1 线程操作
创建线程
挂起线程
终止线程
其它操作
1.1 创建线程
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);功能:创建线程;线程调用pthread_create函数创建新线程后,当前线程会从pthread_create函数返回并继续向下执行,新线程执行函数指针start_routine所指的函数。
参数说明:
- thread:一个传入传出参数,待创建线程的id指针;
- attr:设置待创建线程的属性,通常传入NULL;
- start_routine:一个函数指针,指向一个参数为void *,返回值也为void *的函数,该函数为待创建线程的执行函数;
- arg:传给线程执行函数的参数。
返回值说明:
- 成功:返回0;
- 不成功:返回errno。
特别说明:
- 进程id的类型pid_t是一个正整数,在整个系统都是唯一的;
- 线程id的类型pthread_t并非是一个正整数,只在当前进程中保证唯一;
- 当前进程调用pthread_create后获得的thread为新线程id;
- 线程id不能简单地使用printf函数打印,而应使用pthread_self函数来获取。
【案例1】使用pthread_create函数创建线程,并使原线程与新线程分别打印自己的线程id。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *tfn(void *arg) {printf("tfn--pid=%d,tid=%lu\n", getpid(), pthread_self());return (void*)0;
}//of tfn
int main() {pthread_t tempTid;printf("main--pid=%d, tid=%lu\n", getpid(), pthread_self());int tempRet = pthread_create(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, NULL);if (tempRet != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create error:%s\n", strerror(tempRet));exit(1);}//of ifsleep(1);return 0;
}//of main因为pthread库不是Linux系统默认的库,需要在编译的时候添加选项-lpthread:
gcc pthread_cre.c -o pthread_cre -lpthread执行结果如下:

进程和线程的联系:
- 当一个进程创建一个线程时,原有的进程就会变成线程,两个线程共用一段地址空间;
- 对内核而言,线程和进程没有区别,CPU会为每个线程与进程分配时间片,通过进程控制块来调度不同的线程和进程。
进程和线程的区别:
- 进程拥有独立的地址空间,当使用fork函数创建新进程时,若其中一个进程要对fork之前的数据进行修改,进程会根据“写时复制”原则,先复制一份该数据到子进程的地址空间,再修改数据。即便是全局变量,在进程间也不是共享的。
- 线程间共享地址空间,一个线程对全局取的数据进行了修改,其它线程访问到的也是修改后的数据。
【案例2】创建新线程,在新线程中修改原线程中定义在全局区的变量,并在原线程中打印该数据。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int globVar = 100;
void *tfn(void *arg) {globVar = 200;printf("thread\n");return NULL;
}//of tfn
int main(void) {printf("At first var = %d\n", globVar);pthread_t tempTid;pthread_create(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, NULL);sleep(1);printf("after pthread_create, var = %d\n", globVar);return 0;
}//of main执行结果如下:
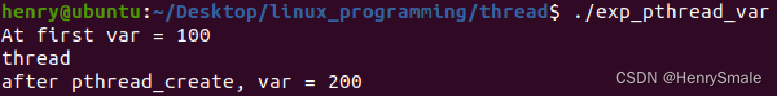
1.2 线程退出
#include <pthread.h>void pthread_exit(void *retval);为什么要用pthread_exit:
- return:用于退出函数,使函数返回函数调用处;
- exit:用于退出进程,若在线程中调用该函数,那么该线程所处的进程也会退出。
功能:退出线程。
参数说明:
- retval:表示线程的退出状态,通常设置为NULL。
返回值说明:
- 无。
【案例 3】:在一个进程中创建4个新线程,分别用pthread_exit, return, exit使其中一个线程退出,观察其它线程的执行状况。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void *tfn(void *paraArg) {long int i;i = (long int)paraArg; //强转if (i == 2) {pthread_exit(NULL); //return, exit(0)}//of ifsleep(i); //通过i来区别每个线程printf("I'm %dth thread, Thread_ID = %lu\n", i + 1, pthread_self());return NULL;
}//of tfn
int main(int paraArgc, char *paraArgv[]) {long int tempNum = 5, i;pthread_t tempTid;if (paraArgc == 2) {tempNum = atoi(paraArgv[1]);}//of iffor (i = 0; i < tempNum; i++) {//将i转换为指针,在tfn中再强转回整型pthread_create(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, (void *)i);}//of for isleep(tempNum);printf("I am main, I'm a thread!\n""main_thread_ID = %lu\n", pthread_self());return 0;
}//of main执行结果如下:
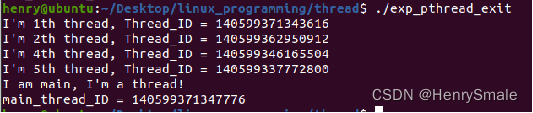
1.3 线程中止
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);功能:
- 向指定线程发送CANCEL信号,使一个线程强行杀死另外一个线程,类似于终止进程函数kill;
- 与进程不同的是,调用该函数杀死线程时,需要等待线程到达某个取消点,线程才会成功被终止;
- 取消点通常伴随阻塞出现,用户也可以在程序中通过调用pthread_testcancel函数创造取消点;
- pthread_exit使线程主动退出,pthread_cancel通过信号使线程被动退出;
- 注意:由于线程机制出现之前信号机制已经出现,信号机制在创建时并未考虑线程,线程与信号机制的兼容性略有不足,因此多线程编程时尽量避免使用信号,以免出现难以调试的错误。
参数说明:
- thread:线程id。
返回值说明:
- 成功:0;
- 不成功:返回errno。
【案例 4】使用pthread_cancel使原线程终止指定线程。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void *tfn(void *paraArg) {while(1) {printf("child thread ...\n");pthread_testcancel();}//of while
}//of tfnint main(void) pthread_t tempTid;void *tempTret = NULL;pthread_create(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, NULL);sleep(1);pthread_cancel(tempTid);pthread_join(tempTid, &tempTret);printf("child thread exit code = %ld\n", (long int)tempTret);return 0;
}//of main执行结果如下:
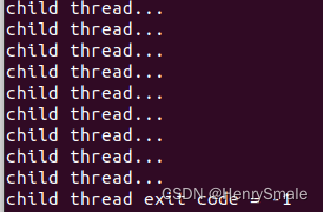
1.4 线程挂起
若将案例3主函数的sleep行删除,程序的执行结果如下:
I am main, I'm a thread!
main_thread_ID = 140186242565888- 问题:其它线程并没有执行,为什么?
- 原因分析:
– 线程与进程不同,若作为程序入口的原线程退出,系统内部会调用exit函数,导致同一进程中的所有线程都退出。 - 解决方案:
– 使用sleep函数使原线程阻塞,保证新创建的线程顺利执行;
– 使用线程挂起函数。
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);功能:
- 挂起线程,等待指定线程thread结束;
- 类似于wait,waitpid将进程挂起,以等待某个子进程结束;
- 该函数中指定的线程必须与调用该函数的线程处于同一个进程中,且多个线程不能同时挂起等待同一个进程,否则pthread_join将会返回错误。
参数说明:
- thread:表示被等待的线程id;
- retval:用于接收thread线程执行函数的返回值指针,该指针的值与thread线程的终止方式有关:
– 通过return返回:retval存放的是thread线程函数的返回值;
– 其它线程通过系统调用pthread_cancel异常终止,retval存放的是常量PTHREAD_CANCELED;
– 自调用pthread_exit终止,retval存放的是pthread_exit的参数ret_val;
– 若不关心它的终止状态,retval设置为NULL。
返回值说明:
- 成功:0;
- 不成功:返回errno。
【案例 5】使用pthread_exit退出线程,为线程设置退出状态并将线程的退出状态输出。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct {int a;int b;
} exit_t;
void *tfn(void *paraArg){exit_t *tempRet;tempRet = malloc(sizeof(exit_t));tempRet->a = 100;tempRet->b = 300;pthread_exit((void *)tempRet); //线程终止return NULL; //线程返回
}//of tfnint main(void){pthread_t tempTid;exit_t *tempRetval;pthread_creat(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, NULL);//调用pthread_join可以获取线程的退出状态pthread_join(tempTid, (void **)&tempRetval);printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", tempRetval->a, tempRetval->b);return 0;
}//of main分析:tfn函数既调用了pthread_exit函数,又设置了关键字return;若如下代码打印不为空,则说明线程通过pthread_exit函数退出。
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", tempRetval->a, tempRetval->b);执行结果如下:
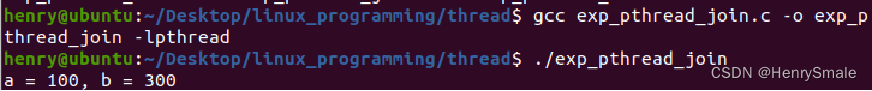
【案例 6】使用pthread_join回收多个新线程,并使用pthread_exit获取每个线程的退出状态。
分析:进程中可以使用waitpid函数结合循环结构使原进程等待多个进程退出,线程中pthread_join同样可以与循环结构结合,等待多个线程退出。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>long int globVar = 100;
void *tfn(void *paraArg){long int i;i = (long int)paraArg;sleep(i);if(i == 1) {globVar = 333;printf("var = %d\n", globVar);pthread_exit((void *)globVar);} else if(i == 3){globVar = 777;printf("I'm %dth pthread, pthread_id = %lu, var = %d\n", i + 1, pthread_self(), globVar);pthread_exit((void *)globVar);} else {printf("I'm %dth pthread, pthread_id = %lu, var = %d\n", i + 1, pthread_self(), globVar);pthread_exit((void *)globVar);}//of ifreturn NULL;
}//of tfnint main(void){pthread_t tempTid[5];long int i;int *tempRet[5];for(i = 0; i < 5; i ++){ //创建新线程pthread_create(&tempTid[i], NULL, tfn, (void *)i);}//of for ifor(i = 0; i < 5; i ++){ //回收新线程pthread_join(tempTid[i], (void **)&tempRet[i]);printf("---%d's ret = %d\n", i, (long int)tempRet[i]);}//of for iprintf("I'm main pthread tid = %lu\t var = %d\n", pthread_self(), globVar);pthread_exit(NULL);
}//of main分析:原线程的退出之所以会导致其它线程退出,是因为原线程执行完毕后,main函数会隐式调用exit函数,而pthread_exit函数可以只使调用该函数的线程退出。若在原线程调用return之前调用pthread_exit,同样可以保证其它线程的正常运行。
执行结果如下:
1.5 线程分离
- 在线程终止后,其它线程调用pthread_join函数获取该线程的终止状态前,该线程会一直保持终止状态,这种状态类似进程中的僵尸态;
- 为避免处于终止状态的线程占用内存,线程机制中提供了pthread_detach函数,可在线程被创建后设置线程分离,被分离的线程在执行结束后将会自动释放,不再等待其它线程回收。
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);功能:
- 将线程从主控线程分离,这样当线程结束后,它的退出状态不需要由其它线程来获取,而是由该线程自身自动释放;
- pthread_join不能终止已处于detach状态的线程,若对于分离态的线程调用pthread_join,函数会调用失败并返回EINVAL。
参数说明:
- thread:待分离的线程id。
返回值说明:
- 成功:0;
- 不成功:返回errno。
【案例 7】使用pthread_detach分离新线程,使新线程自动回收。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void *tfn(void *paraArg) {int tempNum = 5;while (n--) {printf("pthread tfn n = %d\n", tempNum);sleep(1);}//of whilereturn (void *)7;
}//of tfn
int main(void) {pthread_t tempTid;void *tempRet;pthread_create(&tempTid, NULL, tfn, NULL);pthread_detach(tempTid); //分离新线程int tempRetvar = pthread_join(tempTid, (void **)&tempRet);if (tempRetvar != 0) {fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join error %s\n", strerror(tempRetvar));} else {printf("pthread exit with %ld\n", (long int)tempRet);}//of ifreturn 0;
}//of main分析:线程分离后调用pthread_join会失败,因此会执行如下代码:
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join error %s\n", strerror(tempRetvar));执行结果如下:

知识扩展:
- linux线程执行 pthread有两种状态:joinable和unjoinable,默认是joinable;
– 通过pthread_attr_getdetachstate获取线程的状态;
– 方法一:通过如下代码来设置为状态joinable 还是 unjoinable
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&thr, &attr, &thread_start, NULL);– 方法二:在线程中调用 pthread_detach, 如:pthread_detach(pthread_self()),将状态改为unjoinable,确保资源的释放:
void threadFunc( void *ptr ){ pthread_detach(pthread_self());pthread_exit(0) ;
}//of threadFuncpthread_t tid;
int status = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);– 方法三:外部主线程主动调用 pthread_detach(tid):
pthread_t tid;
int status = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, ThreadFunc, NULL);
thread_detach(tid);- 如果线程是joinable状态,当线程函数自己返回退出时或pthread_exit时都不会释放线程所占用堆栈和线程描述符(总计8K多);只有调用pthread_join之后这些资源才会被释放;
- 若是unjoinable状态的线程,堆栈和线程描述符这些资源在线程函数退出时或pthread_exit时自动会被释放。

配置实例教程)





提高并发)











