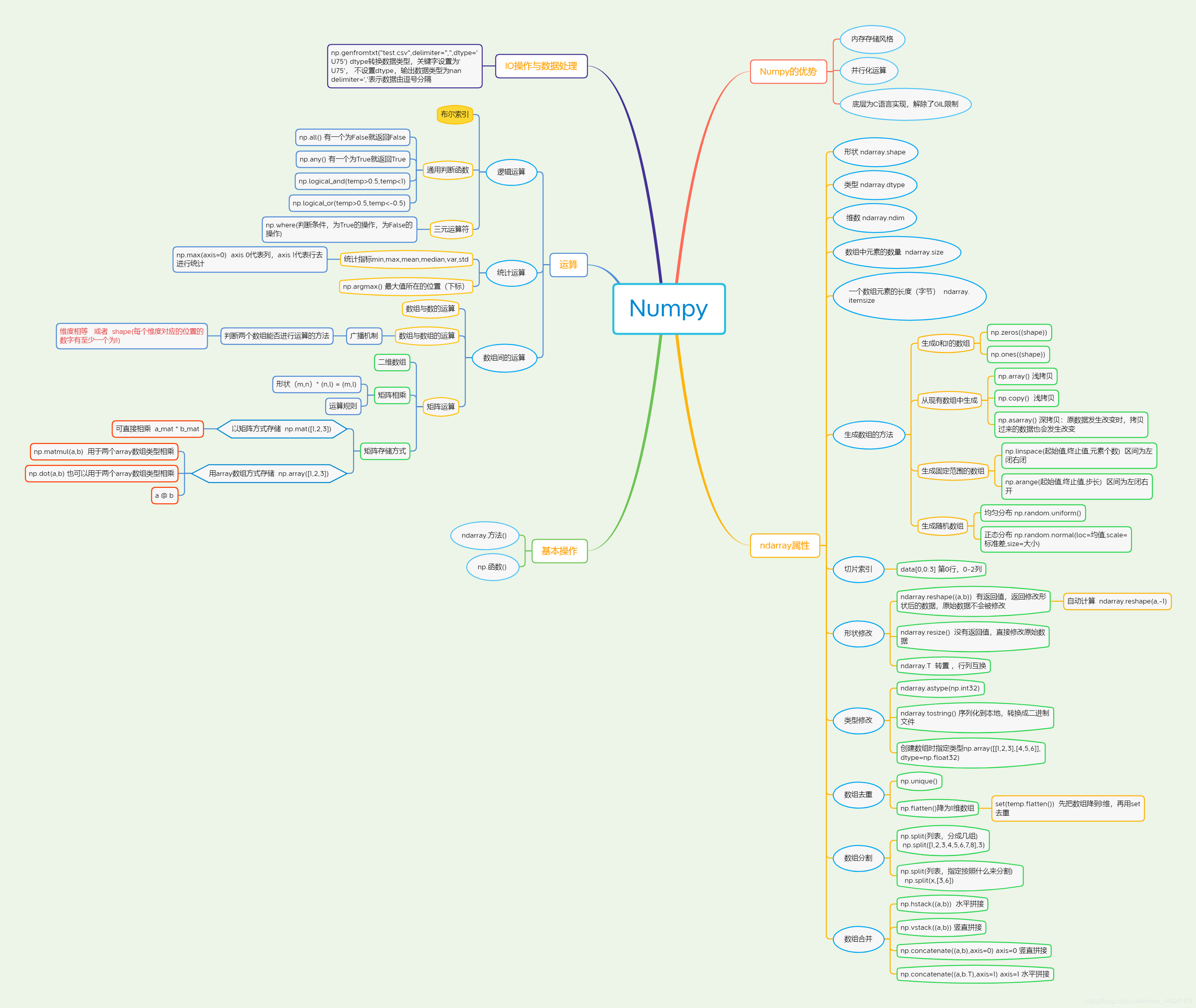
3.1.2 ndarray介绍
点击标题即可获取文章的源代码和笔记
Numpy 高效的运算工具
Numpy的优势
ndarray属性
基本操作ndarray.方法()numpy.函数名()
ndarray运算逻辑运算统计运算数组间运算
合并、分割、IO操作、数据处理3.1 Numpy优势3.1.1 Numpy介绍 - 数值计算库num - numerical 数值化的py - pythonndarrayn - 任意个d - dimension 维度array - 数组3.1.2 ndarray介绍3.1.3 ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比3.1.4 ndarray的优势1)存储风格ndarray - 相同类型 - 通用性不强list - 不同类型 - 通用性很强2)并行化运算ndarray支持向量化运算3)底层语言C语言,解除了GIL
3.2 认识N维数组-ndarray属性3.2.1 ndarray的属性shapendimsizedtypeitemsize在创建ndarray的时候,如果没有指定类型默认整数 int64浮点数 float643.2.2 ndarray的形状[1, 2, 3, 4][[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4]][[[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4]],[[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4]],[[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4],[1, 2, 3, 4]]]3.2.3 ndarray的类型
3.3 基本操作adarray.方法()np.函数名()np.array()3.3.1 生成数组的方法1)生成0和1np.zeros(shape)np.ones(shape)2)从现有数组中生成np.array() np.copy() 深拷贝np.asarray() 浅拷贝3)生成固定范围的数组np.linspace(0, 10, 100)[0, 10] 等距离np.arange(a, b, c)range(a, b, c)[a, b) c是步长4)生成随机数组分布状况 - 直方图1)均匀分布每组的可能性相等2)正态分布σ 幅度、波动程度、集中程度、稳定性、离散程度3.3.2 数组的索引、切片3.3.3 形状修改ndarray.reshape(shape) 返回新的ndarray,原始数据没有改变ndarray.resize(shape) 没有返回值,对原始的ndarray进行了修改ndarray.T 转置 行变成列,列变成行3.3.4 类型修改ndarray.astype(type)ndarray序列化到本地ndarray.tostring()3.3.5 数组的去重set()
3.4 ndarray运算逻辑运算布尔索引通用判断函数np.all(布尔值)只要有一个False就返回False,只有全是True才返回Truenp.any()只要有一个True就返回True,只有全是False才返回Falsenp.where(三元运算符)np.where(布尔值, True的位置的值, False的位置的值)统计运算统计指标函数min, max, mean, median, var, stdnp.函数名ndarray.方法名返回最大值、最小值所在位置np.argmax(temp, axis=)np.argmin(temp, axis=)数组间运算3.5.1 场景3.5.2 数组与数的运算3.5.3 数组与数组的运算3.5.4 广播机制3.5.5 矩阵运算1 什么是矩阵矩阵matrix 二维数组矩阵 & 二维数组两种方法存储矩阵1)ndarray 二维数组矩阵乘法:np.matmulnp.dot2)matrix数据结构2 矩阵乘法运算形状(m, n) * (n, l) = (m, l)运算规则A (2, 3) B(3, 2)A * B = (2, 2)
3.6 合并、分割
3.7 IO操作与数据处理3.7.1 Numpy读取3.7.2 如何处理缺失值两种思路:直接删除含有缺失值的样本替换/插补按列求平均,用平均值进行填补import numpy as np# 创建ndarray
score = np.array([[80,89,86,67,79],
[78,97,89,67,81],
[90,94,78,67,74],
[91,91,90,67,69],
[76,87,75,67,86],
[70,79,84,67,84],
[94,92,93,67,64],
[86,85,83,67,80]])
score
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
type(score)
numpy.ndarray
3.1.3 ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比
import random
import time
import numpy as np# 生成一个大数组
a = []
for i in range(100000000):a.append(random.random())t1 = time.time()
sum1 = sum(a)
t2 = time.time()b = np.array(a)
t4 = time.time()
sum3 = np.sum(b)
t5 = time.time()print(t2-t1,t5-t4)
5.195146083831787 0.23642754554748535
3.2.1 ndarray的属性
score = np.array([[80,89,86,67,79],
[78,97,89,67,81],
[90,94,78,67,74],
[91,91,90,67,69],
[76,87,75,67,86],
[70,79,84,67,84],
[94,92,93,67,64],
[86,85,83,67,80]])type(score)
numpy.ndarray
score.dtype # 数组元素的类型
dtype('int32')
score.shape # 数组维度的元组
(8, 5)
score.ndim # 数组维数
2
score.size # 数组中元素的数量
40
score.itemsize # 一个数组元素的长度(字节)
4
3.2.2 ndarray的形状
#创建不同形状的数组
a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
b=np.array([1,2,3,4])
c=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]])
a
array([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]])
a.shape # 二维数组
(2, 3)
b
array([1, 2, 3, 4])
b.shape # 一维数组
(4,)
c
array([[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]],[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]])
c.shape # 三维数组
(2, 2, 3)
3.2.3 ndarray的类型
data = np.array([1.1,2.2,3.3])
data.dtype
dtype('float64')
创建数组的时候指定类型
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],dtype=np.float32)
# a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],dtype='float32')
a.dtype
dtype('float32')
arr = np.array(['python','tensorflow','scikit-learn','numpy'],dtype=np.string_)
arr
array([b'python', b'tensorflow', b'scikit-learn', b'numpy'], dtype='|S12')
3.3基本操作
1.生成0和1的数组
zero = np.zeros([3,4])
zero
array([[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
zero = np.zeros((3,4))
zero
array([[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
one = np.ones([3,4])
# one = np.ones((3,4))
one
array([[1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
np.ones(shape=[3,4],dtype=np.int32)
array([[1, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 1, 1]])
2.从现有数组生成
score
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
data1 = np.array(score) # 深拷贝
data1
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
data2 = np.asarray(score) # 浅拷贝 ,原数据发生修改后,也会跟着进行修改
data2
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
data3 = np.copy(score) # 深拷贝
data3
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
score[3,1]
91
score[3,1] = 100000
data1
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
data2 # 原数组数据修改后,也会跟着发生变化
array([[ 80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[ 78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[ 90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[ 91, 100000, 90, 67, 69],[ 76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[ 70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[ 94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[ 86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
data3
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
3.生成固定范围的数组
np.linspace(0,10,5) # 左闭右闭 ,等差数列范围在【0,10,个数】,个数为5个
array([ 0. , 2.5, 5. , 7.5, 10. ])
for i in range(0,10,1):print(i)
# range(0,10,1) 左闭右开 【0,10,步长)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
np.arange(0,10,1) # 左闭右开 【0,10,步长)
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
4.生成随机数组
# 生成均匀分布的随机数
x1 = np.random.uniform(-1,1,100000) # uniform(起始值,终点值,个数)
x1
array([ 0.55046079, 0.37804729, -0.89677218, ..., 0.35451722,0.34995045, 0.01961797])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline# 1. 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=100)# 2. 绘制直方图
plt.hist(x1,1000)# 3. 显示图像
plt.show()![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Ao4iqGGx-1592826766291)(output_47_0.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200622195326852.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NDgyNzQxOA==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 生成正态分布的随机数(标准正态分布均值为0,方差为1)
# loc 均值 ,scale 标准差
data4 = np.random.normal(loc=1.75,scale=0.1,size=1000000)
data4
array([1.82548844, 1.91684274, 1.48534258, ..., 1.75064937, 1.8181808 ,1.81005547])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline# 1. 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=100)# 2. 绘制直方图
plt.hist(data4,1000)# 3. 显示图像
plt.show()![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-OXyqKvdX-1592826766294)(output_49_0.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200622195338247.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NDgyNzQxOA==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
案例:随机生成8只股票2周的交易日涨幅数据
8只股票,两周(10天)的涨跌幅数据,如何获取?
-
两周的交易日数量为:2 * 5=10
-
随机生成涨跌幅在某个正态分布内,比如均值0,方差1
stock_change = np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=(8,10))
stock_change
array([[-0.61330497, 0.55840141, 0.41709496, 1.27999683, -1.00183693,1.19508749, -1.30481202, -0.32462183, 0.1629303 , -0.37215778],[-0.67655708, -0.24960482, -0.26775897, -1.54340984, -1.7202066 ,1.38874363, -0.0149956 , 0.66870059, -0.04502848, 0.63144735],[-0.28952395, -1.70484263, 0.61871199, 0.61306774, 0.22872944,1.1493577 , 2.48623902, 0.18940315, -0.44105589, 1.49241966],[ 0.33087272, -0.67879541, -0.6040623 , -1.20256264, -0.76551783,1.31036346, -0.46289576, -0.44254887, -0.20934797, 0.13978528],[ 0.58783968, -2.67898464, -1.41139208, 1.07009707, -2.23082484,0.69616862, 0.38991086, -1.10458314, -1.85230749, -1.59066425],[ 1.46959111, -0.91715307, 0.08142567, 2.86350894, 0.83436522,-2.01224295, -0.28835842, -1.28407105, 1.52191189, -0.09642856],[-0.82991129, 0.83983885, -1.10666366, 0.06332958, 0.42674457,1.491716 , -0.81436095, -0.85603011, 0.72720565, -2.60215313],[ 0.42427358, 0.81760609, 2.48509044, 0.41373531, -0.5184894 ,0.76798932, 0.01676593, -1.35196338, 1.216088 , 0.39931822]])
3.3.2数组的索引、切片
- 获取第一个股票的前3个交易日的涨跌幅数据
stock_change[0,0:3]
array([-0.61330497, 0.55840141, 0.41709496])
一维、二维、三维的数组如何索引?
a1=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[12,3,34],[5,6,7]]])
a1
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],[ 4, 5, 6]],[[12, 3, 34],[ 5, 6, 7]]])
a1.shape
(2, 2, 3)
a1[1,0,2]
34
a1[1,0,2] = 1000000
a1
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],[ 4, 5, 6]],[[ 12, 3, 1000000],[ 5, 6, 7]]])
3.3.3形状修改
需求:让刚才的股票行、日期列反过来,变成日期行,股票列
stock_change.shape
(8, 10)
stock_change
array([[-0.61330497, 0.55840141, 0.41709496, 1.27999683, -1.00183693,1.19508749, -1.30481202, -0.32462183, 0.1629303 , -0.37215778],[-0.67655708, -0.24960482, -0.26775897, -1.54340984, -1.7202066 ,1.38874363, -0.0149956 , 0.66870059, -0.04502848, 0.63144735],[-0.28952395, -1.70484263, 0.61871199, 0.61306774, 0.22872944,1.1493577 , 2.48623902, 0.18940315, -0.44105589, 1.49241966],[ 0.33087272, -0.67879541, -0.6040623 , -1.20256264, -0.76551783,1.31036346, -0.46289576, -0.44254887, -0.20934797, 0.13978528],[ 0.58783968, -2.67898464, -1.41139208, 1.07009707, -2.23082484,0.69616862, 0.38991086, -1.10458314, -1.85230749, -1.59066425],[ 1.46959111, -0.91715307, 0.08142567, 2.86350894, 0.83436522,-2.01224295, -0.28835842, -1.28407105, 1.52191189, -0.09642856],[-0.82991129, 0.83983885, -1.10666366, 0.06332958, 0.42674457,1.491716 , -0.81436095, -0.85603011, 0.72720565, -2.60215313],[ 0.42427358, 0.81760609, 2.48509044, 0.41373531, -0.5184894 ,0.76798932, 0.01676593, -1.35196338, 1.216088 , 0.39931822]])
reshape_stock_change = stock_change.reshape((10,8))
reshape_stock_change.shape# reshape(10,8)返回新的ndarray,但是没有修改原始的数据,只是修改了数组的形状,但并没有让数组的行列进行互换,只是把数组单纯的重新进行了切割
(10, 8)
reshape_stock_change
array([[-0.61330497, 0.55840141, 0.41709496, 1.27999683, -1.00183693,1.19508749, -1.30481202, -0.32462183],[ 0.1629303 , -0.37215778, -0.67655708, -0.24960482, -0.26775897,-1.54340984, -1.7202066 , 1.38874363],[-0.0149956 , 0.66870059, -0.04502848, 0.63144735, -0.28952395,-1.70484263, 0.61871199, 0.61306774],[ 0.22872944, 1.1493577 , 2.48623902, 0.18940315, -0.44105589,1.49241966, 0.33087272, -0.67879541],[-0.6040623 , -1.20256264, -0.76551783, 1.31036346, -0.46289576,-0.44254887, -0.20934797, 0.13978528],[ 0.58783968, -2.67898464, -1.41139208, 1.07009707, -2.23082484,0.69616862, 0.38991086, -1.10458314],[-1.85230749, -1.59066425, 1.46959111, -0.91715307, 0.08142567,2.86350894, 0.83436522, -2.01224295],[-0.28835842, -1.28407105, 1.52191189, -0.09642856, -0.82991129,0.83983885, -1.10666366, 0.06332958],[ 0.42674457, 1.491716 , -0.81436095, -0.85603011, 0.72720565,-2.60215313, 0.42427358, 0.81760609],[ 2.48509044, 0.41373531, -0.5184894 , 0.76798932, 0.01676593,-1.35196338, 1.216088 , 0.39931822]])
stock_change.resize((10,8)) # resize((10,8)) 没有返回值,直接对原始的ndarray进行了修改
# 效果和 reshape()一样,只是修改了数组的形状,但并没有让数组的行列进行互换,只是把数组单纯的重新进行了切割
stock_change
array([[-0.61330497, 0.55840141, 0.41709496, 1.27999683, -1.00183693,1.19508749, -1.30481202, -0.32462183],[ 0.1629303 , -0.37215778, -0.67655708, -0.24960482, -0.26775897,-1.54340984, -1.7202066 , 1.38874363],[-0.0149956 , 0.66870059, -0.04502848, 0.63144735, -0.28952395,-1.70484263, 0.61871199, 0.61306774],[ 0.22872944, 1.1493577 , 2.48623902, 0.18940315, -0.44105589,1.49241966, 0.33087272, -0.67879541],[-0.6040623 , -1.20256264, -0.76551783, 1.31036346, -0.46289576,-0.44254887, -0.20934797, 0.13978528],[ 0.58783968, -2.67898464, -1.41139208, 1.07009707, -2.23082484,0.69616862, 0.38991086, -1.10458314],[-1.85230749, -1.59066425, 1.46959111, -0.91715307, 0.08142567,2.86350894, 0.83436522, -2.01224295],[-0.28835842, -1.28407105, 1.52191189, -0.09642856, -0.82991129,0.83983885, -1.10666366, 0.06332958],[ 0.42674457, 1.491716 , -0.81436095, -0.85603011, 0.72720565,-2.60215313, 0.42427358, 0.81760609],[ 2.48509044, 0.41373531, -0.5184894 , 0.76798932, 0.01676593,-1.35196338, 1.216088 , 0.39931822]])
stock_change.shape
(10, 8)
stock_change.T # 转置,行列互换
array([[-0.61330497, 0.1629303 , -0.0149956 , 0.22872944, -0.6040623 ,0.58783968, -1.85230749, -0.28835842, 0.42674457, 2.48509044],[ 0.55840141, -0.37215778, 0.66870059, 1.1493577 , -1.20256264,-2.67898464, -1.59066425, -1.28407105, 1.491716 , 0.41373531],[ 0.41709496, -0.67655708, -0.04502848, 2.48623902, -0.76551783,-1.41139208, 1.46959111, 1.52191189, -0.81436095, -0.5184894 ],[ 1.27999683, -0.24960482, 0.63144735, 0.18940315, 1.31036346,1.07009707, -0.91715307, -0.09642856, -0.85603011, 0.76798932],[-1.00183693, -0.26775897, -0.28952395, -0.44105589, -0.46289576,-2.23082484, 0.08142567, -0.82991129, 0.72720565, 0.01676593],[ 1.19508749, -1.54340984, -1.70484263, 1.49241966, -0.44254887,0.69616862, 2.86350894, 0.83983885, -2.60215313, -1.35196338],[-1.30481202, -1.7202066 , 0.61871199, 0.33087272, -0.20934797,0.38991086, 0.83436522, -1.10666366, 0.42427358, 1.216088 ],[-0.32462183, 1.38874363, 0.61306774, -0.67879541, 0.13978528,-1.10458314, -2.01224295, 0.06332958, 0.81760609, 0.39931822]])
stock_change.T.shape
(8, 10)
3.3.4类型修改
stock_change.astype(np.int32)
array([[ 0, 0, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0],[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, 1],[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0],[ 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],[ 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],[ 0, -2, -1, 1, -2, 0, 0, -1],[-1, -1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, -2],[ 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0],[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, -2, 0, 0],[ 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0]])
type(stock_change)
numpy.ndarray
# 序列化,转换成bytes
stock_change.tostring()
b'\x9a\xa38\xc11\xa0\xe3\xbf\x10\xa0\t\xa3l\xde\xe1?9\xfaO\x11\xaf\xb1\xda?~\xd3\xf4\xf3\xddz\xf4?\x0f\xae\xd2)\x86\x07\xf0\xbfO\xfb\x1b\x10\x14\x1f\xf3?\xd0d\x18\x92\x82\xe0\xf4\xbf\x0c+\xc2\xa0\x9a\xc6\xd4\xbf\xdd\xfb{f\xe6\xda\xc4?\xc3\xa8\xec\xdbn\xd1\xd7\xbf\xe3\xb0z\t[\xa6\xe5\xbf\xb3\x9b\x01\xf5\x0c\xf3\xcf\xbf\xdd\xeeL\x83\xf6"\xd1\xbf\xc5\xff\xd5\x84\xce\xb1\xf8\xbf\xcd\x92\xd6Y\xf7\x85\xfb\xbf\x1d#\xde>K8\xf6?[-\x15\xa2\x03\xb6\x8e\xbfC\xde \xc7\xfee\xe5?\xbb\x166\xeb\xf8\r\xa7\xbf|\xfd\xcb\x11\xd14\xe4?^\x9e\xdcr\x8f\x87\xd2\xbf\xfe\xa6\n\x12\tG\xfb\xbfa\xfc\xfe\x15}\xcc\xe3?S\xec\xb4>@\x9e\xe3?\x17y\xbb\x9d\x01G\xcd?,c\xe2\xe5\xc4c\xf2?\xa7\x1f,H\xd1\xe3\x03@;\x0e\x9f\xc5\\>\xc8?P\xc1\xcbyB:\xdc\xbf "\xc3o\xf3\xe0\xf7?\x7fx\x8d\xc4\x04-\xd5?\x13BP\'\xb1\xb8\xe5\xbfw3\xdauzT\xe3\xbfb\x0cQQ\xb2=\xf3\xbf\x07\xd4\xee>\x1f\x7f\xe8\xbf\xcd\xf4\t\xae?\xf7\xf4?G\xb3b\x8a\x15\xa0\xdd\xbf\xe9IV\x83\xb8R\xdc\xbf\xc7\x88\x96\x03\xea\xcb\xca\xbf\xc4q\xaf\xe1{\xe4\xc1?\x03$o(\x95\xcf\xe2?l\xb3\xa9\x7f\x8fn\x05\xc0NX/\xdc\x0f\x95\xf6\xbf\xbc\x0e"\x1b\x1e\x1f\xf1?C\xe7\xf7\xb0\xba\xd8\x01\xc0\xdaKPg\x03G\xe6?/J\xbb\xa9L\xf4\xd8?\x7fV\x11`_\xac\xf1\xbf\x7f\x94\xdf-\r\xa3\xfd\xbf\xb1\xe0~\\\\s\xf9\xbfl\xb7\n\xf8q\x83\xf7?4H\xe5fQY\xed\xbf\xdde\x96\x18P\xd8\xb4?\x02\x0c\x1c`w\xe8\x06@\xe8j\x9a\xb1\x1e\xb3\xea?R\'D\xd5\x12\x19\x00\xc0]B\xc7\xdbvt\xd2\xbf<\xcc\xf5\x16\x8e\x8b\xf4\xbfK\xdc)H\xc0Y\xf8?r\xc7\xbc\xba\x8a\xaf\xb8\xbf`\xd5i \xa2\x8e\xea\xbf\x9d\x0b.\xb9\xf5\xdf\xea?\x81\xa6\x16\xf4\xe4\xb4\xf1\xbfEq\xf7\xf6]6\xb0?\xf7\x16_r\xc8O\xdb?\x80\xe8\x18\x99\x11\xde\xf7?\x04M\x16\xb1>\x0f\xea\xbf`\x85\x83D\x99d\xeb\xbf\xe0\x1e\xad\xcaDE\xe7?\xe6\xe6\x9c\xa85\xd1\x04\xc0\x90t\xebaL\'\xdb?5w\xc0@\xd4)\xea?\xce\xbe>\x19w\xe1\x03@\x94q\xdc\xab\xa3z\xda?\x08\xc0/\x16w\x97\xe0\xbf\t_)V^\x93\xe8??\x82\xfb\x82\x16+\x91?\x10\x87\xf3Z\xa4\xa1\xf5\xbf\xd3\x8cX\xb1\x18u\xf3?\xdf\xc5\xb3\xffm\x8e\xd9?'
3.3.5数组的去重
temp = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6]])
temp
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],[3, 4, 5, 6]])
np.unique(temp)
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
temp.flatten() # 降为1维数组
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 6])
type(temp.flatten())
numpy.ndarray
set(temp.flatten()) # 再用set去重
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
3.4 ndarray运算
3.4.1 逻辑运算
stock_change = np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=(8,10))
stock_change
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 2.42922844, -0.70687122,0.58481125, 0.55148057, 1.28943409, -1.44445438, 0.87934969],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.63806518, 1.17037384,-0.44528328, 1.23718753, -1.08925098, -0.26050859, -0.69753153],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 0.81108448, -0.66006311,-0.15948853, 1.58475241, -0.81268957, -1.45337789, -0.06213791],[ 0.45162183, 0.55933576, -0.065766 , -0.40962168, 2.08206249,-0.84223895, -0.57720066, 1.79367669, -0.97694251, -0.33250153],[ 0.60649904, -0.59661935, -0.90621156, 1.79910292, -1.20565147,0.08852257, -0.99133308, 0.96236294, -0.9192948 , -0.03587398],[ 0.43325825, 0.48811556, 1.12822497, -1.27967886, 0.7919012 ,-0.38423972, 0.72962012, 1.74817488, 1.56455728, -1.72640669],[-0.38688515, 0.40048111, 2.51085027, -0.61192208, 0.70982823,-0.14795647, 0.30593344, -0.06915128, -1.34996629, -1.08573709],[-0.04277865, 0.60692697, 0.90975811, -0.5889982 , 0.25598235,-0.88764388, 0.10974295, 0.45449013, -1.03761231, -2.7914244 ]])
# 逻辑判断,如果涨跌幅大于0.5就标记为True,否则标记为False
stock_change>0.5
array([[False, False, False, True, False, True, True, True, False,True],[False, False, False, True, True, False, True, False, False,False],[False, False, False, True, False, False, True, False, False,False],[False, True, False, False, True, False, False, True, False,False],[ True, False, False, True, False, False, False, True, False,False],[False, False, True, False, True, False, True, True, True,False],[False, False, True, False, True, False, False, False, False,False],[False, True, True, False, False, False, False, False, False,False]])
stock_change[stock_change>0.5] # 布尔索引
array([2.42922844, 0.58481125, 0.55148057, 1.28943409, 0.87934969,1.63806518, 1.17037384, 1.23718753, 0.81108448, 1.58475241,0.55933576, 2.08206249, 1.79367669, 0.60649904, 1.79910292,0.96236294, 1.12822497, 0.7919012 , 0.72962012, 1.74817488,1.56455728, 2.51085027, 0.70982823, 0.60692697, 0.90975811])
stock_change[stock_change>0.5] = 1.1
stock_change
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 , -0.70687122,1.1 , 1.1 , 1.1 , -1.44445438, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 , 1.1 ,-0.44528328, 1.1 , -1.08925098, -0.26050859, -0.69753153],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 , -0.66006311,-0.15948853, 1.1 , -0.81268957, -1.45337789, -0.06213791],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168, 1.1 ,-0.84223895, -0.57720066, 1.1 , -0.97694251, -0.33250153],[ 1.1 , -0.59661935, -0.90621156, 1.1 , -1.20565147,0.08852257, -0.99133308, 1.1 , -0.9192948 , -0.03587398],[ 0.43325825, 0.48811556, 1.1 , -1.27967886, 1.1 ,-0.38423972, 1.1 , 1.1 , 1.1 , -1.72640669],[-0.38688515, 0.40048111, 1.1 , -0.61192208, 1.1 ,-0.14795647, 0.30593344, -0.06915128, -1.34996629, -1.08573709],[-0.04277865, 1.1 , 1.1 , -0.5889982 , 0.25598235,-0.88764388, 0.10974295, 0.45449013, -1.03761231, -2.7914244 ]])
3.4.2通用判断函数
stock_change[0:2,0:5]
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 , -0.70687122],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 , 1.1 ]])
# 判断stock_change[0:2,0:5]是否全是上涨的
np.all(stock_change[0:2,0:5] > 0)
# 只有有一个False就返回False,只有全都是True才返回True
False
stock_change[0:5,:]
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 , -0.70687122,1.1 , 1.1 , 1.1 , -1.44445438, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 , 1.1 ,-0.44528328, 1.1 , -1.08925098, -0.26050859, -0.69753153],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 , -0.66006311,-0.15948853, 1.1 , -0.81268957, -1.45337789, -0.06213791],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168, 1.1 ,-0.84223895, -0.57720066, 1.1 , -0.97694251, -0.33250153],[ 1.1 , -0.59661935, -0.90621156, 1.1 , -1.20565147,0.08852257, -0.99133308, 1.1 , -0.9192948 , -0.03587398]])
# 判断前5只股票这段期间是否有上涨的
np.any(stock_change[0:5,:] > 0)
# 只要有一个是True就返回True,全都是False才返回False
True
3.4.3 np.where(三元运算符)
stock_change[:4,:4]
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 ],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 ],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168]])
#判断前四个股票前四天的涨跌幅大于0的置为1,否则为0
temp=stock_change[:4,:4]
np.where(temp > 0 ,1 ,0)
array([[0, 0, 0, 1],[1, 0, 0, 1],[0, 0, 1, 1],[1, 1, 0, 0]])
temp
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 ],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 ],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168]])
#判断前四个服票前四天的涨跌幅大于0.5并且小于1的,换为1,否则为0
#判断前四个般票前四天的涨跌幅大于0.5或者小于-0.5的,换为1,否则为0np.logical_and(temp>0.5,temp<1)
array([[False, False, False, False],[False, False, False, False],[False, False, False, False],[False, False, False, False]])
np.where(np.logical_and(temp>0.5,temp<1),1,0)
array([[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0]])
np.logical_or(temp>0.5,temp<-0.5)
array([[ True, True, False, True],[False, True, True, True],[ True, True, False, True],[False, True, False, False]])
np.where(np.logical_or(temp>0.5,temp<-0.5),1,0)
array([[1, 1, 0, 1],[0, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 0, 1],[0, 1, 0, 0]])
3.4.4 统计运算
2.股票涨跌幅统计运算
进行统计的时候,axis轴的取值并不一定,Numpy中不同的API轴的值都不一样,在这里,axis 0代表列,axis 1代表行去进行统计
temp
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 ],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 ],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168]])
temp.max()
1.1
np.max(temp)
1.1
#接下来对于这4只股票的4天数据,进行一些统计运算
#指定行去统计
print("前四只股票前四天的是大涨幅{}".format(np.max(temp,axis=1)))
前四只股票前四天的是大涨幅[1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1]
#使用min,std,mean
print("前四只股票前四天的最大跌幅{}".format(np.min(temp,axis=1)))
前四只股票前四天的最大跌幅[-2.01191074 -1.43581686 -2.62254681 -0.40962168]
print("前四只股票前四天的波动程度{}".format(np.std(temp,axis=1)))
前四只股票前四天的波动程度[1.17480848 0.93619571 1.61034658 0.56932139]
print("前四只股票前四天的平均涨跌幅{})".format(np.mean(temp,axis=1)))
前四只股票前四天的平均涨跌幅[-0.59605545 -0.21193833 -0.91697138 0.26905854])
返回最大值、最小值所在位置
- np.argmax(temp,axis=)
- np.argmin(temp,axis=)
temp
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 ],[-2.36635008, -2.62254681, 0.22101136, 1.1 ],[ 0.45162183, 1.1 , -0.065766 , -0.40962168]])
np.argmax(temp, axis=1)
array([3, 3, 3, 1], dtype=int64)
np.argmax(temp, axis=-1)
array([3, 3, 3, 1], dtype=int64)
3.5.2 数组与数的运算
arr=np.array([[1,2,3,2,1,4],[5,6,1,2,3,111]])
arr
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4],[ 5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 111]])
arr + 10
array([[ 11, 12, 13, 12, 11, 14],[ 15, 16, 11, 12, 13, 121]])
arr * 10
array([[ 10, 20, 30, 20, 10, 40],[ 50, 60, 10, 20, 30, 1110]])
3.5.3 数组与数组的运算
arr1 = np.array([[1,2,3,2,1,4],[5,6,1,2,3,1]])
arr2 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6]])
arr1
array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4],[5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]])
arr2
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],[3, 4, 5, 6]])
arr1 + arr2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-93-d972d21b639e> in <module>
----> 1 arr1 + arr2ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (2,6) (2,4)
广播机制,判断两个数组能否进行运算的方法:
- 维度相等 或者
- shape(每个维度对应的位置为1)
arr1=np.array([[1,2,3,2,1,4],[5,6,1,2,3,1]])
arr2=np.array([[1],[3]])
arr1
array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4],[5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]])
arr1.shape
(2, 6)
arr2
array([[1],[3]])
arr2.shape
(2, 1)
arr1 + arr2
array([[2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 5],[8, 9, 4, 5, 6, 4]])
(arr1 + arr2).shape
(2, 6)
3.5.5 矩阵运算
# array存储矩阵
a=np.array([[80,86],[82,80],[85,78],[90,90],[86,82],[82,98],[78,80],[92,94]])
a
array([[80, 86],[82, 80],[85, 78],[90, 90],[86, 82],[82, 98],[78, 80],[92, 94]])
b = np.array([[0.3],[0.7]])
b
array([[0.3],[0.7]])
# matrix存储矩阵
a_mat = np.mat([[80,86],[82,80],[85,78],[90,90],[86,82],[82,98],[78,80],[92,94]])
a_mat
matrix([[80, 86],[82, 80],[85, 78],[90, 90],[86, 82],[82, 98],[78, 80],[92, 94]])
type(a_mat)
numpy.matrix
b_mat = np.mat([[0.3],[0.7]])
b_mat
matrix([[0.3],[0.7]])
a_mat * b_mat
matrix([[84.2],[80.6],[80.1],[90. ],[83.2],[93.2],[79.4],[93.4]])
type(a)
numpy.ndarray
np.matmul(a,b) # np.matmul(a,b)用于两个array数组类型相乘
array([[84.2],[80.6],[80.1],[90. ],[83.2],[93.2],[79.4],[93.4]])
np.dot(a,b) # np.dot(a,b) 也可以用于两个array数组类型相乘
array([[84.2],[80.6],[80.1],[90. ],[83.2],[93.2],[79.4],[93.4]])
a @ b
array([[84.2],[80.6],[80.1],[90. ],[83.2],[93.2],[79.4],[93.4]])
3.6 合并、分割
a = np.array((1,2,3))
a
array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array((2,3,4))
b
array([2, 3, 4])
3.6.1 合并
np.hstack((a,b)) # 水平拼接
array([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4])
a = np.array([1,2,3])
a
array([1, 2, 3])
a1 = np.array([[1],[2],[3]])
a1
array([[1],[2],[3]])
b1 = np.array([[2],[3],[4]])
b1
array([[2],[3],[4]])
np.hstack((a1,b1))
array([[1, 2],[2, 3],[3, 4]])
np.vstack((a,b)) # 竖直拼接
array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 3, 4]])
a=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
a
array([[1, 2],[3, 4]])
b=np.array([[5,6]])
b
array([[5, 6]])
np.concatenate((a,b),axis=0) # axis=0 竖直拼接
array([[1, 2],[3, 4],[5, 6]])
b.T
array([[5],[6]])
a
array([[1, 2],[3, 4]])
np.concatenate((a,b.T),axis=1) # axis=1 水平拼接
array([[1, 2, 5],[3, 4, 6]])
3.6.2 分割
x = np.arange(9.0)
x
array([0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8.])
np.split(x,3)
[array([0., 1., 2.]), array([3., 4., 5.]), array([6., 7., 8.])]
np.split(x,[3,6])
[array([0., 1., 2.]), array([3., 4., 5.]), array([6., 7., 8.])]
3.7 IO操作与数据处理
3.7.1 Numpy读取
data = np.genfromtxt("test.csv",delimiter=",",dtype='U75') # dtype转换数据类型,关键字设置为'U75', 不设置dtype,输出数据类型为nan
# delimiter=','表示数据由逗号分隔
data
array([['id', 'value1.value2', 'value3', ''],['1', '123', '1.4', '23'],['2', '110', '', '18'],['3', '', '2.1', '19']], dtype='<U75')
3.7.2 如何处理缺失值
data = np.genfromtxt("test.csv",delimiter=",")
data
array([[ nan, nan, nan, nan],[ 1. , 123. , 1.4, 23. ],[ 2. , 110. , nan, 18. ],[ 3. , nan, 2.1, 19. ]])
data[2,2]
nan
type(data[2,2])
numpy.float64
def fill_nan_by_column_mean(t):# 先遍历每一列for i in range(t.shape[1]):# 计算nan的个数nan_num = np.count_nonzero(t[:,i][t[:,i] != t[:,i]])if nan_num>0:now_col=t[:,i]# 求和now_col_not_nan = now_col[np.isnan(now_col)==False].sum()# 和/个数now_col_mean = now_col_not_nan / (t.shape[0] - nan_num)# 赋值给now col now_col[np.isnan(now_col)] = now_col_mean#赋值给t,即更新t的当前列t[:,i]=now_col return t
data
array([[ nan, nan, nan, nan],[ 1. , 123. , 1.4, 23. ],[ 2. , 110. , nan, 18. ],[ 3. , nan, 2.1, 19. ]])
fill_nan_by_column_mean(data)
array([[ 2. , 116.5 , 1.75, 20. ],[ 1. , 123. , 1.4 , 23. ],[ 2. , 110. , 1.75, 18. ],[ 3. , 116.5 , 2.1 , 19. ]])
data[0,0] = np.nan
nan_num = np.count_nonzero(data[:,0][data[:,0] != data[:,0]]) # numpy.count_nonzero是用于统计数组中非零元素的个数
nan_num
1
data[:,0]
array([nan, 1., 2., 3.])
data[:,0] != data[:,0]
array([ True, False, False, False])
np.nan != np.nan # np.nan 原意为 not a number,所以当然不能判断两个np.nan 是否相等啦
True
a
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074, -0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686, -0.63207426, 1.1 ]])
a.shape
(2, 4)
a.reshape(-1,2) # 自动计算功能,不想指定的位置用-1来填补即可
array([[-1.28396641, -2.01191074],[-0.18834465, 1.1 ],[ 0.12013781, -1.43581686],[-0.63207426, 1.1 ]])
3.8 总结



![4个强大的Linux服务器监控工具[转]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/4个强大的Linux服务器监控工具[转])
)





)

)





)
 Lasso 岭回归 分箱处理非线性问题 多项式回归)