简介: KubeVela 是一个简单易用又高度可扩展的云原生应用管理引擎,是基于 Kubernetes 及阿里云与微软云共同发布的云原生应用开发模型 OAM 构建。本文主要目的是探索 KubeVela 如何将一个 appfile 文件转换为 K8s 中特定的资源对象。

作者 | 樊大勇
KubeVela 是一个简单易用又高度可扩展的云原生应用管理引擎,是基于 Kubernetes 及阿里云与微软云共同发布的云原生应用开发模型 OAM 构建。
KubeVela 基于 OAM 模型构建了一套具体的实现,通过 Golang 编写,可以端到端地为用户构建云原生应用的平台,提供一个相对完整的解决方案。
KubeVela 项目自 2020 年 7 月份在社区里面发起,受到包括阿里、微软、Crossplane 等公司工程师在内的广大社区志愿者的欢迎,并一起投入到项目开发工作中。他们把在 OAM 实践里面的各种经验与教训,都总结沉淀到 KubeVela 项目中。
本文主要目的是探索 KubeVela 如何将一个 appfile 文件转换为 K8s 中特定的资源对象。
该过程总的来说分为两个阶段:
- appfile 转为 K8s 中的 application
- application 转换为对应的 K8s 资源对象
# vela.yaml
name: test
services:nginx:type: webserviceimage: nginxenv:- name: NAMEvalue: kubevela# svc traitsvc:type: NodePortports:- port: 80nodePort: 32017利用 vela up 命令可以完成部署。
vela up 命令
建议:在看 vela 命令行工具代码之前,先去简单了解一下 cobra 框架。
// references/cli/up.go
// NewUpCommand will create command for applying an AppFile
func NewUpCommand(c types.Args, ioStream cmdutil.IOStreams) *cobra.Command {cmd := &cobra.Command{Use: "up",DisableFlagsInUseLine: true,Short: "Apply an appfile",Long: "Apply an appfile",Annotations: map[string]string{types.TagCommandType: types.TypeStart,},PersistentPreRunE: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) error {return c.SetConfig()},RunE: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) error {velaEnv, err := GetEnv(cmd)if err != nil {return err}kubecli, err := c.GetClient()if err != nil {return err}o := &common.AppfileOptions{Kubecli: kubecli,IO: ioStream,Env: velaEnv,}filePath, err := cmd.Flags().GetString(appFilePath)if err != nil {return err}return o.Run(filePath, velaEnv.Namespace, c)},}cmd.SetOut(ioStream.Out)cmd.Flags().StringP(appFilePath, "f", "", "specify file path for appfile")return cmd
}上面源码展示的是 vela up 命令的入口。
在 PresistentPreRunE 函数中,通过调用 c.SetConfig() 完成 Kuberentes 配置信息 kubeconfig 的注入。
在 RunE 函数中:
- 首先,获取 vela 的 env 变量,velaEnv.Namespace 对应 Kubernetes 的命名空间。
- 其次,获取 Kubernetes 的客户端,kubectl。
- 接着,利用 Kubernetes 客户端和 vleaEnv 来构建渲染 Appfile 需要的 AppfileOptions。
-
最后,调用 o.Run(filePath, velaEnv.Namespace, c)。
-
该函数需要三个参数,其中 filePath 用于指定 appfile 的位置,velaEnv.Namespace 和 c 用来将渲染后的 Application 创建到指定命名空间。
- filePath: appfile 的路径
- velaEnv.Namespace:对应 K8s 的 namespace
- c:K8s 客户端
-
如何将一个 appfile 转为 Kubernetes 中的 Application
- 起点:appfile
- 终点:applicatioin
-
路径:appfile -> application (services -> component)
- comp[workload, traits]
1. 起点:AppFile
// references/appfile/api/appfile.go
// AppFile defines the spec of KubeVela Appfile
type AppFile struct {Name string `json:"name"`CreateTime time.Time `json:"createTime,omitempty"`UpdateTime time.Time `json:"updateTime,omitempty"`Services map[string]Service `json:"services"`Secrets map[string]string `json:"secrets,omitempty"`configGetter config.Storeinitialized bool
}// NewAppFile init an empty AppFile struct
func NewAppFile() *AppFile {return &AppFile{Services: make(map[string]Service),Secrets: make(map[string]string),configGetter: &config.Local{},}
}// references/appfile/api/service.go
// Service defines the service spec for AppFile, it will contain all related information including OAM component, traits, source to image, etc...
type Service map[string]interface{}上面两段代码是 AppFile 在客户端的声明,vela 会将指定路径的 yaml 文件读取后,赋值给一个 AppFile。
// references/appfile/api/appfile.go
// LoadFromFile will read the file and load the AppFile struct
func LoadFromFile(filename string) (*AppFile, error) {b, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filepath.Clean(filename))if err != nil {return nil, err}af := NewAppFile()// Add JSON format appfile supportext := filepath.Ext(filename)switch ext {case ".yaml", ".yml":err = yaml.Unmarshal(b, af)case ".json":af, err = JSONToYaml(b, af)default:if json.Valid(b) {af, err = JSONToYaml(b, af)} else {err = yaml.Unmarshal(b, af)}}if err != nil {return nil, err}return af, nil
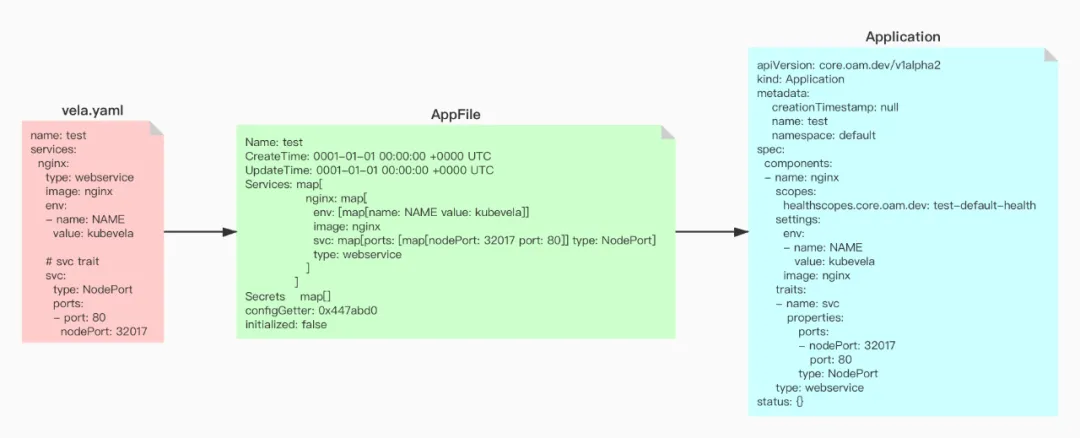
}下面为读取 vela.yaml 文件后,加载到 AppFile 中的数据:
# vela.yaml
name: test
services:nginx:type: webserviceimage: nginxenv:- name: NAMEvalue: kubevela# svc traitsvc:type: NodePortports:- port: 80nodePort: 32017Name: test
CreateTime: 0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC
UpdateTime: 0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC
Services: map[nginx: map[env: [map[name: NAME value: kubevela]] image: nginx svc: map[ports: [map[nodePort: 32017 port: 80]] type: NodePort] type: webservice]]
Secrets map[]
configGetter: 0x447abd0
initialized: false2. 终点:application
// apis/core.oam.dev/application_types.go
type Application struct {metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`Spec ApplicationSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`Status AppStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
}// ApplicationSpec is the spec of Application
type ApplicationSpec struct {Components []ApplicationComponent `json:"components"`// TODO(wonderflow): we should have application level scopes supported here// RolloutPlan is the details on how to rollout the resources// The controller simply replace the old resources with the new one if there is no rollout plan involved// +optionalRolloutPlan *v1alpha1.RolloutPlan `json:"rolloutPlan,omitempty"`
}上面代码,为 Application 的声明,结合 .vela/deploy.yaml(见下面代码),可以看出,要将一个 AppFile 渲染为 Application 主要就是将 AppFile 的 Services 转化为 Application 的 Components。
# .vela/deploy.yaml
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1alpha2
kind: Application
metadata:creationTimestamp: nullname: testnamespace: default
spec:components:- name: nginxscopes:healthscopes.core.oam.dev: test-default-healthsettings:env:- name: NAMEvalue: kubevelaimage: nginxtraits:- name: svcproperties:ports:- nodePort: 32017port: 80type: NodePorttype: webservice
status: {}3. 路径:Services -> Components
结合以上内容可以看出,将 Appfile 转化为 Application 主要是将 Services 渲染为 Components。
// references/appfile/api/appfile.go
// BuildOAMApplication renders Appfile into Application, Scopes and other K8s Resources.
func (app *AppFile) BuildOAMApplication(env *types.EnvMeta, io cmdutil.IOStreams, tm template.Manager, silence bool) (*v1alpha2.Application, []oam.Object, error) {...servApp := new(v1alpha2.Application)servApp.SetNamespace(env.Namespace)servApp.SetName(app.Name)servApp.Spec.Components = []v1alpha2.ApplicationComponent{}for serviceName, svc := range app.GetServices() {...// 完成 Service 到 Component 的转化comp, err := svc.RenderServiceToApplicationComponent(tm, serviceName)if err != nil {return nil, nil, err}servApp.Spec.Components = append(servApp.Spec.Components, comp)}servApp.SetGroupVersionKind(v1alpha2.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind("Application"))auxiliaryObjects = append(auxiliaryObjects, addDefaultHealthScopeToApplication(servApp))return servApp, auxiliaryObjects, nil
}上面的代码是 vela 将 Appfile 转化为 Application 代码实现的位置。其中 comp, err := svc.RenderServiceToApplicationComponent(tm, serviceName) 完成 Service 到 Component 的转化。
// references/appfile/api/service.go
// RenderServiceToApplicationComponent render all capabilities of a service to CUE values to KubeVela Application.
func (s Service) RenderServiceToApplicationComponent(tm template.Manager, serviceName string) (v1alpha2.ApplicationComponent, error) {// sort out configs by workload/traitworkloadKeys := map[string]interface{}{}var traits []v1alpha2.ApplicationTraitwtype := s.GetType()comp := v1alpha2.ApplicationComponent{Name: serviceName,WorkloadType: wtype,}for k, v := range s.GetApplicationConfig() {// 判断是否为 traitif tm.IsTrait(k) {trait := v1alpha2.ApplicationTrait{Name: k,}....// 如果是 triat 加入 traits 中traits = append(traits, trait)continue}workloadKeys[k] = v}// Handle workloadKeys to settingssettings := &runtime.RawExte nsion{}pt, err := json.Marshal(workloadKeys)if err != nil {return comp, err}if err := settings.UnmarshalJSON(pt); err != nil {return comp, err}comp.Settings = *settingsif len(traits) > 0 {comp.Traits = traits}return comp, nil
}4. 总结
执行 vela up 命令,渲染 appfile 为 Application,将数据写入到 .vela/deploy.yaml 中,并在 K8s 中创建。
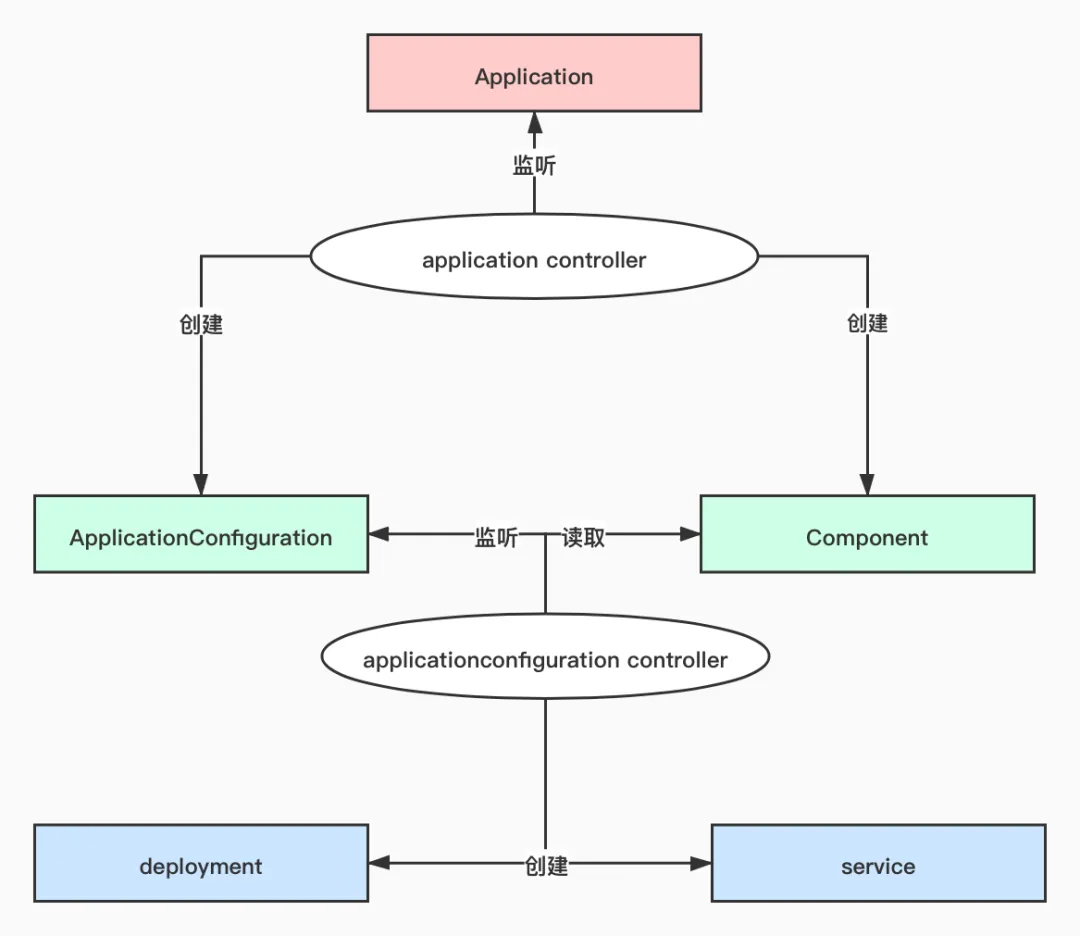
Application 是如何转换为对应 K8s 资源对象
- 起点:Application
- 中点:ApplicationConfiguration, Component
- 终点:Deployment, Service
-
路径:
- application_controller
- applicationconfiguration controller
【建议】> 了解一下内容:> - client-to
- controller-runtime
- operator
1. Application
# 获取集群中的 Application
$ kubectl get application
NAMESPACE NAME AGE
default test 24h2. ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component
当 application controller 获取到 Application 资源对象之后,会根据其内容创建出对应的 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component。
# 获取 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component
$ kubectl get ApplicationConfiguration,Component
NAME AGE
applicationconfiguration.core.oam.dev/test 24hNAME WORKLOAD-KIND AGE
component.core.oam.dev/nginx Deployment 24hApplicationiConfiguration 中以名字的方式引入 Component:

3. application controller
基本逻辑:
- 获取一个 Application 资源对象。
- 将 Application 资源对象渲染为 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component。
- 创建 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component 资源对象。
代码:
// pkg/controller/core.oam.dev/v1alpha2/application/application_controller.go// Reconcile process app event
func (r *Reconciler) Reconcile(req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {ctx := context.Background()applog := r.Log.WithValues("application", req.NamespacedName)// 1. 获取 Applicationapp := new(v1alpha2.Application)if err := r.Get(ctx, client.ObjectKey{Name: req.Name,Namespace: req.Namespace,}, app); err != nil {...}...// 2. 将 Application 转换为 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Componenthandler := &appHandler{r, app, applog}...appParser := appfile.NewApplicationParser(r.Client, r.dm)...appfile, err := appParser.GenerateAppFile(ctx, app.Name, app)...ac, comps, err := appParser.GenerateApplicationConfiguration(appfile, app.Namespace)...// 3. 在集群中创建 ApplicationConfiguration 和 Component // apply appConfig & component to the clusterif err := handler.apply(ctx, ac, comps); err != nil {applog.Error(err, "[Handle apply]")app.Status.SetConditions(errorCondition("Applied", err))return handler.handleErr(err)}...return ctrl.Result{}, r.UpdateStatus(ctx, app)
}4. applicationconfiguration controller
基本逻辑:
- 获取 ApplicationConfiguration 资源对象。
- 循环遍历,获取每一个 Component 并将 workload 和 trait 渲染为对应的 K8s 资源对象。
- 创建对应的 K8s 资源对象。
代码:
// pkg/controller/core.oam.dev/v1alpha2/applicationcinfiguratioin/applicationconfiguratioin.go// Reconcile an OAM ApplicationConfigurations by rendering and instantiating its
// Components and Traits.
func (r *OAMApplicationReconciler) Reconcile(req reconcile.Request) (reconcile.Result, error) {...ac := &v1alpha2.ApplicationConfiguration{}// 1. 获取 ApplicationConfigurationif err := r.client.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, ac); err != nil {...}return r.ACReconcile(ctx, ac, log)
}// ACReconcile contains all the reconcile logic of an AC, it can be used by other controller
func (r *OAMApplicationReconciler) ACReconcile(ctx context.Context, ac *v1alpha2.ApplicationConfiguration,log logging.Logger) (result reconcile.Result, returnErr error) {...// 2. 渲染// 此处 workloads 包含所有Component对应的的 workload 和 tratis 的 k8s 资源对象workloads, depStatus, err := r.components.Render(ctx, ac)...applyOpts := []apply.ApplyOption{apply.MustBeControllableBy(ac.GetUID()), applyOnceOnly(ac, r.applyOnceOnlyMode, log)}// 3. 创建 workload 和 traits 对应的 k8s 资源对象if err := r.workloads.Apply(ctx, ac.Status.Workloads, workloads, applyOpts...); err != nil {...}...// the defer function will do the final status updatereturn reconcile.Result{RequeueAfter: waitTime}, nil
}5. 总结
当 vela up 将一个 AppFile 渲染为一个 Application 后,后续的流程由 application controller 和 applicationconfiguration controller 完成。
作者简介
樊大勇,华胜天成研发工程师,GitHub ID:@just-do1。
原文链接
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。
)


















