文章目录
- 1. BF(Brute Force)暴力匹配
- BF代码
- 2. RK(Rabin-Karp)算法
- RK代码
- 3. 思考题:(二维匹配)
1. BF(Brute Force)暴力匹配
BF算法的思想,在主串中,检查起始位置分别是0、1、2…n-m且长度为m的n-m+1个子串,看有没有跟模式串匹配的。最坏情况下每次都要对比m个字符,对比次数n-m+1次,复杂度O(m*n),适用小规模字符串匹配

BF代码
/*** @description: BF暴力匹配* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/6/17 20:11* @modified by: */
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int str_BFM(string s, int pos, string t)
{if(s.length()== 0 || t.length() == 0)return 0;int i = pos - 1, j = 0;while(i < s.length() && j < t.length()){if(s[i] == t[j]){i++;j++;}else//字符串匹配失败,主串查找开始位置i+1,模式串从头开始{i = i - j + 1;j = 0;}}if(j >= t.length())return i-j+1;elsereturn 0;
}
int main()
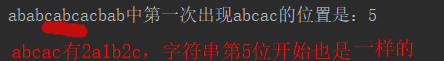
{string a = "ababcabcacbab", b = "abcac";cout << a << "中第一次出现" << b << "的位置是:" << str_BFM(a,1,b) << endl;return 0;
}

2. RK(Rabin-Karp)算法
- 上面BF算法,每次检查主串与子串是否匹配,需要逐次对比每个字符
- 引入哈希,降低复杂度
- RK算法思路:对n-m+1个子串分别求哈希值,然后与模式串的哈希值比较;如果某个子串的哈希值和模式串的哈希值匹配(需要考虑哈希冲突),比较数字是否相等是非常快的,所以效率比BF效率高

- But, 计算子串的哈希值的时候,需要遍历每个字符;虽然比较效率高了,但是整体效率没有提高
- 哈希算法设计技巧:K进制数表示子串(无冲突)(K为字符集内字符种数)
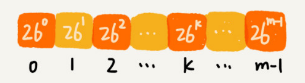
- K进制法,相邻子串的哈希值计算公式有一定的关系:


- 26(m-1)可以提前算好存放在数组中,指数就是数组的下标,计算26的x次方时,直接去数组下标x位置读取
- 复杂度,计算子串哈希值需要扫描一遍主串O(n);比较n-m+1个子串哈希值O(n);所以整体复杂度O(n)(取决于哈希函数冲突概率)
- 问题:如果模式串很长,子串的哈希值很大,超过计算机可表示的范围,怎么办?
针对哈希值范围溢出,改造哈希函数:
(1) 将a对应1,以此类推z对应26,将字符串每个字符对应数字相加作为哈希值,值的范围小了 (但是冲突概率有点大)
(2) 将每个字符对应一个质数(冲突概率降低) - 存在冲突的情况下,如果模式串和子串哈希值相等,再比较一下它两真的相等否。
- 哈希算法冲突概率要比较低,否则RK算法复杂度退化,效率下降
RK代码
/*** @description:RK匹配算法,计算子串哈希值,进行对比* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/6/17 22:40* @modified by: */
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool same(char* a, char* b, int m)
{for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){if(a[i] != b[i])return false;}return true;
}
int str_RK(string s, string t)//s是主串,t是模式串
{int n = s.length(), m = t.length();int table[26] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43,47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101};//质数表对应a-zint i, j, hash_val, value = 0;for(i = 0; i < m; ++i) //计算模式串的hash值value{value += table[t[i]-'a'];}for(i = 0; i < n-m+1; ++i)//最多n-m+1次比较{hash_val = 0;for(j = i; j < m+i; ++j)//计算第i个子串的哈希值{hash_val += table[s[j]-'a'];}if(hash_val == value && same(&s[i],&t[0],m)){//如果子串哈希值等于模式串的,且"真的"字符串匹配(避免冲突带来的假匹配)return i+1;//返回匹配位置,第i位开始,i从1开始}}return 0;
}
int main()
{string a = "ababcabcacbab", b = "abcac";cout << a << "中第一次出现" << b << "的位置是:" << str_RK(a,b) << endl;return 0;
}

如果不检查冲突,删除以下条件,匹配会出错
same(&s[i],&t[0],m)
3. 思考题:(二维匹配)

对RK算法进行改造得到答案
nr 主串行数
nc 主串列数
mr 模式串行数
mc 模式串列数
复杂度则为O((nr-mr+1)*(nc-mc+1)),简写为O(nr * nc)
/*** @description: 2维字符串匹配* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/6/18 0:07* @modified by: */
#include <iostream>
#define nr 5 //主串行数
#define nc 5 //主串列数
#define mr 2 //模式串行数
#define mc 2 //模式串列数
int cal_hash_t(int* table, int r, int c, char ch[][mc])
{int i, j, value = 0;for (i = 0; i < r; ++i) //计算2d模式串的hash值value{for(j = 0; j < c; ++j)value += table[ch[i][j]-'a'];}return value;
}
int cal_hash_s_child(int* table, int i0, int j0, int r, int c, char ch[][nc])
{int i, j, hash_value = 0;for (i = i0; i < r; ++i) //计算2d子串的hash值value{for(j = j0; j < c; ++j)hash_value += table[ch[i][j]-'a'];}return hash_value;
}
bool same(char s[][nc], char t[][mc], int i0, int j0)
{int x = i0, y = j0, i, j;for(i = 0; i < mr; ++i,++x){for(j = 0, y = j0; j < mc; ++j,++y)//记得写y=j0,换行后y复位{if(s[x][y] != t[i][j])return false;}}return true;
}
bool str_RK_2d(char s[][nc], char t[][mc])//s是主串,t是模式串
{int table[26] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43,47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101};//质数表对应a-zint i, j, hash_val, value;value = cal_hash_t(table,mr,mc,t);//计算2d模式串哈希值for(i = 0; i < nr-mr+1; ++i)//行最多nr-mr+1次比较{for(j = 0; j < nc-mc+1; ++j)//列最多nc-mc+1次比较{hash_val = cal_hash_s_child(table,i,j,mr+i,mc+j,s);//计算2d子串哈希值if(hash_val == value && same(s,t,i,j)){//如果2d子串哈希值等于模式串的,且"真的"字符串匹配(避免冲突带来的假匹配)std::cout << "找到模式矩阵,其左上角在 " << i+1 << " 行," << j+1 << " 列." << std::endl;return true;}}}return false;
}int main()
{char s[ ][nc] = {{ 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a' },{ 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a' },{ 'a', 'b', 'b', 'a', 'a' },{ 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'b' },{ 'b', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a' }};char t[ ][mc] = {{ 'a', 'b' },{ 'b', 'a' }};str_RK_2d(s,t);char a[ ][nc] = {{ 'd', 'a', 'b', 'c' },{ 'e', 'f', 'a', 'd' },{ 'c', 'c', 'a', 'f' },{ 'd', 'e', 'f', 'c' },{ 'b', 'b', 'a', 'b' }};char b[ ][mc] = {{ 'c', 'a' },{ 'e', 'f' }};str_RK_2d(a,b);return 0;
}






:事务+List集合+慢查询SQL+Redis+秒杀设计)
)
)


落地的思考)
:Redis缓存的设计、性能、应用与数据集群同步)

)
)


)

:Redis的内存回收原理,及内存过期淘汰策略详解)
)
)