一、数据增强的方法介绍
增加训练数据, 则能够提升算法的准确率, 因为这样可以避免过拟合, 而避免了过拟合你就可以增大你的网络结构了。 当训练数据有限的时候, 可以通过一些变换来从已有的训练数据集中生成一些新的数据, 来扩大训练数据。 数据增强的方法有:
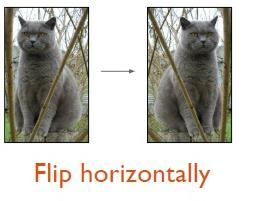
1) 图片的水平翻转(主要包括对称处理, 度数旋转等)
2) 随机裁剪(可以裁剪成不同大小的数据)
如原始图像大小为256*256,随机裁剪出一些图像224*224的图像。如下图,红色方框内为随机裁剪出的224*224的图片。 AlexNet 训练时,对左上、右上、左下、右下、中间做了5次裁剪,然后翻转,得到一些剪切图片。防止大网络过拟合(under ubstantial overfitting)。

3) fancy PCA (就是从像素的角度变化, 形成新的图片)
在训练集像素值的RGB颜色空间进行PCA, 得到RGB空间的3个主方向向量,3个特征值, p1,p2, p3, λ1, λ2, λ3. 对每幅图像的每个像素加上如下的变化:
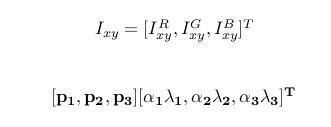 其中:α i 是满足均值为0,方差为0.1的随机变量.
其中:α i 是满足均值为0,方差为0.1的随机变量.
4) 样本不均衡( 解决方案: 增加小众类别的图像数据)
样本数据的不均衡的问题是日常中较多遇到的问题, 在机器学习中我们对于数据不平衡有上采样和下采样等处理方法, 在这里我们一般使用的是小众类别增强的方法处理.
一般根据数据集中的图像最多的种类的数量进行随机采样, 使得每个样本的数量均相等.然后将这些样本图片混合打乱形成新的数据集.

5)其它方法
- 如平移变换;
- 旋转/仿射变换;
- 高斯噪声、 模糊处理、
- 对颜色的数据增强: 图像亮度、 饱和度、 对比度变化.
6)训练和测试要协调
在训练的时候,我们通常都需要做数据增强,在测试的时候,我们通常很少去做数据增强。这其中似乎有些不协调,因为你训练和测试之间有些不一致。实验发现,训练的最后几个迭代,移除数据增强,和传统一样测试,可以提升一点性能。
如果训练的时候一直使用尺度和长宽比增强数据增强,在测试的时候也同样做这个变化,随机取32个裁剪图片来测试,也可以在最后的模型上提升一点性能。就是多尺度的训练,多尺度的测试。
二、数据增强的TensorFlow实现
# -- encoding:utf-8 --
"""
图像处理的Python库:OpenCV、PIL、matplotlib、tensorflow等
"""import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf# 打印numpy的数组对象的时候,中间不省略
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)def show_image_tensor(image_tensor):# 要求:使用交互式会话# 获取图像tensor对象对应的image对象,image对象时一个[h,w,c]# print(image_tensor)image = image_tensor.eval()# print(image)print("图像大小为:{}".format(image.shape))if len(image.shape) == 3 and image.shape[2] == 1:# 黑白图像plt.imshow(image[:, :, 0], cmap='Greys_r')plt.show()elif len(image.shape) == 3:# 彩色图像plt.imshow(image)plt.show()# 1. 交互式会话启动
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()image_path = 'data/xiaoren.png'
# image_path = 'data/gray.png'
# image_path = 'data/black_white.jpg'# 一、图像格式的转换
# 读取数据
file_contents = tf.read_file(image_path)
# 将图像数据转换为像素点的数据格式,返回对象为: [height, width, num_channels], 如果是gif的图像返回[num_frames, height, width, num_channels]
# height: 图片的高度的像素大小
# width: 图片的水平宽度的像素大小
# num_channels: 图像的通道数,也就是API中的channels的值
# num_frames: 因为gif的图像是一个动态图像,可以将每一个动的画面看成一个静态图像,num_frames相当于在这个gif图像中有多少个静态图像
# 参数channels:可选值:0 1 3 4,默认为0, 一般使用0 1 3,不建议使用4
# 0:使用图像的默认通道,也就是图像是几通道的就使用几通道
# 1:使用灰度级别的图像数据作为返回值(只有一个通道:黑白)
# 3:使用RGB三通道读取数据
# 4:使用RGBA四通道读取数据(R:红色,G:绿色,B:蓝色,A:透明度)
image_tensor = tf.image.decode_png(contents=file_contents, channels=3)
# show_image_tensor(image_tensor)# 二、图像大小重置
"""
BILINEAR = 0 线性插值,默认
NEAREST_NEIGHBOR = 1 最近邻插值,失真最小
BICUBIC = 2 三次插值
AREA = 3 面积插值
"""
# images: 给定需要进行大小转换的图像对应的tensor对象,格式为:[height, width, num_channels]或者[batch, height, width, num_channels]
# API返回值和images格式一样,唯一区别是height和width变化为给定的值
resize_image_tensor = tf.image.resize_images(images=image_tensor, size=(200, 200),method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
# show_image_tensor(resize_image_tensor)# 三、图片的剪切&填充
# 图片重置大小,通过图片的剪切或者填充(从中间开始计算新图片的大小)
crop_or_pad_image_tensor = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image_tensor, 200, 200)
# show_image_tensor(crop_or_pad_image_tensor)# 中间等比例剪切
central_crop_image_tensor = tf.image.central_crop(image_tensor, central_fraction=0.2)
# show_image_tensor(central_crop_image_tensor)# 填充数据(给定位置开始填充)
pad_to_bounding_box_image_tensor = tf.image.pad_to_bounding_box(image_tensor, offset_height=400, offset_width=490,target_height=1000,target_width=1000)
# show_image_tensor(pad_to_bounding_box_image_tensor)# 剪切数据(给定位置开始剪切)
crop_to_bounding_box_image_tensor = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image_tensor, offset_height=10, offset_width=40,target_height=200, target_width=300)
# show_image_tensor(crop_to_bounding_box_image_tensor)# 四、旋转
# 上下交换
flip_up_down_image_tensor = tf.image.flip_up_down(image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(flip_up_down_image_tensor)# 左右交换
flip_left_right_image_tensor = tf.image.flip_left_right(image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(flip_left_right_image_tensor)# 转置
transpose_image_tensor = tf.image.transpose_image(image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(transpose_image_tensor)# 旋转(90度、180度、270度....)
# k*90度旋转,逆时针旋转
k_rot90_image_tensor = tf.image.rot90(image_tensor, k=4)
# show_image_tensor(k_rot90_image_tensor)# 五、颜色空间的转换(rgb、hsv、gray)
# 颜色空间的转换必须讲image的值转换为float32类型,不能使用unit8类型
float32_image_tensor = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image_tensor, dtype=tf.float32)
# show_image_tensor(float32_image_tensor)# rgb -> hsv(h: 图像的色彩/色度,s:图像的饱和度,v:图像的亮度)
hsv_image_tensor = tf.image.rgb_to_hsv(float32_image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(hsv_image_tensor)# hsv -> rgb
rgb_image_tensor = tf.image.hsv_to_rgb(hsv_image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(rgb_image_tensor)# rgb -> gray
gray_image_tensor = tf.image.rgb_to_grayscale(rgb_image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(gray_image_tensor)# 可以从颜色空间中提取图像的轮廓信息(图像的二值化)
a = gray_image_tensor
b = tf.less_equal(a, 0.9)
# 0是黑,1是白
# condition?true:false
# condition、x、y格式必须一模一样,当condition中的值为true的之后,返回x对应位置的值,否则返回y对应位置的值
# 对于a中所有大于0.9的像素值,设置为0
c = tf.where(condition=b, x=a, y=a - a)
# 对于a中所有小于等于0.9的像素值,设置为1
d = tf.where(condition=b, x=c - c + 1, y=c)
# show_image_tensor(d)# 六、图像的调整
# 亮度调整
# image: RGB图像信息,设置为float类型和unit8类型的效果不一样,一般建议设置为float类型
# delta: 取值范围(-1,1)之间的float类型的值,表示对于亮度的减弱或者增强的系数值
# 底层执行:rgb -> hsv -> h,s,v*delta -> rgb
adjust_brightness_image_tensor = tf.image.adjust_brightness(image=image_tensor, delta=0.8)
# show_image_tensor(adjust_brightness_image_tensor)# 色调调整
# image: RGB图像信息,设置为float类型和unit8类型的效果不一样,一般建议设置为float类型
# delta: 取值范围(-1,1)之间的float类型的值,表示对于色调的减弱或者增强的系数值
# 底层执行:rgb -> hsv -> h*delta,s,v -> rgb
adjust_hue_image_tensor = tf.image.adjust_hue(image_tensor, delta=-0.8)
# show_image_tensor(adjust_hue_image_tensor)# 饱和度调整
# image: RGB图像信息,设置为float类型和unit8类型的效果不一样,一般建议设置为float类型
# saturation_factor: 一个float类型的值,表示对于饱和度的减弱或者增强的系数值,饱和因子
# 底层执行:rgb -> hsv -> h,s*saturation_factor,v -> rgb
adjust_saturation_image_tensor = tf.image.adjust_saturation(image_tensor, saturation_factor=20)
# show_image_tensor(adjust_saturation_image_tensor)# 对比度调整,公式:(x-mean) * contrast_factor + mean
adjust_contrast_image_tensor = tf.image.adjust_contrast(image_tensor, contrast_factor=10)
# show_image_tensor(adjust_contrast_image_tensor)# 图像的gamma校正
# images: 要求必须是float类型的数据
# gamma:任意值,Oup = In * Gamma
adjust_gamma_image_tensor = tf.image.adjust_gamma(float32_image_tensor, gamma=100)
# show_image_tensor(adjust_gamma_image_tensor)# 图像的归一化(x-mean)/adjusted_sttdev, adjusted_sttdev=max(stddev, 1.0/sqrt(image.NumElements()))
per_image_standardization_image_tensor = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image_tensor)
# show_image_tensor(per_image_standardization_image_tensor)# 七、噪音数据的加入
noisy_image_tensor = image_tensor + tf.cast(5 * tf.random_normal(shape=[600, 510, 3], mean=0, stddev=0.1), tf.uint8)
show_image_tensor(noisy_image_tensor)
)


















