路径压缩继续优化并查集
在实现的并查集中,在合并操作merge(item1, item2)时,会不管两个元素所在的分组大小,总是将item
1的分组合并到item2的分组,这样可能会导致树的深度无必要地增加:

如果是大树合并到小树上,会导致树的深度增加,进而造成增删改查等操作的代价增大
因此我们要对并查集的合并操作进行优化。
优化合并方式
- 每次合并时,都将小分组的元素往大分组合并,由于本例初始化都是一个元素,对应一个分组,它合并的情况可能会变成如下这样(箭头代表分组之间的edge),类似一颗星状的树:
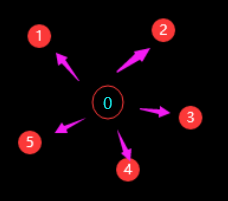
属性和方法说明
- self.num_groups 分组数量
- self.groups 一个数组,索引代表传入的item的值,元素代表分组编号
- nums_in_each_group 一个数组,索引代表分组编号,元素代表每个分组的元素个数
- count_groups() 获取当前总共分数的数量
- in_the_same_group(item1, item2) 判断两个传入的item是否在同一分组
- which_group(item) 获取传入的item的所在分组
- unite(item1, item2) 合并两个元素到同一分组,小的分组总是会往大的分组合并
Python代码实现及测试
class UF_Tree_Weighted:def __init__(self, n):self.num_groups = nself.groups = [i for i in range(n)]self.nums_in_each_group = [1 for _ in range(n)]def count_groups(self):return self.num_groupsdef in_the_same_group(self, item1, item2):return self.which_group(item1) == self.which_group(item2)def which_group(self, item):"""Find item's root------>groups[groups[groups[...groups[item]...]]]"""while self.groups[item] != item:item = self.groups[item]return itemdef unite(self, item1, item2):p = self.which_group(item1)q = self.which_group(item2)if p == q:returnif self.nums_in_each_group[p] <= self.nums_in_each_group[q]:# Merge the smaller group into the bigger'sself.nums_in_each_group[q] += self.nums_in_each_group[p]self.nums_in_each_group[p] = 0# Change the smaller group-number to the bigger's group-numberself.groups[p] = self.groups[q]else:# Merge the smaller group into the bigger'sself.nums_in_each_group[p] += self.nums_in_each_group[q]self.nums_in_each_group[q] = 0self.groups[q] = self.groups[p]# Numbers of group subtract 1self.num_groups -= 1if __name__ == '__main__':UF = UF_Tree_Weighted(5)print(f"The initial number of groups is {UF.num_groups}")while True:p = int(input(f'Input the to-be-merge element: '))q = int(input(f"Merge to the target element's group: "))if UF.in_the_same_group(p, q):print(f"They are already in the same group")continueUF.unite(p, q)print(f"The number of groups now is {UF.count_groups()}")print(UF.groups)print(f"Elements in each group: {UF.nums_in_each_group}")
运行结果
The initial number of groups is 5
Input the to-be-merge element: 0
Merge to the target element's group: 1
The number of groups now is 4
[1, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Elements in each group: [0, 2, 1, 1, 1]
Input the to-be-merge element: 1
Merge to the target element's group: 2
The number of groups now is 3
[1, 1, 1, 3, 4]
Elements in each group: [0, 3, 0, 1, 1]
Input the to-be-merge element: 3
Merge to the target element's group: 2
The number of groups now is 2
[1, 1, 1, 1, 4]
Elements in each group: [0, 4, 0, 0, 1]
Input the to-be-merge element: 2
Merge to the target element's group: 4
The number of groups now is 1
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
Elements in each group: [0, 5, 0, 0, 0]
Input the to-be-merge element:
当调用unite()合并时,合并时不考虑参数的先后位置,而是考虑分组的大小,总是会有小的分组合并到大的分组










 Function3 函数参数二)







 empty() in function cv::CascadeClassifier)
)