String
package com.practise.string.heima.StringBase;/*
java.lang.String类代表字符串。
API当中说:Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例实现。
其实就是说:程序当中所有的双引号字符串,都是String类的对象。(就算没有new,也照样是。)字符串的特点:
1. 字符串的内容永不可变。【重点】
2. 正是因为字符串不可改变,所以字符串是可以共享使用的。
3. 字符串效果上相当于是char[]字符数组,但是底层原理是byte[]字节数组。创建字符串的常见3+1种方式。
三种构造方法:
public String():创建一个空白字符串,不含有任何内容。
public String(char[] array):根据字符数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
public String(byte[] array):根据字节数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
一种直接创建:
String str = "Hello"; // 右边直接用双引号注意:直接写上双引号,就是字符串对象。*/
public class Demo01String {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用空参构造String str1 = new String(); // 小括号留空,说明字符串什么内容都没有。System.out.println("第1个字符串:" + str1);// 根据字符数组创建字符串char[] charArray = { 'A', 'B', 'C' };String str2 = new String(charArray);System.out.println("第2个字符串:" + str2);// 根据字节数组创建字符串byte[] byteArray = { 97, 98, 99 };String str3 = new String(byteArray);System.out.println("第3个字符串:" + str3);// 直接创建String str4 = "Hello";System.out.println("第4个字符串:" + str4);}}
StringPool
package com.practise.string.heima.StringBase;/*
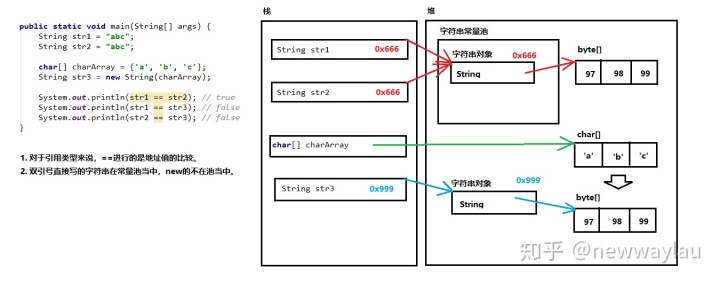
字符串常量池:程序当中直接写上的双引号字符串,就在字符串常量池中。对于基本类型来说,==是进行数值的比较。
对于引用类型来说,==是进行【地址值】的比较。*/
public class Demo02StringPool {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "abc";String str2 = "abc";char[] charArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'};String str3 = new String(charArray);System.out.println(str1 == str2); // trueSystem.out.println(str1 == str3); // falseSystem.out.println(str2 == str3); // false}}
equals
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
==是进行对象的地址值比较,如果确实需要字符串的内容比较,可以使用两个方法:public boolean equals(Object obj):参数可以是任何对象,只有参数是一个字符串并且内容相同的才会给true;否则返回false。
注意事项:
1. 任何对象都能用Object进行接收。
2. equals方法具有对称性,也就是a.equals(b)和b.equals(a)效果一样。
3. 如果比较双方一个常量一个变量,推荐把常量字符串写在前面。
推荐:"abc".equals(str) 不推荐:str.equals("abc")public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):忽略大小写,进行内容比较。*/
public class Demo01StringEquals {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "Hello";String str2 = "Hello";char[] charArray = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};String str3 = new String(charArray);System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // trueSystem.out.println(str2.equals(str3)); // trueSystem.out.println(str3.equals("Hello")); // trueSystem.out.println("Hello".equals(str1)); // trueString str4 = "hello";System.out.println(str1.equals(str4)); // falseSystem.out.println("=================");String str5 = null;System.out.println("abc".equals(str5)); // 推荐:false
// System.out.println(str5.equals("abc")); // 不推荐:报错,空指针异常NullPointerExceptionSystem.out.println("=================");String strA = "Java";String strB = "java";System.out.println(strA.equals(strB)); // false,严格区分大小写System.out.println(strA.equalsIgnoreCase(strB)); // true,忽略大小写// 注意,只有英文字母区分大小写,其他都不区分大小写System.out.println("abc一123".equalsIgnoreCase("abc壹123")); // false}}
StringGet
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
String当中与获取相关的常用方法有:public int length():获取字符串当中含有的字符个数,拿到字符串长度。
public String concat(String str):将当前字符串和参数字符串拼接成为返回值新的字符串。
public char charAt(int index):获取指定索引位置的单个字符。(索引从0开始。)
public int indexOf(String str):查找参数字符串在本字符串当中首次出现的索引位置,如果没有返回-1值。*/
public class Demo02StringGet {public static void main(String[] args) {// 获取字符串的长度int length = "asdasfeutrvauevbueyvb".length();System.out.println("字符串的长度是:" + length);// 拼接字符串String str1 = "Hello";String str2 = "World";String str3 = str1.concat(str2);System.out.println(str1); // Hello,原封不动System.out.println(str2); // World,原封不动System.out.println(str3); // HelloWorld,新的字符串System.out.println("==============");// 获取指定索引位置的单个字符char ch = "Hello".charAt(1);System.out.println("在1号索引位置的字符是:" + ch);System.out.println("==============");// 查找参数字符串在本来字符串当中出现的第一次索引位置// 如果根本没有,返回-1值String original = "HelloWorldHelloWorld";int index = original.indexOf("llo");System.out.println("第一次索引值是:" + index); // 2System.out.println("HelloWorld".indexOf("abc")); // -1}}
Substring
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
字符串的截取方法:public String substring(int index):截取从参数位置一直到字符串末尾,返回新字符串。
public String substring(int begin, int end):截取从begin开始,一直到end结束,中间的字符串。
备注:[begin,end),包含左边,不包含右边。*/
public class Demo03Substring {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "HelloWorld";String str2 = str1.substring(5);System.out.println(str1); // HelloWorld,原封不动System.out.println(str2); // World,新字符串System.out.println("================");String str3 = str1.substring(4, 7);System.out.println(str3); // oWoSystem.out.println("================");// 下面这种写法,字符串的内容仍然是没有改变的// 下面有两个字符串:"Hello","Java"// strA当中保存的是地址值。// 本来地址值是Hello的0x666,// 后来地址值变成了Java的0x999String strA = "Hello";System.out.println(strA); // HellostrA = "Java";System.out.println(strA); // Java}}
StringConvert
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
String当中与转换相关的常用方法有:public char[] toCharArray():将当前字符串拆分成为字符数组作为返回值。
public byte[] getBytes():获得当前字符串底层的字节数组。
public String replace(CharSequence oldString, CharSequence newString):
将所有出现的老字符串替换成为新的字符串,返回替换之后的结果新字符串。
备注:CharSequence意思就是说可以接受字符串类型。*/
public class Demo04StringConvert {public static void main(String[] args) {// 转换成为字符数组char[] chars = "Hello".toCharArray();System.out.println(chars[0]); // HSystem.out.println(chars.length); // 5System.out.println("==============");// 转换成为字节数组byte[] bytes = "abc".getBytes();for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {System.out.println(bytes[i]);}System.out.println("==============");// 字符串的内容替换String str1 = "How do you do?";String str2 = str1.replace("o", "*");System.out.println(str1); // How do you do?System.out.println(str2); // H*w d* y*u d*?System.out.println("==============");String lang1 = "会不会玩儿呀!你大爷的!你大爷的!你大爷的!!!";String lang2 = lang1.replace("你大爷的", "****");System.out.println(lang2); // 会不会玩儿呀!****!****!****!!!}}
StringSplit
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
分割字符串的方法:
public String[] split(String regex):按照参数的规则,将字符串切分成为若干部分。注意事项:
split方法的参数其实是一个“正则表达式”,今后学习。
今天要注意:如果按照英文句点“.”进行切分,必须写"."(两个反斜杠)*/
public class Demo05StringSplit {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "aaa,bbb,ccc";String[] array1 = str1.split(",");for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {System.out.println(array1[i]);}System.out.println("===============");String str2 = "aaa bbb ccc";String[] array2 = str2.split(" ");for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {System.out.println(array2[i]);}System.out.println("===============");String str3 = "XXX.YYY.ZZZ";String[] array3 = str3.split(".");System.out.println(array3.length); // 0for (int i = 0; i < array3.length; i++) {System.out.println(array3[i]);}}}
StringPractise
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;/*
题目:
定义一个方法,把数组{1,2,3}按照指定格式拼接成一个字符串。格式参照如下:[word1#word2#word3]。分析:
1. 首先准备一个int[]数组,内容是:1、2、3
2. 定义一个方法,用来将数组变成字符串
三要素
返回值类型:String
方法名称:fromArrayToString
参数列表:int[]
3. 格式:[word1#word2#word3]
用到:for循环、字符串拼接、每个数组元素之前都有一个word字样、分隔使用的是#、区分一下是不是最后一个
4. 调用方法,得到返回值,并打印结果字符串*/
public class Demo06StringPractise {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4};String result = fromArrayToString(array);System.out.println(result);}public static String fromArrayToString(int[] array) {String str = "[";for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {if (i == array.length - 1) {str += "word" + array[i] + "]";} else {str += "word" + array[i] + "#";}}return str;}}
StringCount
package com.practise.string.heima.heima_String;import java.util.Scanner;/*
题目:
键盘输入一个字符串,并且统计其中各种字符出现的次数。
种类有:大写字母、小写字母、数字、其他思路:
1. 既然用到键盘输入,肯定是Scanner
2. 键盘输入的是字符串,那么:String str = sc.next();
3. 定义四个变量,分别代表四种字符各自的出现次数。
4. 需要对字符串一个字、一个字检查,String-->char[],方法就是toCharArray()
5. 遍历char[]字符数组,对当前字符的种类进行判断,并且用四个变量进行++动作。
6. 打印输出四个变量,分别代表四种字符出现次数。*/
public class Demo07StringCount {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");String input = sc.next(); // 获取键盘输入的一个字符串int countUpper = 0; // 大写字母int countLower = 0; // 小写字母int countNumber = 0; // 数字int countOther = 0; // 其他字符char[] charArray = input.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {char ch = charArray[i]; // 当前单个字符if ('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z') {countUpper++;} else if ('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z') {countLower++;} else if ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') {countNumber++;} else {countOther++;}}System.out.println("大写字母有:" + countUpper);System.out.println("小写字母有:" + countLower);System.out.println("数字有:" + countNumber);System.out.println("其他字符有:" + countOther);}}



![[转载]我的WafBypass之道(upload篇)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[转载]我的WafBypass之道(upload篇))














