
1. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目描述:

题解:
1.p或者q其中一个等于root,那么root就是最进公共祖先
2.p和q分布在root的左右两侧,那么root就是最进公共祖先
3.p和q在root的同一侧,就是要遍历这棵树,遇到p或者q返回
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null) {return null;}//1.p或q在root的位置if (p == root || q == root) {return root;}TreeNode leftTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode rightTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);//2.左边和右边都不空if (leftTree != null && rightTree != null) {return root;} else if (leftTree != null) {return leftTree; //3.左边不为空} else {return rightTree; //4。右边不为空}}第二种解法:
以链表思路求节解:就相当于求链表的交点
问题的关键就是如何存储,从根节点到p或者q的路径上的所有节点
//部分代码
//存储从根节点到p或者q路径上的所有节点private boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack) {if (root == null) {return false;}stack.push(root);if (root == node) {return true;}boolean fag1 = getPath(root.left, node, stack);if (fag1) {return true;}boolean fag2 = getPath(root.right, node, stack);if (fag2) {return true;}stack.pop();return false;}2. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目描述:
![]()
题解:
前序遍历(根 左 右)
大方向:遍历前序遍历数组,在中序遍历数组找到相对应的下标,左边是左树,右边是右树
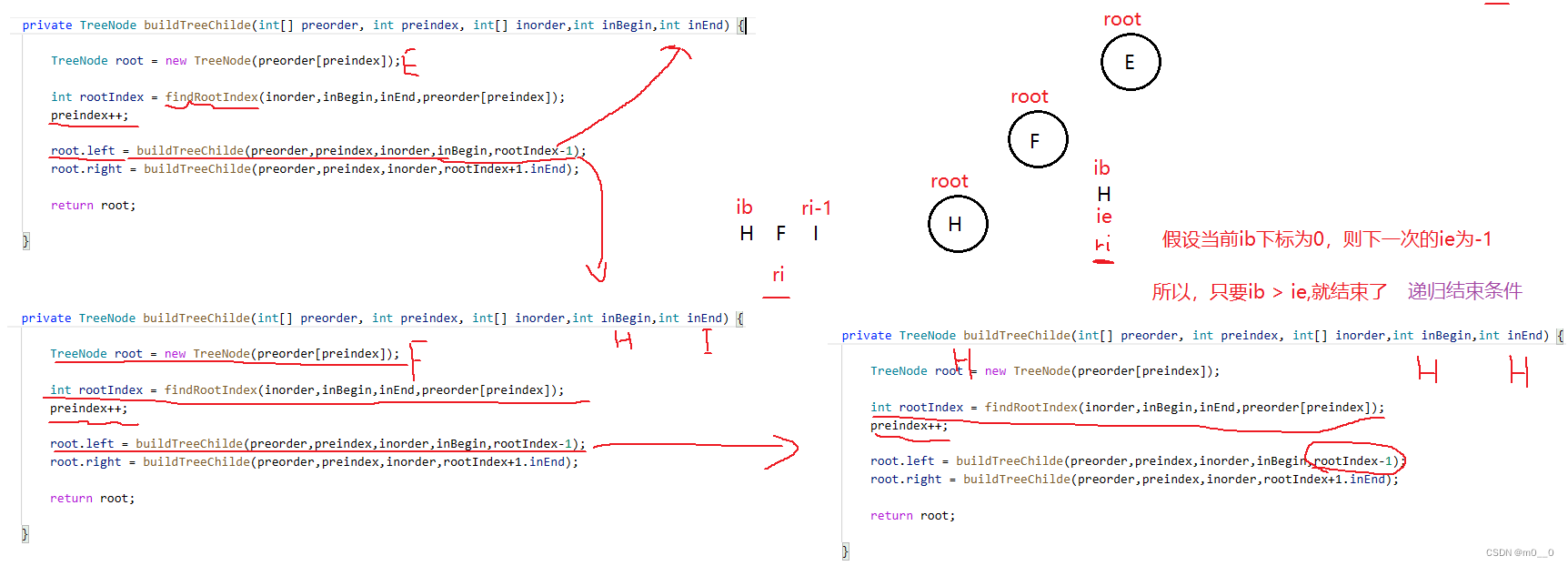
2.找递归结束条件
下次下标ib肯定是大于ie的,所以,只要ib>ie,就结束了
public int preindex;public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChilde(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inBegin,int inEnd) {if(inBegin > inEnd) {return null; //没有左树 或者 右树 }TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preindex]);int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder,inBegin,inEnd,preorder[preindex]);if(rootIndex == -1) {return null;}preindex++;root.left = buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,inBegin,rootIndex-1);root.right = buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inEnd);return root;}private int findRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inBegin,int inEnd,int key) {for(int i = inBegin; i <= inEnd; i++) {if(inorder[i] == key) {return i;} }return -1;}3.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目描述:
![]()
题解:
后序遍历(左 右 根)
1.遍历后序遍历,先创建的是右子树
2.遍历后序遍历下标是--
其它跟上题一致,稍微修改下代码
4.根据二叉树创建字符串
题目描述:


题解:
不怕大家笑话,开始的时候,读了题也没搞懂要做什么,一脸懵。也是看这示例明白的。
看这示例一:
1.根节点直接写
2.左边不为空&&右边为空
3.左边为空&&右边为空,什么都不做
示例二:
1.左边为空&&右边不为空,加一对括号
左边不为空与右边不为空,就是分别递归了!
private void tree2strChlide(TreeNode r, StringBuilder stringbuilder) {if (r == null) {return;}stringbuilder.append(r.val);if (r.left != null) {stringbuilder.append("(");tree2strChlide(r.left, stringbuilder);stringbuilder.append(")");} else {if (r.right == null) {return;} else {stringbuilder.append("()");}}//判断右树if (r.right != null) {stringbuilder.append("(");tree2strChlide(r.right, stringbuilder);stringbuilder.append(")");} else {return;}}5. 二叉树前序非递归遍历实现
题目描述:
![]()

题解:
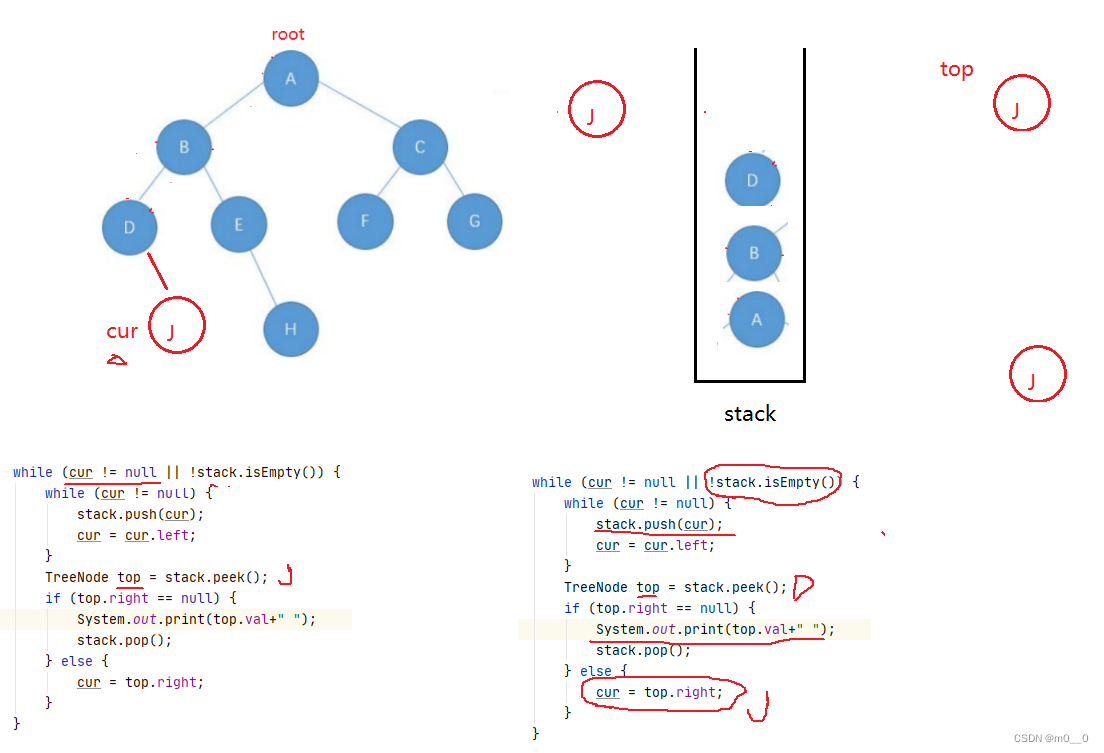
非递归打印,最好还是引入栈来解决。
1.让cur指向root
2. 把cur放到栈中 打印 cur在指向左树
3.当cur == null 弹出栈顶元素并用top记录 让cur指向top的右树
关键是循环条件!

public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) {return ret;}TreeNode cur = root;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);//System.out.print(cur.val + " ");ret.add(cur.val);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.pop();cur = top.right;}return ret;}5.1二叉树中序非递归遍历实现
题解:
5.2 二叉树后序非递归遍历实现

题解:
后序遍历(左 右 根)
首先,会有两种情况 cur != null或者 cur == null
1.cur != null,一直往左走
2.cur == null ,就不能在用pop(),要用peek(),判断右子树是否为null。
此时,会形成一个死循环!所以,打印这个top的时候,有两种情况。
1.右边 == null
2. 右边已经被打印完了(要记录一下)
public void posOrderNor(TreeNode root){if(root == null) {return;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode prev = null;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.peek();if (top.right == null || top.right == prev) {System.out.print(top.val+" ");stack.pop();prev = top;} else {cur = top.right;}}}










Explain使用与详解)












