因为项目需要使用z3库来解决问题,所以自己学习了一下,结果发现网上教程比较少,而且大部分都是使用Python,而我本人是C++的忠实信徒,在知道C++也可以使用z3库以后我毫不犹豫地着手用C++使用z3,但是我很快发现,网上基本没有关于C++使用z3的教程(中文社区一点都没有),因此我记录一下我自己的学习过程希望能够帮助到其他学习的人。
教程链接
网上现有的有三个教程:
官方example.cpp文档:https://github.com/Z3Prover/z3/blob/master/examples/c%2B%2B/example.cpp
入门笔记:
http://www.cs.utah.edu/~vinu/research/formal/tools/notes/z3-notes.html
API接口:
https://z3prover.github.io/api/html/group__cppapi.html
其中主要教程是官方的example.cpp
第二个入门教程也非常不错,里面包含了环境的搭建,例子的说明(其实就是example.cpp的说明)
第三个API没有什么用觉得
不过上面的教程都没有说如何在一个普通文件中使用z3库,我在StackOverflow上找到一个回答解决了这个问题:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17514923/need-help-in-using-z3-api-in-a-c-program。简单来讲在install之后要在文件中包含z3++.h头文件,而且在编译参数上要加上-lz3
我一开始是学习使用Python使用z3的,因此也发现一些很好的教程,其中对我帮助最大的是一个用z3解决背包问题的博客,让我明白如何用z3解决极值问题:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41950078/article/details/111416573
性能测试
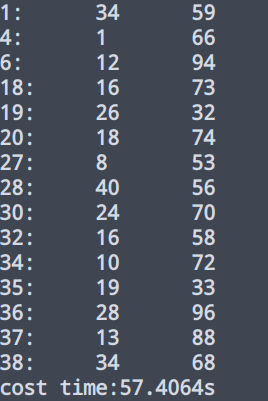
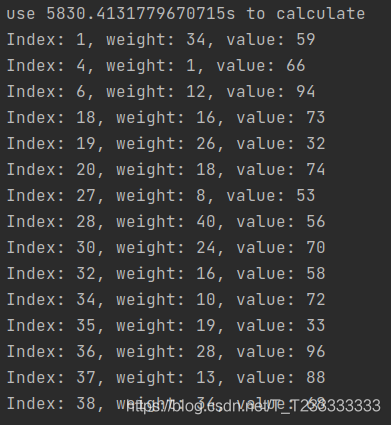
同时我测试了Python和C++的性能差距,以上面学习到的01背包问题为例,在数据量为40的时候,Python的运行时间是5830.4131779670715s(我没有写错),C++的运行时间是57s。
希望的我的测试能够坚定大家用C++使用z3库的决心(狗头
下符测试代码和运行截图:
Python
测试代码
import timefrom z3 import *
def zero_one_knapsack(weights, values, cap):solver = Optimize()# the decision variablesflags = [Int(f"x_{i}") for i in range(len(weights))]for flag in flags:solver.add(Or(flag == 0, flag == 1))weight_arr = []i = 0for w in weights:weight_arr.append(w * flags[i])i += 1# add weight constraintsolver.add(sum(weight_arr) <= cap)value_arr = []i = 0for v in values:value_arr.append(v * flags[i])i += 1solver.maximize(sum(value_arr))start = time.time()# calculateresult = solver.check()print(f"use {time.time() - start}s to calculate")if result == sat:model = solver.model()print("\n".join([f"Index: {index}, weight: {weights[index]}, value: {values[index]}"for index, flag in enumerate(flags) if model[flag] == 1]))else:print("empty")if __name__ == '__main__':C = 300W = [71,34,82,23,1,88,12,57,10,68,5,33,37,69,98,24,26,83,16,26,18,43,52,71,22,65,68,8,40,40,24,72,16,34,10,19,28,13,34,98]V = [26,59,30,19,66,85,94,8,3,44,5,1,41,82,76,1,12,81,73,32,74,54,62,41,19,10,65,53,56,53,70,66,58,22,72,33,96,88,68,45]zero_one_knapsack(W, V, C)
运行结果
C++
运行代码
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <string>
#include <z3++.h>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>using namespace z3;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::vector;void knapsack(const vector<int> &weights, const vector<int> &values, int cap)
{context c;optimize opt(c);vector<expr> flags;for (decltype(weights.size()) i = 0; i < weights.size(); ++i) {flags.push_back(c.int_const( ("x" + std::to_string(i)).c_str() ));}for (auto &flag : flags) {opt.add(flag == 0 || flag == 1);}expr tmp = c.int_const("tmp");tmp = c.int_val(0);for (decltype(weights.size()) i = 0; i < weights.size(); ++i) {tmp = tmp + weights[i] * flags[i];}opt.add(tmp <= cap);tmp = c.int_val(0);for (decltype(values.size()) i = 0; i < values.size(); ++i) {tmp = tmp + values[i] * flags[i];}opt.maximize(tmp);//cout << opt << endl;clock_t begin = clock();auto result = opt.check();clock_t end = clock();if (result == sat) {model m = opt.get_model();//cout << m << endl;for (unsigned i = 0; i < flags.size(); ++i) {auto item = flags[i];if (m.eval(item).get_numeral_int() == 0) continue;cout << i << ":\t" << weights[i] << "\t" << values[i] << endl;}} else {cout << "no solution" << endl;}cout << "cost time:" << static_cast<double>(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}void work()
{vector<int> W,V;int C,n,w,v;cin >> C >> n;while (n--) {cin >> w >> v;W.push_back(w);V.push_back(v);}knapsack(W, V, C);
}int main()
{std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);work();return 0;
}为了在输出结果的时候判断是否选择该物品需要从model中获取结果,但是我不知道如何比较结果是否为0(在程序中0表示不选),在网上找来找去都没有,最后没有办法只能自己尝试,终于在成员列表里面找到了一个好像能够把expr转换成int的函数,即上面的if (m.eval(item).get_numeral_int() == 0) continue;语句,卡了好久,没有教程太惨了。
运行结果