hopper
建筑学与数据科学 (Architectonics and Data Science)
Understanding the site and topography are crucial first step of any architectural project. Site modelling can become very daunting, expensive, or just cumbersome, often having to use various software to just grasp a general awareness of the site. I found the most efficient method using QGIS and Rhino Grasshopper to cover most of my analysis, such as contour mapping, wind flow, solar radiation, sun path and shadow, natural topography, and so on. I also want to control all of these tests parametrically in one software. This is now possible thanks to the wonderful community of Grasshopper who create various plugins.
了解场地和地形是任何建筑项目中至关重要的第一步。 站点建模可能会变得非常艰巨,昂贵或非常麻烦,通常必须使用各种软件来掌握站点的一般知识。 我发现了使用QGIS和Rhino Grasshopper覆盖我的大部分分析的最有效方法,例如等高线图,风流,太阳辐射,太阳路径和阴影,自然地形等。 我还想在一个软件中参数控制所有这些测试。 现在这可以归功于Grasshopper的精彩社区,他们创建了各种插件。
The second step is gathering topographical data. Satellites make data gathering very simple as the data is made freely available. An architectural project is not just defined within its site boundary. The context is very important. Maybe it’s situated in a valley or on a mountain, next to a river that is prone to flooding, or in a city where the adjacent buildings block sunlight. In terms of topography, you would generally require a larger area to perform a proper analysis and understand the surrounding context.
第二步是收集地形数据。 卫星使数据收集变得非常简单,因为可以免费获得数据。 建筑项目不仅在其场地边界内定义。 上下文非常重要。 也许它位于山谷或山脉中,靠近容易泛滥的河流,或者位于邻近建筑物阻挡阳光的城市中。 在地形方面,通常需要较大的区域来执行适当的分析并了解周围的环境。
For this larger area, I would use the satellite gathered data. Remote sensing is increasingly becoming more accurate heading towards the true conditions. Therefore, data from satellite scanning could become a very reliable data source for almost anywhere on the earth.
对于更大的区域,我将使用卫星收集的数据。 朝向真实条件的遥感越来越准确。 因此,来自卫星扫描的数据几乎可以成为地球上任何地方的非常可靠的数据源。
任务 (Task)
Model the site using openly available datasets
使用公开可用的数据集对网站进行建模
目的 (Objective)
My objective is to attain elevation as point values on a grid of 20 and 25 m. I want to use this to strategically position buildings in the masterplan, such that each department/building is at least 20 or 25m apart from each other. I also want to control the heights of buildings, while also maintain the view for each. Therefore, at a later stage, I will use an evolutionary solver setting multi-objective optimisation with the height of the building, elevation, and view as constrains.
我的目标是在20和25 m的网格上获得高程作为点值。 我想用它来在总体规划中对建筑物进行战略性定位,以使每个部门/建筑物之间至少相距20或25m。 我还想控制建筑物的高度,同时还要保持每个建筑物的视图。 因此,在以后的阶段中,我将使用演化求解器设置多目标优化,并以建筑物的高度,立面和视图为约束。
计划 (Plan)
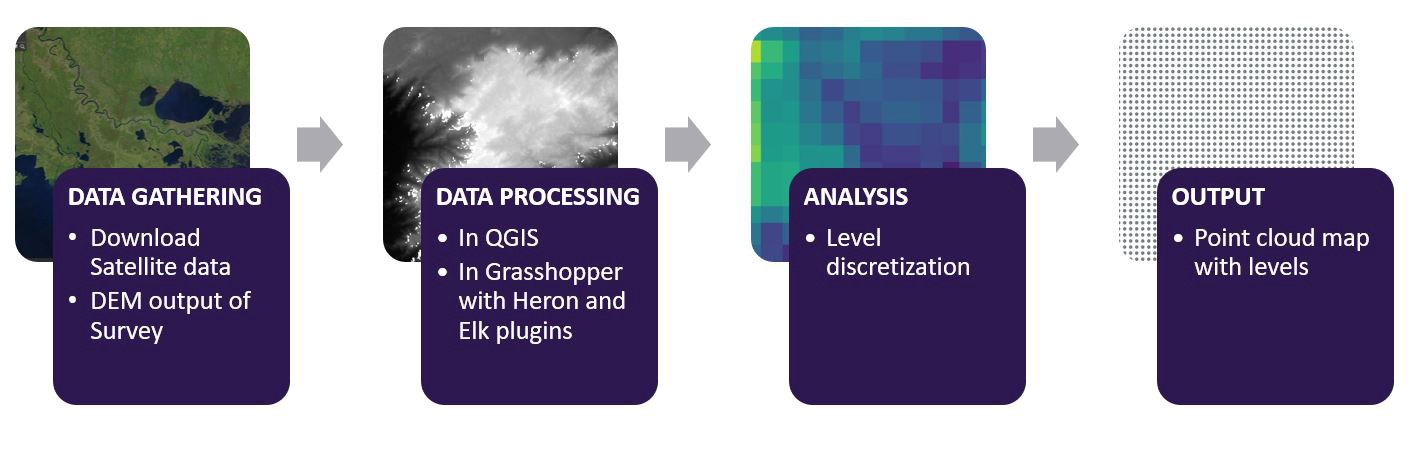
1.以DEM(数字高程模型)收集高程数据 (1. Collecting data on elevation as DEM (Digital Elevation Model))
Using Elk, OpenStreetMap, and QGIS
使用Elk,OpenStreetMap和QGIS
Step 1: Download information acquired from remote sensing (satellite scan) that are freely available from USGS as LANDSAT Image for the region. Satellite scanning is increasingly becoming more accurate depending on the site location and could hold valuable information. They can give a good indication of the surrounding topography and could be at a later stage correlated with more accurate data made from surveying.
步骤1:下载从遥感(卫星扫描)获得的信息,该信息可以从USGS免费获得为该地区的LANDSAT图像。 卫星扫描越来越精确,具体取决于站点的位置,并且可以保存有价值的信息。 它们可以很好地指示周围的地形,并且可以在以后与测量得出的更准确的数据相关联。
USGS Earth Explorer > Select region > Download DEM
USGS Earth Explorer >选择区域>下载DEM
Alternatively, you might come in possession of a DEM (.tiff) Survey map from a surveyor.
另外,您可能拥有测量师的DEM(.tiff)测量图。
Step 2: Gather GIS layers such as road network, building layer, waterbody, etc, in Grasshopper using Elk plugin, & OpenStreetMap data.
步骤2:使用Elk插件和OpenStreetMap数据在Grasshopper中收集GIS图层,例如道路网,建筑物层,水体等。
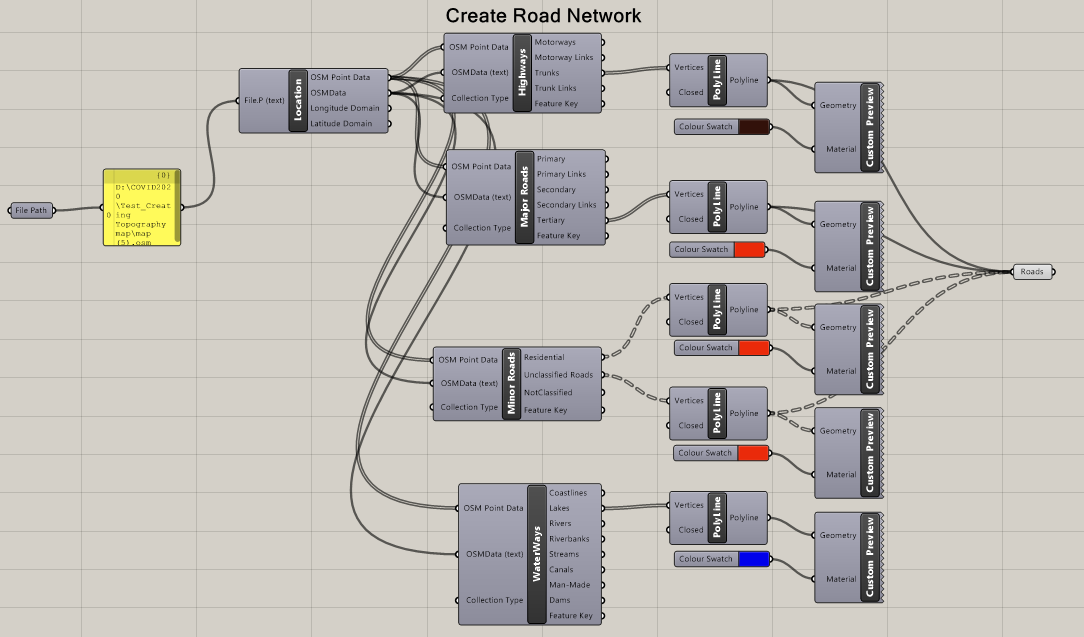
I also found an alternate method using Heron plugin in grasshopper. Heron is a wonderful plugin that imports GIS data directly onto Grasshopper without having to go through Method 1. There are plenty of tutorials online on this. The definitions are also available on Heron@food4rhino in the examples.
我还找到了在草hopper中使用Heron插件的替代方法。 Heron是一个很棒的插件,可以将GIS数据直接导入Grasshopper,而无需经过方法1。在线提供了很多教程。 示例中的Heron @ food4rhino也提供了这些定义。
I followed the Elk option.
我遵循了麋鹿的选择。
2.处理和提取DEM的高程值 (2. Processing and Extracting Elevation values from DEM)
Digital elevations are available in various GIS compatible formats, such as .tiff, ASCII, .shp. For extracting the elevation, I downloaded the DEM raster in .tiff format. Using QGIS GRASS 3.2 (particularly, as this latest release with GRASS can only do the resample step), an open-source geographic information software, the image was processed, resampled and converted to points holding the Z value.
数字高程具有各种GIS兼容格式,例如.tiff,ASCII,.shp。 为了提取高程,我下载了.tiff格式的DEM栅格。 使用开源地理信息软件QGIS GRASS 3.2(特别是因为该最新版本的GRASS只能执行重采样步骤),这是一种开源地理信息软件,图像经过处理,重采样并转换为具有Z值的点。
QGIS with GRASS > Processing Toolbox > Resample to 25 m grid > Calculate Z value > Save layer as points
带有GRASS的QGIS>处理工具箱>重采样到25 m网格>计算Z值>将图层另存为点
Next step is to import this into Grasshopper.
下一步是将其导入Grasshopper。
3.蚱hopper的分析 (3. Analysis in Grasshopper)
Input for this stage is the point cloud with x,y and z values as obtained from QGIS. The output will be parametrically controlled discrete groups based on their elevation.
该阶段的输入是从QGIS获得的具有x,y和z值的点云。 输出将是基于其高程的参数控制的离散组。
As a rule, always parameterise items which you are not necessarily certain of, or want to maintain some flexibility.
通常,请始终对不一定要确定的项目或要保持一定灵活性的项目进行参数化。
For example, size of a room for which area is 10 sq.m but length and breadth are not definite. You would then make length and breadth a function of the area controlled by sliders.
例如,面积为10平方米但长度和宽度不确定的房间大小。 然后,您将使长度和宽度成为由滑块控制的区域的函数。
I want to be able to control the grouping of points based on their elevation in order to parametrically discretise the levels. Parameterising the levels enables control over the criteria for selection of points.
我希望能够基于其高程来控制点的分组,以便参数化水平。 通过对级别进行参数化,可以控制选择点的标准。
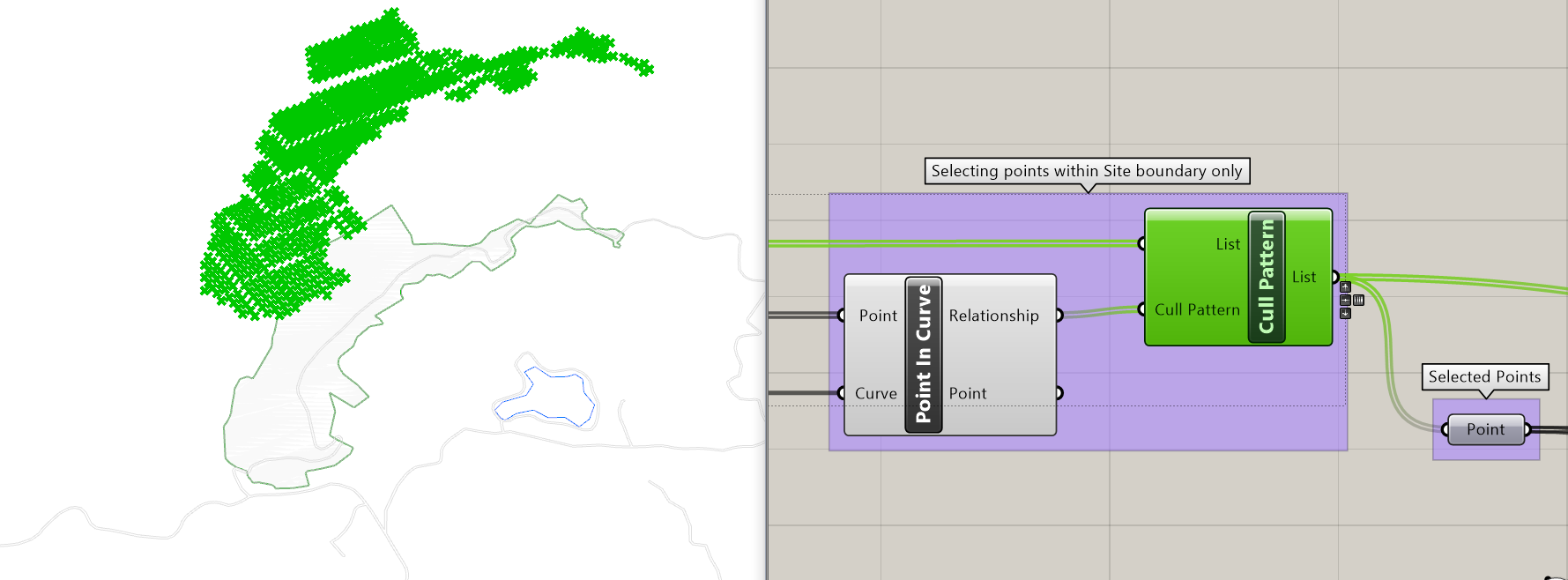
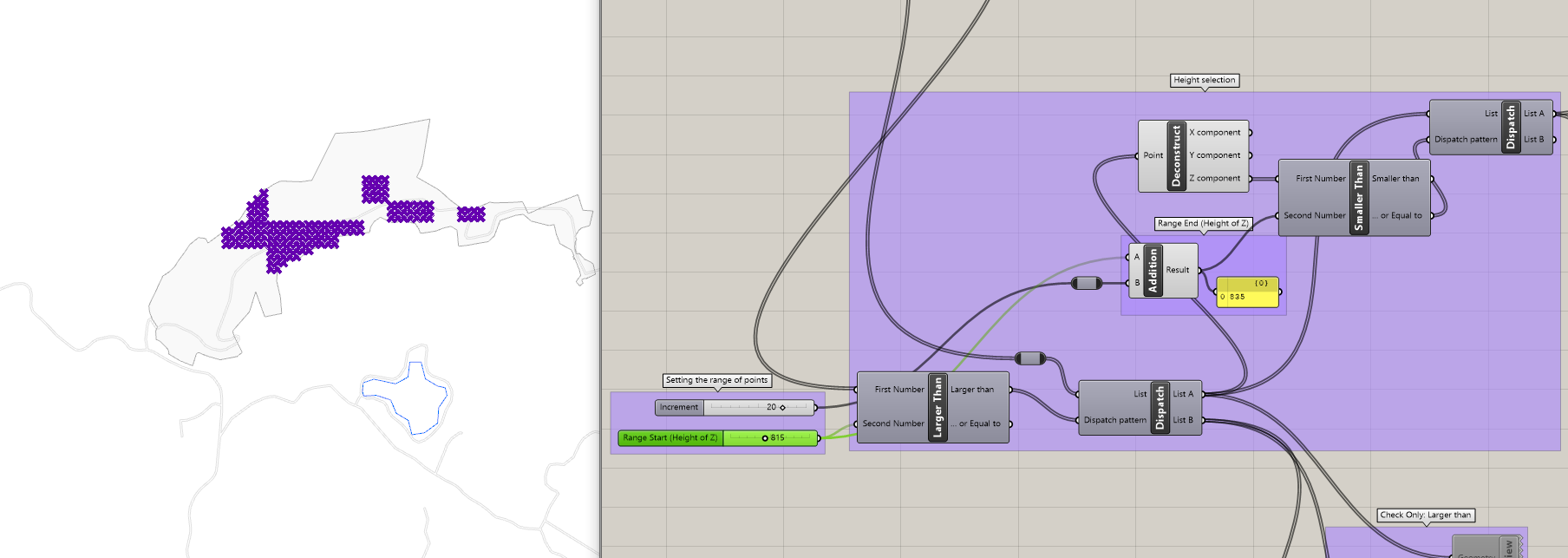
4.输出 (4. Output)
With this I have;
我有了这个
- Organised the levels as controllable parametric features. 将级别组织为可控制的参数特征。
- Parameterised grouping levels into bands at increments of 5 m 参数化的分组级别按5 m的增量分成频段
- Identified low and high-level regions across the site to plan for grazing and farmland as required from my project brief 根据我的项目简介中的要求,确定了站点的低层和高层区域,以计划放牧和耕地
- Set the stage for running an evolutionary solver to generate options at a later stage 设置运行演化求解器以在以后生成选项的阶段
下一步 (Next Step)
Package 2: Massing and zoning
套餐2:批量和分区
Hello and thanks for checking out my post! Feel free to shoot any questions you may have as comments. Also, get in touch with me on LinkedIn if you would like any help.
您好,感谢您检查我的帖子! 随意拍摄您可能有任何疑问的问题。 另外, 如果您需要任何帮助,请 通过 LinkedIn 与我联系 。
I am an architect (COA) and tech enthusiast from London. I am interested in the built environment and leveraging data sciences for architecture broadly around design, performance, and insights. I work on various topics from time to time such as generative design, spatial analytics, and energy and environmental studies. I am a Project Manager (AEC) at a biotech innovation company, developing a large-scale sustainable project in North Africa.
我是伦敦的一名建筑师(COA)和技术爱好者。 我对构建环境以及将数据科学广泛应用于设计,性能和洞察力的架构感兴趣。 我不时从事各种主题的工作,例如生成设计,空间分析以及能源和环境研究。 我是一家生物技术创新公司的项目经理(AEC),正在开发北非的大型可持续项目。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-leverage-on-the-data-gathered-by-satellites-from-remote-sensing-to-easily-model-a-site-in-afc73a006e43
hopper
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.mzph.cn/news/390639.shtml
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系多彩编程网进行投诉反馈email:809451989@qq.com,一经查实,立即删除!


)
构造函数)



)










