saga模式是分布式事务中使用比较多的一种模式,他主要应用在长流程的服务,对一个全局事务,如果某个节点抛出了异常,则从这个节点往前依次回滚或补偿事务。今天我们就来看看它的源码实现。
状态机初始化
在之前的文章《springcloud+eureka整合阿里seata-saga模式》模式中,我定义了订单服务、账户服务和库存服务,我们了解了saga模式是基于状态机来实现了,我们定义了一个状态机需要的json文件,代码如下:
{ "Name": "buyGoodsOnline", "Comment": "buy a goods on line, add order, deduct account, deduct storage ", "StartState": "SaveOrder", "Version": "0.0.1", "States": { "SaveOrder": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "orderSave", "ServiceMethod": "saveOrder", "CompensateState": "DeleteOrder", "Next": "ChoiceAccountState", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[order]" ], "Output": { "SaveOrderResult": "$.#root" }, "Status": { "#root == true": "SU", "#root == false": "FA", "$Exception{java.lang.Throwable}": "UN" } }, "ChoiceAccountState":{ "Type": "Choice", "Choices":[ { "Expression":"[SaveOrderResult] == true", "Next":"ReduceAccount" } ], "Default":"Fail" }, "ReduceAccount": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "accountService", "ServiceMethod": "decrease", "CompensateState": "CompensateReduceAccount", "Next": "ChoiceStorageState", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[userId]", "$.[money]", { "throwException" : "$.[mockReduceAccountFail]" } ], "Output": { "ReduceAccountResult": "$.#root" }, "Status": { "#root == true": "SU", "#root == false": "FA", "$Exception{java.lang.Throwable}": "UN" }, "Catch": [ { "Exceptions": [ "java.lang.Throwable" ], "Next": "CompensationTrigger" } ] }, "ChoiceStorageState":{ "Type": "Choice", "Choices":[ { "Expression":"[ReduceAccountResult] == true", "Next":"ReduceStorage" } ], "Default":"Fail" }, "ReduceStorage": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "storageService", "ServiceMethod": "decrease", "CompensateState": "CompensateReduceStorage", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[productId]", "$.[count]", { "throwException" : "$.[mockReduceStorageFail]" } ], "Output": { "ReduceStorageResult": "$.#root" }, "Status": { "#root == true": "SU", "#root == false": "FA", "$Exception{java.lang.Throwable}": "UN" }, "Catch": [ { "Exceptions": [ "java.lang.Throwable" ], "Next": "CompensationTrigger" } ], "Next": "Succeed" }, "DeleteOrder": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "orderSave", "ServiceMethod": "deleteOrder", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[order]" ] }, "CompensateReduceAccount": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "accountService", "ServiceMethod": "compensateDecrease", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[userId]", "$.[money]" ] }, "CompensateReduceStorage": { "Type": "ServiceTask", "ServiceName": "storageService", "ServiceMethod": "compensateDecrease", "Input": [ "$.[businessKey]", "$.[productId]", "$.[count]" ] }, "CompensationTrigger": { "Type": "CompensationTrigger", "Next": "Fail" }, "Succeed": { "Type":"Succeed" }, "Fail": { "Type":"Fail", "ErrorCode": "PURCHASE_FAILED", "Message": "purchase failed" } }}这个状态机在TM控制,而在我们的代码示例中,TM在订单服务,当外部下单时,订单服务首先会创建一个订单,然后调用账户服务扣减金额,最后调用库存服务扣减库存。这个流程在上面的json文件中做了定义。
订单服务创建订单的方法会启动状态机,代码如下:
StateMachineEngine stateMachineEngine = (StateMachineEngine) ApplicationContextUtils.getApplicationContext().getBean("stateMachineEngine");Map<String, Object> startParams = new HashMap<>(3);String businessKey = String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis());startParams.put("businessKey", businessKey);startParams.put("order", order);startParams.put("mockReduceAccountFail", "true");startParams.put("userId", order.getUserId());startParams.put("money", order.getPayAmount());startParams.put("productId", order.getProductId());startParams.put("count", order.getCount());//sync testStateMachineInstance inst = stateMachineEngine.startWithBusinessKey("buyGoodsOnline", null, businessKey, startParams);可以看到,上面代码定义的buyGoodsOnline,正是json文件中name这个key的value值。
那上面创建订单代码中的stateMachineEngine这个bean是在哪里定义的呢?订单服务的demo中有一个类StateMachineConfiguration来进行定义,代码如下:
public class StateMachineConfiguration { @Bean public ThreadPoolExecutorFactoryBean threadExecutor(){ ThreadPoolExecutorFactoryBean threadExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutorFactoryBean(); threadExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("SAGA_ASYNC_EXE_"); threadExecutor.setCorePoolSize(1); threadExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(20); return threadExecutor; } @Bean public DbStateMachineConfig dbStateMachineConfig(ThreadPoolExecutorFactoryBean threadExecutor, DataSource hikariDataSource) throws IOException { DbStateMachineConfig dbStateMachineConfig = new DbStateMachineConfig(); dbStateMachineConfig.setDataSource(hikariDataSource); dbStateMachineConfig.setThreadPoolExecutor((ThreadPoolExecutor) threadExecutor.getObject()); /** *这里配置了json文件的路径,TM在初始化的时候,会把json文件解析成StateMachineImpl类,如果数据库没有保存这个状态机,则存入数据库seata_state_machine_def表 *如果数据库有记录,则取最新的一条记录,并且注册到StateMachineRepositoryImpl,注册方式有2种,一种是(stateMachineName + "_" + tenantId),一种是stateMachine.getId() *具体代码见StateMachineRepositoryImpl类registryStateMachine方法 *这个注册的触发方法在DefaultStateMachineConfig的初始化方法init() */ dbStateMachineConfig.setResources(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:statelang/*.json"));//json文件 dbStateMachineConfig.setEnableAsync(true); dbStateMachineConfig.setApplicationId("order-server"); dbStateMachineConfig.setTxServiceGroup("my_test_tx_group"); return dbStateMachineConfig; } @Bean public ProcessCtrlStateMachineEngine stateMachineEngine(DbStateMachineConfig dbStateMachineConfig){ ProcessCtrlStateMachineEngine stateMachineEngine = new ProcessCtrlStateMachineEngine(); stateMachineEngine.setStateMachineConfig(dbStateMachineConfig); return stateMachineEngine; } @Bean public StateMachineEngineHolder stateMachineEngineHolder(ProcessCtrlStateMachineEngine stateMachineEngine){ StateMachineEngineHolder stateMachineEngineHolder = new StateMachineEngineHolder(); stateMachineEngineHolder.setStateMachineEngine(stateMachineEngine); return stateMachineEngineHolder; }}可以看到,我们在DbStateMachineConfig中配置了状态机的json文件,同时配置了applicationId和txServiceGroup。在DbStateMachineConfig初始化的时候,子类DefaultStateMachineConfig的init的方法会把json文件解析成状态机,并注册。
附:我提供的demo解析后的状态机类StateMachineImpl的参数记录了我们在json里面定义的状态机流程,内容如下:
id = nulltenantId = nullappName = "SEATA"name = "buyGoodsOnline"comment = "buy a goods on line, add order, deduct account, deduct storage "version = "0.0.1"startState = "SaveOrder"status = {StateMachine$Status@9135} "AC"recoverStrategy = nullisPersist = truetype = "STATE_LANG"content = nullgmtCreate = nullstates = {LinkedHashMap@9137} size = 11 "SaveOrder" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9153} "ChoiceAccountState" -> {ChoiceStateImpl@9155} "ReduceAccount" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9157} "ChoiceStorageState" -> {ChoiceStateImpl@9159} "ReduceStorage" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9161} "DeleteOrder" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9163} "CompensateReduceAccount" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9165} "CompensateReduceStorage" -> {ServiceTaskStateImpl@9167} "CompensationTrigger" -> {CompensationTriggerStateImpl@9169} "Succeed" -> {SucceedEndStateImpl@9171} "Fail" -> {FailEndStateImpl@9173}启动状态机
在上面的创建订单的代码中,startWithBusinessKey方法进行了整个事务的启动,这个方法还有一个异步模式startWithBusinessKeyAsync,这里我们以同步模式来讲解,源代码如下:
public StateMachineInstance startWithBusinessKey(String stateMachineName, String tenantId, String businessKey, Map<String, Object> startParams) throws EngineExecutionException { return startInternal(stateMachineName, tenantId, businessKey, startParams, false, null);}private StateMachineInstance startInternal(String stateMachineName, String tenantId, String businessKey, Map<String, Object> startParams, boolean async, AsyncCallback callback) throws EngineExecutionException { //省略部分源代码 //创建一个状态机实例 StateMachineInstance instance = createMachineInstance(stateMachineName, tenantId, businessKey, startParams);//tenantId="000001",默认值 ProcessContextBuilder contextBuilder = ProcessContextBuilder.create().withProcessType(ProcessType.STATE_LANG) .withOperationName(DomainConstants.OPERATION_NAME_START).withAsyncCallback(callback).withInstruction( new StateInstruction(stateMachineName, tenantId)).withStateMachineInstance(instance) .withStateMachineConfig(getStateMachineConfig()).withStateMachineEngine(this); Map<String, Object> contextVariables; if (startParams != null) { contextVariables = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(startParams.size()); nullSafeCopy(startParams, contextVariables); } else { contextVariables = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); } instance.setContext(contextVariables);//把启动参数赋值给状态机实例的context //给ProcessContextImpl的variables加参数 contextBuilder.withStateMachineContextVariables(contextVariables); contextBuilder.withIsAsyncExecution(async); ProcessContext processContext = contextBuilder.build();//创建一个ProcessContextImpl if (instance.getStateMachine().isPersist() && stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore() != null) {//这个条件是true stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore().recordStateMachineStarted(instance, processContext);//记录状态机开始状态 } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(instance.getId())) { instance.setId( stateMachineConfig.getSeqGenerator().generate(DomainConstants.SEQ_ENTITY_STATE_MACHINE_INST)); } if (async) { stateMachineConfig.getAsyncProcessCtrlEventPublisher().publish(processContext); } else { //发送消息到EventBus,这里的消费者是ProcessCtrlEventConsumer,在DefaultStateMachineConfig初始化时设置 stateMachineConfig.getProcessCtrlEventPublisher().publish(processContext); } return instance;}上面的代码中我们可以看出,启动状态记得时候主要做了2件事情,一个是记录状态机开始的状态,一个是发送消息到EventBus,下面我们详细看一下这2个过程。
全局事务处理
上面的代码分析中,有一个记录状态机开始状态的代码,如下:
stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore().recordStateMachineStarted(instance, processContext);这里调用了类DbAndReportTcStateLogStore的recordStateMachineStarted方法,代码如下:
public void recordStateMachineStarted(StateMachineInstance machineInstance, ProcessContext context) { if (machineInstance != null) { //if parentId is not null, machineInstance is a SubStateMachine, do not start a new global transaction, //use parent transaction instead. String parentId = machineInstance.getParentId(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(parentId)) { if (StringUtils.isEmpty(machineInstance.getId())) { machineInstance.setId(parentId); } } else {//走这个分支 /** *这里的beginTransaction就是开启全局事务,这里跟之前 *《阿里中间件seata源码剖析五:聊聊seata中全局事务的开启》 *讲的开启全局事务是一样的,都是调用TC开启全局事务,感兴趣的可以看这篇文章 */ beginTransaction(machineInstance, context); } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(machineInstance.getId()) && seqGenerator != null) { machineInstance.setId(seqGenerator.generate(DomainConstants.SEQ_ENTITY_STATE_MACHINE_INST)); } // save to db machineInstance.setSerializedStartParams(paramsSerializer.serialize(machineInstance.getStartParams())); executeUpdate(stateLogStoreSqls.getRecordStateMachineStartedSql(dbType), STATE_MACHINE_INSTANCE_TO_STATEMENT_FOR_INSERT, machineInstance); }}上面executeUpdate方法在子类AbstractStore,代码如下:
protected int executeUpdate(String sql, ObjectToStatement objectToStatement, T o) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement stmt = null; try { connection = dataSource.getConnection(); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Preparing SQL: {}", sql); } stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("setting params to PreparedStatement: {}", BeanUtils.beanToString(o)); } objectToStatement.toStatement(o, stmt); int count = stmt.executeUpdate(); if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) { connection.commit(); } return count; } catch (SQLException e) { throw new StoreException(e); } finally { closeSilent(stmt); closeSilent(connection); }}debug一下这个代码,这里执行的sql如下:
INSERT INTO seata_state_machine_inst(id, machine_id, tenant_id, parent_id, gmt_started, business_key, start_params, is_running, status, gmt_updated)VALUES ('192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', '06a098cab53241ca7ed09433342e9f07', '000001', null, '2020-10-31 17:18:24.773', '1604135904773', '{"@type":"java.util.HashMap","money":50.,"productId":1L,"_business_key_":"1604135904773","businessKey":"1604135904773","count":1,"mockReduceAccountFail":"true","userId":1L,"order":{"@type":"io.seata.sample.entity.Order","count":1,"payAmount":50,"productId":1,"userId":1}}', 1, 'RU', '2020-10-31 17:18:24.773')可以看到,这个全局事务记录在了表seata_state_machine_inst,记录的是我们启动状态机的参数,记录的状态是"RU"也就是RUNNING。
分支事务处理
上一节我们提到,启动状态机后,向EventBus发了一条消息,这个消息的消费者是ProcessCtrlEventConsumer,我们看一下这个类的代码:
public class ProcessCtrlEventConsumer implements EventConsumer<ProcessContext> { private ProcessController processController; @Override public void process(ProcessContext event) throws FrameworkException { //这里的processController是ProcessControllerImpl processController.process(event); } @Override public boolean accept(Class clazz) { return ProcessContext.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz); } public void setProcessController(ProcessController processController) { this.processController = processController; }}ProcessControllerImpl类的process方法代码如下:
public void process(ProcessContext context) throws FrameworkException { try { businessProcessor.process(context); businessProcessor.route(context); } catch (FrameworkException fex) { throw fex; } catch (Exception ex) { LOGGER.error("Unknown exception occurred, context = {}", context, ex); throw new FrameworkException(ex, "Unknown exception occurred", FrameworkErrorCode.UnknownAppError); }}这里的处理逻辑有些复杂,先上一张UML类图:
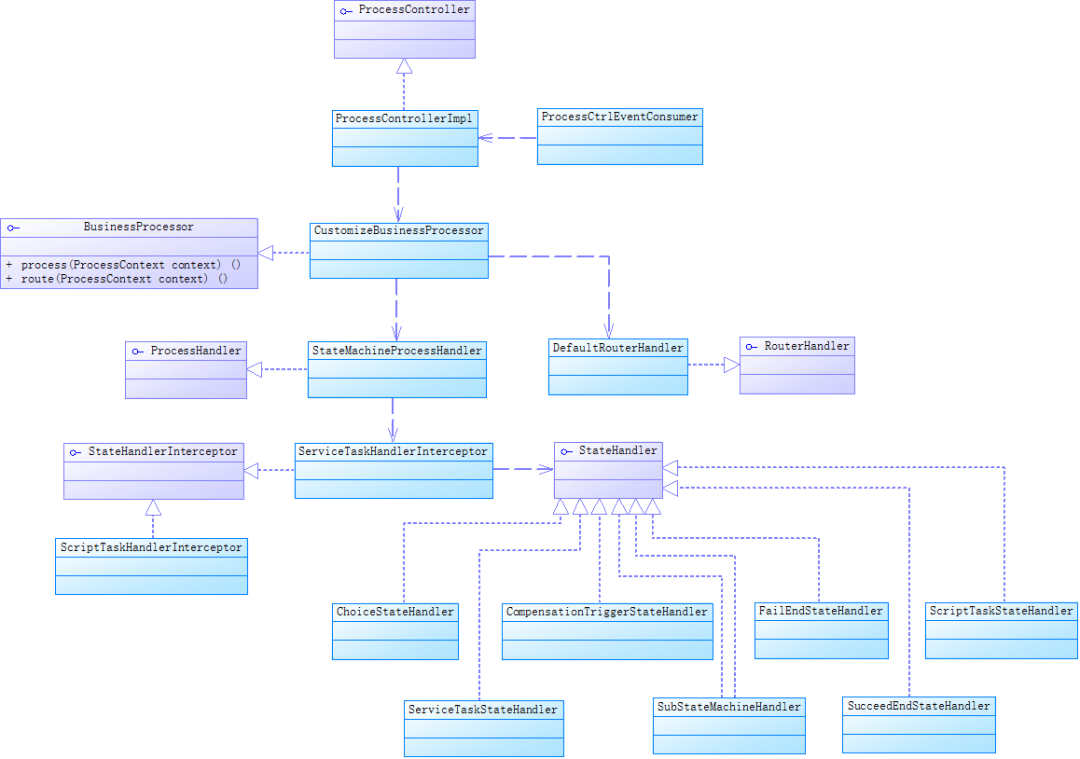
我们看一下StateMachineProcessHandler类中process方法,代码如下:
public void process(ProcessContext context) throws FrameworkException { StateInstruction instruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); State state = instruction.getState(context); String stateType = state.getType(); StateHandler stateHandler = stateHandlers.get(stateType); List interceptors = null; if (stateHandler instanceof InterceptableStateHandler) { interceptors = ((InterceptableStateHandler)stateHandler).getInterceptors(); } List executedInterceptors = null; Exception exception = null; try { if (interceptors != null && interceptors.size() > 0) { executedInterceptors = new ArrayList<>(interceptors.size()); for (StateHandlerInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { executedInterceptors.add(interceptor); interceptor.preProcess(context); } } stateHandler.process(context); } catch (Exception e) { exception = e; throw e; } finally { if (executedInterceptors != null && executedInterceptors.size() > 0) { for (int i = executedInterceptors.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { StateHandlerInterceptor interceptor = executedInterceptors.get(i); interceptor.postProcess(context, exception); } } }}这个方法使用了代理模式。我们看到了StateHandlerInterceptor,stateHandler.process方式的前后分别调用了interceptor的preProcess和postProcess。
我们先来看一下代理,这里是ServiceTaskHandlerInterceptor,代码如下:
public class ServiceTaskHandlerInterceptor implements StateHandlerInterceptor { //省略部分代码 @Override public void preProcess(ProcessContext context) throws EngineExecutionException { StateInstruction instruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); StateMachineInstance stateMachineInstance = (StateMachineInstance)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_INST); StateMachineConfig stateMachineConfig = (StateMachineConfig)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONFIG); if (EngineUtils.isTimeout(stateMachineInstance.getGmtUpdated(), stateMachineConfig.getTransOperationTimeout())) { String message = "Saga Transaction [stateMachineInstanceId:" + stateMachineInstance.getId() + "] has timed out, stop execution now."; EngineUtils.failStateMachine(context, exception);//修改状态机状态FA throw exception; } StateInstanceImpl stateInstance = new StateInstanceImpl(); Map<String, Object> contextVariables = (Map<String, Object>)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONTEXT); ServiceTaskStateImpl state = (ServiceTaskStateImpl)instruction.getState(context); List<Object> serviceInputParams = null; Object isForCompensation = state.isForCompensation(); if (isForCompensation != null && (Boolean)isForCompensation) { CompensationHolder compensationHolder = CompensationHolder.getCurrent(context, true); StateInstance stateToBeCompensated = compensationHolder.getStatesNeedCompensation().get(state.getName()); if (stateToBeCompensated != null) { stateToBeCompensated.setCompensationState(stateInstance); stateInstance.setStateIdCompensatedFor(stateToBeCompensated.getId()); } else { LOGGER.error("Compensation State[{}] has no state to compensate, maybe this is a bug.", state.getName()); } CompensationHolder.getCurrent(context, true).addForCompensationState(stateInstance.getName(), stateInstance);//加入补偿集合 } //省略部分代码 stateInstance.setInputParams(serviceInputParams); if (stateMachineInstance.getStateMachine().isPersist() && state.isPersist() && stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore() != null) { try { //记录一个分支事务的状态到数据库 /** *INSERT INTO seata_state_inst (id, machine_inst_id, name, type, gmt_started, service_name, service_method, service_type, is_for_update, input_params, status, business_key, state_id_compensated_for, state_id_retried_for) *VALUES ('4fe5f602452c84ba5e88fd2ee9c13b35', '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', 'SaveOrder', 'ServiceTask', '2020-10-31 17:18:40.84', 'orderSave', *'saveOrder', null, 1, '["1604135904773",{"@type":"io.seata.sample.entity.Order","count":1,"payAmount":50,"productId":1,"userId":1}]', 'RU', null, null, null) */ stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore().recordStateStarted(stateInstance, context); } } //省略部分代码 //放入StateMachineInstanceImpl的stateMap用于重试或交易补偿 stateMachineInstance.putStateInstance(stateInstance.getId(), stateInstance); //记录状态后面传给TaskStateRouter判断全局事务结束 ((HierarchicalProcessContext)context).setVariableLocally(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATE_INST, stateInstance); } @Override public void postProcess(ProcessContext context, Exception exp) throws EngineExecutionException { StateInstruction instruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); ServiceTaskStateImpl state = (ServiceTaskStateImpl)instruction.getState(context); StateMachineInstance stateMachineInstance = (StateMachineInstance)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_INST); StateInstance stateInstance = (StateInstance)context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATE_INST); if (stateInstance == null || !stateMachineInstance.isRunning()) { LOGGER.warn("StateMachineInstance[id:" + stateMachineInstance.getId() + "] is end. stop running"); return; } StateMachineConfig stateMachineConfig = (StateMachineConfig)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONFIG); if (exp == null) { exp = (Exception)context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_EXCEPTION); } stateInstance.setException(exp); decideExecutionStatus(context, stateInstance, state, exp);//设置事务状态 //省略部分代码 Map<String, Object> contextVariables = (Map<String, Object>)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONTEXT); //省略部分代码 context.removeVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_OUTPUT_PARAMS); context.removeVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_INPUT_PARAMS); stateInstance.setGmtEnd(new Date()); if (stateMachineInstance.getStateMachine().isPersist() && state.isPersist() && stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore() != null) { //更新分支事务的状态 /** *UPDATE seata_state_inst SET gmt_end = '2020-10-31 17:18:49.919', excep = null, status = 'SU', output_params = 'true' WHERE id = '4fe5f602452c84ba5e88fd2ee9c13b35' AND machine_inst_id = '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016' */ stateMachineConfig.getStateLogStore().recordStateFinished(stateInstance, context); } //省略部分代码 }}从这个代码我们能看到,分支事务执行前,封装了一个StateInstanceImpl赋值给了ProcessContext,分支事务执行后,对这个StateInstanceImpl进行了修改,这个StateInstanceImpl有3个作用:
1.传入StateMachineInstanceImpl的stateMap用于重试或交易补偿
2.记录了分支事务的执行情况,同时支持持久化到seata_state_inst表
3.传入TaskStateRouter用作判断全局事务结束
看完了代理中的增强逻辑,我们看一下被代理的方法stateHandler.process(context),这个stateHandler的实现类比较多,我们以ServiceTaskStateHandler为例来讲解,代码如下:
public void process(ProcessContext context) throws EngineExecutionException { StateInstruction instruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); ServiceTaskStateImpl state = (ServiceTaskStateImpl) instruction.getState(context); StateInstance stateInstance = (StateInstance) context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATE_INST); Object result; try { List<Object> input = (List<Object>) context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_INPUT_PARAMS); //Set the current task execution status to RU (Running) stateInstance.setStatus(ExecutionStatus.RU);//设置状态 if (state instanceof CompensateSubStateMachineState) { //省略子状态机的研究 } else { StateMachineConfig stateMachineConfig = (StateMachineConfig) context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONFIG); ServiceInvoker serviceInvoker = stateMachineConfig.getServiceInvokerManager().getServiceInvoker( state.getServiceType()); if (serviceInvoker == null) { throw new EngineExecutionException("No such ServiceInvoker[" + state.getServiceType() + "]", FrameworkErrorCode.ObjectNotExists); } if (serviceInvoker instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) serviceInvoker).setApplicationContext( stateMachineConfig.getApplicationContext()); } result = serviceInvoker.invoke(state, input.toArray());//反射来触发要调用的方法 } if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< State[{}], ServiceName[{}], Method[{}] Execute finish. result: {}", state.getName(), serviceName, methodName, result); } //省略部分代码 } //省略异常处理代码}这段代码触发了我们定义的ServiceTaskState,调用了我们定义的next或者compensate。
下面我们再看一下CustomizeBusinessProcessor的route方法,代码如下:
public void route(ProcessContext context) throws FrameworkException { //code = "STATE_LANG" //message = "SEATA State Language" //name = "STATE_LANG" //ordinal = 0 ProcessType processType = matchProcessType(context); RouterHandler router = routerHandlers.get(processType.getCode()); router.route(context);//DefaultRouterHandler的route方法}看一下DefaultRouterHandler的route方法,代码如下:
public void route(ProcessContext context) throws FrameworkException { try { ProcessType processType = matchProcessType(context); ProcessRouter processRouter = processRouters.get(processType.getCode());//StateMachineProcessRouter Instruction instruction = processRouter.route(context); if (instruction == null) { LOGGER.info("route instruction is null, process end"); } else { context.setInstruction(instruction); eventPublisher.publish(context); } } catch (FrameworkException e) { throw e; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new FrameworkException(ex, ex.getMessage(), FrameworkErrorCode.UnknownAppError); }}看一下StateMachineProcessRouter的route方法,这里也是用了代理模式,代码如下:
public Instruction route(ProcessContext context) throws FrameworkException { StateInstruction stateInstruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); State state; if (stateInstruction.getTemporaryState() != null) { state = stateInstruction.getTemporaryState(); stateInstruction.setTemporaryState(null); } else {//走这个分支 StateMachineConfig stateMachineConfig = (StateMachineConfig)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_STATEMACHINE_CONFIG); StateMachine stateMachine = stateMachineConfig.getStateMachineRepository().getStateMachine( stateInstruction.getStateMachineName(), stateInstruction.getTenantId()); state = stateMachine.getStates().get(stateInstruction.getStateName()); } String stateType = state.getType(); StateRouter router = stateRouters.get(stateType); Instruction instruction = null; List interceptors = null; if (router instanceof InterceptableStateRouter) {//这里只有EndStateRouter interceptors = ((InterceptableStateRouter)router).getInterceptors();//EndStateRouterInterceptor } List executedInterceptors = null; Exception exception = null; try { //前置增量实现方法是空,这里省略代码 instruction = router.route(context, state); } catch (Exception e) { exception = e; throw e; } finally { if (executedInterceptors != null && executedInterceptors.size() > 0) { for (int i = executedInterceptors.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { StateRouterInterceptor interceptor = executedInterceptors.get(i); interceptor.postRoute(context, state, instruction, exception);//结束状态机 } } //if 'Succeed' or 'Fail' State did not configured, we must end the state machine if (instruction == null && !stateInstruction.isEnd()) { EngineUtils.endStateMachine(context); } } return instruction;}这里的代理只实现了一个后置增强,做的事情就是结束状态机。
StateRouter的UML类图如下:
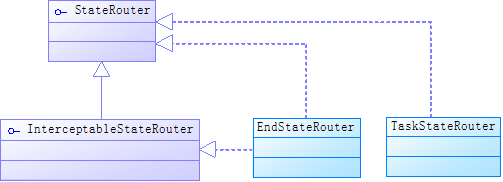
可以看到,除了EndStateRouter,只有一个TaskStateRouter了。而EndStateRouter并没有做什么事情,因为关闭状态机的逻辑已经由代理做了。这里我们看一下TaskStateRouter,代码如下:
public Instruction route(ProcessContext context, State state) throws EngineExecutionException { StateInstruction stateInstruction = context.getInstruction(StateInstruction.class); if (stateInstruction.isEnd()) {//如果已经结束,直接返回 //省略代码 } //The current CompensationTriggerState can mark the compensation process is started and perform compensation // route processing. State compensationTriggerState = (State)context.getVariable( DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_COMPEN_TRIGGER_STATE); if (compensationTriggerState != null) { return compensateRoute(context, compensationTriggerState);//加入补偿集合进行补偿 } //There is an exception route, indicating that an exception is thrown, and the exception route is prioritized. String next = (String)context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_EXCEPTION_ROUTE); if (StringUtils.hasLength(next)) { context.removeVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_EXCEPTION_ROUTE); } else { next = state.getNext(); } //If next is empty, the state selected by the Choice state was taken. if (!StringUtils.hasLength(next) && context.hasVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_CHOICE)) { next = (String)context.getVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_CHOICE); context.removeVariable(DomainConstants.VAR_NAME_CURRENT_CHOICE); } if (!StringUtils.hasLength(next)) { return null; } StateMachine stateMachine = state.getStateMachine(); State nextState = stateMachine.getState(next); if (nextState == null) { throw new EngineExecutionException("Next state[" + next + "] is not exits", FrameworkErrorCode.ObjectNotExists); } stateInstruction.setStateName(next);//获取到下一个要流转的状态并且赋值给stateInstruction return stateInstruction;}到这里,我们就分析完成了状态机的原理,ProcessControllerImpl类中,调用CustomizeBusinessProcessor的process处理一个状态,然后调用route方法获取到下一个节点进行处理。
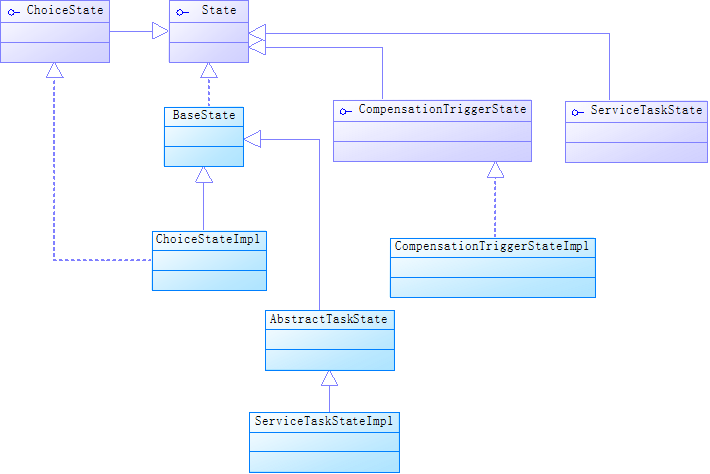
需要注意的是,这里获取到下一个节点后,并没有直接处理,而是使用观察者模式,先发送到EventBus,等待观察者来处理,循环往复,直到EndStateRouter结束状态机。
这里还要注意,这里观察者模式的Event是ProcessContext,里面包含了Instruction,而Instruction里面包含了State,这个State里面就决定了下一个处理的节点直到结束。UML类图如下:
总结
seata中间件中的saga模式使用比较广泛,但是代码还是比较复杂的。我从下面几个方面进行了梳理:
1.我们定义的json文件加载到了类StateMachineImpl中。
2.启动状态机,我们也就启动了全局事务,这个普通模式启动全局事务是一样的,都会向TC发送消息。
3.处理状态机状态和控制状态流转的入口类在ProcessControllerImpl,从process方法可以跟代码。
4.saga模式额外引入了3张表,我们也可以根据跟全局事务和分支事务相关的2张表来跟踪代码,我之前给出的demo,如果事务成功,这2张表的写sql按照状态机执行顺序给出一个成功sql,代码如下:
INSERT INTO seata_state_machine_inst(id, machine_id, tenant_id, parent_id, gmt_started, business_key, start_params, is_running, status, gmt_updated)VALUES ('192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', '06a098cab53241ca7ed09433342e9f07', '000001', null, '2020-10-31 17:18:24.773', '1604135904773', '{"@type":"java.util.HashMap","money":50.,"productId":1L,"_business_key_":"1604135904773","businessKey":"1604135904773","count":1,"mockReduceAccountFail":"true","userId":1L,"order":{"@type":"io.seata.sample.entity.Order","count":1,"payAmount":50,"productId":1,"userId":1}}', 1, 'RU', '2020-10-31 17:18:24.773')INSERT INTO seata_state_inst (id, machine_inst_id, name, type, gmt_started, service_name, service_method, service_type, is_for_update, input_params, status, business_key, state_id_compensated_for, state_id_retried_for)VALUES ('4fe5f602452c84ba5e88fd2ee9c13b35', '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', 'SaveOrder', 'ServiceTask', '2020-10-31 17:18:40.84', 'orderSave', 'saveOrder', null, 1, '["1604135904773",{"@type":"io.seata.sample.entity.Order","count":1,"payAmount":50,"productId":1,"userId":1}]', 'RU', null, null, null)UPDATE seata_state_inst SET gmt_end = '2020-10-31 17:18:49.919', excep = null, status = 'SU', output_params = 'true' WHERE id = '4fe5f602452c84ba5e88fd2ee9c13b35' AND machine_inst_id = '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016'INSERT INTO seata_state_inst (id, machine_inst_id, name, type, gmt_started, service_name, service_method, service_type, is_for_update, input_params, status, business_key, state_id_compensated_for, state_id_retried_for)VALUES ('8371235cb2c66c8626e148f66123d3b4', '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', 'ReduceAccount', 'ServiceTask', '2020-10-31 17:19:00.441', 'accountService', 'decrease', null, 1, '["1604135904773",1L,50.,{"@type":"java.util.LinkedHashMap","throwException":"true"}]', 'RU', null, null, null)UPDATE seata_state_inst SET gmt_end = '2020-10-31 17:19:09.593', excep = null, status = 'SU', output_params = 'true' WHERE id = '8371235cb2c66c8626e148f66123d3b4' AND machine_inst_id = '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016'INSERT INTO seata_state_inst (id, machine_inst_id, name, type, gmt_started, service_name, service_method, service_type, is_for_update, input_params, status, business_key, state_id_compensated_for, state_id_retried_for)VALUES ('e70a49f1eac72f929085f4e82c2b4de2', '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016', 'ReduceStorage', 'ServiceTask', '2020-10-31 17:19:18.494', 'storageService', 'decrease', null, 1, '["1604135904773",1L,1,{"@type":"java.util.LinkedHashMap"}]', 'RU', null, null, null)UPDATE seata_state_inst SET gmt_end = '2020-10-31 17:19:26.613', excep = null, status = 'SU', output_params = 'true' WHERE id = 'e70a49f1eac72f929085f4e82c2b4de2' AND machine_inst_id = '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016'UPDATE seata_state_machine_inst SET gmt_end = '2020-10-31 17:19:33.581', excep = null, end_params = '{"@type":"java.util.HashMap","productId":1L,"count":1,"ReduceAccountResult":true,"mockReduceAccountFail":"true","userId":1L,"money":50.,"SaveOrderResult":true,"_business_key_":"1604135904773","businessKey":"1604135904773","ReduceStorageResult":true,"order":{"@type":"io.seata.sample.entity.Order","count":1,"id":60,"payAmount":50,"productId":1,"userId":1}}',status = 'SU', compensation_status = null, is_running = 0, gmt_updated = '2020-10-31 17:19:33.582' WHERE id = '192.168.59.146:8091:65853497147990016' and gmt_updated = '2020-10-31 17:18:24.773'由于能力和精力有限,可能有一些理解上的错误,欢迎大佬们批评指正。
seata专栏往期回顾
《springcloud+eureka整合阿里seata-xa模式》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析六:TCC模式中2阶段提交实现》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析五:聊聊seata中全局事务的开启》
《springcloud+eureka整合阿里seata-saga模式》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析四:AT模式2阶段提交》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析三:聊聊seata中的ShutdownHook》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析二:聊聊TC的初始化》
《阿里中间件seata源码剖析一:聊聊RM和TM客户端初始化》
《springcloud+eureka整合seata-tcc模式》
《springcloud+eureka整合分布式事务中间件seata AT模式》
《springboot多数据源整合分布式事务中间件seata AT模式》

(建议收藏)❤️)
(建议收藏)❤️)

(建议收藏)❤️)

(建议收藏)❤️)

(建议收藏)❤️)

(建议收藏)❤️)

❤️)


)




