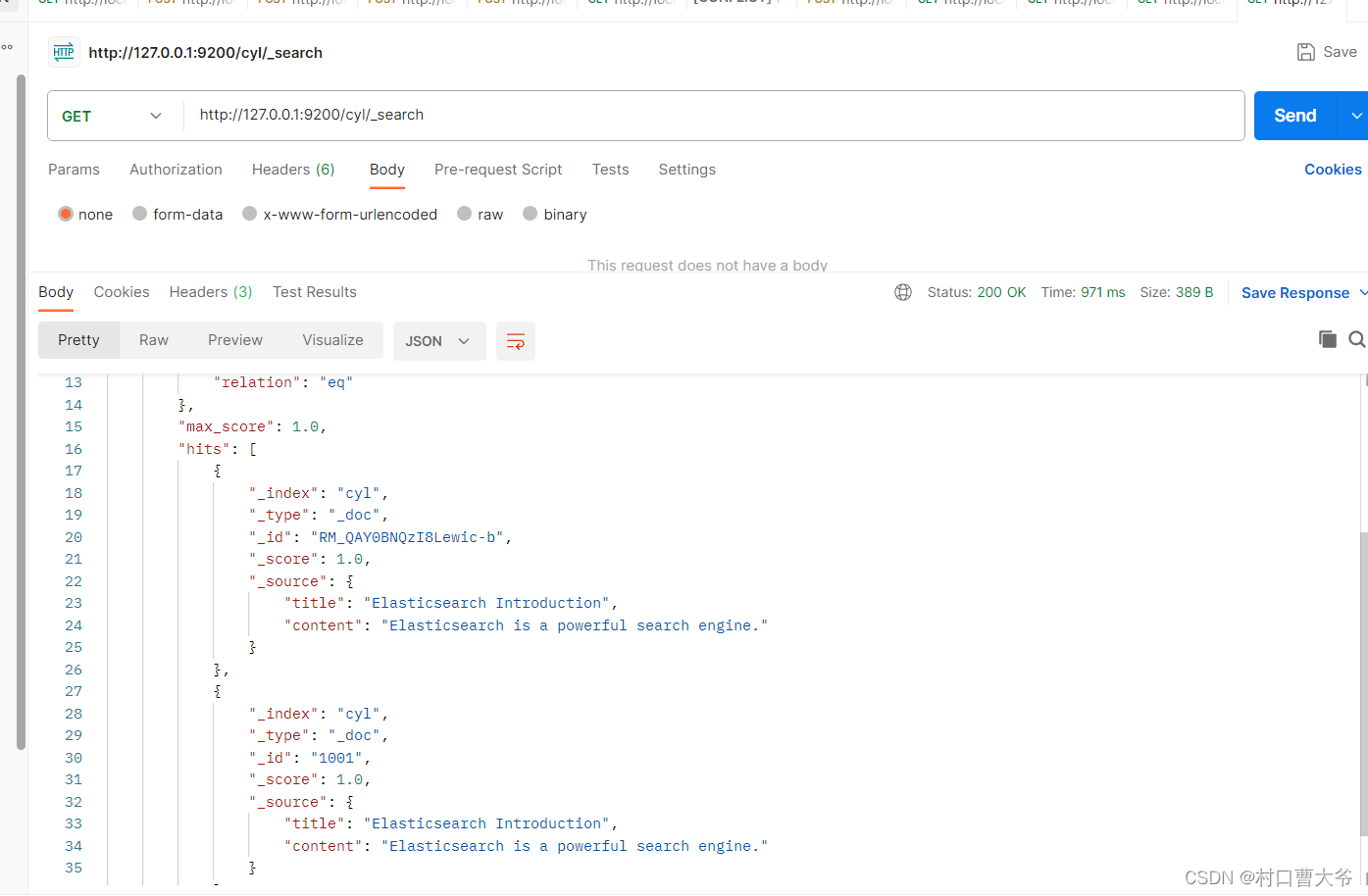
查询cyl索引下的全部数据
Get请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_search
删除文档
DELETE 请求http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_doc/1001

Elasticsearch的使用:文档数据修改
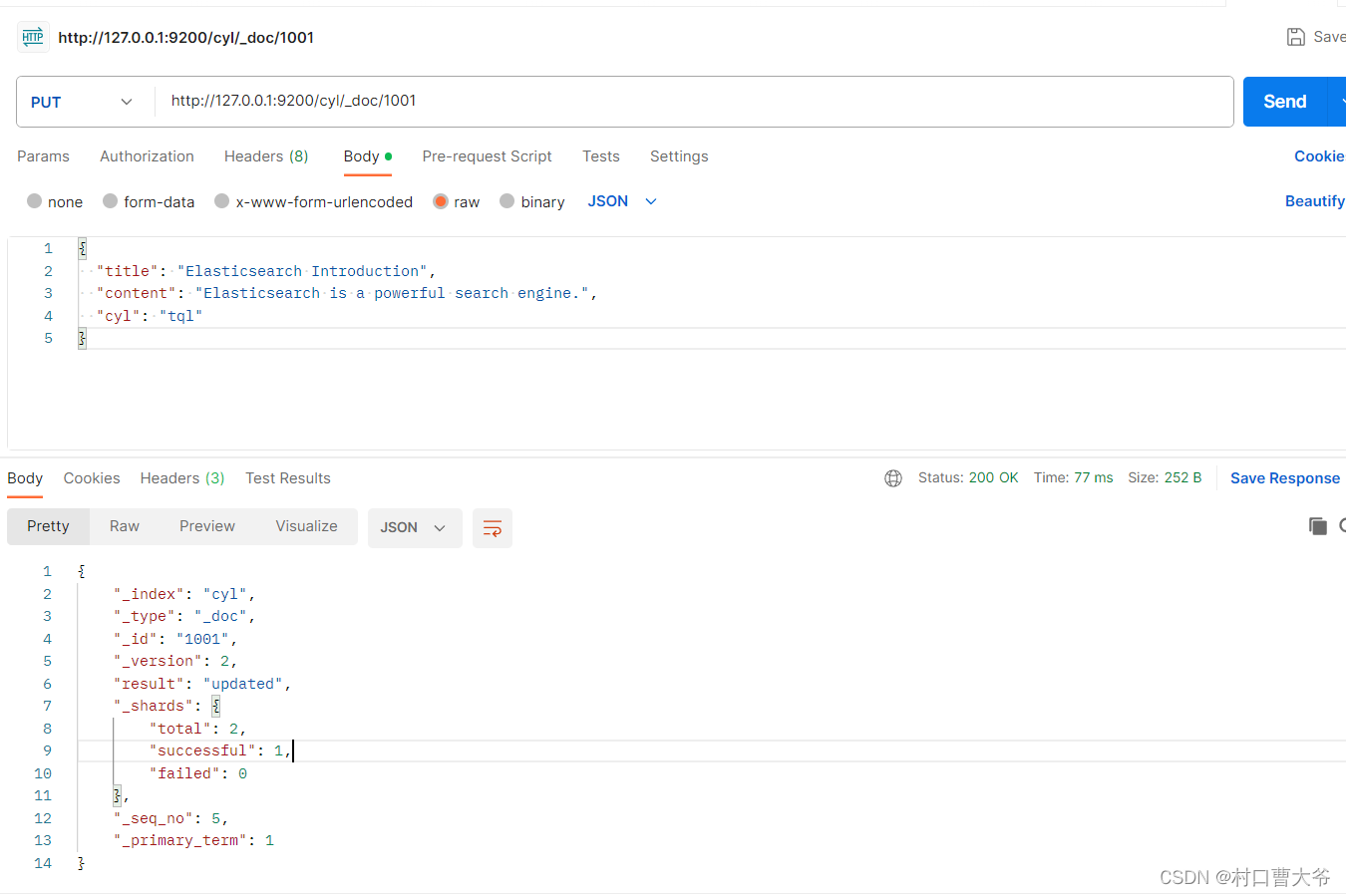
全量修改
Put请求 http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_doc/1001
{"title": "Elasticsearch Introduction","content": "Elasticsearch is a powerful search engine.","cyl": "tql"
}
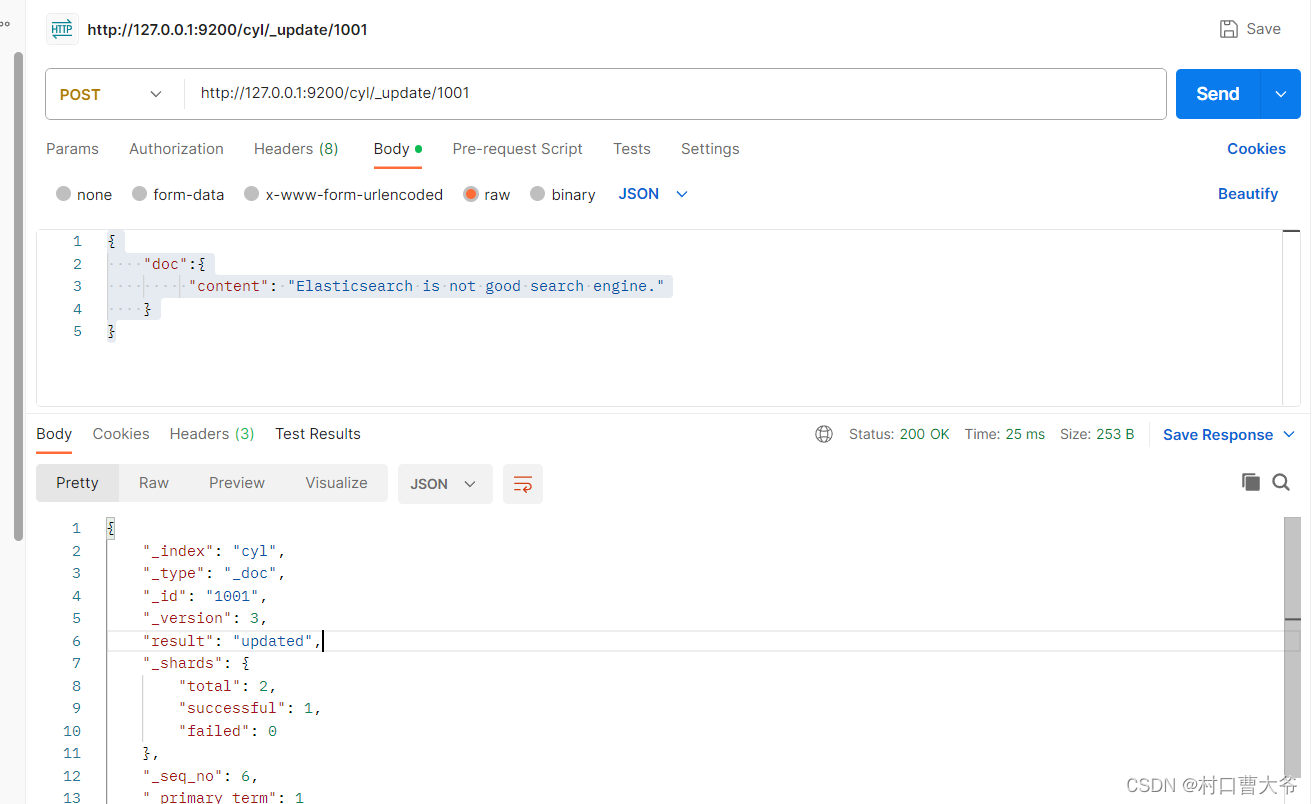
局部修改
Post请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_update/1001
{"doc":{"content": "Elasticsearch is not good search engine."}
}
Elasticsearch的使用:条件查询
条件查询
Get请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_search?q=cyl:tql
q后面接字段:值
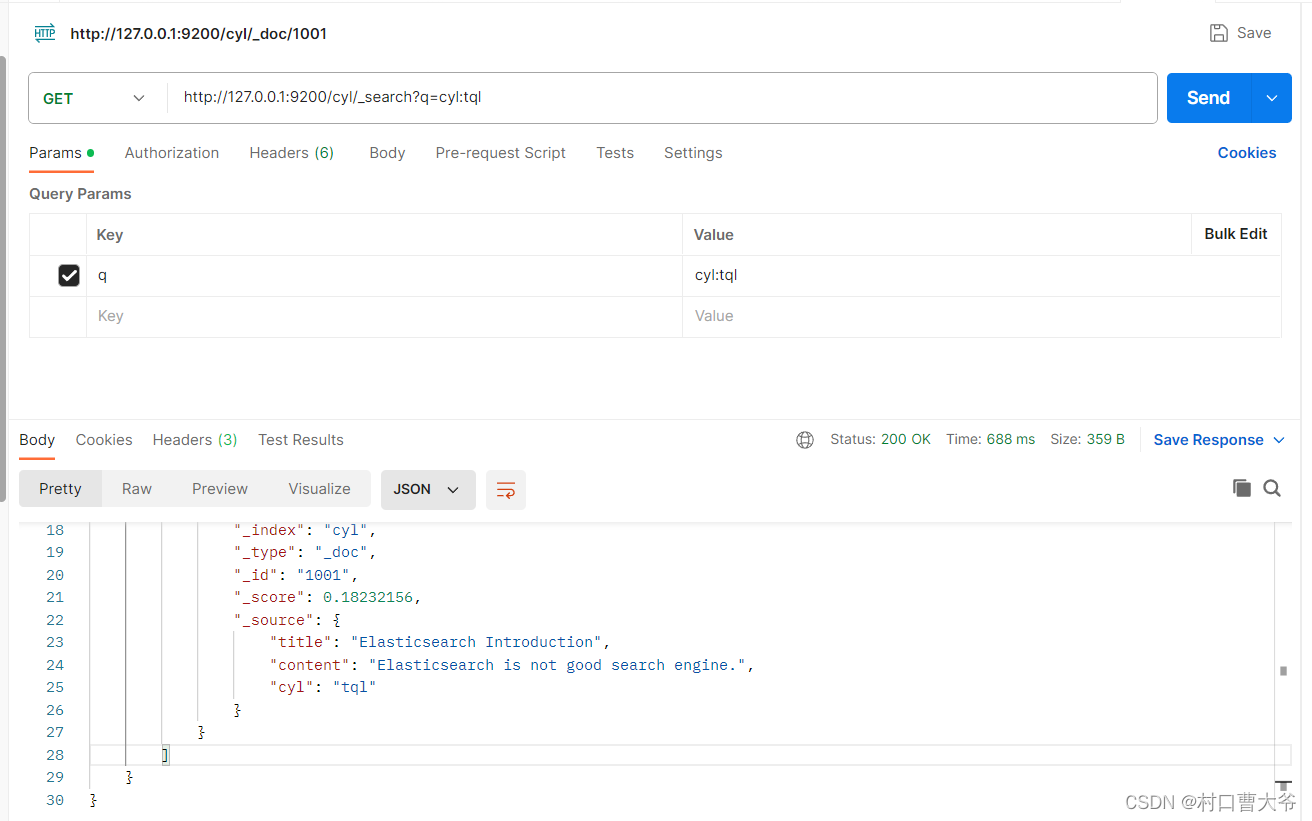
一般是按照请求体查询。
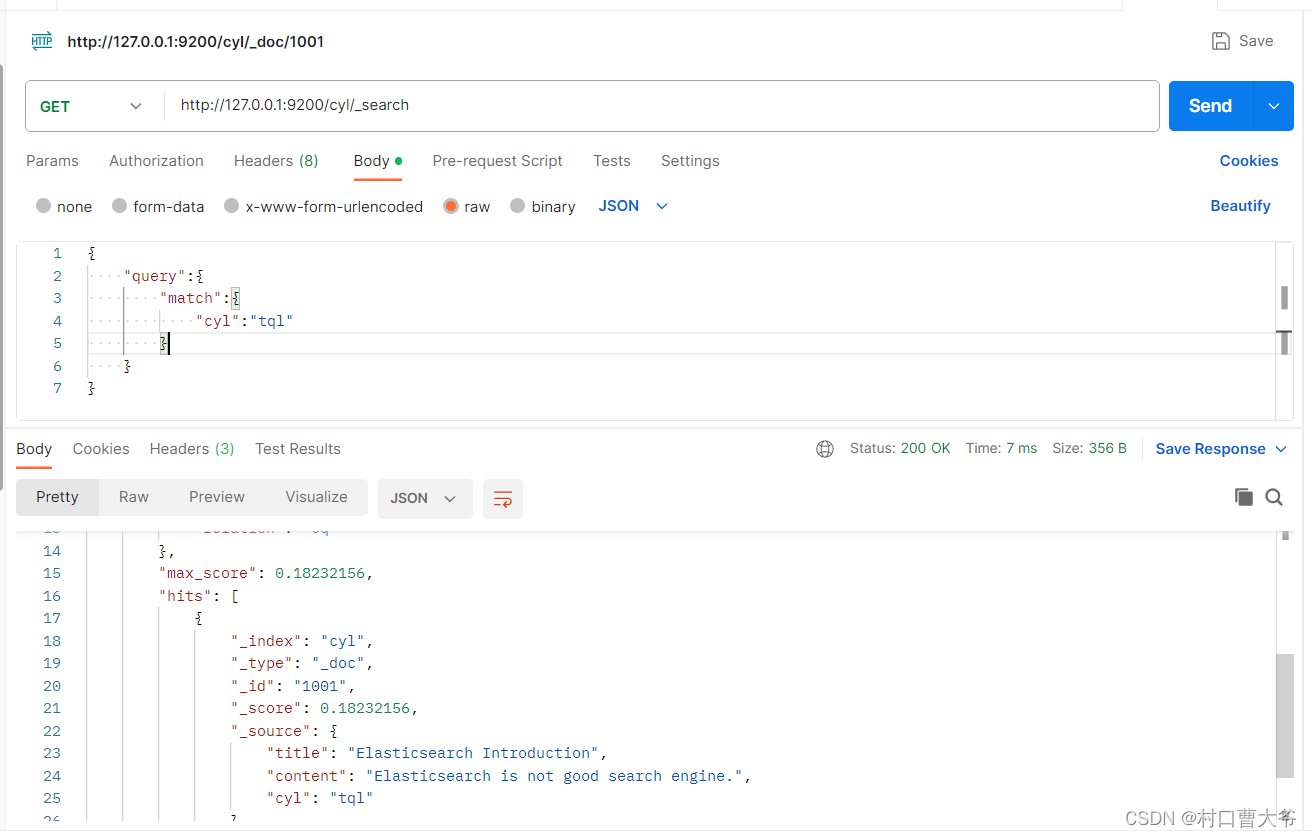
Get请求:http://127.0.0.1:9200/cyl/_search
{"query":{"match":{"cyl":"tql"}}
}
查询所有:
{"query":{"match_all":{}}}
分页查询
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"from":0,"size":1}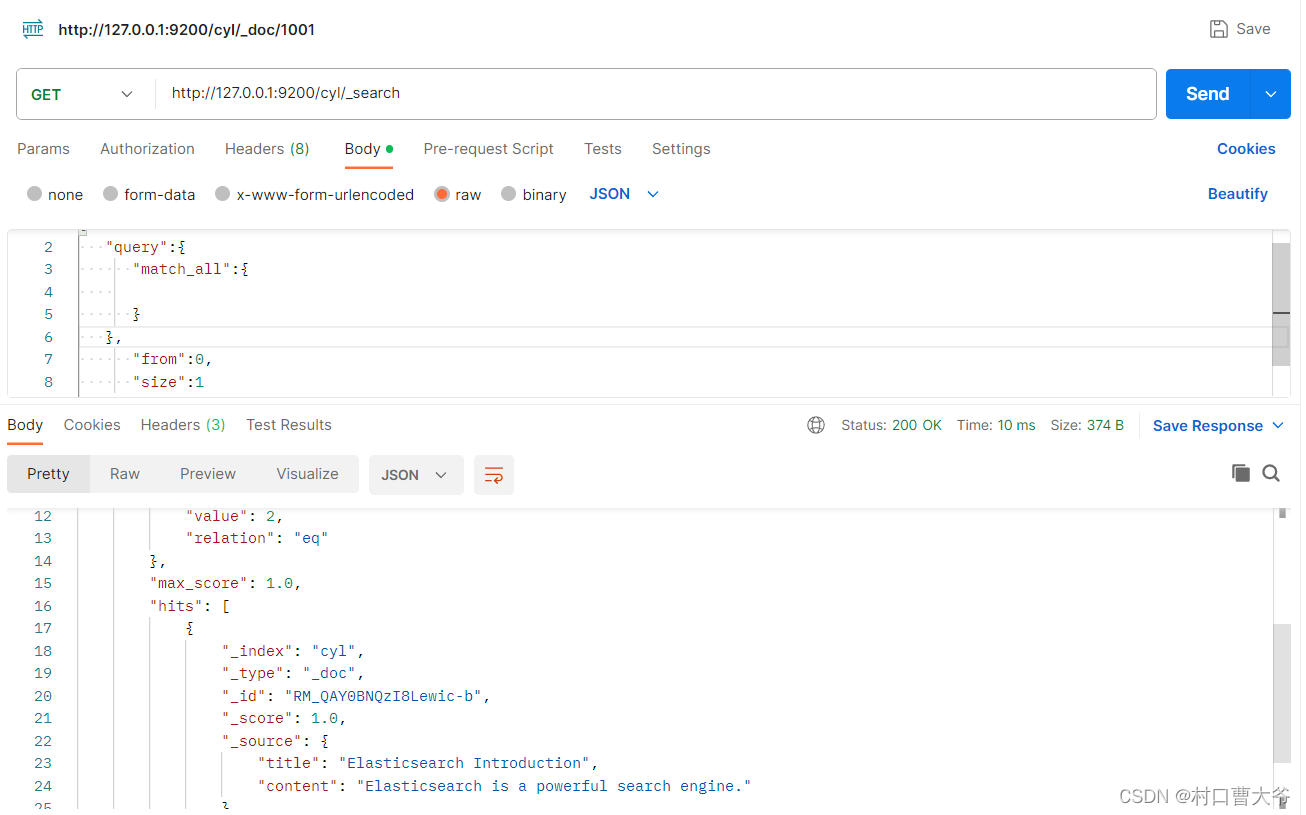
分页查询只查看某个关键字
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"from":0,"size":1,"_source":"title"}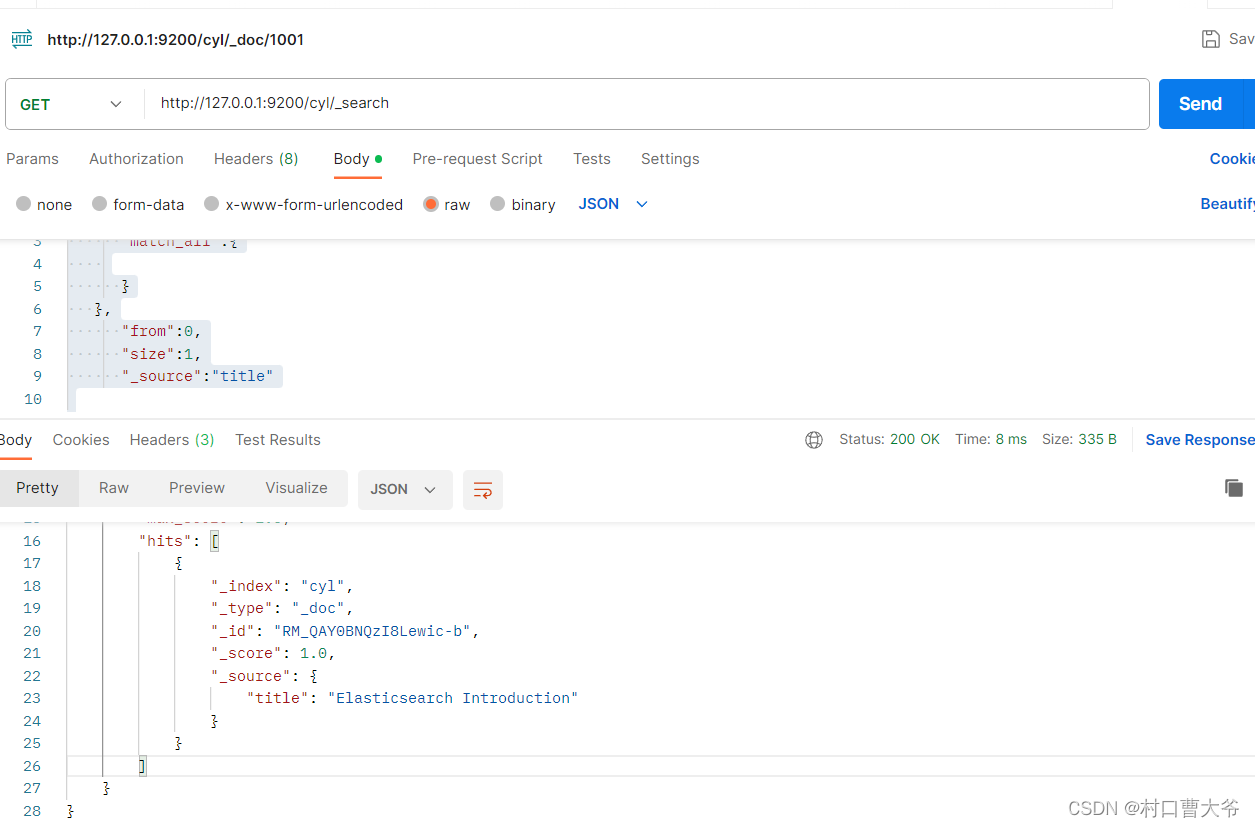
分页查询并排序
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"from":0,"size":1,"_source":"title","sort":{"title":{"order":"desc"}}}由于不是数字,可能会出错。
Elasticsearch的使用:其他查询
布尔查询(Boolean Query):
- 布尔查询是 Elasticsearch 中最基本的多条件查询方式,可以通过
must、should、must_not等关键词组合多个查询条件。 must:所有查询条件都必须匹配。should:至少有一个查询条件匹配,增加文档的相关性。must_not:查询条件不能匹配。
{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{ "match": { "title": "Elasticsearch" } },{ "range": { "publish_date": { "gte": "2022-01-01" } } }],"should": [{ "match": { "content": "search engine" } }],"must_not": [{ "term": { "status": "archived" } }]}}
}
范围查询(Range Query)
- 使用范围查询可以按照某个字段的范围条件进行检索。
- 例如,检索某个时间范围内的文档。
{"query": {"range": {"publish_date": {"gte": "2022-01-01","lte": "2022-12-31"}}}
}
通配符查询(Wildcard Query):
- 使用通配符查询来匹配符合通配符模式的字段值。
- 例如,匹配以 "elasticsearch" 开头的文档。
{"query": {"wildcard": {"title.keyword": "elasticsearch*"}}
}
模糊查询(Fuzzy Query):
- 模糊查询用于在查询中包含拼写错误或相似度较高的文档。
- 例如,查找与 "elasticsearch" 相似的文档。
{"query": {"fuzzy": {"title": {"value": "elasticsearch","fuzziness": 2}}}
}
全文检索(Full-Text Search):
- 全文检索是一种用于搜索文本数据的技术,它允许用户在大量文本数据中查找包含特定关键词或短语的文档。
- Elasticsearch 默认情况下对文本字段使用全文检索。全文检索考虑到词的位置、频率和其他文本特征,以提供更准确和相关性高的搜索结果。
- 使用
match、match_phrase等查询来执行全文检索。
{"query": {"match": {"content": "Elasticsearch tutorial"}}
}
上述查询将返回包含 "Elasticsearch" 和 "tutorial" 中任意一个或两者的文档。
完全匹配(Exact Match):
- 完全匹配是指只搜索精确匹配搜索条件的文档。它不考虑文本的分词和相关性,而是要求字段的值与搜索条件完全相等。
- 使用
term或terms查询来执行完全匹配。
{"query": {"term": {"title.keyword": "Elasticsearch"}}
}
上述查询将返回具有 "title.keyword" 字段值完全等于 "Elasticsearch" 的文档。注意,这里使用了 ".keyword" 后缀,表示确切匹配。
词条聚合(Terms Aggregation):
- 词条聚合用于对文档中某个字段的值进行分组,并统计每个分组中的文档数量。
{"aggs": {"group_by_category": {"terms": {"field": "category.keyword"}}}
}
范围聚合(Range Aggregation):
- 范围聚合用于将文档分组到指定的数值范围内,并计算每个范围的文档数量。
{"aggs": {"price_ranges": {"range": {"field": "price","ranges": [{ "from": 0, "to": 50 },{ "from": 50, "to": 100 },{ "from": 100, "to": 200 }]}}}
}
日期直方图聚合(Date Histogram Aggregation):
日期直方图聚合用于按时间间隔对文档进行分组,并统计每个时间间隔的文档数量。
{"aggs": {"monthly_sales": {"date_histogram": {"field": "sale_date","calendar_interval": "month"}}}
}
嵌套聚合(Nested Aggregation):
- 嵌套聚合用于在另一个聚合的结果上执行额外的聚合操作。
{"aggs": {"group_by_category": {"terms": {"field": "category.keyword"},"aggs": {"avg_price": {"avg": {"field": "price"}}}}}
}
Elasticsearch映射关系
在Elasticsearch中,映射(Mapping)是定义索引中字段的数据类型及其属性的过程。每个索引都有一个映射,而映射定义了索引中存储的数据的结构和特性。以下是关于Elasticsearch映射的一些重要概念:
字段数据类型(Field Data Types):
-
- Elasticsearch支持多种字段数据类型,如文本、数值、日期、地理位置等。每个字段都必须有一个明确定义的数据类型,以确保数据的正确性和一致性。
-
动态映射(Dynamic Mapping):
- Elasticsearch具有动态映射的功能,即当你索引一个文档时,Elasticsearch能够自动检测文档中的字段及其数据类型,并创建相应的映射。这使得索引可以适应不同类型的文档。
-
映射属性(Mapping Properties):
- 映射属性定义了字段的一些特性,例如是否存储原始值、是否启用全文搜索、是否启用聚合等。通过映射属性,你可以调整字段的行为以满足特定的需求。
-
嵌套字段(Nested Fields):
- Elasticsearch支持嵌套字段,允许在一个文档中嵌套另一个文档。这对于处理复杂的数据结构非常有用,如嵌套的JSON对象。
-
复杂字段类型(Complex Field Types):
- 复杂字段类型包括对象、数组等,允许在一个字段中存储多个值或复杂的结构化数据。
-
索引模板(Index Templates):
- 索引模板允许你在创建索引时自动应用映射,以确保新创建的索引具有一致的结构。这对于管理大量相似索引的情况非常有用。
以下是一个简单的映射示例,用于说明映射的基本结构:
{"mappings": {"properties": {"title": {"type": "text","analyzer": "standard"},"price": {"type": "float"},"timestamp": {"type": "date"},"tags": {"type": "keyword"},"location": {"type": "geo_point"}}}
}
上述映射定义了一个包含标题、价格、时间戳、标签和地理位置的文档的索引。每个字段都有指定的数据类型和可能的映射属性。
javaApi,用java操作Elasticsearch
创建一个maven项目
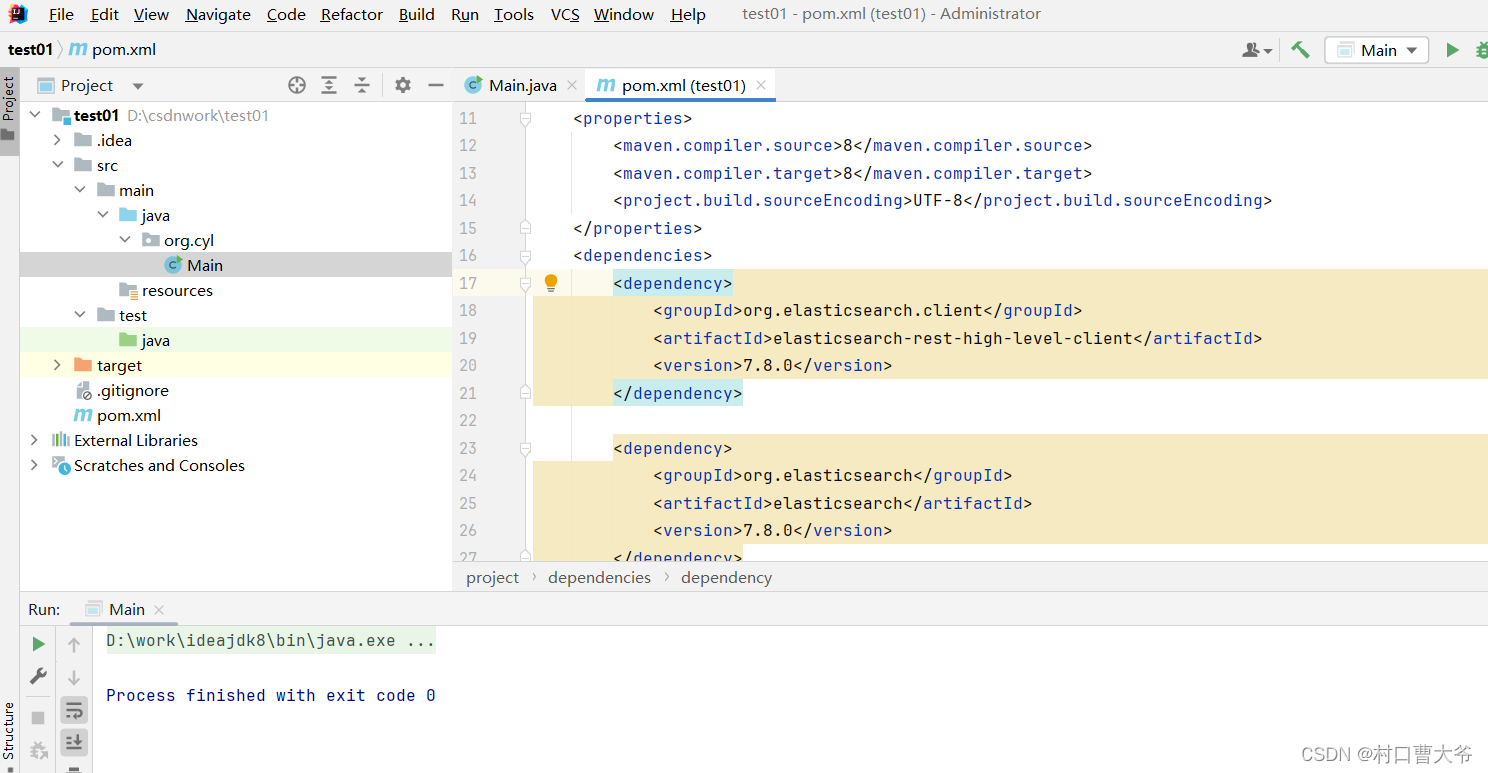
pom文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>org.cyl</groupId><artifactId>test01</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId><artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId><version>7.8.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId><artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId><version>7.8.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.13.2</version><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies></project>运行一个简单的项目
package org.cyl;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;import java.io.IOException;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}JavaApi 索引的创建
package org.cyl;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class ESIndex_Create {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//创建索引CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("user");CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//响应状态boolean acknowledged = createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged();System.out.println("索引操作:"+acknowledged);//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
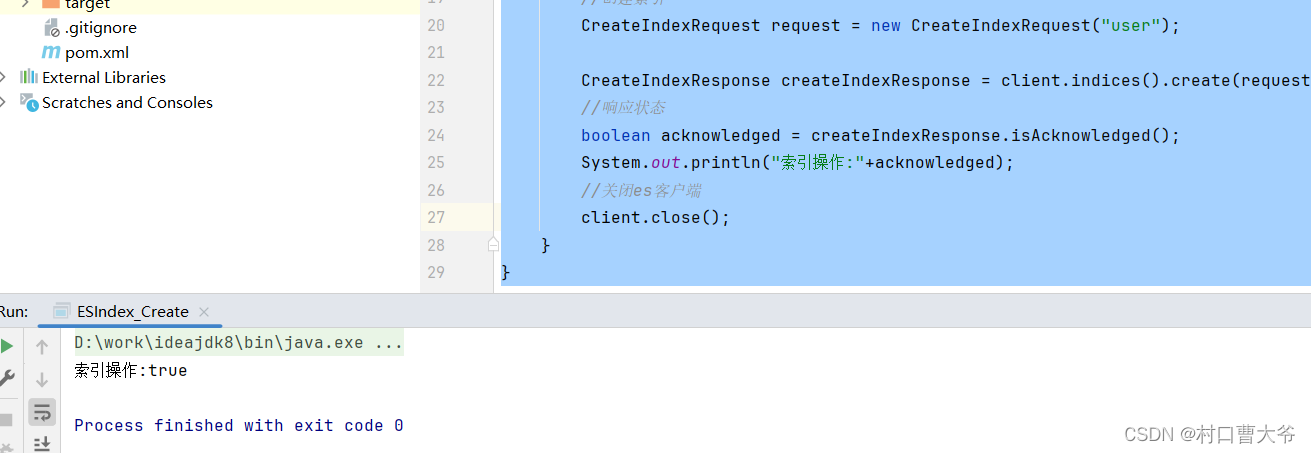
Java Api 索引的查询
package org.cyl;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class ESIndex_Search {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//查询索引GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("user");GetIndexResponse getIndexResponse = client.indices().get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//响应状态System.out.println(getIndexResponse.getAliases());System.out.println(getIndexResponse.getMappings());System.out.println(getIndexResponse.getSettings());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
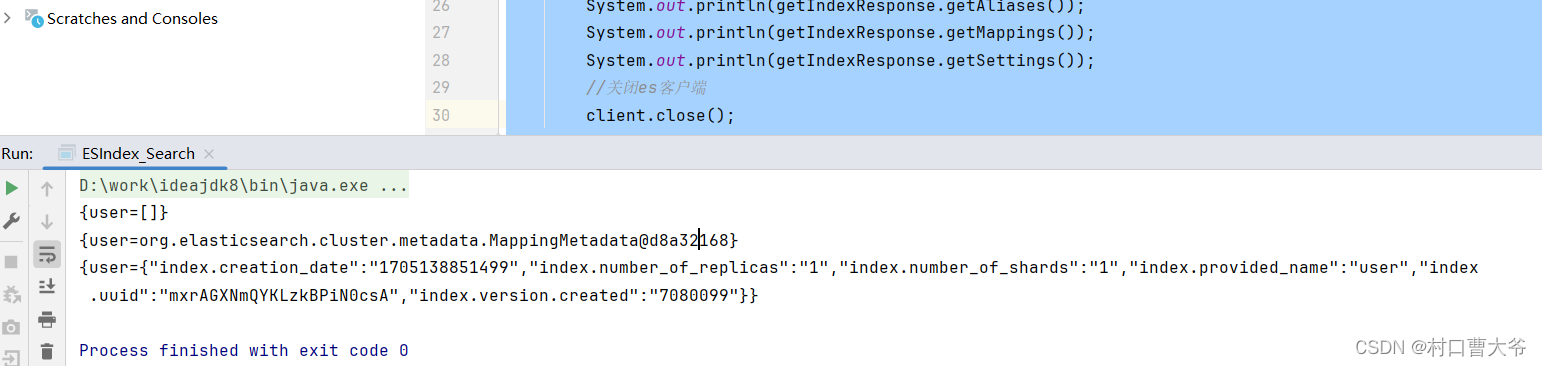
Java Api 索引的删除
package org.cyl;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.support.master.AcknowledgedResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class ESIndex_Delete {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//查询索引DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("user");AcknowledgedResponse delete = client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//响应状态System.out.println("删除索引:"+delete.isAcknowledged());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
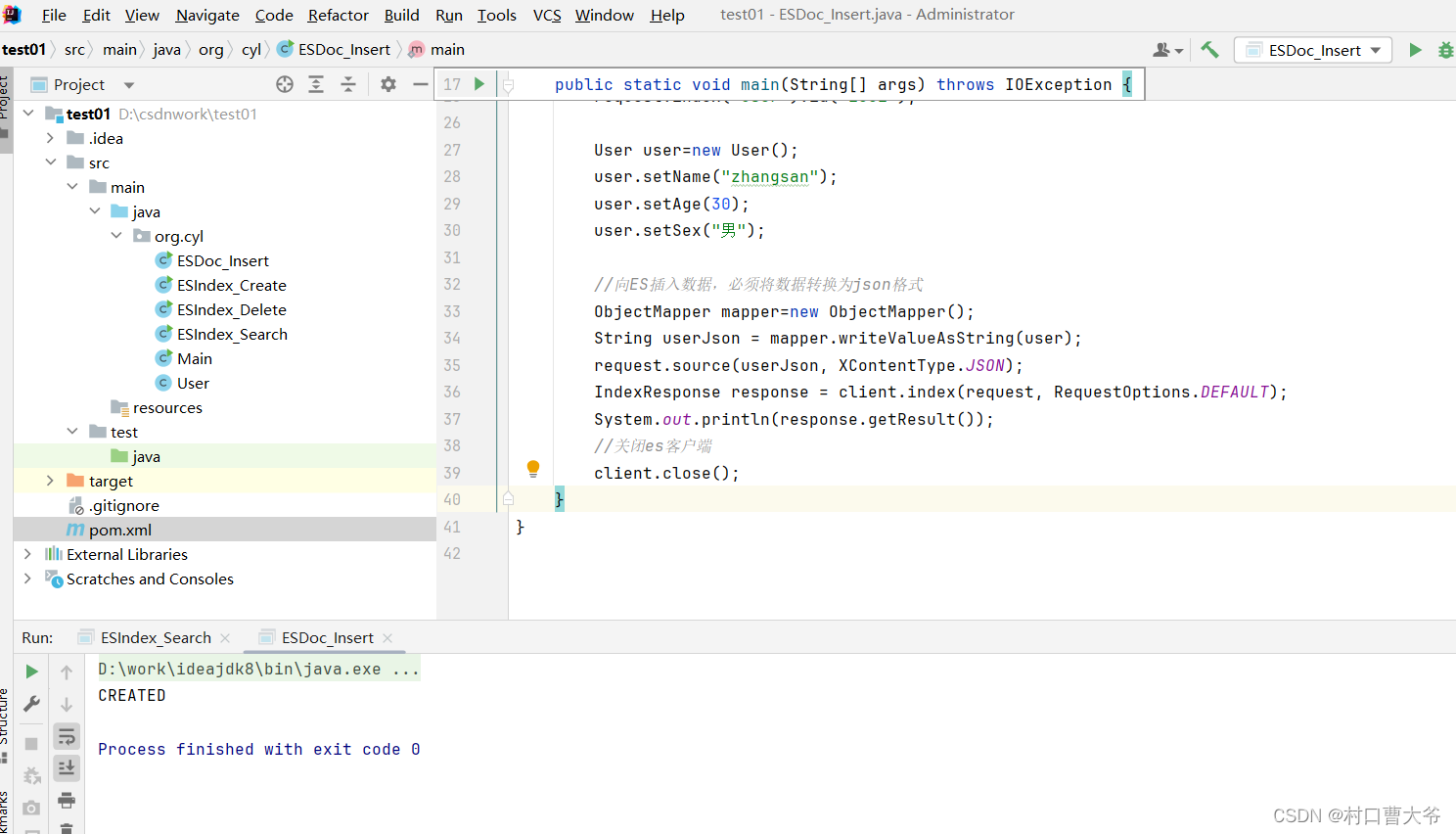
Java Api 文档的添加
创建user类
package org.cyl;public class User {private String name;private String sex;private Integer age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getSex() {return sex;}public void setSex(String sex) {this.sex = sex;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}
}
添加pom文件内容
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId><version>2.9.9</version></dependency>package org.cyl;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;import java.io.IOException;public class ESDoc_Insert {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//插入数据IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest();request.index("user").id("1001");User user=new User();user.setName("zhangsan");user.setAge(30);user.setSex("男");//向ES插入数据,必须将数据转换为json格式ObjectMapper mapper=new ObjectMapper();String userJson = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);request.source(userJson, XContentType.JSON);IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(response.getResult());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
Java Api 文档的修改
package org.cyl;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
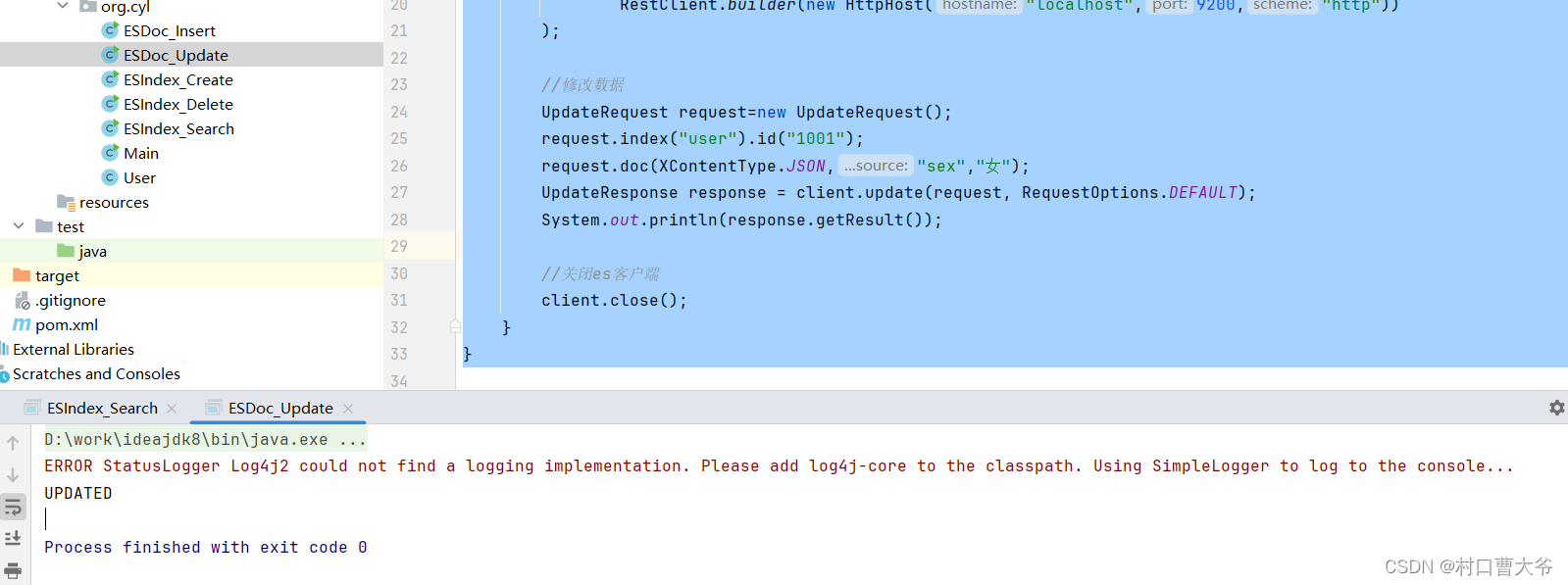
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;import java.io.IOException;public class ESDoc_Update {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//修改数据UpdateRequest request=new UpdateRequest();request.index("user").id("1001");request.doc(XContentType.JSON,"sex","女");UpdateResponse response = client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(response.getResult());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
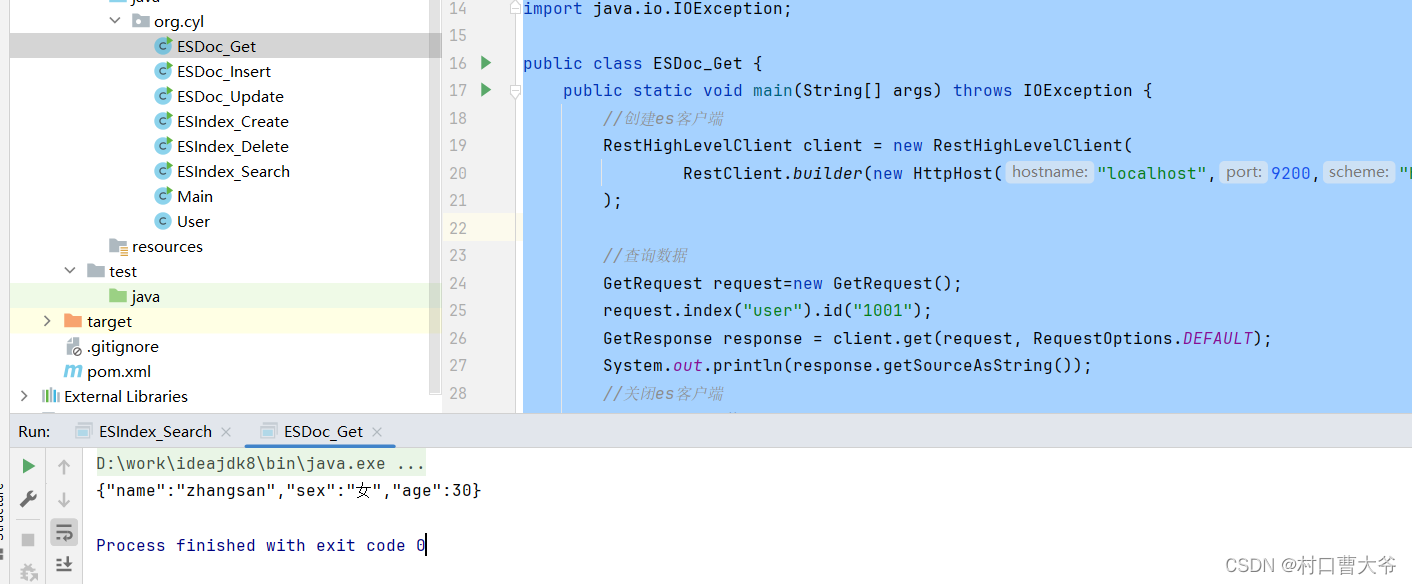
Java Api 文档的查询和删除
package org.cyl;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;import java.io.IOException;public class ESDoc_Get {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//查询数据GetRequest request=new GetRequest();request.index("user").id("1001");GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(response.getSourceAsString());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
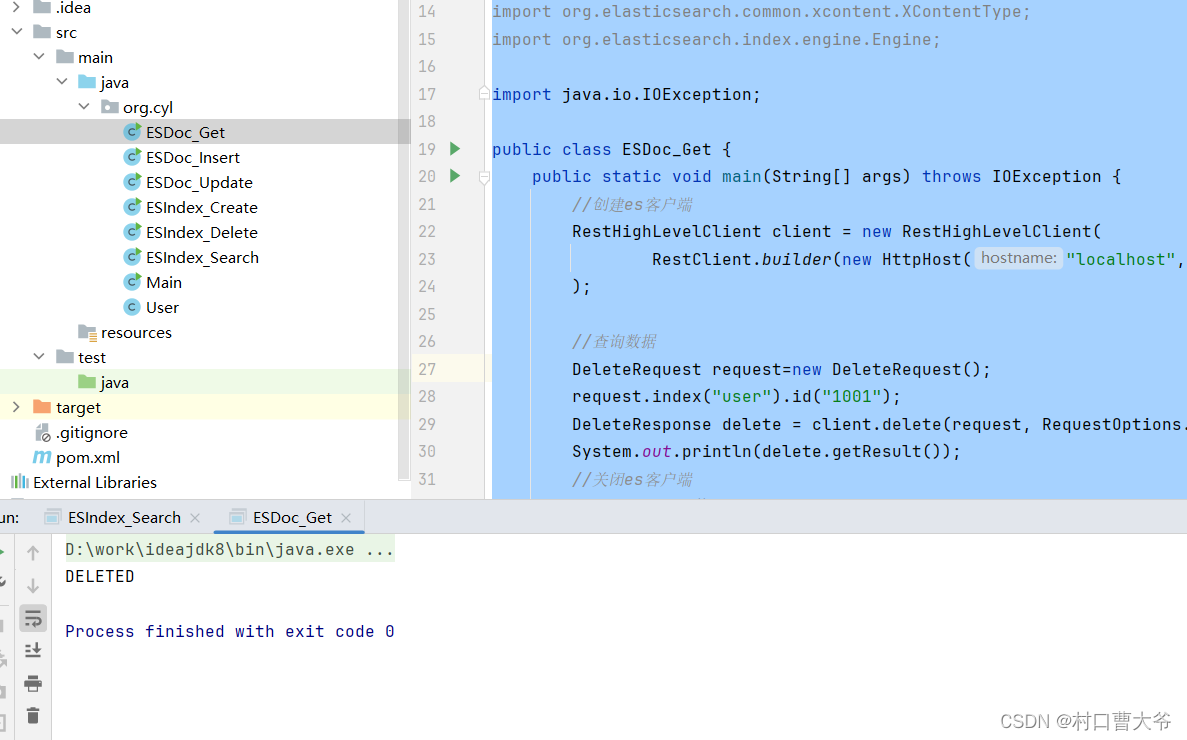
package org.cyl;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.engine.Engine;import java.io.IOException;public class ESDoc_Get {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建es客户端RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http")));//查询数据DeleteRequest request=new DeleteRequest();request.index("user").id("1001");DeleteResponse delete = client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(delete.getResult());//关闭es客户端client.close();}
}
当然可以批量删除和批量插入。
Kibana7.8.0的配置
官网:Kibana 7.8.0 | Elastic

然后解压:
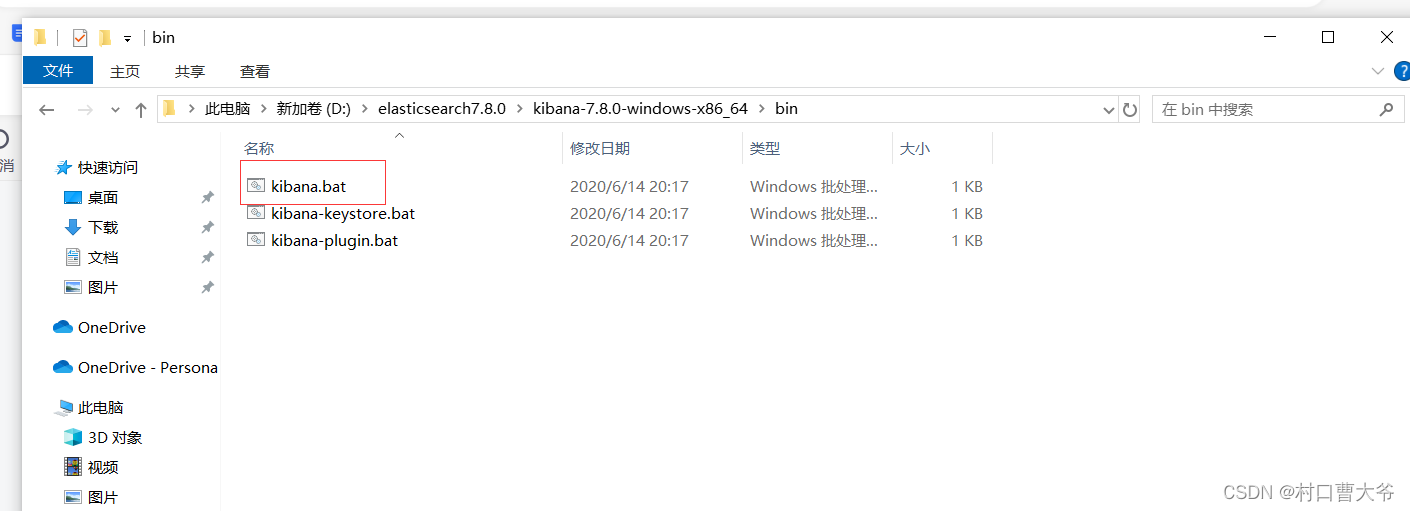
双击即可开启:
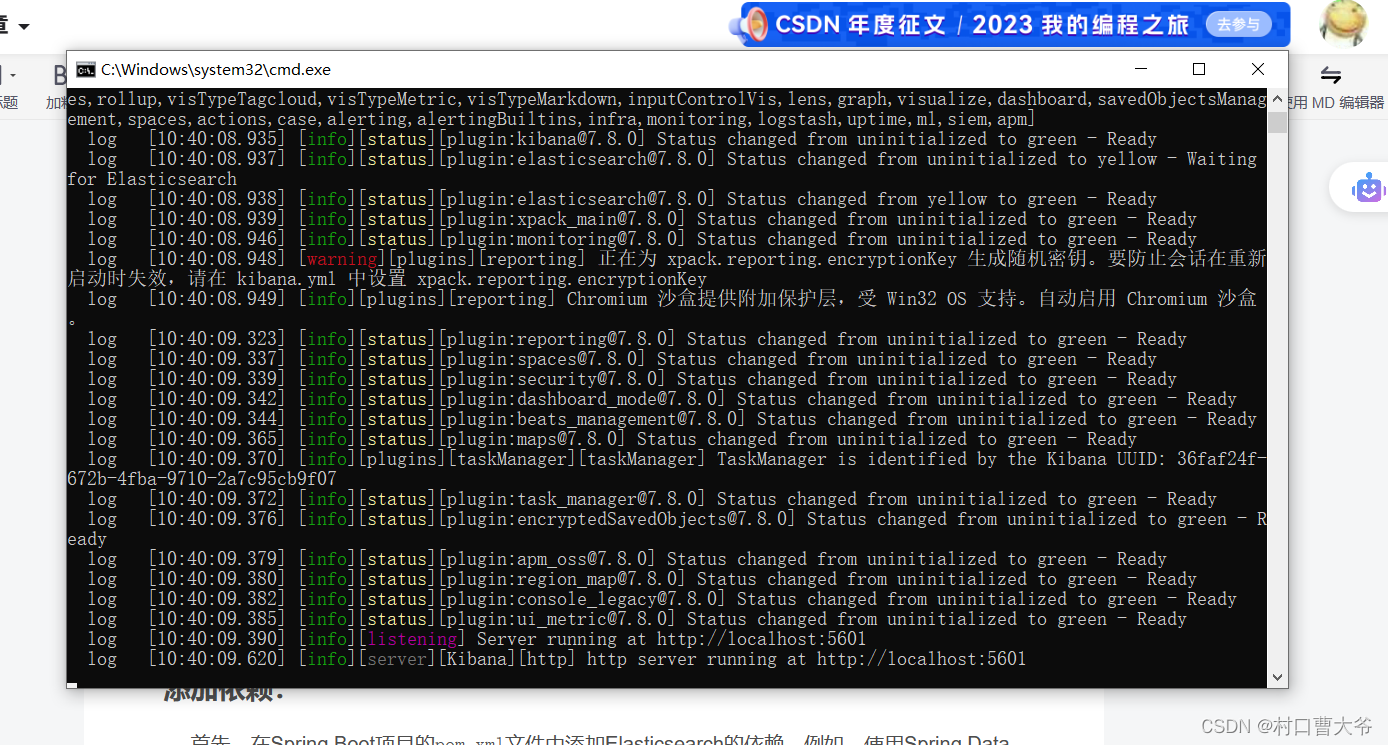
访问http://localhost:5601/
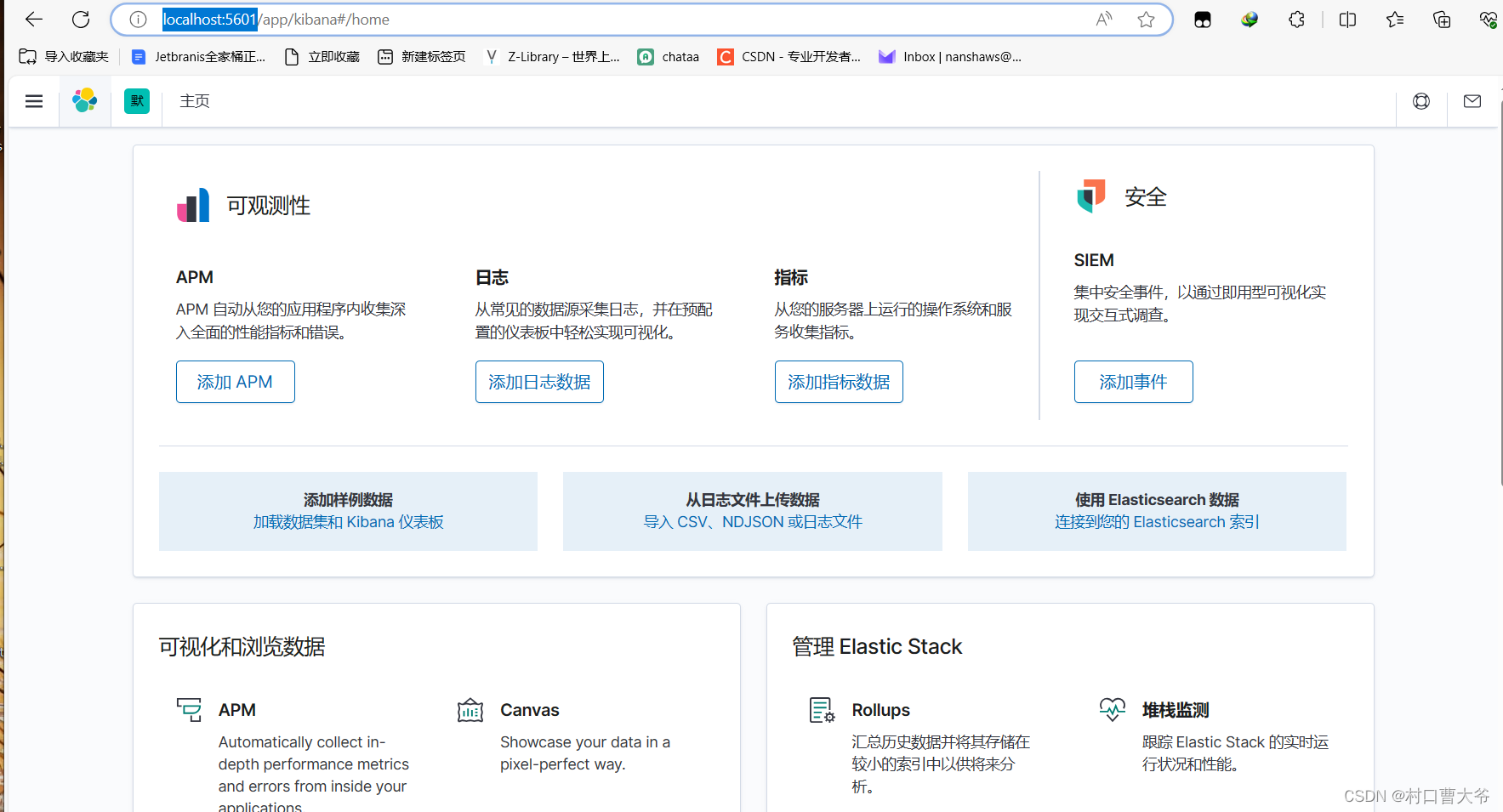
springboot整合Elasticsearch
添加依赖:
首先,在Spring Boot项目的pom.xml文件中添加Elasticsearch的依赖。例如,使用Spring Data Elasticsearch提供的依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置Elasticsearch连接:
在application.properties或application.yml中配置Elasticsearch连接信息,包括集群地址、端口等。
spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes=localhost:9200
创建实体类:
创建与Elasticsearch索引文档对应的实体类,并使用注解配置映射关系。
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;@Document(indexName = "your_index_name", type = "your_type_name")
public class YourEntity {@Idprivate String id;private String field1;private String field2;// Getters and setters
}
创建Repository接口:
创建一个继承自ElasticsearchRepository的接口,用于操作Elasticsearch索引。
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;public interface YourEntityRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<YourEntity, String> {// Custom queries if needed
}
使用Repository进行操作:
在服务或控制器中使用创建的Repository接口进行Elasticsearch索引的增、删、改、查等操作。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class YourEntityService {@Autowiredprivate YourEntityRepository repository;public YourEntity save(YourEntity entity) {return repository.save(entity);}// Other methods for CRUD operations
}
启动应用程序:
启动Spring Boot应用程序,并确保Elasticsearch服务器在指定的地址和端口上运行。





![P1094 [NOIP2007 普及组] 纪念品分组](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/P1094 [NOIP2007 普及组] 纪念品分组)

第606题根据二叉树创建字符串(Python))











