一、伸展树的数据结构
typedef struct Node
{int key; struct Node *lch,*rch,*parent;
}* Node ,* Tree;二、伸展树的基础操作
下面几个函数中,设x 的父节点为 p, p的父节点为g 。
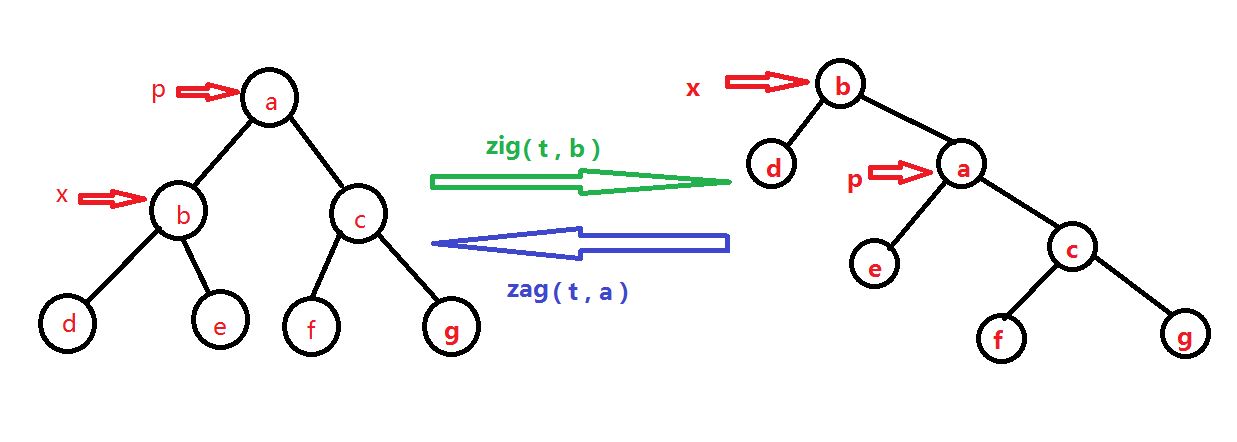
- zig( t , x )
右旋。当p是根节点,x是p的左孩子,将x右旋。
代码如下:
//单次右旋以 root 节点 为根节点的树
Node zig( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node lc = root->lch;Node parent = root->parent;//处理父节点关系 if( parent ){if( root == parent->lch ){parent->lch = lc;}else{parent->rch = lc;}lc->parent = parent;}else{lc->parent = NULL;}//翻转 if( lc != NULL ){root->lch = lc->rch;if( lc->rch ){lc->rch->parent = root;} lc->rch = root;root->parent = lc;if( parent ){return tree;}else{return lc; }}return tree;
}- zag( t , x )
左旋。当p是根节点,x是p的右孩子,将x左旋
//单次左旋以 root 节点 为根节点的树
Node zag( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node rc = root->rch;Node parent = root->parent;//处理父节点关系 if( parent ){if( root == parent->lch ){parent->lch = rc;}else{parent->rch = rc;}rc->parent = parent;}else{rc->parent = NULL;}//翻转 if( rc != NULL ){root->rch = rc->lch;if( rc->lch ){rc->lch->parent = root;} rc->lch = root;root->parent = rc;if( parent ){return tree;}else{return rc; }}return tree;
}- zig_zig( t , x )
右双旋。x是p的左节点,当p是g的左节点,先将p右旋,再将x右旋
//右双旋以 root 节点 为根节点的树
Node zig_zig( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node lc = root->lch;Node node=zig( tree , root );return zig( node , lc );
}- zag_zag( t , x )
左双旋。x是p的右节点,当p是g的右节点,先将p左旋,再将x左旋
//左双旋以 root 节点 为根节点的树
Node zag_zag( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node rc = root->rch;Node node=zag( tree , root );return zag( node , rc );
}- zig_zag( t , x )
右旋再左旋。x是p的左节点,当p是g的右节点,先将x右旋,再将x左旋
Node zig_zag( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node node=zig( tree , root->rch );return zag( node , root );
}- zag_zig( t , x )
左旋再右旋。x是p的右节点,当p是g的左节点,先将x左旋,再将x右旋
Node zag_zig( Tree tree , Node root)
{Node node=zag( tree , root->lch ); return zig( node , root );
}- zig_zag_manager( t , x)
旋转管理者。 找到x,分析x与父亲节点,父亲节点与祖父节点的关系,选择恰当的旋转方式。
//根据目标节点的结构选择相应的算法,策略模式
Node zig_zag_manager( Tree tree , Node node )
{ Node parent = node->parent;if( parent == tree ) //1{if( parent->lch == node ){return zig( tree , parent );}else{return zag( tree , parent );}}else if( parent->lch == node ){ //2Node grand = parent->parent; if( grand->lch == parent ){ /*左左*/return zig_zig( tree , grand ); }else{ /*右左*/ return zig_zag( tree , grand );}}else if( parent->rch == node ){ //3Node grand = parent->parent; if( grand->lch == parent ){ /*左右*/return zag_zig( tree , grand ); }else{ /*右右*/return zag_zag( tree , grand );}}return tree;
}- splay( t ,x )
将x调至根部。循环调用zig_zag_manager( t , x) 方法,直到x == t
//将目标节点调整到树的根部,并返回树根
Node splay(Tree tree , Node node)
{while( node->parent!=NULL ){zig_zag_manager( tree , node );}return node;
}- find( t , x )
找到x。找到x,然后将x旋转到树根。
//寻找key节点
Node find( Tree tree , int key )
{Node curr = tree;while( curr != NULL ){if( curr->key == key ){splay( tree , curr );return curr; } else if( curr->key > key ){curr = curr->lch;}else{curr = curr->rch;}}return NULL;
}- spilt( t , x)
以x为界分离t。找到x,将x旋转到树根,然后将x的左子树和剩余部分分离
//以 node 为届,分离 tree 的左子树 ,返回剩余部分
Node spilt( Tree tree , Node node )
{tree = splay( tree , node ); //将 node 调至根部Node lc = tree->lch;tree->lch = NULL;if( lc ) {lc->parent = NULL;}return tree;
}注意这里,要获得左子树可以在分离之前获得。
- join( t1 , t2 )
合并子树 t1和t2,要求t1所有元素小于t2的任一元素。找到t1的最大元素,并调整到根部,将t2作为根的右子树插入
//合并tree1 和 tree2 ,要求 tree1 所有元素小于 tree2 任一元素
Node join( Tree tree1, Tree tree2)
{//找打 tree1 中最大的元素 Node temp = tree1;while( temp->rch != NULL ){temp = temp->rch;} //将 temp调至 tree1的根部 splay( tree1 ,temp );//将 tree2 作为 temp的右子树temp->rch = tree2;tree2->parent = temp;return temp;
}附件:
1. C-free工程,也可直接打开文件.zip
2. 广东工业大学-计算机学院-伸展树.pdf
















MaterialDesign风格的博客园皮肤)


