PFH的理论上的时间复杂度是O(nk的平方),n是点的数量,k是最近邻的个数。对于实时系统来说,这压根就是不行的,所以作为PFH规划的简化版本,FPFH把计算复杂度减少成O(nk),但是还具有很好的和PFH差不多的区分能力。
第一步我们先计算了每个查询点Pq的一系列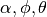
第二步每个点的最近邻是重新分配,SPFH值将用来权衡FPFH的值:
这里的Wk代表了两点的距离。权重(weight)的组合是非常重要的,下面的图显示了这一点:
可以看到越近的权重越大,线越粗。
因此,给定一个点Pq,这个算法第一步评估了SPFH的值,通过创造它和它的近邻的匹配。这个过程将一直重复,通过近邻SPFH的值不停的改变权重,最终生成了Pq的FPFH。
PFH与FPFH之间的差异
1.FPFH没有和它所有的近邻有着联系,因此可能会丢失一些值的匹配。
2.PFH模型可以更精确的描述表面,而FPFH则包括了额外的点的配对在半径为r的圆的外面(最多不会超过2r)
3.因为权重的组合,FPFH结合了SPFH的值并且重新获取了一些点的近邻。
4.FPFH复杂度大大降低,计算更快。
5.最终的直方图是简化了。
预估FPFH的特征值
FPFH的执行使用了11个分发的子区间,和一个非相关的组合(33位的数组),把它存在pcl::FPFHSignature33这个点类型里面。
下面的代码段,预估了一个所有点的FPFH的特征集合
#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/features/fpfh.h> { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> ()); ... read, pass in or create a point cloud with normals ... ... (note: you can create a single PointCloud<PointNormal> if you want) ... // Create the FPFH estimation class, and pass the input dataset+normals to it pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> fpfh; fpfh.setInputCloud (cloud); fpfh.setInputNormals (normals); // alternatively, if cloud is of tpe PointNormal, do fpfh.setInputNormals (cloud); // Create an empty kdtree representation, and pass it to the FPFH estimation object. // Its content will be filled inside the object, based on the given input dataset (as no other search surface is given). pcl::search::KdTree<PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<PointXYZ>); fpfh.setSearchMethod (tree); // Output datasets pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr fpfhs (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33> ()); // Use all neighbors in a sphere of radius 5cm // IMPORTANT: the radius used here has to be larger than the radius used to estimate the surface normals!!! fpfh.setRadiusSearch (0.05); // Compute the features fpfh.compute (*fpfhs); // fpfhs->points.size () should have the same size as the input cloud->points.size ()* }
调用FPFHEstimation时实际做了这么几步
1.PFH的步骤
2.使用每个SPFH,通过一个权重组合来赋值给FPFH。
类似于PFH我们可以把这段代码反正compute()函数前,进行优化
for (int i = 0; i < normals->points.size(); i++) { if (!pcl::isFinite<pcl::Normal>(normals->points[i])) { PCL_WARN("normals[%d] is not finite\n", i); } }
我们可以用OpenMP进行优化
使用OpenMP可以进行多线程计算。类名叫做pcl::FPFHEstimationOMP,
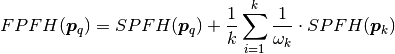


)




)











