银行家算法
银行家算法是著名的死锁避免算法,其思想是:把操作系统视为银行家,操作系统管理的资源相当于银行家管理的资金,进程向操作系统请求分配资源相当于用户向银行家贷款。操作系统按照银行家制定的规则为进程分配资源。进程运行之前先声明对各种资源的最大需求量,当进程在执行中继续申请资源时,先测试该进程已占用的资源数与本次申请的资源数之和是否超过该进程声明的最大需求量。若超过则拒绝分配资源,若未超过则再测试系统现存的资源能否满足该进程尚须的最大资源量,若能满足则按当前的申请量分配资源,否则也要推迟分配。
问题描述
设计程序模拟避免死锁的银行家算法的工作过程。假设系统中有n个进程:P1,P2,…,PnP_1,P_2,\dots,P_nP1,P2,…,Pn,有m类可分配资源R1,…,RmR_1,\dots,R_mR1,…,Rm,在某时刻,进程PiP_iPi已分配到的j类资源为Allocation[i][j]Allocation[i][j]Allocation[i][j]个,还需要j类资源need[i][j]need[i][j]need[i][j]个,目前系统剩余j类资源Available[j]Available[j]Available[j]个。
实验要求
- 判断当前状态是否安全。若安全,给出安全序列;若不安全,给出理由。
- 对于下一个时刻,某个进程提出资源请求Request(R1,…,Rm),使用银行家算法作为判读是否相应该响应该请求的决策依据。
- 输入某时刻的资源分配表和进程请求信息,输出安全序列分析,给出决策方案。
数据结构描述
- 系统可用资源向量Available[m]Available[m]Available[m]
- 最大需求矩阵Max[n][m]Max[n][m]Max[n][m]
- 分配矩阵Allocation[n][m]Allocation[n][m]Allocation[n][m]
- 需求矩阵Need[n][m]Need[n][m]Need[n][m]
其中,n是进程数量,m是资源种类数量。
算法描述
- 输入:T0时刻的资源分配表
- 输出:Pi发出资源请求后,进行的安全序列分析表和安全序列。若不安全,则给出不安全产生的原因。
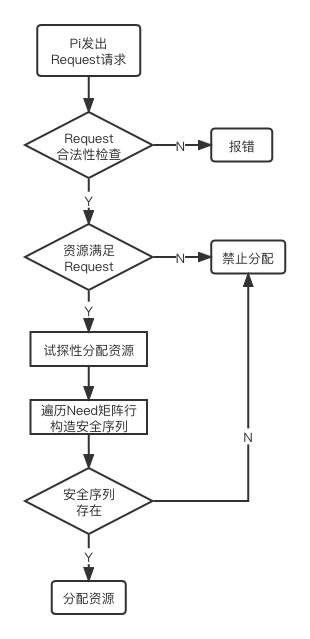
- 进程Pi发出请求RequestiRequest_iRequesti,首先检查其合法性,若Requesti≤Need[i]Request_i\le Need[i]Requesti≤Need[i]则继续进行,否则报错;
- 若Requesti≤AvailableRequest_i\le AvailableRequesti≤Available,则继续进行,否则认为当前资源不足,不响应当前请求;
- 系统试探性把资源分配给进程Pi:
Available−=RequestiAvailable-=Request_iAvailable−=Requesti
Allocation[i]+=RequestiAllocation[i]+=Request_iAllocation[i]+=Requesti
Need[i]−=RequestiNeed[i]-=Request_iNeed[i]−=Requesti - 使用银行家算法进行安全性检查,检查此次资源分配后,系统是否处于安全状态,若安全才正式将资源分配给进程Pi;否则本次的试探作废,Pi继续等待。安全性检查算法如下:
- 设置工作量Work[m]Work[m]Work[m],表示系统中剩余的可用资源数目。在安全性检查开始时,置Work=Available;
- 初始时安全序列为空;
- 遍历Need矩阵行,找出一行k,该行对应的Pk不在安全序列中,且Need[k]≤WorkNeed[k]\le WorkNeed[k]≤Work,将对应Pk插入安全序列,若找不到则跳过下一步;
- 更新Work=Work+Allocation[k]Work=Work+Allocation[k]Work=Work+Allocation[k],表征Pk获取资源并运行结束后,将资源释放的过程。返回上步,继续寻找下一个可以分配资源的进程;
- 此时,安全序列中若存在所有进程,则系统处于安全状态,否则系统不安全。
算法流程图
结果分析
设置n=5;m=3
T0时刻资源分配表
Available: [3 3 2]
P Allocation Need
0 [0 1 0] [7 4 3]
1 [2 0 0] [1 2 2]
2 [3 0 2] [6 0 0]
3 [2 1 1] [0 1 1]
4 [0 0 2] [4 3 1]
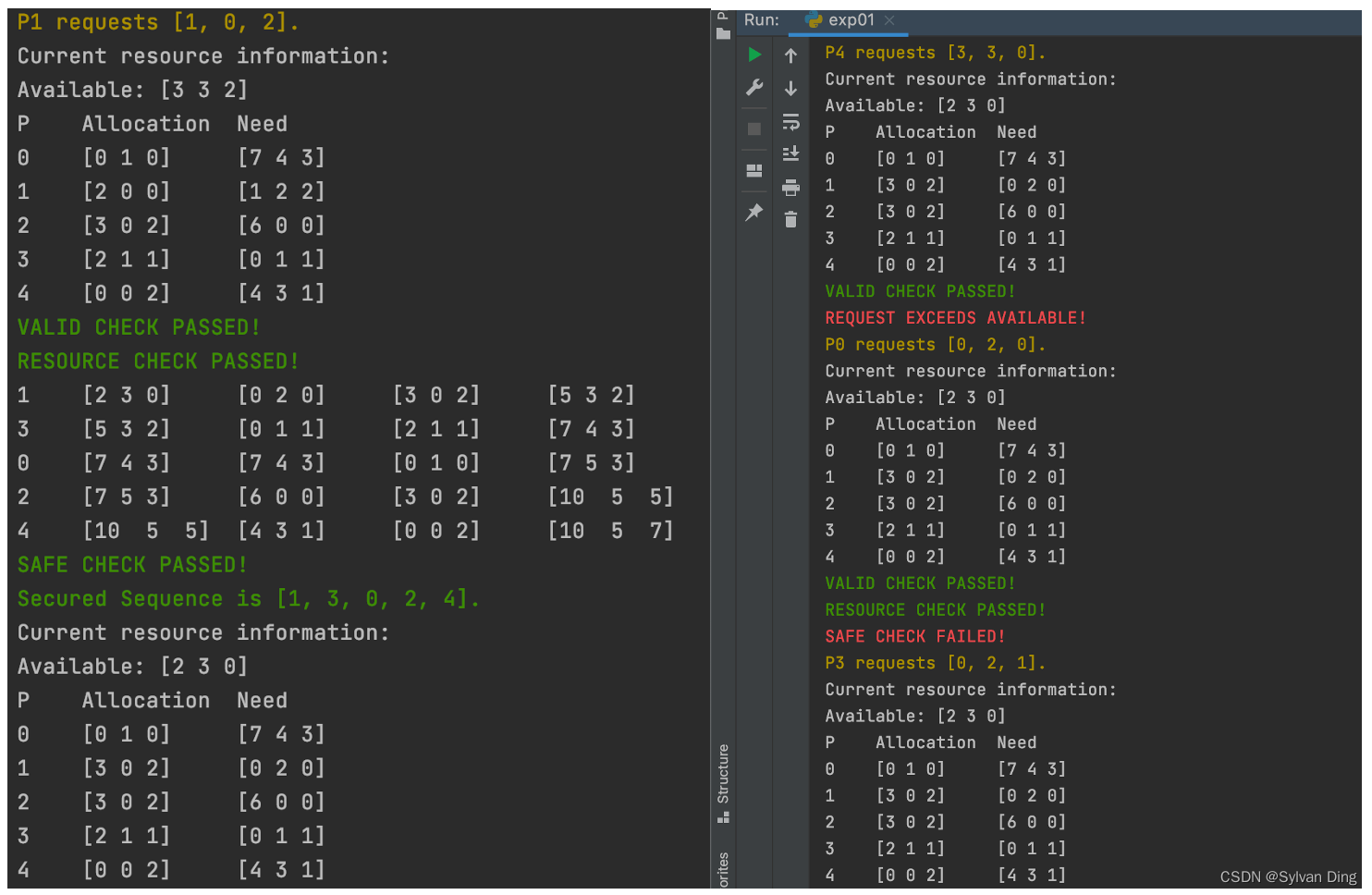
(1)P1请求资源,Request1 = [1, 0, 2]
✅VALID CHECK PASSED!
✅RESOURCE CHECK PASSED!
通过合法性和资源检查,假定为P1分配资源,然后进行安全性检查:
P Work Need Allocation Work+Allocation
1 [2 3 0] [0 2 0] [3 0 2] [5 3 2]
3 [5 3 2] [0 1 1] [2 1 1] [7 4 3]
0 [7 4 3] [7 4 3] [0 1 0] [7 5 3]
2 [7 5 3] [6 0 0] [3 0 2] [10 5 5]
4 [10 5 5] [4 3 1] [0 0 2] [10 5 7]
✅SAFE CHECK PASSED!
Secured Sequence is [1, 3, 0, 2, 4].
通过安全性检查,为P1分配资源,输出当前资源分配信息:
Available: [2 3 0]
P Allocation Need
0 [0 1 0] [7 4 3]
1 [3 0 2] [0 2 0]
2 [3 0 2] [6 0 0]
3 [2 1 1] [0 1 1]
4 [0 0 2] [4 3 1]
(2)T1时刻,P4继续请求资源:
Request4 = [3, 3, 0]
✅VALID CHECK PASSED!
⭕️REQUEST EXCEEDS AVAILABLE!
Request4<=Need[4],但Request4>Available,资源检查失败,P4等待分配资源
(3)T2时刻,P0请求资源:
Request0 = [0, 2, 0]
✅VALID CHECK PASSED!
✅RESOURCE CHECK PASSED!
⭕️SAFE CHECK FAILED!
通过合法性和资源检验,假设为P0分配资源,此时Available不满足银行家算法,安全性检验失败,若为P0分配资源会导致死锁,故返回原始状态。
(4)T3时刻,P3请求资源:
Request3 = [0, 2, 1]
⭕️Exception: ERROR!P3 REQUEST EXCEEDS ITS NEED!
报错,因为请求资源大于了需求量!
附录:代码
# @Sylvan Ding 2022.05.31import numpy as npdef err(P):raise Exception("ERROR!P{} REQUEST EXCEEDS ITS NEED!".format(P))def valid_check(P, Request, Need):if np.sum(Request > Need[P, :]):err(P)print("\033[0;32mVALID CHECK PASSED!\033[0m")def resource_check(Request, Available):if np.sum(Request > Available):print("\033[0;31mREQUEST EXCEEDS AVAILABLE!\033[0m")return Falseelse:print("\033[0;32mRESOURCE CHECK PASSED!\033[0m")return Truedef safe_check(Work, Need, Allocation, n):Q = []while True:i = 0while i < n:if i not in Q and not np.sum(Need[i, :] > Work):Q.append(i)temp = Work.copy()Work = Work + Allocation[i, :]print_safe_check(i, temp, Need, Allocation, Work)breaki = i + 1if i == n:breakif len(Q) < n:print("\033[0;31mSAFE CHECK FAILED!\033[0m")return Falseelse:print("\033[0;32mSAFE CHECK PASSED!\nSecured Sequence is {}.\033[0m".format(Q))return Truedef try_allocate(Available, Allocation, Need, Request, P):Available = Available - RequestAllocation[P, :] = Allocation[P, :] + RequestNeed[P, :] = Need[P, :] - Requestreturn Available, Need, Allocationdef print_safe_check(k, Work, Need, Allocation, Work_Allocation):print("{}\t {}\t {}\t {}\t {}".format(k,Work,Need[k, :],Allocation[k, :],Work_Allocation))def print_resource(Available, Need, Allocation, n):print("Current resource information: ")print("Available: {}".format(Available))print("P\t Allocation\t Need")for i in range(n):print("{}\t {}\t {}".format(i, Allocation[i, :], Need[i, :]))def print_request_info(P, Request):print("\033[0;33mP{} requests {}.\033[0m".format(P, Request))def Banker(n, Available, Max, Allocation, P, Request):""":param n: int:param Available: array[n][m]:param Max: array[n][m]:param Allocation: array[n][m]:param P: index of process to request:param Request: array[m]:return: Available, Need, Allocation"""print_request_info(P, Request)Available = np.asarray(Available)Max = np.asarray(Max)Allocation = np.asarray(Allocation)Request = np.asarray(Request)Need = Max - Allocationprint_resource(Available, Need, Allocation, n)valid_check(P, Request, Need)if (resource_check(Request, Available) andsafe_check(*try_allocate(Available.copy(),Allocation.copy(),Need.copy(),Request, P), n)):Available, Need, Allocation = try_allocate(Available.copy(),Allocation.copy(),Need.copy(),Request, P)print_resource(Available, Need, Allocation, n)return Available, Need, Allocationdef BankerAlgorithm():n = 5# m = 3Available = [3, 3, 2]Max = [[7, 5, 3],[3, 2, 2],[9, 0, 2],[2, 2, 2],[4, 3, 3]]Allocation = [[0, 1, 0],[2, 0, 0],[3, 0, 2],[2, 1, 1],[0, 0, 2]]P1 = 1Request1 = [1, 0, 2]Available, Need, Allocation = Banker(n, Available, Max, Allocation, P1, Request1)P4 = 4Request4 = [3, 3, 0]Available, Need, Allocation = Banker(n, Available, Max, Allocation, P4, Request4)P0 = 0Request0 = [0, 2, 0]Available, Need, Allocation = Banker(n, Available, Max, Allocation, P0, Request0)P3 = 3Request3 = [0, 2, 1]Banker(n, Available, Max, Allocation, P3, Request3)if __name__ == '__main__':BankerAlgorithm()原创文章:转载请注明出处 ©️ Sylvan Ding
参考文献
- 2023年操作系统考研复习指导/王道论坛考研组编.——北京:电子工业出版社,2021.12

,putchar()用法)
![[操作系统]页面置换算法实验及C++实现(OPT、FIFO、LRU)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[操作系统]页面置换算法实验及C++实现(OPT、FIFO、LRU))



![2020-2021学年(2)操作系统考试重点[华侨大学]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/2020-2021学年(2)操作系统考试重点[华侨大学])



)



:线性表的顺序存储结构)



![2021-2022学年编译原理考试重点[华侨大学]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/2021-2022学年编译原理考试重点[华侨大学])
