已经搞定了怎样获取页面的内容,不过还差一步,这么多杂乱的代码夹杂文字我们怎样把它提取出来整理呢?下面就开始介绍一个十分强大的工具,正则表达式
1.了解正则表达式
正则表达式是用来匹配字符串非常强大的工具,在其他编程语言中同样有正则表达式的概念,Python 同样不例外。正则表达式的大致匹配过程是:
- 依次拿出表达式和文本中的字符比较,
- 如果每一个字符都能匹配,则匹配成功;一旦有匹配不成功的字符则匹配失败。
- 如果表达式中有量词或边界,这个过程会稍微有一些不同。
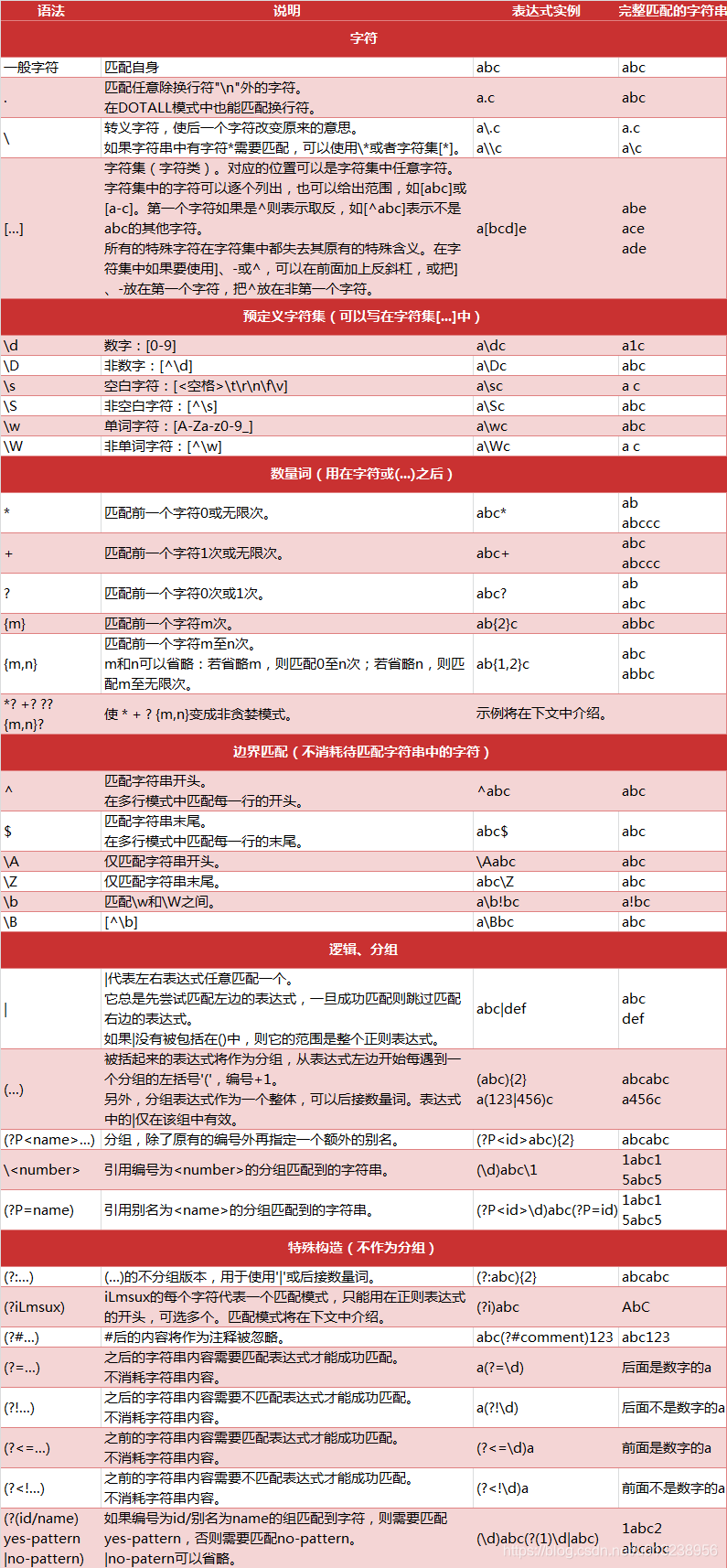
2.正则表达式的语法规则
下面是 Python 中正则表达式的一些匹配规则
3.正则表达式相关注释
(1)数量词的贪婪模式和非贪婪模式
正则表达式通常用于在文本中查找匹配的字符串。Python 里数量词默认是贪婪的(在少数语言里也可能是默认非贪婪),总是尝试匹配尽可能多的字符;非贪婪的则相反,总是尝试匹配尽可能少的字符。例如:正则表达式”ab“如果用于查找” abbbc”,将找到”abbb”。而如果使用非贪婪的数量词”ab?”,将找到”a”。 注:我们一般使用非贪婪模式来提取。
(2)反斜杠问题
与大多数编程语言相同,正则表达式里使用”\“作为转义字符,这就可能造成反斜杠困扰。假如你需要匹配文本中的字符”\“,那么使用编程语言表示的正则表达式里将需要 4 个反斜杠”\\“:前两个和后两个分别用于在编程语言里转义成反斜杠,转换成两个反斜杠后再在正则表达式里转义成一个反斜杠。 Python 里的原生字符串很好地解决了这个问题,这个例子中的正则表达式可以使用 r”\“表示。同样,匹配一个数字的”\d” 可以写成 r”\d”。有了原生字符串,不用担心是不是漏写了反斜杠,写出来的表达式也更直观
4.Python Re模块
Python 自带了 re 模块,它提供了对正则表达式的支持。主要用到的方法列举如下
#返回pattern对象
re.compile(string[,flag])
#以下为匹配所用函数
re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit])
re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
re.subn(pattern, repl, string[, count])
在介绍这几个方法之前,我们先来介绍一下 pattern 的概念,pattern 可以理解为一个匹配模式,那么我们怎么获得这个匹配模式呢?很简单,我们需要利用 re.compile 方法就可以。例如
pattern = re.compile(r'hello')
在参数中我们传入了原生字符串对象,通过 compile 方法编译生成一个 pattern 对象,然后我们利用这个对象来进行进一步的匹配。 另外大家可能注意到了另一个参数 flags,在这里解释一下这个参数的含义: 参数 flag 是匹配模式,取值可以使用按位或运算符’|’表示同时生效,比如 re.I | re.M。 可选值有:
- re.I(全拼:IGNORECASE): 忽略大小写(括号内是完整写法,下同)
- re.M(全拼:MULTILINE): 多行模式,改变’^‘和’$'的行为(参见上图)
- re.S(全拼:DOTALL): 点任意匹配模式,改变’.'的行为
- re.L(全拼:LOCALE): 使预定字符类 \w \W \b \B \s \S 取决于当前区域设定
- re.U(全拼:UNICODE): 使预定字符类 \w \W \b \B \s \S \d \D 取决于unicode定义的字符属性
- re.X(全拼:VERBOSE): 详细模式。这个模式下正则表达式可以是多行,忽略空白字符,并可以加入注释。
以下七个方法中的 flags 同样是代表匹配模式的意思,如果在 pattern 生成时已经指明了 flags,那么在下面的方法中就不需要传入这个参数了。
(1)re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
这个方法将会从 string(我们要匹配的字符串)的开头开始,尝试匹配 pattern,一直向后匹配,如果遇到无法匹配的字符,立即返回 None,如果匹配未结束已经到达 string 的末尾,也会返回 None。两个结果均表示匹配失败,否则匹配 pattern 成功,同时匹配终止,不再对 string 向后匹配。下面我们通过一个例子理解一下
#导入re模块
import re# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象,注意hello前面的r的意思是“原生字符串”
pattern = re.compile(r'hello')# 使用re.match匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
result1 = re.match(pattern,'hello')
result2 = re.match(pattern,'helloo CQC!')
result3 = re.match(pattern,'helo CQC!')
result4 = re.match(pattern,'hello CQC!')#如果1匹配成功
if result1:# 使用Match获得分组信息print result1.group()
else:print '1匹配失败!'
#如果2匹配成功
if result2:# 使用Match获得分组信息print result2.group()
else:print '2匹配失败!'
#如果3匹配成功
if result3:# 使用Match获得分组信息print result3.group()
else:print '3匹配失败!'
#如果4匹配成功
if result4:# 使用Match获得分组信息print result4.group()
else:print '4匹配失败!'
输出:
hello
hello
3匹配失败!
hello
匹配分析
- 第一个匹配,pattern 正则表达式为’hello’,我们匹配的目标字符串 string 也为 hello,从头至尾完全匹配,匹配成功。
- 第二个匹配,string 为 helloo CQC,从 string 头开始匹配 pattern 完全可以匹配,pattern 匹配结束,同时匹配终止,后面的 o CQC 不再匹配,返回匹配成功的信息。
- 第三个匹配,string 为 helo CQC,从 string 头开始匹配 pattern,发现到 ‘o’ 时无法完成匹配,匹配终止,返回 None
- 第四个匹配,同第二个匹配原理,即使遇到了空格符也不会受影响。
我们还看到最后打印出了 result.group (),这个是什么意思呢?下面我们说一下关于 match 对象的的属性和方法 Match 对象是一次匹配的结果,包含了很多关于此次匹配的信息,可以使用 Match 提供的可读属性或方法来获取这些信息。
属性:
- string: 匹配时使用的文本。
- re: 匹配时使用的 Pattern 对象。
- pos: 文本中正则表达式开始搜索的索引。值与 Pattern.match () 和 Pattern.seach () 方法的同名参数相同。
- endpos: 文本中正则表达式结束搜索的索引。值与 Pattern.match () 和 Pattern.seach () 方法的同名参数相同。
- lastindex: 最后一个被捕获的分组在文本中的索引。如果没有被捕获的分组,将为 None。
- lastgroup: 最后一个被捕获的分组的别名。如果这个分组没有别名或者没有被捕获的分组,将为 None。
方法:
- group ([group1, …]): 获得一个或多个分组截获的字符串;指定多个参数时将以元组形式返回。group1 可以使用编号也可以使用别名;编号 0 代表整个匹配的子串;不填写参数时,返回 group (0);没有截获字符串的组返回None;截获了多次的组返回最后一次截获的子串。
- groups ([default]): 以元组形式返回全部分组截获的字符串。相当于调用 group (1,2,…last)。default 表示没有截获字符串的组以这个值替代,默认为 None。
- groupdict ([default]): 返回以有别名的组的别名为键、以该组截获的子串为值的字典,没有别名的组不包含在内。default 含义同上。
- start ([group]): 返回指定的组截获的子串在 string 中的起始索引(子串第一个字符的索引)。group 默认值为 0。
- end ([group]): 返回指定的组截获的子串在 string 中的结束索引(子串最后一个字符的索引 + 1)。group 默认值为 0。
- .span ([group]): 返回 (start (group), end (group))。
- expand (template): 将匹配到的分组代入 template 中然后返回。template 中可以使用 \id 或 \g、\g 引用分组,但不能使用编号 0。\id 与 \g 是等价的;但 \10 将被认为是第 10 个分组,如果你想表达 \1 之后是字符’0’,只能使用 \g0。
import re
# 匹配如下内容:单词+空格+单词+任意字符
m = re.match(r'(\w+) (\w+)(?P<sign>.*)', 'hello world!')print "m.string:", m.string
print "m.re:", m.re
print "m.pos:", m.pos
print "m.endpos:", m.endpos
print "m.lastindex:", m.lastindex
print "m.lastgroup:", m.lastgroup
print "m.group():", m.group()
print "m.group(0):", m.group(0)
print "m.group(1,2):", m.group(1, 2)
print "m.groups():", m.groups()
print "m.groupdict():", m.groupdict()
print "m.start(2):", m.start(2)
print "m.end(2):", m.end(2)
print "m.span(2):", m.span(2)
print r"m.expand(r'\g \g\g'):", m.expand(r'\2 \1\3')
m.string: hello world!
m.re: <_sre.SRE_Pattern object at 0x0000000002547690>
m.pos: 0
m.endpos: 12
m.lastindex: 3
m.lastgroup: sign
m.group(): hello world!
m.group(0): hello world!
m.group(1,2): ('hello', 'world')
m.groups(): ('hello', 'world', '!')
m.groupdict(): {'sign': '!'}
m.start(2): 6
m.end(2): 11
m.span(2): (6, 11)
m.expand(r'\g \g\g'): world hello!
(2)re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
search 方法与 match 方法极其类似,区别在于 match () 函数只检测 re 是不是在 string 的开始位置匹配,search () 会扫描整个 string 查找匹配,match()只有在 0 位置匹配成功的话才有返回,如果不是开始位置匹配成功的话,match () 就返回 None。同样,search 方法的返回对象同样 match () 返回对象的方法和属性。我们用一个例子感受一下
import re# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象
pattern = re.compile(r'world')
# 使用search()查找匹配的子串,不存在能匹配的子串时将返回None
# 这个例子中使用match()无法成功匹配
match = re.search(pattern,'hello world!')
if match:# 使用Match获得分组信息print match.group()
world
(3)re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit])
按照能够匹配的子串将 string 分割后返回列表。maxsplit 用于指定最大分割次数,不指定将全部分割。我们通过下面的例子感受一下。
import repattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
print re.split(pattern,'one1two2three3four4')
['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', '']
(4)re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
搜索 string,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串。我们通过这个例子来感受一下
import repattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
print re.findall(pattern,'one1two2three3four4')
['1', '2', '3', '4']
(5)re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
搜索 string,返回一个顺序访问每一个匹配结果(Match 对象)的迭代器。我们通过下面的例子来感受一下
import repattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
for m in re.finditer(pattern,'one1two2three3four4'):print m.group(),
1 2 3 4
(6)re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
使用 repl 替换 string 中每一个匹配的子串后返回替换后的字符串。 当 repl 是一个字符串时,可以使用 \id 或 \g、\g 引用分组,但不能使用编号 0。 当 repl 是一个方法时,这个方法应当只接受一个参数(Match 对象),并返回一个字符串用于替换(返回的字符串中不能再引用分组)。 count 用于指定最多替换次数,不指定时全部替换。
import repattern = re.compile(r'(\w+) (\w+)')
s = 'i say, hello world!'print re.sub(pattern,r'\2 \1', s)
print re.sub(pattern,r'beijing', s)
def func(m):return m.group(1).title() + ' ' + m.group(2).title()print re.sub(pattern,func, s)
say i, world hello!
beijing, beijing!
I Say, Hello World!
(7)re.subn(pattern, repl, string[, count])
返回元组(sub (repl, string [, count]), 替换次数)。
import repattern = re.compile(r'(\w+) (\w+)')
s = 'i say, hello world!'print re.subn(pattern,r'\2 \1', s)def func(m):return m.group(1).title() + ' ' + m.group(2).title()print re.subn(pattern,func, s)
('say i, world hello!', 2)
('I Say, Hello World!', 2)
5.Python Re 模块的另一种使用方式
在上面我们介绍了 7 个工具方法,例如 match,search 等等,不过调用方式都是 re.match,re.search 的方式,其实还有另外一种调用方式,可以通过 pattern.match,pattern.search 调用,这样调用便不用将 pattern 作为第一个参数传入了,大家想怎样调用皆可。 函数 API 列表
match(string[, pos[, endpos]]) | re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
search(string[, pos[, endpos]]) | re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
split(string[, maxsplit]) | re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit])
findall(string[, pos[, endpos]]) | re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
finditer(string[, pos[, endpos]]) | re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
sub(repl, string[, count]) | re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
subn(repl, string[, count]) |re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
—— udev 设备文件系统)




—— VFS 虚拟文件系统解析)



)


![[C#]Attribute特性(3)——AttributeUsage特性和特性标识符](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C#]Attribute特性(3)——AttributeUsage特性和特性标识符)






